MYCOVIRO LEC 8 - Automated Identification System for Fungal Pathogens
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What year was the automated instruments were introduced to microbiology?
1970s
- conventional methods base on ___ and ___
- were the gold standard
morphology and biochemical characteristic
is time-consuming, very operator-dependent, and lacks sensitivity
conventional identification
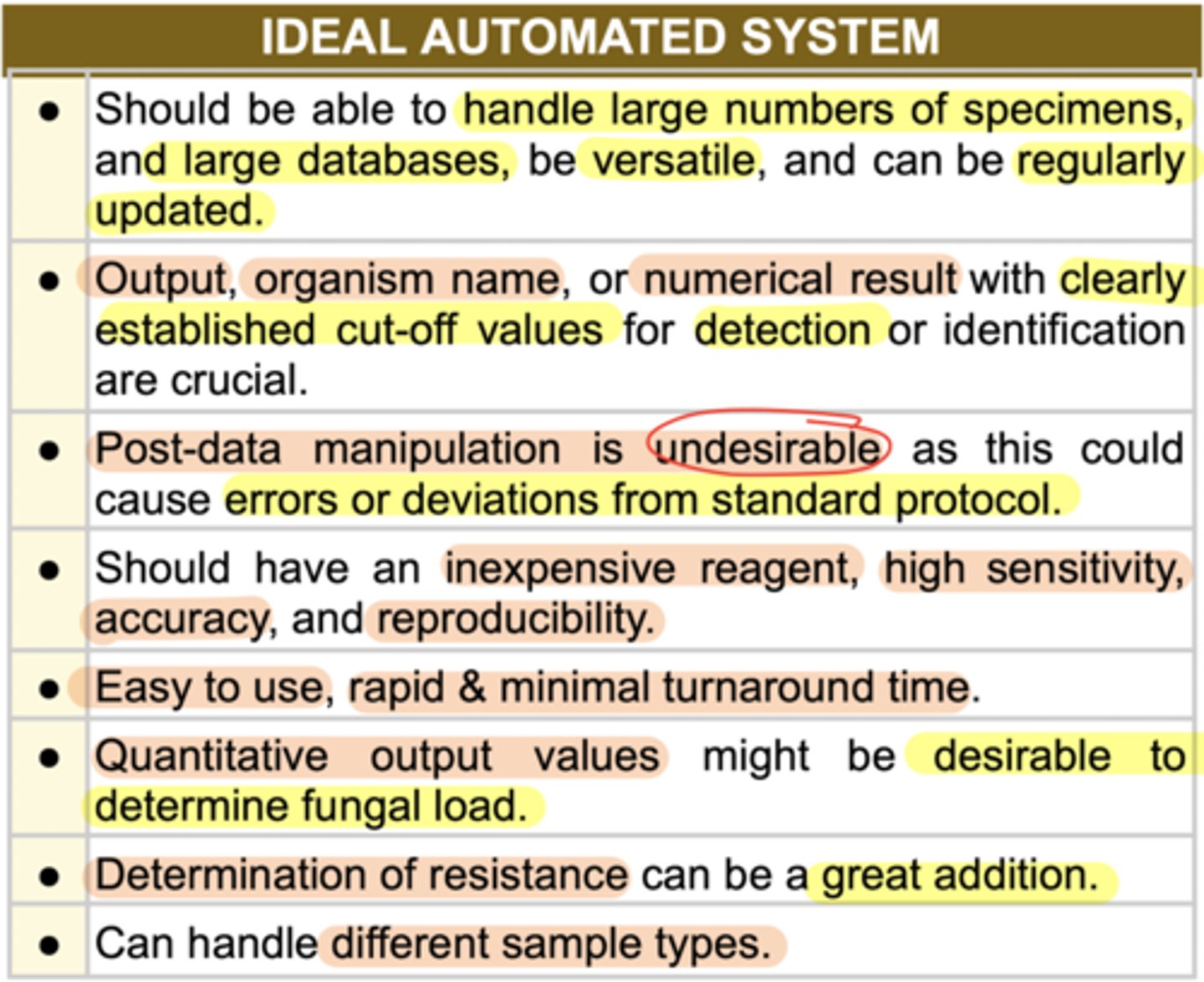
Ideal Automated system
Automated identification and detection systems
1. Colorimetric
2. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF)
3. Syndromic panel (molecular-based)
4. T2MR biosystem for Candida
5. Multiplex PCR assays
Principle: using colorimetric technology in a compact system to determine individual biochemical reactions for ease of identification
Colorimetric system
- Colorimetric is commonly in ____ format
- It contains a panel of biochemical test
card format
Colorimetric system is limited to ___ species
yeast
Must be done before selecting the identification cards in colorimetric system
gram staining
Colorimetric procedures
1. gram stain
2. inocolum
3. card and inoculum on the cassette rack
4. Use Vitek 2 machine
The sample within the matrix is ionized with a laser beam and will generate singly, protonated ions from analytes in the sample
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF)
The protonated ions are then accelerated at a fixed
potential, where these separate from each other on the
basis of their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z)
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF)
It is measured by determining the time required for it to travel the length of the flight tube
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF)
Based on the Time of Flight (TOF) information,
a characteristic spectrum called Peptide Mass Fingerprint (PMF) is generated for analytes in the sample
