Psych - Senses
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
sensation
process in which sense organ receptors are stimulated and that information is sent to the brain
sensory adaptation
loss of responsiveness in receptor cells after stimulation has remained unchanged for a while
absolute threshold
minimum level of stimuli needed to excite perceptual system
different threshold (JND)
the amount of stimulus change needed for one to detect a change at least 50% of the time
Method of Limits
values of stimuli are presented in ascending or descending order; test level at which stimuli can be detected
Method of constant stimuli
values of a signal are presented in random order; tests absolute and difference threshold
Weber’s law
the size of JND is proportional to intensity of stimulus
Fechner’s law
allows an estimate of the magnitude of the stimulus and expresses relationship between actual magnitude and perceived magnitude of stimuli
Steven’s Power Law
more accurate version of Fechner’s Law, especially for pain and temperature
subliminal perception
stimuli are below the threshold of awareness, but perception occurs outside of conscious experience
Cocktail Party Phenomenon
you cannot hear all of the conversations in a party, but you can notice if you hear your name from across the room
Allocation
to apportion for specific attention, to use netal resources for attention
Filter Theory
information is screened out due to limited processing ability
Attenuation theory
all information is analyzed but factors inhibit attention so not all information is processed
Transduction
transformation of one form of energy into another; stimulus information into nerve impulses
Synesthesia
a neurological condition where stimulating one sense triggers an involuntary experience in another sense, resulting in perceptions like seeing colors when hearing music
McGurk effect
a perceptual phenomenon and auditory illusion where visual information from lip movements conflicts with auditory information, causing the brain to perceive a third, different sound than what was actually spoken
cornea
small transparent bulge covering the pupil/iris
pupil
dark opening at the center of the eye
Iris
pigmented part of the eye
Lens
part behind pupil
retina
light-sensitive layer at the back of the eyeball
photoreceptors
light-sensitive cells in the retina that convert light energy to neural impulses
Rods
sensitive to dim light but not colors
cones
sensitive to colors but not dim light
Duplicity
the retina has two different receptor systems (rods and cones)
