3.1 Antimicrobial Drugs
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What do antimicrobial drugs specifically kill?
microbes

A type of antimicrobial drug that kills bacteria is called “Anti-bacterial” , otherwise known as an _____?
antibiotic
When selecting an antibiotic, what do we want the toxicity to be to the bacteria?
selectively toxic
What is the range or spectrum of activity of an antibiotic?
narrow ←→ broad
What does narrow spectrum indicate?
kills small, select subset of bacteria
What does broad spectrum indicate?
kills most pathogenic bacteria
What are the 4 things an Antibiotic Targets?
cell wall, DNA replication, transcription, translation
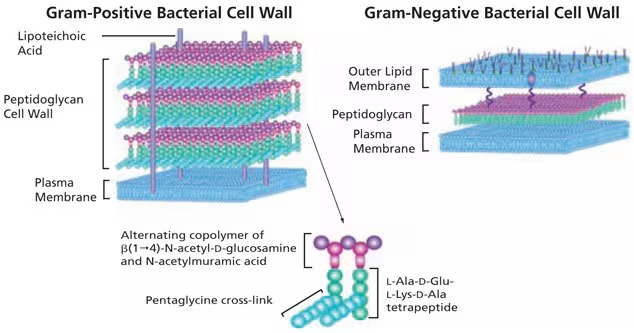
What do antibiotics specifically target on the cell wall? (composition)
peptidoglycan
What does the antibiotic want to render the bacteria as by targetting DNA replication?
non-viable
transcription and translation are the ones that do ____ ?
gene expression
What part of Penicillin is the suffix? (use quotes)
“cillin”
Do all penicillin derived antibiotics have the same Mechanism of Action or MoA
yes
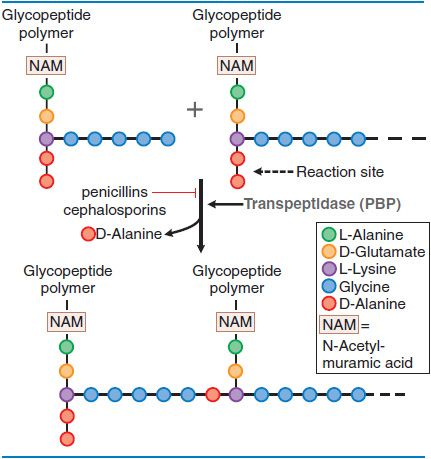
What’s the MoA of penicillin?
inhibits bacterial enzyme responsible for inserting the crosslink (bridge) into peptidoglycan
What’s the result from insufficient crosslinking of the tetrapeptides on the NAM?
weakens the peptidoglycan and is unable to counteract osmotic pressure
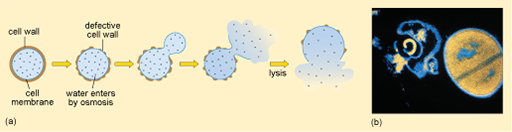
Since the bacterial cell can’t counteract osmotic pressure what happens?
cell lysis (bursts)
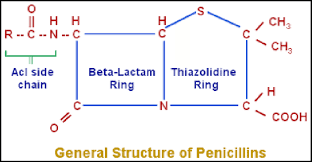
What is the active component of penicillin called? (never changes)
nucleus
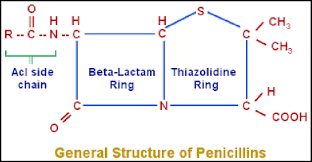
What is the square part next to the house called?
Beta-lactam ring
What does the variable side chain or R-group allow the pencillin to have?
various properties
What is the ORIGINAL pencillin antibiotic strain called?
Penicillin G
What type of spectrum does Pencillin G have?
narrow spectrum
Specifically, what did Pencillin G work well against? (2 types of bacterial cells)
Streptococcus, Staphylococcus
How was the Pencillin G admistered? (2)
IM shot or IV hook up
Was oral dosing available when Penicllin G was being used?
no
What was the main problem with Penicllin G? (short answ)
it was rapidly cleared from body (peeing, etc) so hard to keep up with dosage, since no oral dosing available
What did soldiers back then have to do to keep as much Penicillin G as they could?
drink their pee
What’s Penicillin 5 (V) essentially?
like Penicillin G
What changed between Penicillin V?
oral dosing
What type of adminstration did Ampicillin/Amoxiacillin use?
oral dosing
What bacterial types did Ampicillin/Amoxiacillin target?
