all ceramic restorations
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
fixed dental prosthesis
the general term for any prosthesis that is securely fixed to a natural tooth or teeth, to one or more dental implants; it CANNOT be removed
examples of fixed dental prosthesis
partial coverage restoration
complete crowns
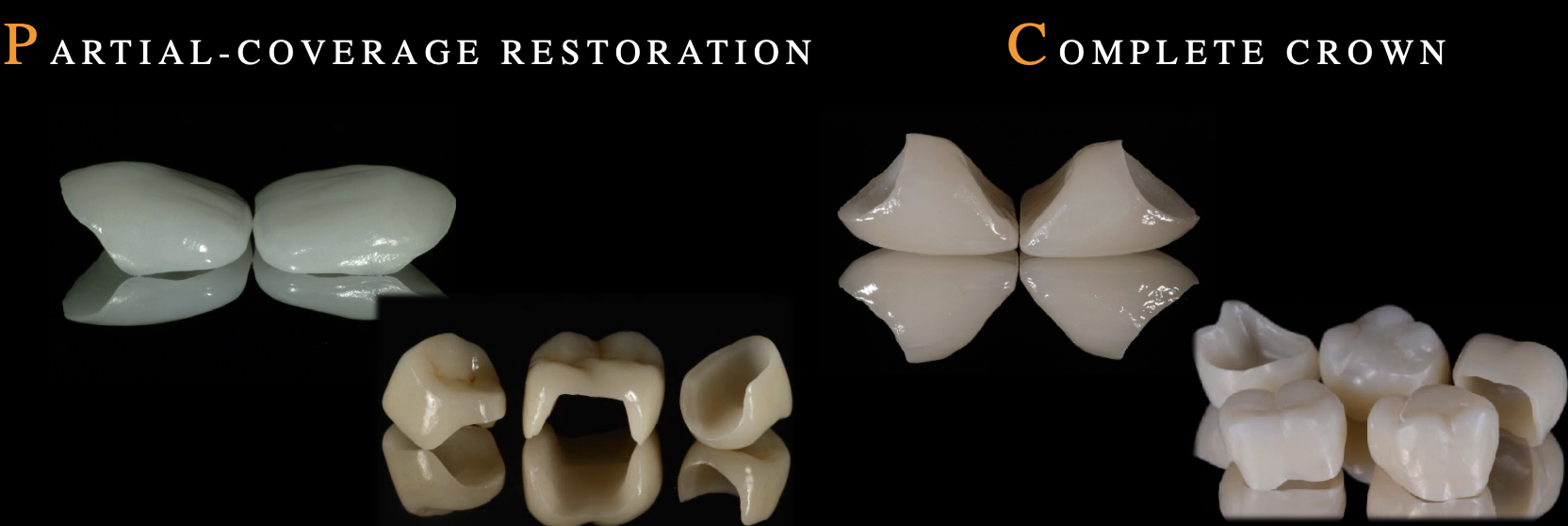
partial coverage restoration
an artificial replacement that restores missing tooth structure by surrounding part of the remaining structure w a material such as cast metal alloy, ceramics, or resin
indications for complete ceramic crowns (4)
extensive loss of tooth structure
existing complete crown
major morphological modification
significant shade change
types of complete crowns
complete cast crown
metal-ceramic crown
all ceramic crown
advantages of all ceramic restoration
superior esthetics
good tissue response
digital workflow capability
higher mechanical strength
disadvantages of all ceramic crown
critical preparation design
strict bonding protocol
opposing tooth wear
brittle nature
indications for all ceramic restorations
high esthetic requirements
favorable distribution of occlusal load
contraindications of all ceramic restorations
