AP Biology - Unit 1
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
by: Gabe Parr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Cohesion
water is attracted and will bond with other water molecules(hydrogen bonds)
Polarity
property of water that is due to the unequal sharing of electrons between oxygen and hydrogen within a water molecule(gives hydrogen slightly positive charge and oxygen slightly negative charge)
7 Properties of Water
Polarity, Cohesion, Adhesion, Capillary Action, Temperature Control(High Specific Heat and High Heat of Vaporization), Density, Excellent Solvent
Basic Solutions
bitter taste, also referred to as alkaline, slippery/soapy feel
Acidic Solutions
sour taste, strong ones can dissolve metals and cause burns
Solution is Acidic if…
dissolving something in water causes it to have more H+ than OH-
Ionic Bonds
giving up or gaining of electrons to have a full valence(outer) shell *(weak)
Dissociation of Water
H2O —> H+(hydrogen ion) + OH-(hydroxide ion)
Solution
result of one substance dissolving into another substance
Isotopes
form of an element that has a different number of neutrons
Solvent
substance doing the dissolving in a solution
Polar Covalent Bonds
atoms share the electrons unequally (Ex: water)
Amino (Functional Group)
-NH2
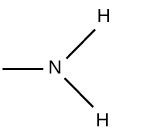
Sulfhydryl (Functional Group)
-SH

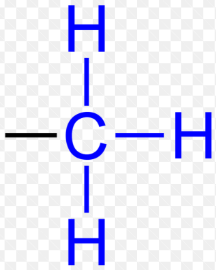
Methyl (Functional Group)
-CH3
Characteristics of Hydrocarbons
nonpolar, not soluble in water, hydrophobic, stable
Isomers
molecules with same molecular formula, but different structure/chemical properties
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
atoms share the electrons equally (balanced/stable)
Covalent Bonds
sharing of electrons to have a full valence (outer) shell *(strong)
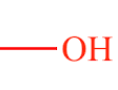
Hydroxyl (Functional Group)
OH
4 Classes of Macromolecules
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Lipids
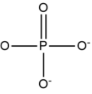
Phosphate
PO4
Dehydration Synthesis/Condensation Reaction
process of joining monomers to a make a polymer by losing water
Hydrolysis
process of breaking a polymer into monomers by adding water (Ex: digestion)
Buffers
substance that when added to a solution enables the solution to resist changes in pH
6 Most Common Elements of Life
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur
Hydrocarbons
simplest carbon molecules, combination of carbon and hydrogen
Macromolecules
large molecules formed by carbon
pH scale
acids 0-6 pH, bases 8-14 pH, neutral liquid = 7 pH, scale works by powers of 10
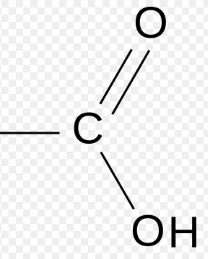
Carboxyl
-COOH
Solute
dissolved substance in solution
Carbonyl
C=O
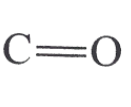
Polymers
chain like macromolecules of similar or identical monomers that are covalently bonded together
Molecule
combination of two or more elements that are bonded together
Solution is Basic if…
dissolving something in water causes it to have more OH- than H+
Monomers
repeating units that make up polymers
Adhesion
water is attracted to other polar molecules and ionic substances(will form hydrogen bonds with them)
Capillary Action
the upward movement of water due to the forces of adhesion being greater than cohesion(surface tension also involved)
Temperature Control
High Specific Heat: water resists changes in temperature due to hydrogen bonds
High Heat of Vaporization: water requires a lot of energy to vaporize(transform liquid to gas) due to strong hydrogen bonds
Density
as water solidifies it expands and becomes less dense
Solvent (Property of Water)
water is an excellent solvent with other polar(hydrophilic) molecules and ionic substances(forms hydrogen bonds with them)
Living Systems need…
a constant input of energy in order to grow, reproduce, and maintain organization
All Organisms are built from the same 4 types of molecules. Which are…
Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids
Carbohydrates
Definition: main source of energy for living things
Polymers: sugars, starches, plant fiber(cellulose)
Monomers: monosaccharides(simple sugars)
composed of carbon,hydrogen,oxygen(1-2-1 ratio in monosaccharides)
Functions: energy, energy storage, raw and structural materials
General Carbohydrate Formula
(CH2O)x
Lipids
Definition: high energy, hydrophobic molecule
Polymers: fats, oils, waxes, cholesterol, steroid hormones
Important Building Block: fatty acids
composed of lots of carbon and hydrogen, little oxygen
Proteins
Definition: a polymer of amino acids, many diverse functions
Polymers: muscle tissue(meat), enzymes, antibodies
Monomers: amino acids
*most diverse macromolecules
*shape determines function
Monosaccharide
simple sugar (Ex: glucose)
Disaccharide
two monosaccharides joined together through a glycosidic linkage after dehydration synthesis (Ex: sucrose/table sugar)
Polysaccharide
