HS 346 - Week 1 Lecture
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Undernutrition
increases the risk of death & illness, particularly among young children.
In early life (and during pregnancy) has lifelong consequences for health as well as cognitive development, schooling & wages.
High rates result in substantial economic losses for families, communities & countries.
SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals) links to nutrition
1: end poverty
2: end hunger, achieve food security, improve nutrient, sustainable agriculture
3: healthy lives
4: quality education/learning
5: gender equality and empowerment
12: sustainable consumption and production patterns
17:revitalize global partnerships
UN System standing committee on nutrition
Explicit attention to nutrition is needed in considering achieving the SDGs.
malnutrition
Deficiency or excess of nutrients affecting health.
Nutrition
What are people consuming and how does it affect health
Food security
Availability, access, utilization, and stability of food and the surrounding food system
Macronutrients
consumed in large quantities
provide cals (energy), carbs/fats/proteins
Micronutrients (vitamins and minerals)
Consumed in small quantities, don't provide cals (energy), required for body processes. Ex: vitamin A, folate, iron, zinc
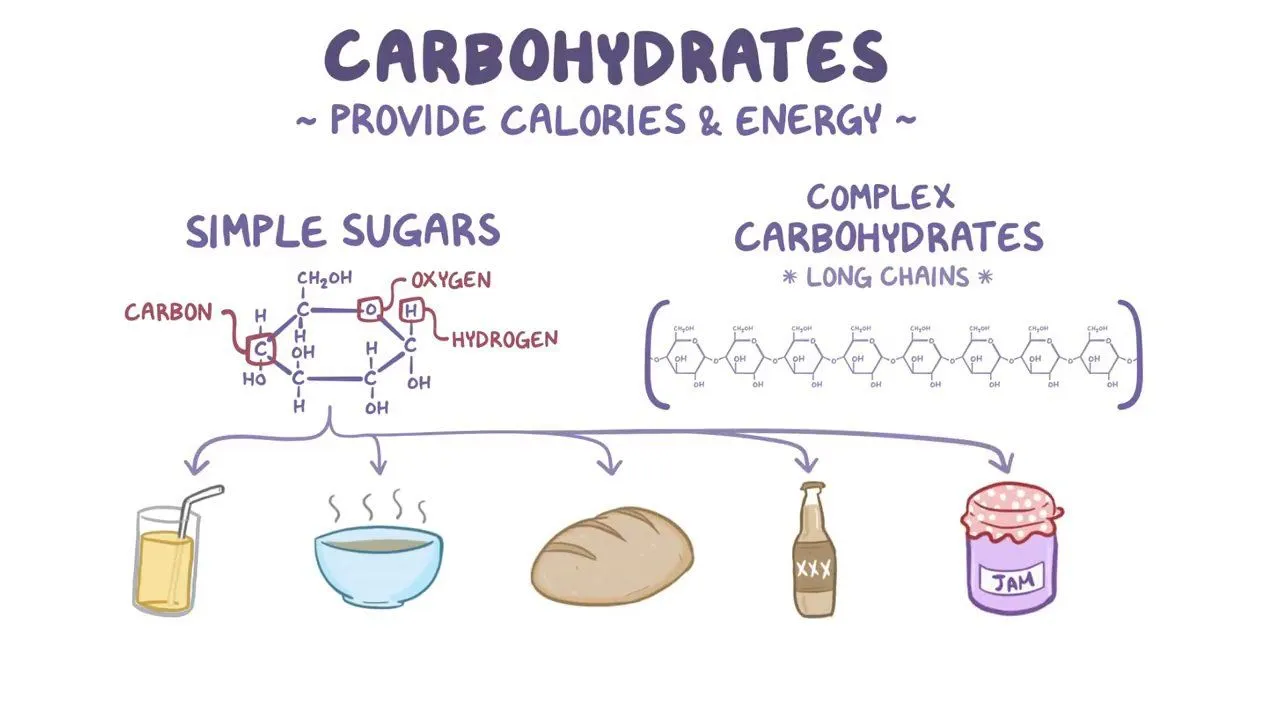
Carbohydrates
Biomolecules consisting of…
carbon (C)
hydrogen (H)
oxygen (O)
usually with a H:O atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) → Cm(H2O)n (where m may be different from n)
How many calories are in a gram of carbohydrates?
4 calories per gram
glycemic index (GI)
indicator of the ability of different types of foods that contain carbohydrate(s) to raise the blood glucose levels within 2 hours.