more conservative restorations applicable
unfavorable distribution of occlusal load
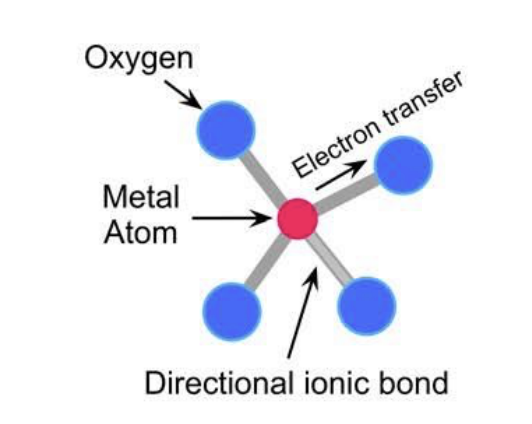
how do you define a ceramic dental ceramic
ceramics contain strong, direction, ionic bonds between metals and oxygen that impart strength but will not tolerate distortion
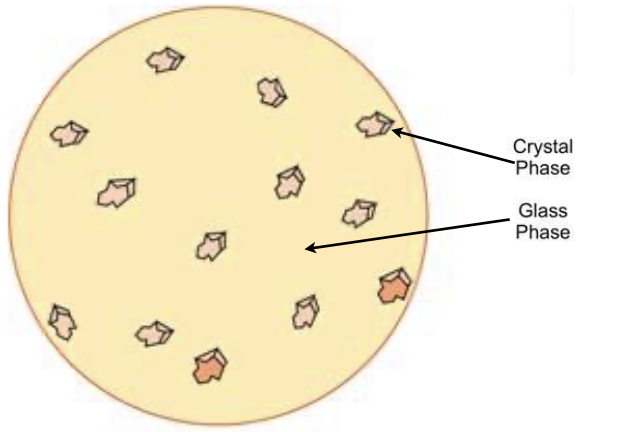
2 phases that dental ceramics are composed of
glassy phase
one or more crystalline phases
inc the amount of crystalline phases lead to…
crystalline reinforcement and inc the resistance of crack propagation but also can dec translucent (zirconia)
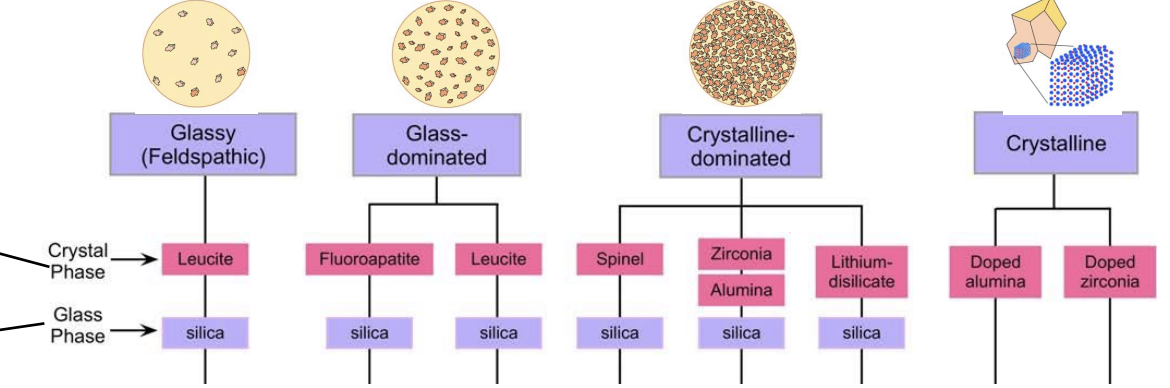
rank these from inc (low to high) mechanical strength
glassy (feldspathic) → glass-dominated → crystalline-dominated → crystalline
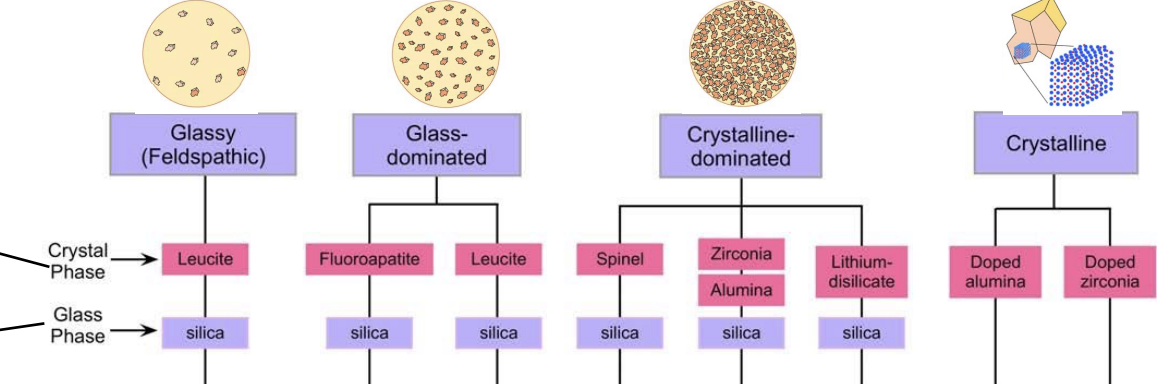
rank these from inc (low to high) optical translucency
crystalline → crystalline- dominated → glass-dominated → glassy (feldspathic)
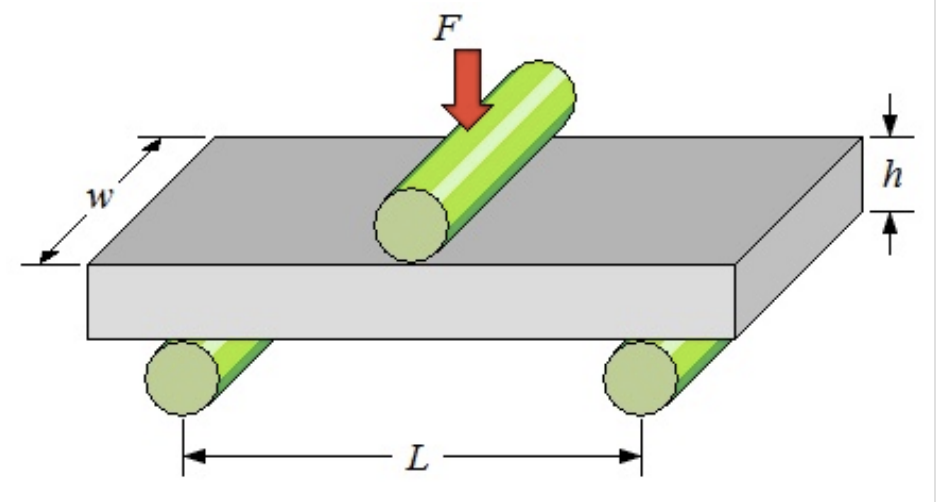
what is flexural strength
material’s ability to withstand bending forces without breaking or deforming
flexural strength of enamel
80-90 MPa
feldspathic ceramics are porcelains that are composed of primarily….