Gram negative
What was the spectrum of Ampicillin/Amoxiacillin?
moderate spectrum
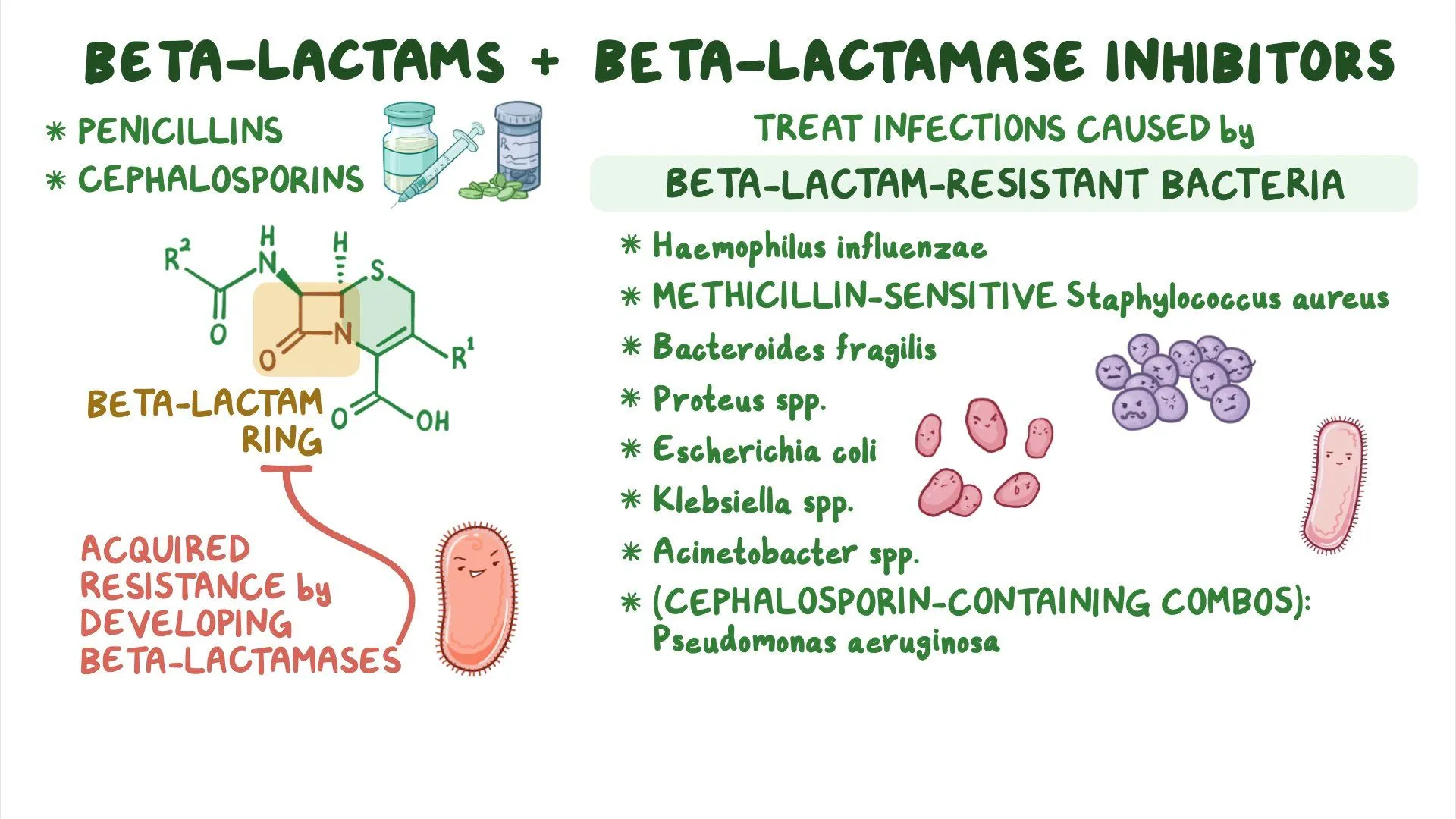
What did the enzyme Beta-lactamase do?
snips beta-lactam ring of penicillin to make it ineffective against bacteria
Do some bacterias carry the Beta-lactamase gene?