Optic nerve
bundle of neurons that carry visual information from retina to brain
Fovea
area of sharpest vision in retina
Blindspot
There are no photoreceptors where the optic nerve exits the eyeball
nearsighted/myopic
one can see things clearly up close (elongated eyeballs)
farsighted/hyperopic
One can see things clearly far away (shortened eyeballs)
visual activity test
measures the ability to see fine detail and visual clarity
Bipolar cells
layer of the retina that collect neural impulses from photoreceptor and shuttles them to ganglion cell layer
Ganglion cells
layer of the retina that gathers neural impulses from the bipolar layer and the axons make up the optic nerve
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
region of the thalamus that receives fibers from the cone-rich area of the retina and relays messages to the visual cortex
Striate cortex
first area of visual cortex to recieve visual input from the thalamus
Optic chiasm
X-shaped structure formed by the crossing of the optic nerves in the brain
parallel processing
brain simultaneously processes parts on an image
sequential processing
brain uses a step-by-step linear processing of an image
dark adaptation
increase in the sensitivity of light when illumination goes from high to low
receptive fields
specialized areas of the retina that produce a firing of cells in the visual system
prosopagnosia
special type of agnosia resulting in an inability to recognize faces
saccades
rapid voluntary movements of the eyes
perceptual span
size of the region a person sees while fixating visually
Hue
psychological sensation derived from the wavelength of visible color
Brightness
psychological sensation caused by the intensity of light waves
saturation
depth of hue determined by homogeneity of wavelengths
trichromats
people with normal color vision who have all three types of cones
trichromatic theory
There are three types of cones that are sensitive to red, blue, and green wavelengths
opponent-process theory
Three types of cones process color in complementary pairs. all fire, but one is stronger (red-green, yellow-blue, black-white)
Dichromats
one can only perceive 2 of 3 basic colors
monochromats
no colors are perceived
tetreachromats
4 cones instead of 3; can see more color than normal
afterimages
sensation that lingers after the stimulus is removed
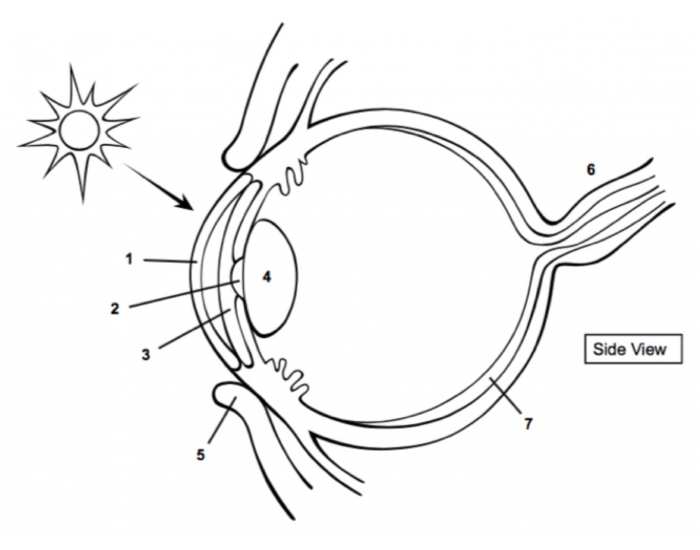
cornea
1
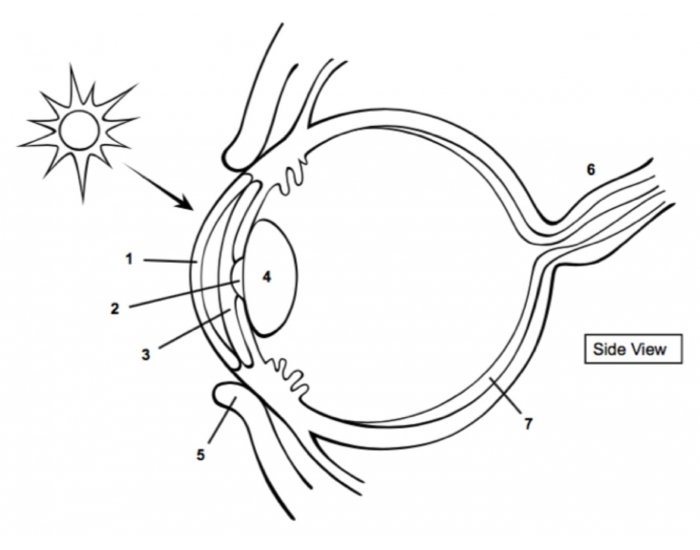
pupil
2
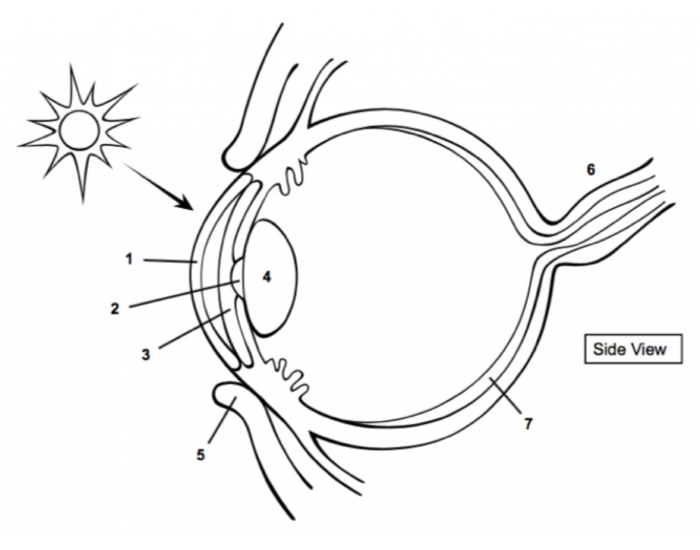
Iris
3
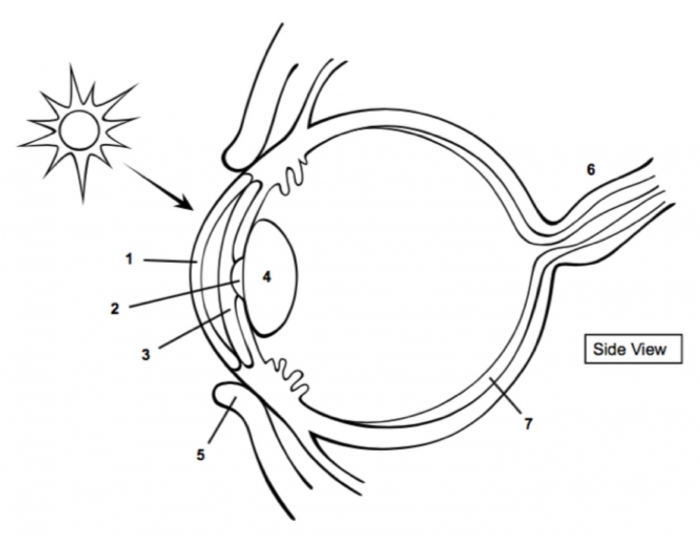
Lens
4