glassy phase w embedded leucite crystals
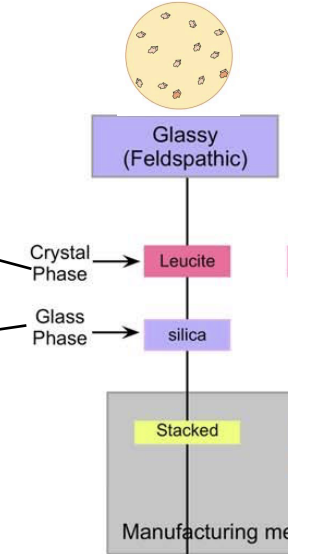
properties of feldspathic porcelain (4)
high translucency
highly esthetic results
technique sensitivity
low flexural strength
restorations that use feldspathic porcelain
ceramic veneers
metal-ceramic restorations
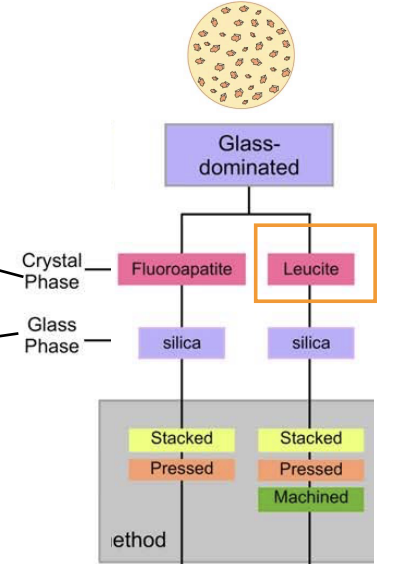
glass-dominated ceramics contains…
increased amounts of crystalline phase relativve to the glassy ceramic
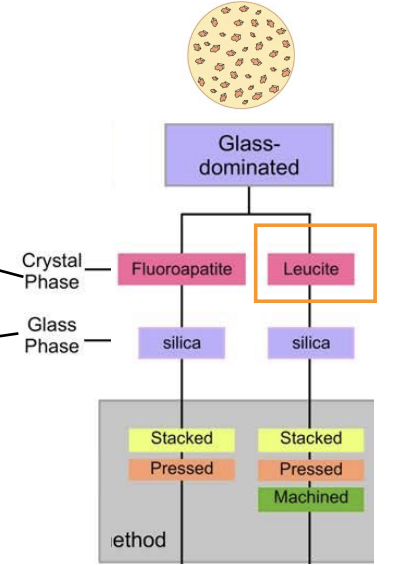
crystals in glass-dominated dental ceramics may be ________ or _________
fluroapatite or leucite
leucite-reinforced glass properties
sufficient translucency
moderate esthetic results- only one shade so may have ot stain
less technique sensitivity
higher flexural strength- 85-112 MPa) than feldspathic