What foods have the highest GI
Carbs
GI of 100
Standard, equivalent amount of pure glucose
Glycemic load (GL)
measure related to Glycemic Index (GI).
multiplies the GI of a food by the carbohydrate content of a common serving.
focuses on carbohydrate quality.
GI is based on a standardized amount of each carbohydrate, while GL takes quality & quantity of average serving size into account.
Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load have been associated with a greater risk of what disease
Type 2 diabetes
How to lower risk of cardiovascular disease
Replace products made w white flour and potatoes w whole-grain, minimally refined cereal products
Whole grain
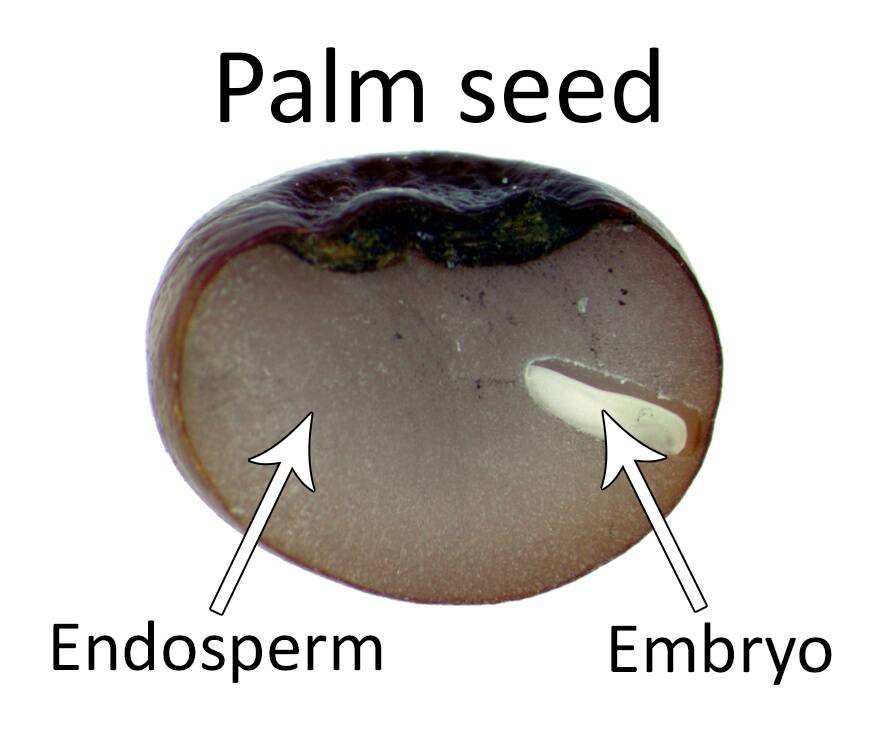
a grain that maintains the same relative proportions of starchy endosperm, germ, and bran as the original (all but the husk); not refined.
Germ
embryo which has the potential to sprout into a new plant. It contains many B vitamins, some protein, minerals, and healthy fats.
Bran
Multi-layered outer skin of the edible kernel. Contains antioxidants, B vitamins, and fiber
Endosperm
the germ's food supply, provides energy to the young plant so it can grow roots and sprouts.
Largest portion of the kernel.
Contains starchy carbohydrates, proteins and small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Proteins
Large molecules comprised of amino acids.
Essential for all living beings.
Main structural components of body tissues such as muscle, hair, collagen, etc.
Serve as enzymes, antibodies & part of some hormones.
Structure of an amino acid
Central carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, variable side chain (R).
How many calories per gram are there in protein?
4 calories per gram
Essential amino acid
An amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by an organism and must be supplied in its diet. There are 9 essential amino acids for humans (including tryptophan & methionine).
Complete protein
food source of protein that contains an adequate proportion of each of the 9 essential amino acids (for humans).
Kwashikor
protein malnutrition/the sickness the baby gets when the new baby comes (Ga language, Ghana)
Edema
Swelling in the ankles, feet, and abdomen.
Enlarged liver with fatty infiltrates, thinning of hair, loss of teeth, skin depigmentation and dermatitis.
T/F: edema can be treated with PROTEIN but it can have long term effects on children.
True. It can be treated by adding protein to the diet, however it can have a long-term impact on a child's physical and mental development (severe cases, death).
Fats (lipids)
Essential for cell membranes (lipid bilayers).
Precursor to steroids (ex: cholesterol and testosterone).
Long molecules made up primarily of carbon and hydrogen.