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF)
Identification of microbes is done by comparing the PMF of unknown organisms with the PMFs contained in the database
Matrix-assisted laser desorpt
2 main systems of MALDI-TOF
1. Bruker
2. Vitek MS
Advantages of MALDI-TOF
1. Fast turn-around time, reliable, only small amount of sample
2. Prior knowledge on organisms is not necessary
3. does not require gram stain
4. Easy to use
5. Single colony is required
MALDI-TOF detects what species?
yeasts and filamentous molds
Bruker MS
database contains 25 genera and 42 species of filamentous fungi (72% of clinical isolates)
Vitek MS
32 genera and 81 species of filamentous fungi (66.8% of clinical isolates)
Saramis (Ruo)
45 genera and 168 species of filamentous fungi.
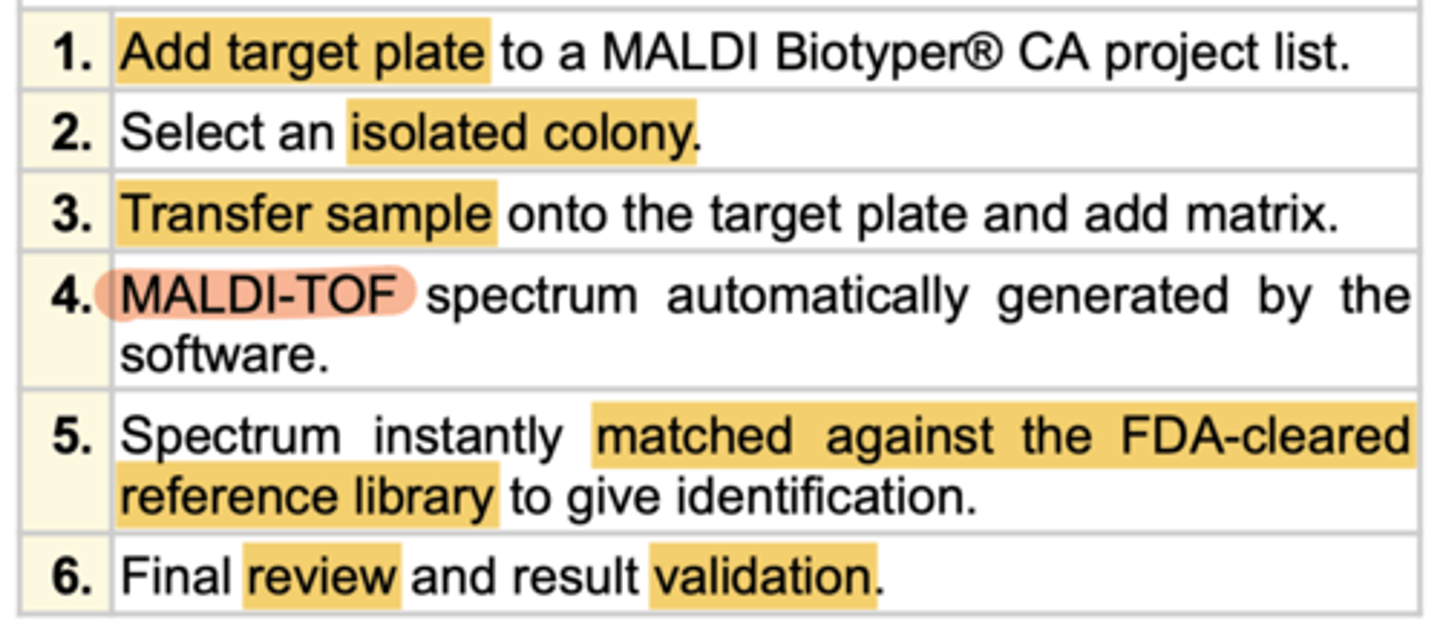
MALDI-TOF procedure
Molecular assay which allows rapid detection of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites from a sample with high sensitivity and specificity
Syndromic panel (molecular-based)
Usually in the form of a cartridge
Syndromic panel (molecular-based)
This test is expensive
Syndromic panel (molecular-based)
Syndromic panel (molecular-based) kits are designed according to the infection of the physiologic system:
1. Systemic (blood)
2. Central nervous system (meningitis & encephalitis)
3. Respiratory system
4. Gastrointestinal system
5. Gastrointestinal system
Tests for 14 of the most common bacteria, viruses and yeast associated with central nervous system infections
Biodire Filmarray meningitis/ encephalitis (ME) panel
TAT of Biodire Filmarray meningitis/ encephalitis (ME) panel
1 hour
CSF volume used in Biodire Filmarray meningitis/ encephalitis (ME) panel
0.2 mL
Combines the nuclear magnetic and PCR molecular assay to directly detect 5 Candida species from whole blood samples.