yes
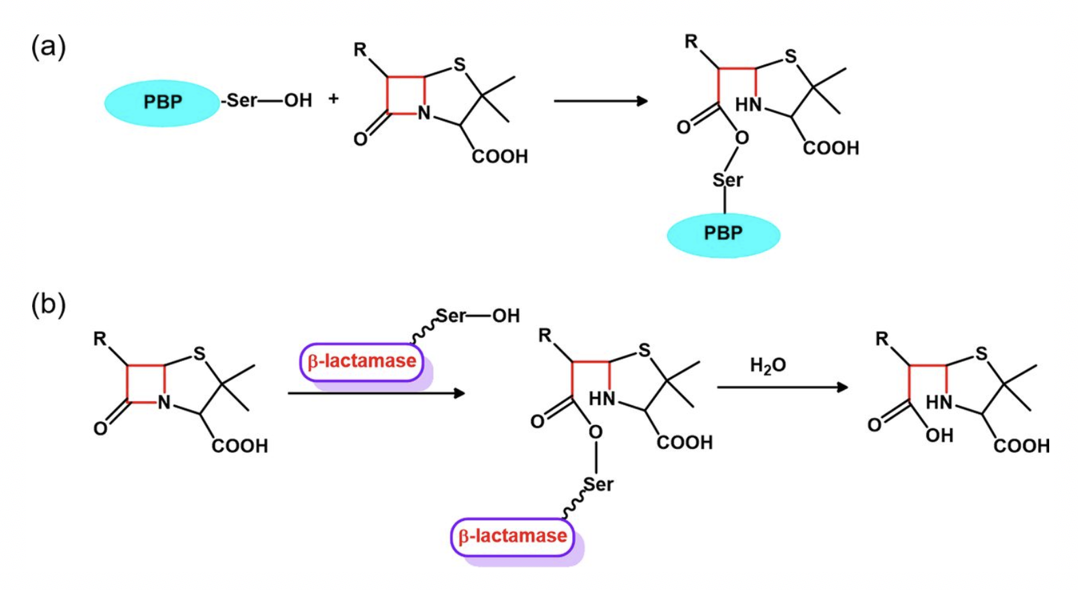
How does the R chain somewhat prevent Beta-lactamase from snipping the Beta-lactam?
can make beta-lactam unable to fit in the beta-lactamase’s active cite
What is an antibiotic that inhibits Beta-lactamase from working by protecting the B-Lactam ring?
Methicillin
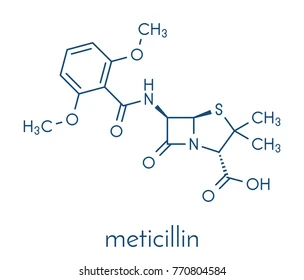
So, what does Methicillin have to protect the Beta-Lactam ring?
bulky R chain
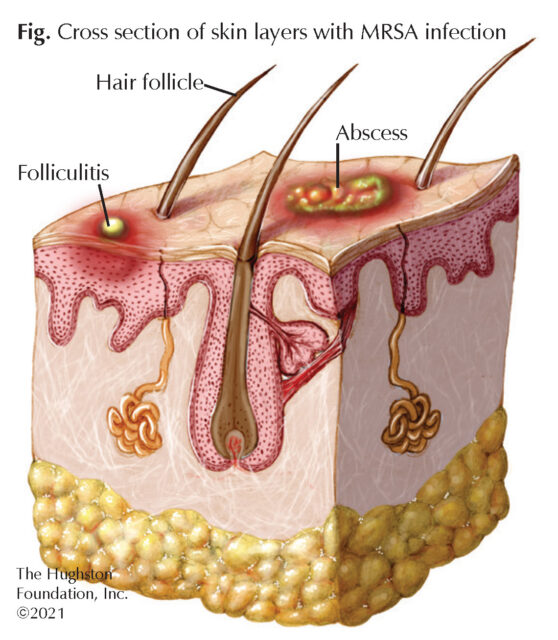
What does MRSA stand for?
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
What’s the antibiotic used to treat MRSA?
Vancomycin
Does Vancomycin have a Beta-lactam ring?
no
What type of spectrum does Vancomycin have?
narrow spectrum
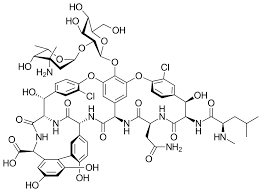
What’s physically significant about Vancomycin (has to do with why it’s narrow spectrum antibiotic)?
huge molecule
Is Vancomycin even apart of the penicillin class of antibiotics?
no
What type of bacteria does Vancomycin target?