crystalline-dominated ceramics are composed of…
most (70% volume) of crystalline phase
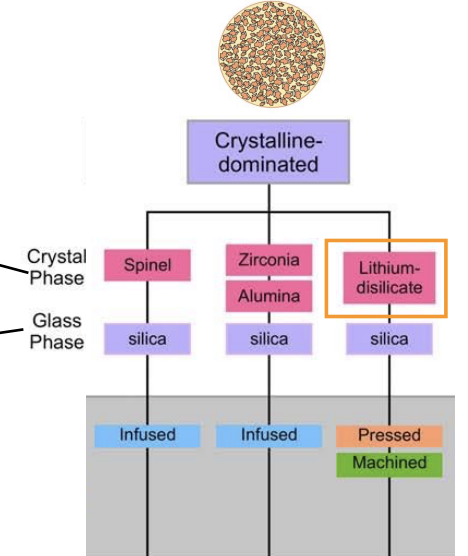
what are the crystals in crystalline dominated ceramics
spinel (MgAl2O4)
zirconia (ZrO2)
alumina (Al2O3)
lithium disilicate
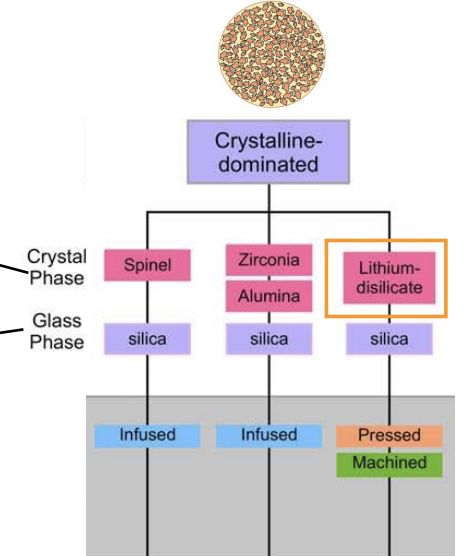
crystalline ceramics are formed from either…
alumina or zirconia that has been doped, w other ions such as Mg or yttrium to optimize them for use in dental applications
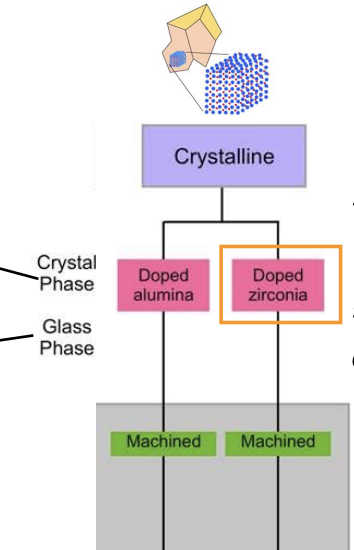
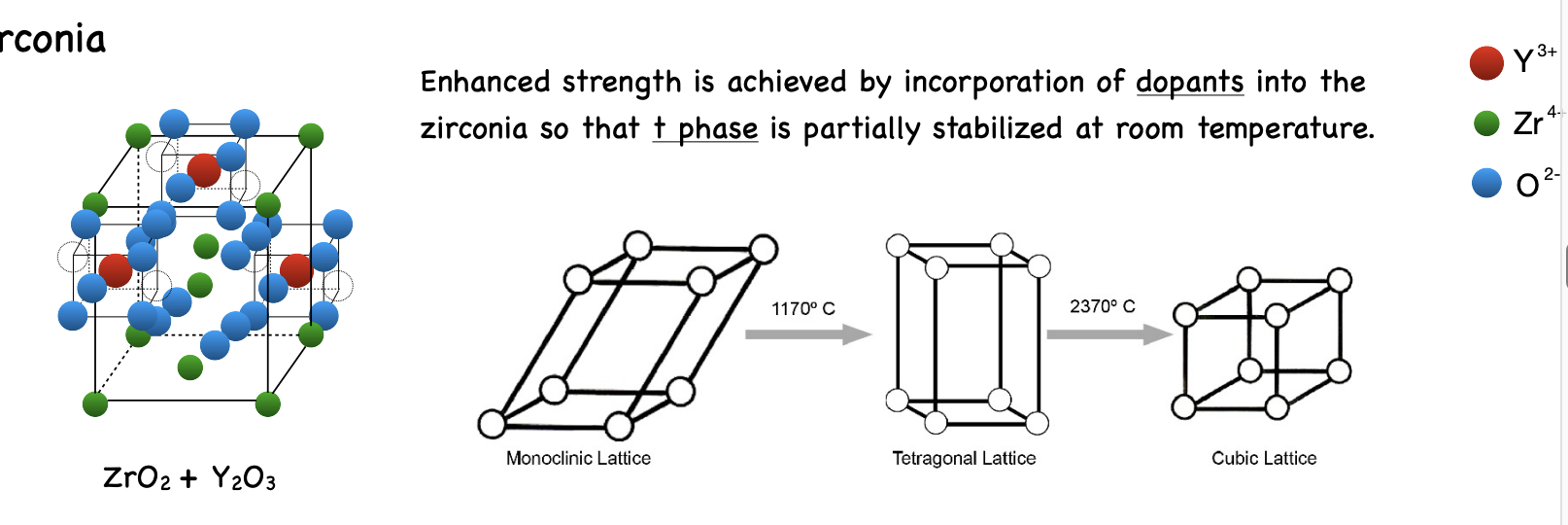
zirconia is a ________ material
polymorphic
what are the 3 phases that zirconia can exist in
monoclinic phase (m)
tetragonal phase (t)
cubic phase (c)
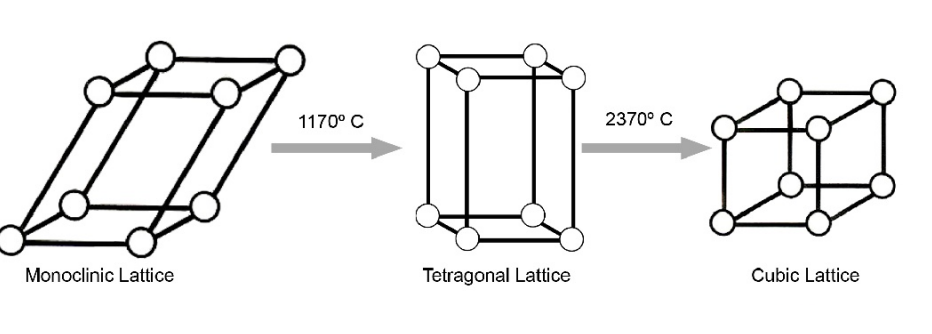
what phase is used more dental-wise
tetragonal phase
phases of zirconia are based on
temperature