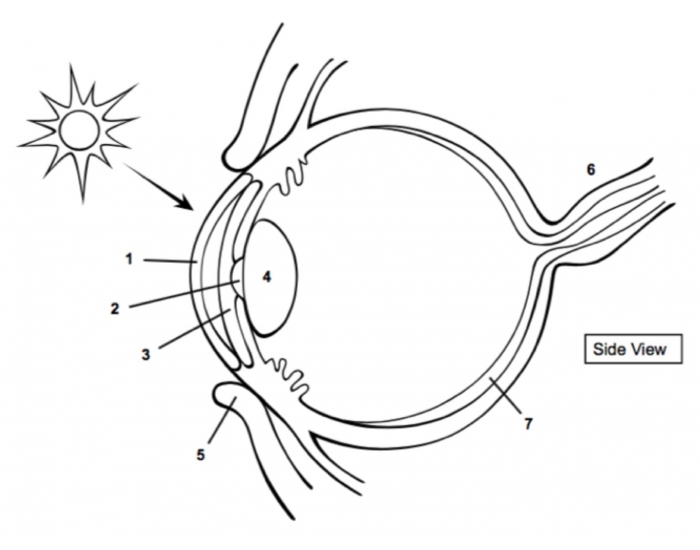
optic nerve
6
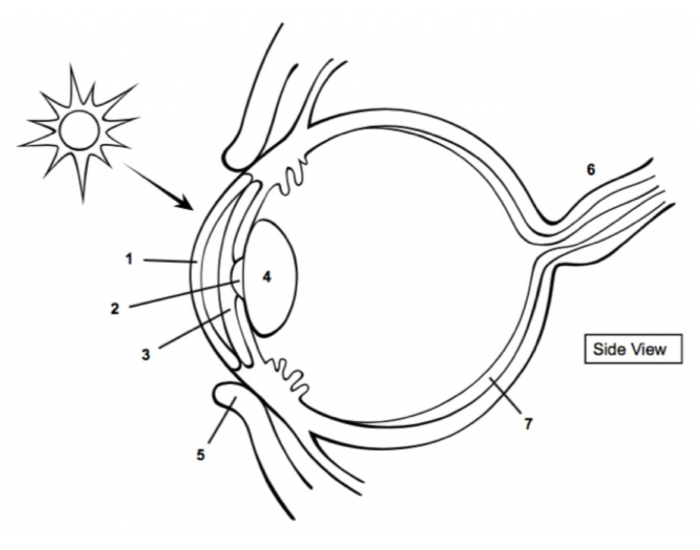
retina
7
sound
psychological experience that occurs as changes in air pressure stimulate the receptive organ for hearing
frequency
number of cycles completed by a wave in a given amount of time
Amplitude
physical strength of a wave
Tympanic membrane
the eardrum
ossicles
Hammer (malleus), anvil (ineus), stirrup (stapes)
cochlea
where sound waves are transduced
basilar membrane
thin strip of tissue sensitive to vibrations
auditory nerve
neural pathway connecting the ear and the brain
Pitch
sensory characteristic of sound produced by the frequency of the sound wave
Volume
sensory characteristic of sound produced by the amplitude os a sound wave
timbre
quality of a sound wave that derived from the waves complexity
conduction deafness
inability to hear resulting from damage to structures of the middle or inner ear; cochlea not getting info
nerve deafness
inability to hear linked to a deficit in the body’s ability to transmit impulses from the cochlea to the brain; auditory nerve
audiogram
graph showing hearing sensitivity at selected frequencies
place theory
states that our perception of sound depends on where each frequency produces vibrations along the basilar membrane
frequency theory
states that the frequency of the auditory nerve impulses corresponds to the frequency of a tone, which allows us to detect pitch
volley theory
states that groups of neurons in the auditory system fire action potentials in rapid, overlapping succession to encode sound frequencies that exceed the firing rate of any single neuron
interaural time difference
sound reaches ears at different intensities due to space
interaural intensity difference
sound coming from left will be louder in left ear
vestibular sense
sense of body orientation with respect to gravity
kinesthetic sense
sense of body position and movement of body parts relative to each other
epidermis
outer layer of the skin
dermis
layer under epidermis; contains live cells, nerve endings, blood, hair cells, and sebaceous glands
hypodermis
underlayer; thick insulating cushion
gate-control theory
There are “neural gates” that can block incoming pain impulses across the “gates”
olfaction
sense of smell
pheromones
chemical signals released by organisms to communicate with other members of the species
gustation
sense of taste
taste buds
receptors for taste
papillae
bumps on your tongue
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami, oleogustus
What are the different tastes?