G+
Why can’t Vancomycin target G-?
too large to fit through its porins
How is Vancomycin provided to a patient?
IV
Can vancomycin be orally ingested? If not, why?
no, doesn’t get absorbed across intestinal wall (too large)
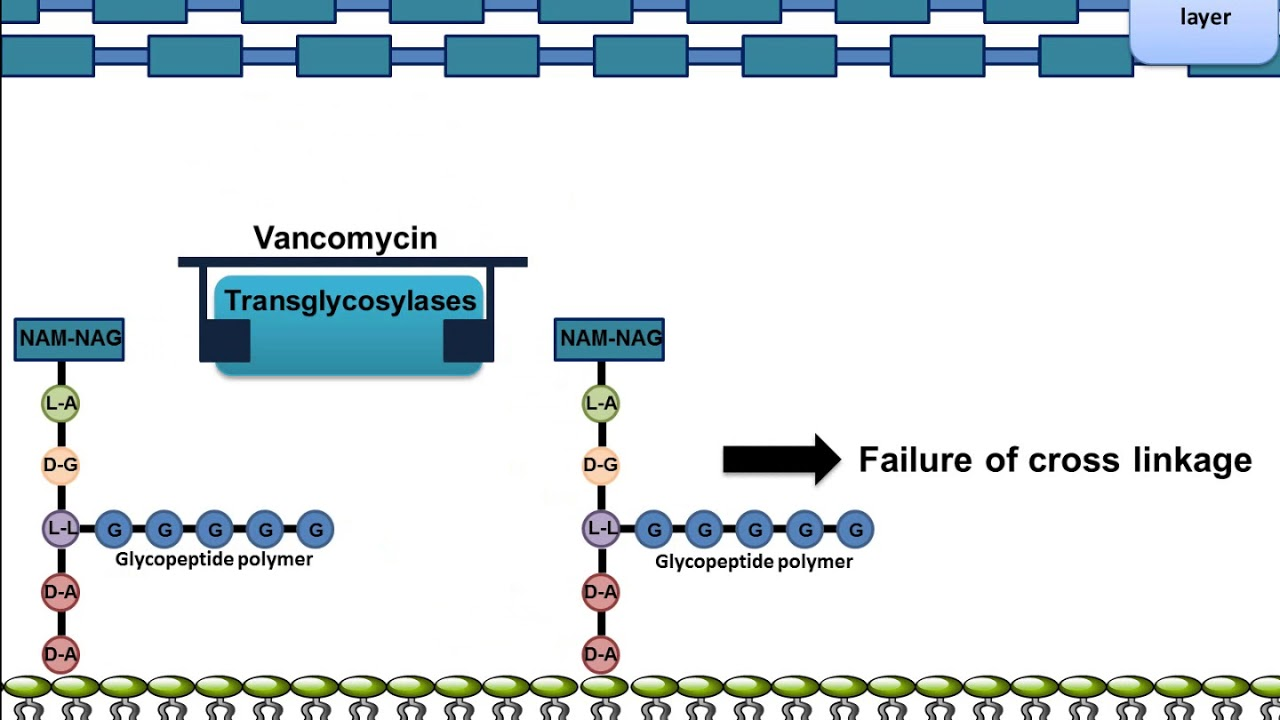
Vancomycin MoA: Where does Vancomycin go on the bacteria it targets? What does it do?
sits in between tetrapeptides and takes up space
Vancomycin MoA: Since the Vancomycin is taking up space, what can the peptidoglycan enzyme not do?