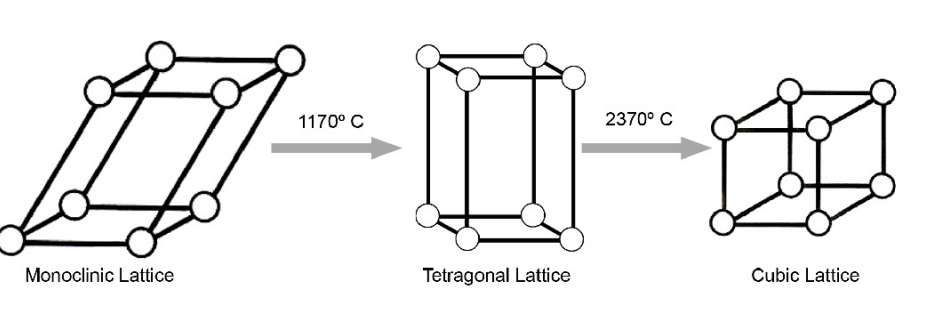
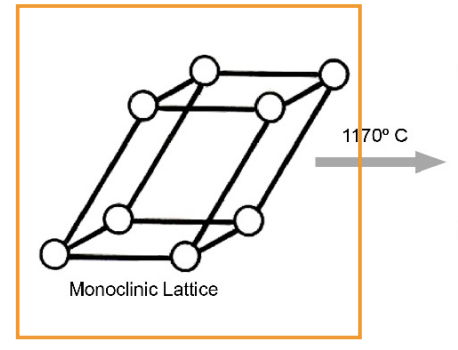
temp change to get from monoclinic phase to tetragonal phase
1190 degree C
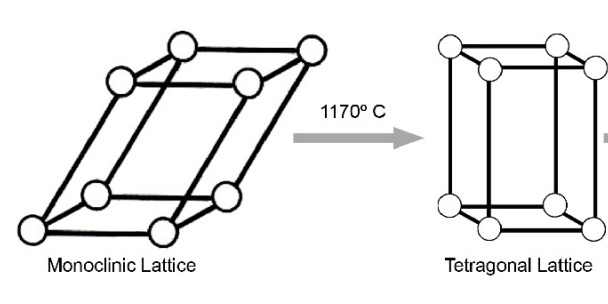
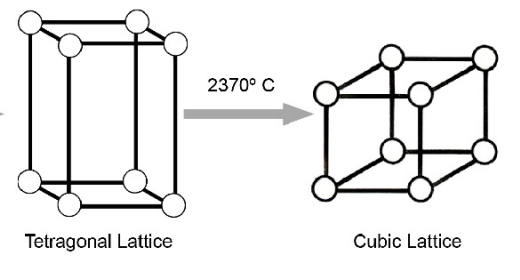
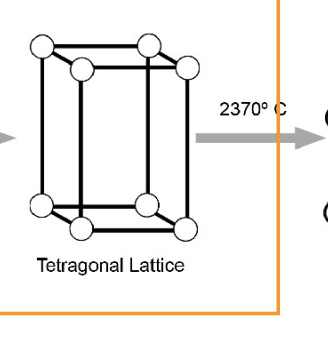
temp change to get from tetragonal phase to cubic phase
2370 degree C
the monoclinic phase of zirconia mechanical properties
exceptional mechanical properties
tetragonal phase of zirconia possesses _________ mechanical properties but…
superior mechanical properties BUT is NOT stable at room temp
how to achieve enhanced strength in zirconia
by incorporation of dopants into the zirconia so that the tetragonal phase is partially stabalized at room temp
two materials you would debate on if you were doing anterior full coverage ceramic crowns