T2MR biosystem for Candida
lyses candida cells by mechanical bead beating using pan-Candida PCR primers to amplify the internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2) region within the Candida ribosomal DNA operon
T2MR biosystem for Candida
Introduces superparamagnetic nanoparticles coated with binding agents that target species-specific capture probes nested within the pan-Candida amplicons into whole-blood samples
T2MR biosystem for Candida
Detects and provides species-level identification by measuring the magnetic resonance signal produced as the result of the agglomeration of the superparamagnetic particle
T2MR biosystem for Candida
5 candida species detected by T2MR biosystem
1. Candida albicans
2. Candida glabrata
3. Candida parapsilosis
4. Candida tropicalis
5. Candida krusei
T2MR biosystem Cannot differentiate the species of Candida
parapsilosis complex, namely:
1. Candida parapsilosis
2. Candida orthoparapsilosis
3. Candida metapsilosis
T2MR biosystem Has a limit of detection of:
• _____ CFU/mL for C. albicans and C. tropicalis
• _____ CFU/mL for C. krusei and C. glabrata
• _____ CFU/mL for C. parapsilosis
• 3 CFU/mL for C. albicans and C. tropicalis
• 2 CFU/mL for C. krusei and C. glabrata
• 1 CFU/mL for C. parapsilosis
T2MR biosystem:
____ sensitivity
____ specificity
91% sensitivity
99% specificity
Identifies clinically relevant species of Candida directly from whole blood
T2MR biosystem:
users can do semi automation by using an automated nucleic acid extractor system, automated liquid handler for master mix preparation and transfer to PCR tubes.
Commercial Multiplex PCR
Interpretation requires an experienced person in qPCR.
Commercial Multiplex PCR
Commercial Multiplex PCR procedure

T/F
Automation can replace conventional method for filamentous mold and rare yeast species
F
CANNOT COMPLETELY REPLACE