can’t add crosslink to peptidoglycan
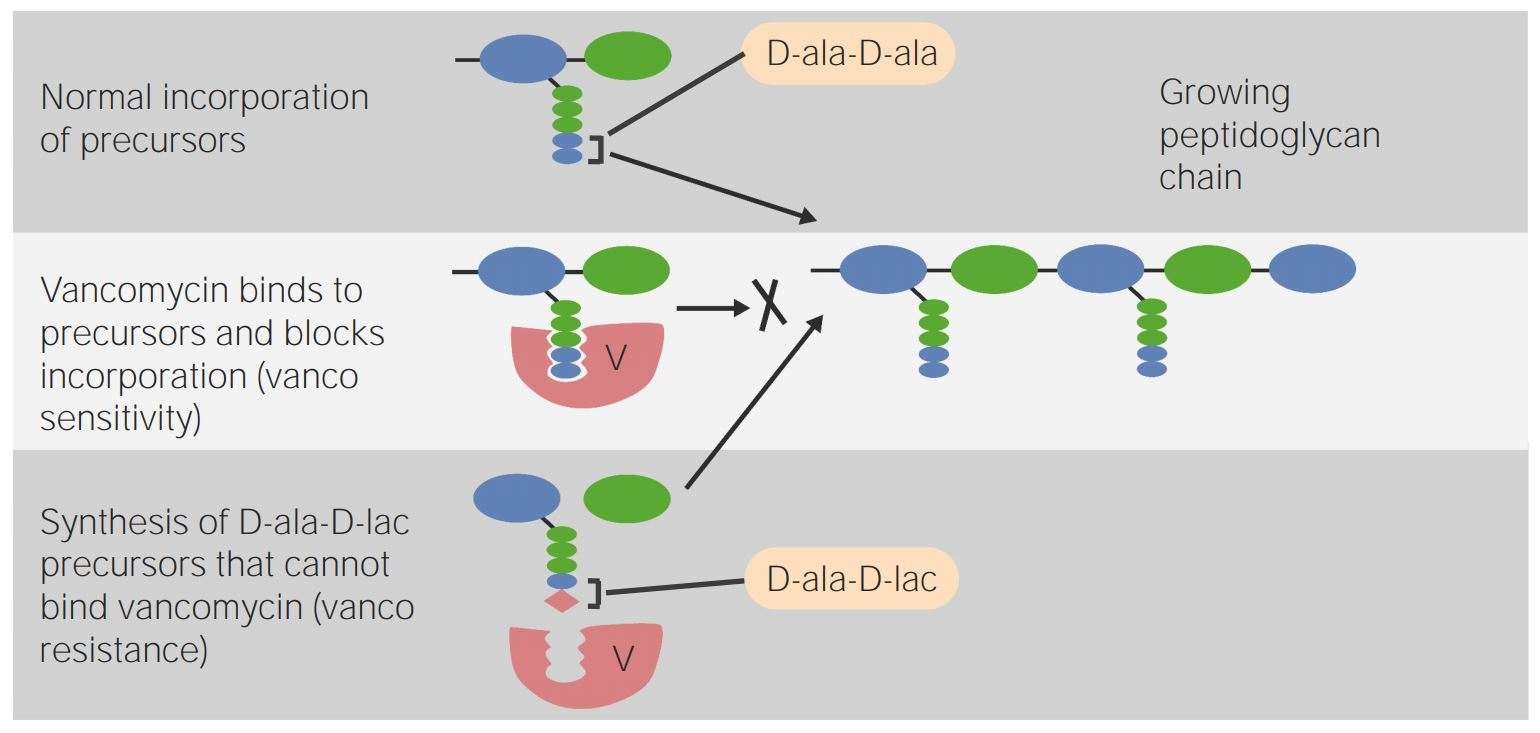
Vancomycin MoA: Since crosslinks can’t be added to peptidoglycan what happens? (2)
peptidoglycan is weak and cell lysis
What is the antibiotic Augmentin made of? (2)
penicillin drug and Beta-lactamase inhibitor
What is the most prescribed antibiotic to those who are allergic to Penicillin?
Cephalosporins
Does Cephalosporin have the same MoA as penicillin?
yes (both inhibit cell wall synthesis by interfering with peptidoglycan cross-linking.)
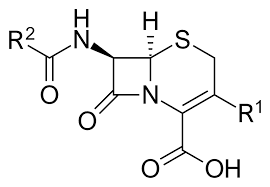
What is Cephalosporin naturally more resistant to due to their bulky nucleus?
Beta-lactamase
Does Cephalosporin have a Beta-lactam ring?
yes
What is the spectrum of Cephalosporins?
moderate spectrum
What are two Broad Spectrum Antibiotics?
floroquinolones, rifampin
What does Floroquinolones impact on the bacteria?