multiple monosaccharides joined together through glycosidic linkages after dehydration synthesis that require little energy to build (Ex: starch)
Glycosidic linkage
type of covalent bond between sugars after dehydration synthesis
Glycogen
polysaccharide used for energy in animals
Diverse Groups of Lipids
fats, phospholipids, steroids
Structure of Fats
glycerol + fatty acids
Ester linkage
type of covalent bond that forms 3 times between a hydroxyl and carboxyl in a fat molecule
Saturated fats have…
no carbon double bonds
Unsaturated fats have…
carbon double bonds that will give a little bend in structure of fatty acid
Structure of Phospholipids
phosphate group + 2 fatty acids
Phospholipids Head vs Tails
Head = hydrophilic, Tails = hydrophobic
Structure of Steroids
4 fused carbon rings
Fats are…
non-polar(little amount of oxygen) and hydrophobic
Lipoproteins
combination of a lipid and protein, carries cholesterol around body
Low-density Lipoprotein (LDL)
carries cholesterol to body tissues, "bad" cholesterol
High-density Lipoprotein (HDL)
carries cholesterol away from body tissues, "good" cholesterol
Glucose and Fructose both act as energy sources and have…
the same chemical formula(C6H12O6), but different atom arrangements
Deoxyribose
5-carbon sugar that is found in DNA, storages genetic information
Ribose
5-carbon sugar that is found in RNA, takes genetic information from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm in order to make protein
Glyceraldehyde
3-carbon sugar that has a key role in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis
Fructose
6-carbon sugar found in fruit
Glucose
6-carbon sugar that is an important source of energy for living organisms
Chemical Formula of 2 Monosaccharides, both C6H12O6, combining through Dehydration Synthesis
C12H22O11
Purposes of Cholesterol
precursor of hormones, keeps cell membranes flexible
Functions of Proteins: C-MEATS
C: Contraction
M: Messenger
E: Enzymes
A: Antibodies
T: Transport/Storage
S: Structural
Structure of Amino Acids
Central carbon atom, left side: amino group, right side: carboxyl group, top: hydrogen atom, bottom: R-Group/Side Chain
R Groups of Amino Acids can be…
nonpolar(hydrophobic), polar(hydrophilic), charged/ionic
Peptide bond
type of covalent bond between amino acids after dehydration synthesis
Name of Ends of Polypeptide Chain
Starting End: N terminus (exposed amino functional group)
Ending End: C terminus (exposed carboxyl group)
Amino acid "residue"
what's left after an amino acid has been connected to a polypeptide chain after dehydration synthesis(whole amino acid without peptide bonds)
Polypeptide
multiple amino acids joined together by peptide bonds after dehydration synthesis
Primary Structure
"beads on a string", sequence of amino acids
*order of amino acids is determined by genes
*order determines the 3D shape of protein
Alpha Helix
secondary protein structure: corkscrew shape due to hydrogen bonding between the atoms of the amino acids of the polypeptide backbone
Beta Pleated Sheet
secondary protein structure: back-and-forth folded shape due to hydrogen bonding between the atoms of the amino acids of the polypeptide backbone
Tertiary Structure
3D folding due to interactions between R-Groups; mainly hydrophobic interactions but can also be hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and disulfide bridges
*3D folding establishes the protein's function
Quaternary Structure
2 or more polypeptides combined through weak bonds to make a more complex and stable protein structure (*found only in some proteins)
Why should the final shape of a protein be at a low energy state and not a high energy state?
Because at a high energy state, the protein will be unstable and easily break, while a protein that is at a low energy state will be stable.
Hydrophobic Side Chains in a Protein will…
bend and fold into the polypeptide backbone to shield themselves from the water
Acidic/Basic Side Chains in a Protein will…
come close together to neutralize each others charges
Cysteine Side Chains in a Protein will…
move closer together to form disulfide bridges
Hydrophilic Side Chains in a Protein will…
bend to the outside of the polypeptide backbone to be closer to the water
Electronegativity
atoms that are greedy for electrons (Ex: oxygen)
Hydration Shell
the sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion
Molarity
common measure of solute concentration
Change in Amino Acid Subunits at the Primary Level of Structure will…
lead to changes in structure and function of the protein
Denaturation
protein loses its 3D shape due to changes in pH, increase in temperature, or salinity, causing it to unravel back to the primary structure
In the denaturing of a protein, the protein loses its original…
shape and function
Phospholipids are an important structural component of…
cell membranes
Cellulose
structural polysaccharide for plants
Chitin
structural polysaccharide for fungus/arthropods
Starch
polysaccharide used for energy in plants