lithium disilicate
zirconia
between lithium disilicate and zirconia, which would give you a higher esthetic outcome for anterior full-coverage crowns
lithium disilicate
when comparing the optical properties of lithium disilicate and zirconia, which is more translucent and which is more reflective
zirconia: more reflective
lithium disilicate: more translucent
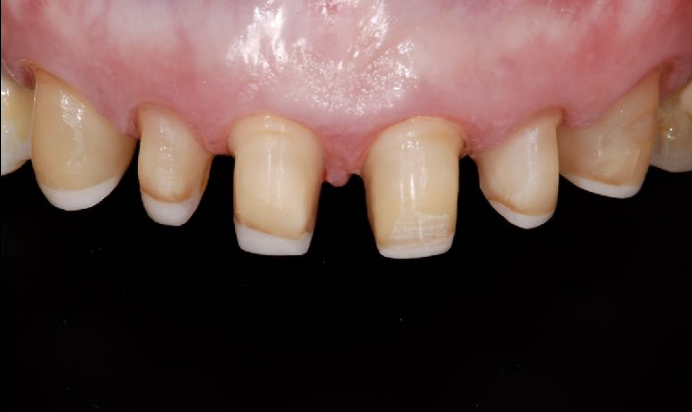
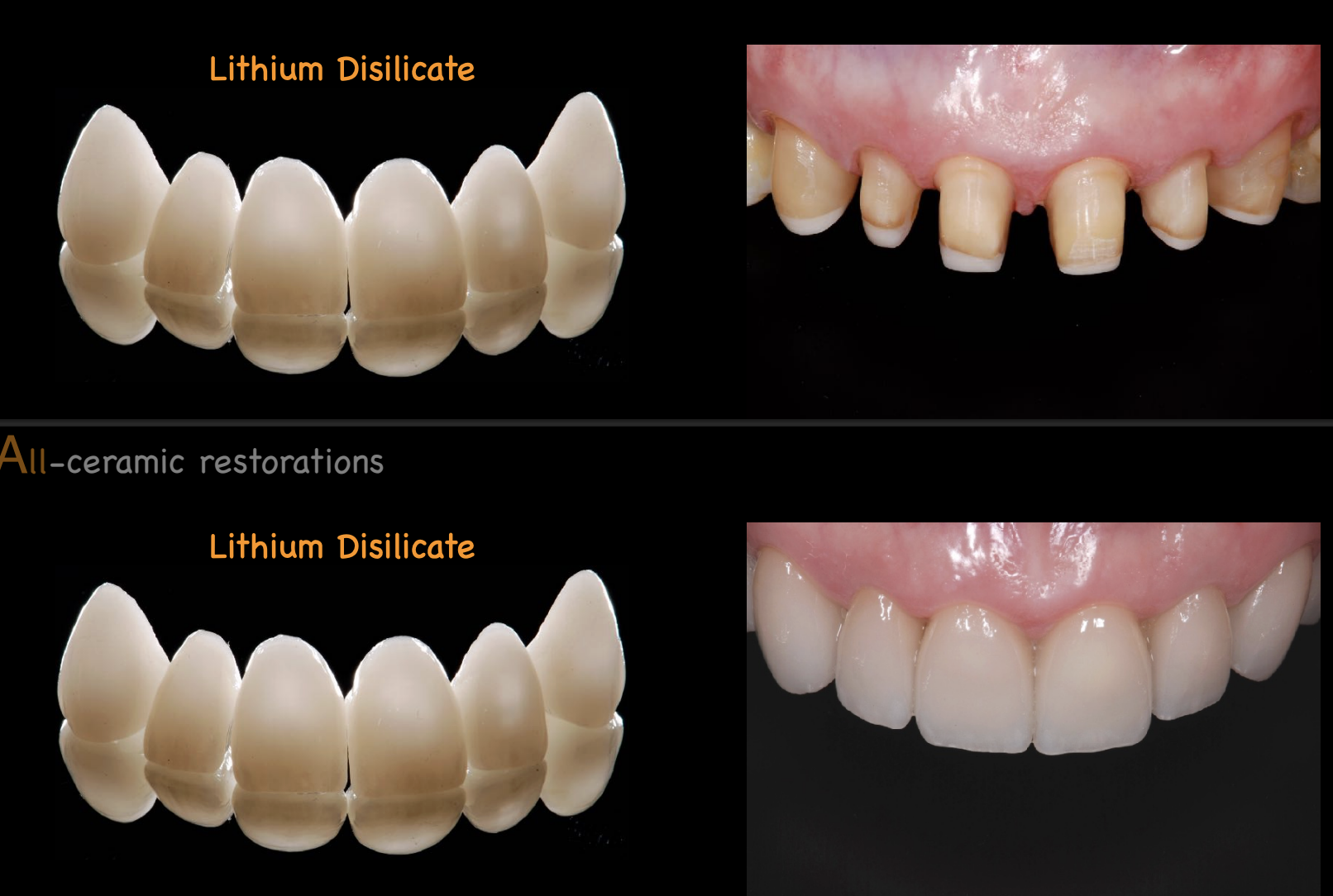
if the anterior tooth substrate color is dark, and your pt wants “hollywood white” which material would you use for a full coverage all ceramic crown
lithium disilicate is still fine
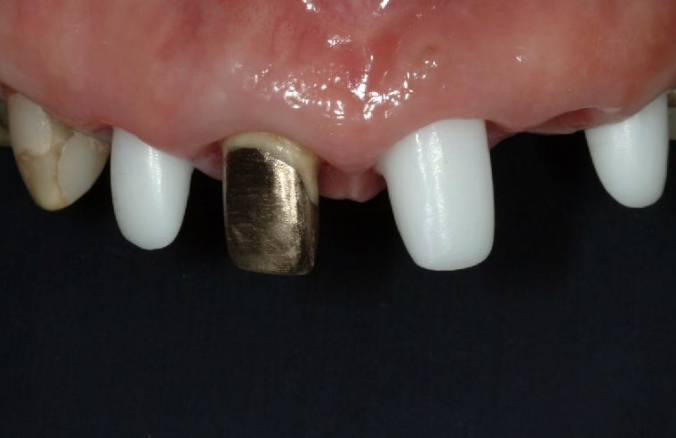
if the anterior tooth has a gold foil on the tooth substrate, what material would you use for a full coverage all ceramic crown