Dna Replication
Specifically, what accessory enzymes does Floroquinolones impact on DNA replication? (2)
DNA gyrase and topoisomerase
What are 4 Broad Spectrum Drugs/Antibiotics that specifically Inhibit Ribosomes (translation)
streptomyocin, erythromycin, chloramphenical, tetracycline
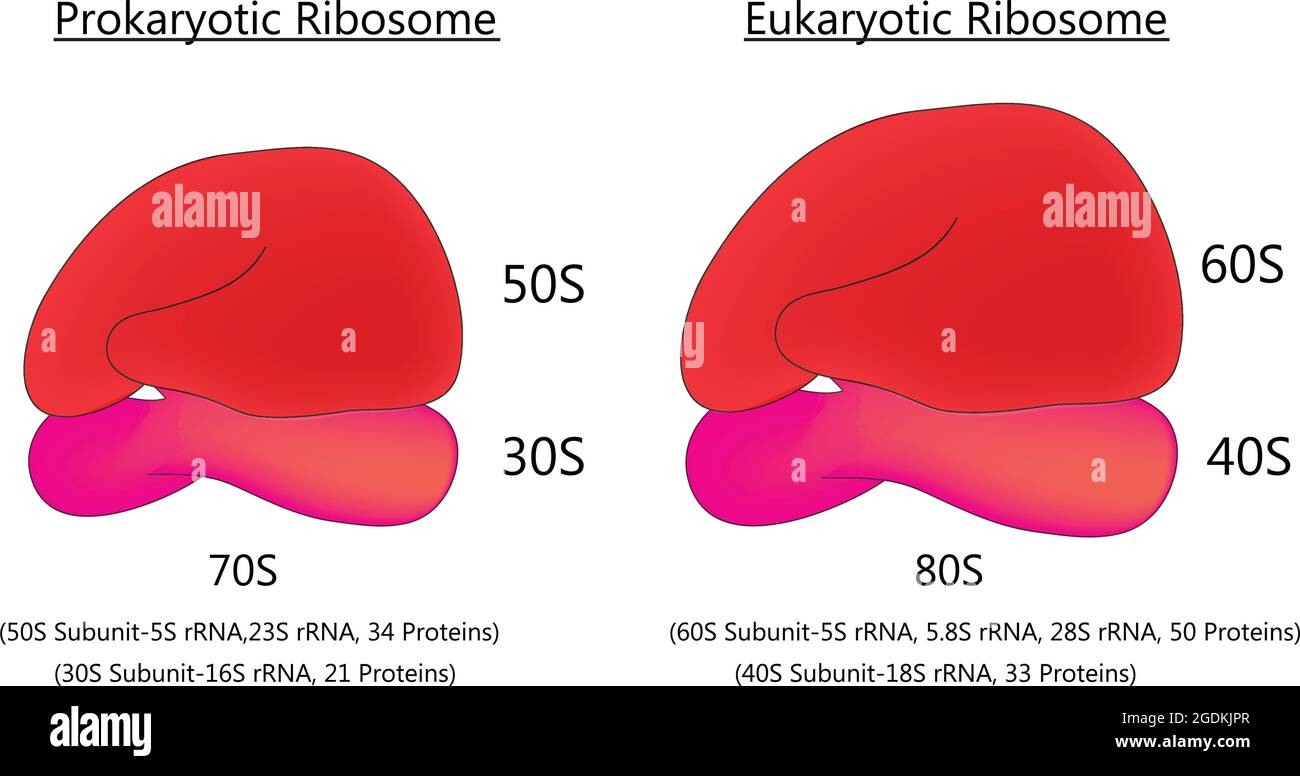
Are bacterial ribosomes smaller or larger than human ribosomes?
smaller
How do drugs that inhibit ribosomes kill the bacteria? (what does it prevent, and what occurs)
it prevents protein synthesis; death occurs without proteins
So since bacterial ribosomes are smaller, the drug can fit nicely into the active site but …
not fit into the eukaryote active site
However, what’s the one eukaryotic ribosome that IS similar to bacterial ribosomes?
mitochondrial ribosomes
So are mitochondrial ribosomes impacted by the 4 drugs listed before? What is the drug to the mitochondria ribosomes?
yes; toxic
What does Rifampin do?
inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase (transcription)
Is Rifampin prescribed by itself, or in a mixed or “drug cocktail”?
drug cocktail
Why is Rifampin in a drug cocktail? —> lets say you have two bacterial species, one that is resistant to rifampin and one that’s sensitive to rifampin; If you just give them rifampin, what will you see?
species of resistant rifamprin flourishes
Why is Rifampin in a drug cocktail? —> Let’s say you give Rifampin and Cephalosporin to the patient, what will happen?
no bacterial growth
So overall, what’s the major benefit of a drug cocktail?
slows the emergence of drug resistance
List all 6 Broad Spectrum Toxicity Drugs/Antibiotics?
Floroquinolones, Streptomycin, Erythromycin, Chloramphenical, Tetracycline, Rifampin