phantom limb sensation
the perception of sensations, such as pain, tingling, or warmth, in a limb that has been amputated or lost
semicircular canals
three fluid-filled tubes in the inner ear that work together to detect head rotation and maintain balance
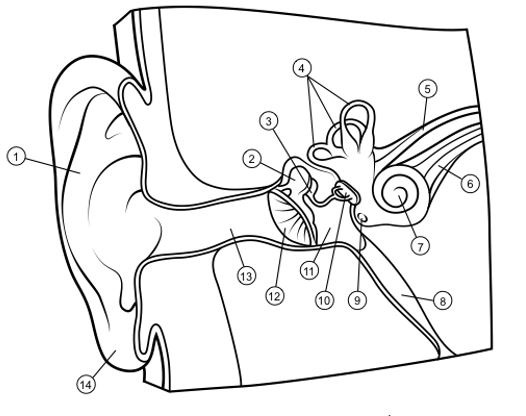
outer ear
1
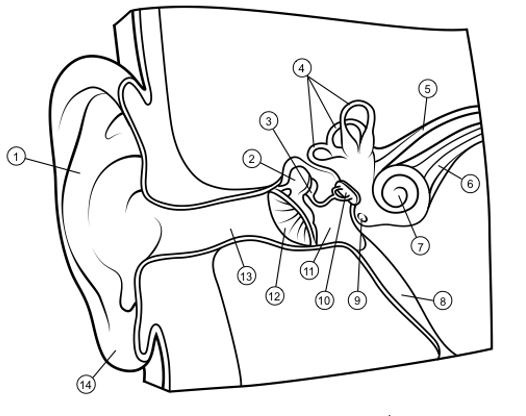
hammer
2
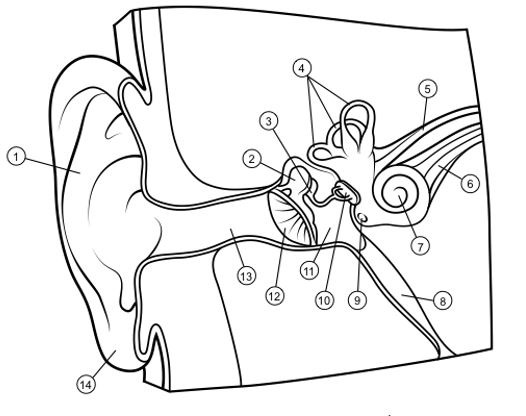
anvil
3
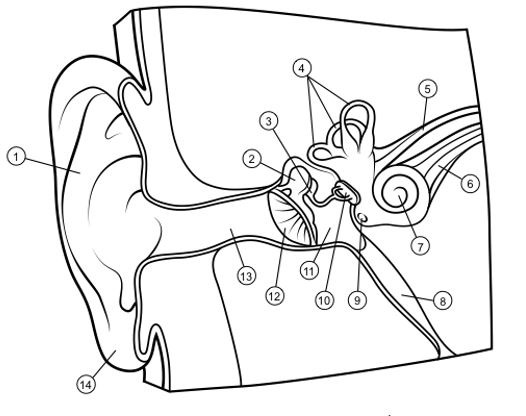
semicircular canals
4
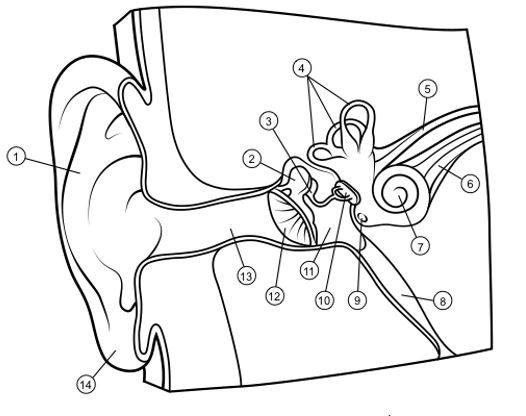
vestibular nerve
5
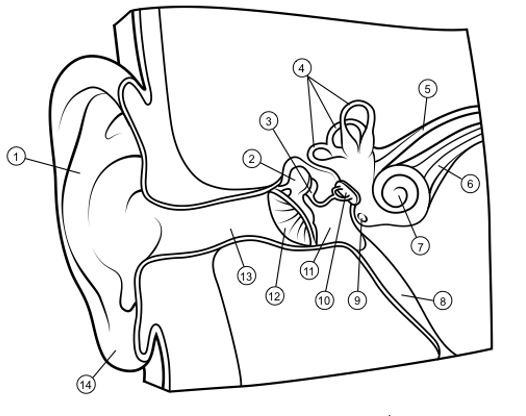
auditory nerve
6
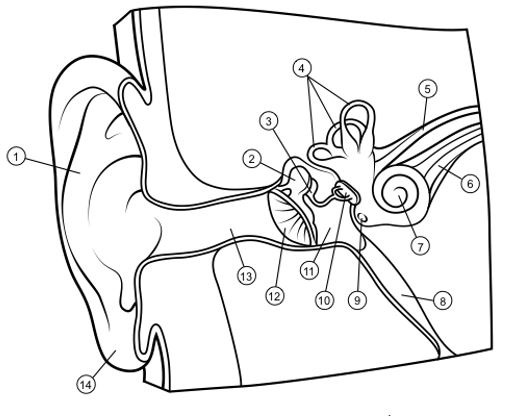
cochlea
7