zirconia → would rlly need to mask the gold
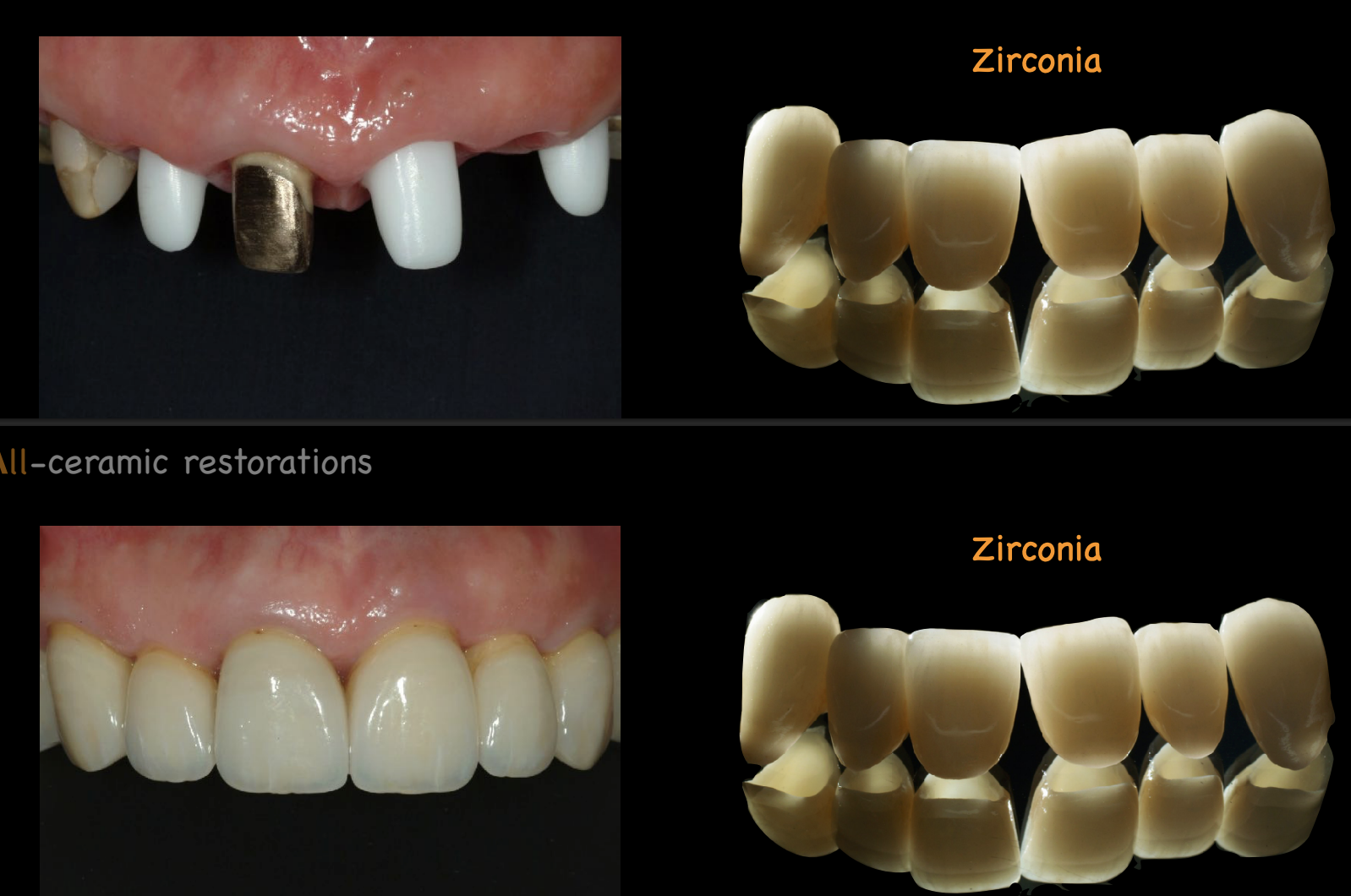
when comparing lithium disilicate and zirconia, which use either press or CAD/CAM tehcnique and the other only can use CAD/CAM technique
zirconia: CAD/CAM
lithium disilicate: press and CAD/CAM
why can’t you press zirconia
temp is too high
when comparing lithium disilicate and zirconia, which laminated/monolithic
both zirconia and lithium disilicate are laminated/monolithic
what is laminated
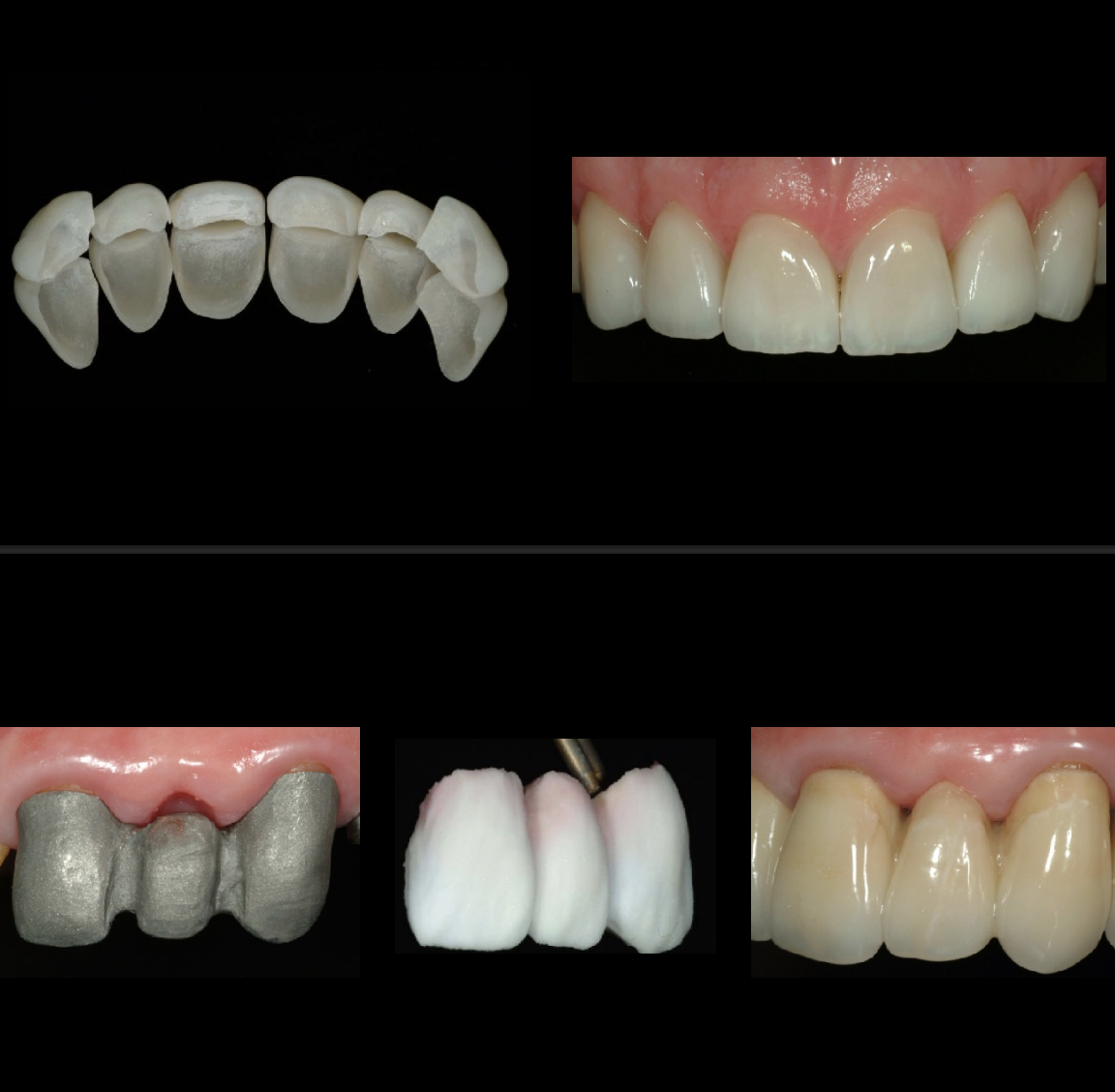
high strength core w porcelain- photo shows coping w zirconia and feldspathic layered ontop
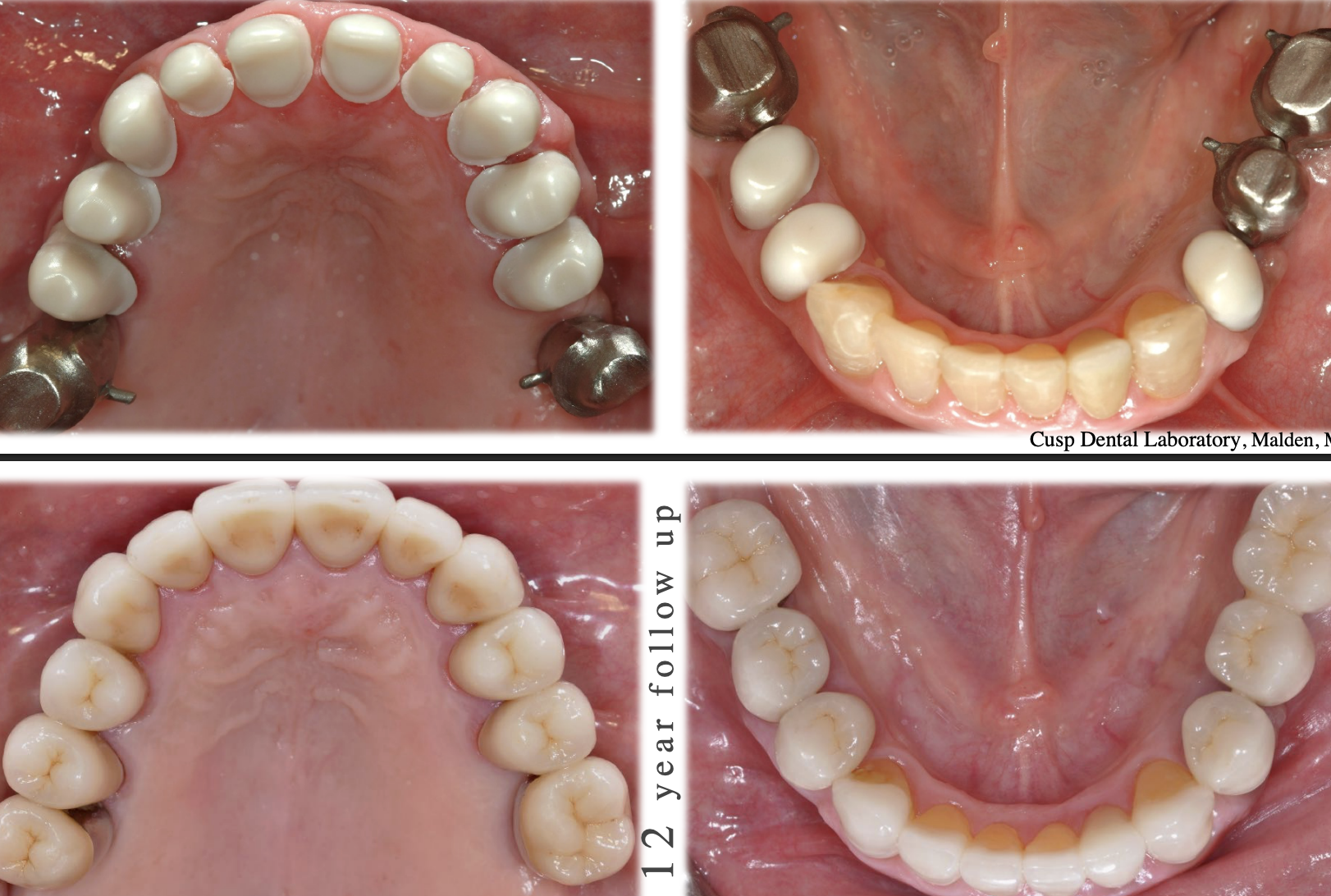
laminated technique
uses a layered technique → get higher esthetics → more time consuming
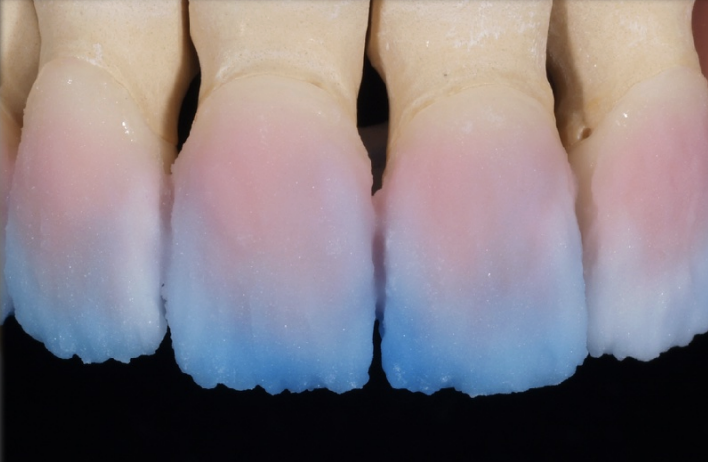
what is monolithic
full contour ceramics w stain; only one material then aid custon shading
when would you lead towards the monolithic technique
posterior teeth for strength
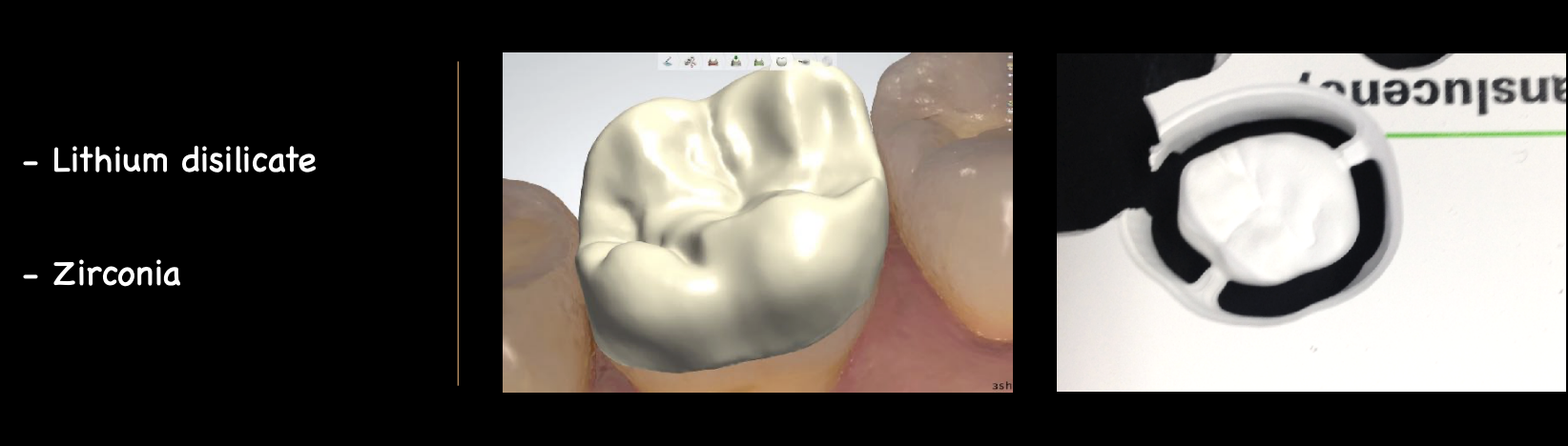
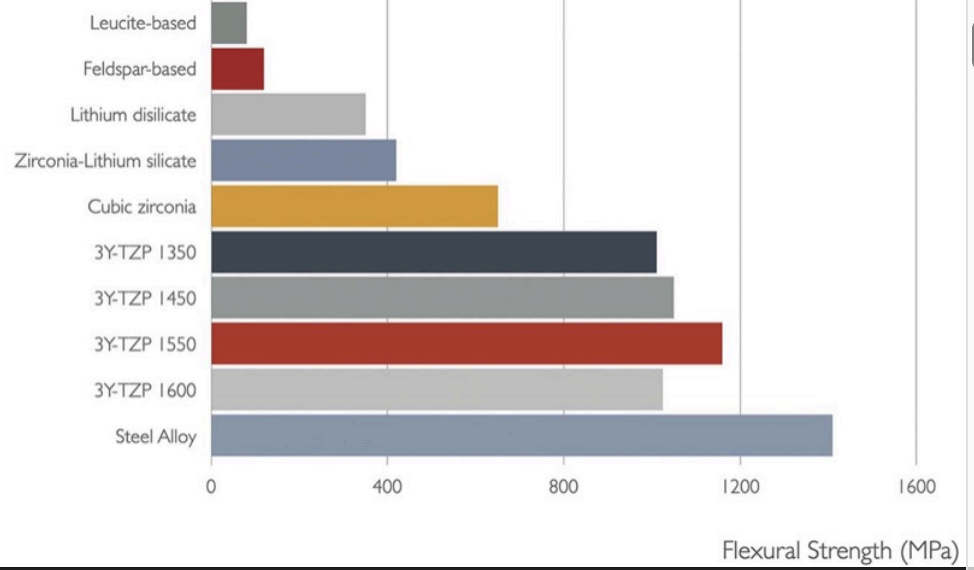
when comparing lithium disilicate and zirconia, which has a higher flexural strength and what are each of the values
zirconia IS HIGHER: 900-1200 MPa
lithium disilicate: 215-400 MPa

survival and complications of monolithic single ceramic crowns
monolithic ceramic can be conisdered a favorable tx for single crowns and FPDs, w HIGH survival and LOW complication rates

although an in-vitro study reported that monolithic zirconia presented a high fx resistance than lithium disilicate crowns, ___________ was observed in the survival and complication rates
no difference