Store energy in the body (energy dense).
Transport other molecules.
How many calories are in a gram of fat?
9 calories per gram
What is the most common fat in the human diet?
Triglycerides (glycerol + 3 fatty acids).
2 essential fatty acids for humans
linoleic acid (omega-6) and alpha-linolenic acid (omega-3).
these fatty acids are considered essential because the human body cannot synthesize them and must be obtained through diet
seeds, nuts, and vegetable oils
docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
comes from breast milk, fish, and algae oil.
can be synthesized from ALA.
fatty acid that become essential during specific developmental conditions.
primary structural component of the brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina.

T/F: high total fat consumption is related to obesity, chronic disease, and mortality.
False! There is little scientific evidence that total fat consumption is causally related to obesity, chronic diseases or mortality → TYPE of fat is more important than quantity
How are fats classified?
saturated, mono-unsaturated, poly-unsaturated, trans-fats (# of double bonds)
Monounsaturated fatty acids
An unsaturated fatty acid with a single double bond.
Most common in human diet - oleic acid (found in canola/vegetable oil).
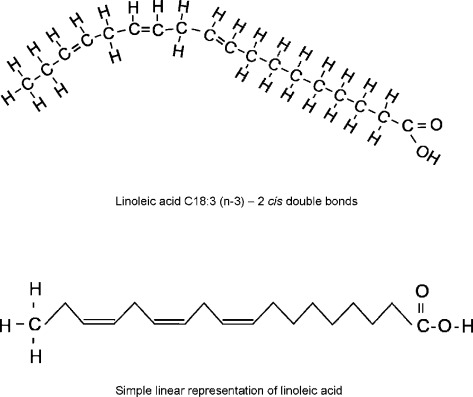
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
A fatty acid with multiple double bonds.
Most common…
linoleic acid (LA, an omega-6 FA)
alpha-linolenic acids (ALA, an omega-3 FA)
There is evidence that replacing saturated fatty acids with ____ decreases the risk for coronary heart disease
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA)
There is evidence that replacing carbohydrates with ____ increases HDL (good cholesterol) and that replacing saturated fat with ____ reduces LDL/total HEL cholesterol ratio (bad cholesterol).
Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs)
There is POSSIBLE evidence that _____ may decrease the risk of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome
Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs)
Saturated fats
fats that are solid at room temperature
Total intake of SFA should not exceed ___% of energy
10
Do saturated fatty acids have a relationship with cancer or metabolic syndrome?
No. They are more related to increasing the risk of coronary heart disease.
Trans fats
partially hydrogenated oils (margarine). Cause ~500k premature deaths worldwide each year.
First country to eliminate trans fat from their food supply
Denmark, 2004
How much of the world's population suffers from hidden hunger (a lack of vitamins/minerals)?
1/3
T/F: most people affected by hidden hunger do not show physical symptoms usually associated with hunger and malnutrition.
True. Instead, they may have impaired health & development due to these micronutrient deficiencies.
Vitamins are organic or inorganic?
organic (contain carbon)
Minerals are organic or inorganic?
inorganic (cannot be broken down, elements from the earth)
Examples of minerals (diet relevant)
zinc, iron, iodine
examples of water soluble vitamins (diet relevant)
Folate (vitamin B9), vitamin b12 (cobalamin)
Examples of fat-soluble vitamins (diet relevant)
Vitamin A (retinol), vitamin D (cholecalciferol)
Fat soluble vitamins
Don't dissolve in water.
Absorption and metabolism require dietary fat intake (vitamin D fortified milk).
Excess not easily excreted.
Stored in adipose tissue.
water soluble vitamins
Dissolve easily in water (vitamin C fortified juice). Excess amounts are excreted. Consistent daily intake is required.
Anemia
Condition where the # of red blood cells or their oxygen carrying capacity is insufficient to meet physiologic needs.
What causes anemia
iron Deficiency (50% of cases are due to this)
folate (B9), B12, or vitamin C deficiency
Non-nutritional causes include parasitic infections, sickle cell.
Consequences of anemia
Fatigue, weakness, dizziness, drowsiness, complications during pregnancy, increased risk of low birth weight, maternal mortality due to hemorrhage, impaired cognitive development
Potential interventions for anemia
Iron + folate acid (IFA) supplements. Micronutrients. Dietary diversification. Infection control/delayed cord clamping.
T/F: iron deficiency is the most common nutritional deficiency in the world.
True! Most common nutritional deficiency in the world.
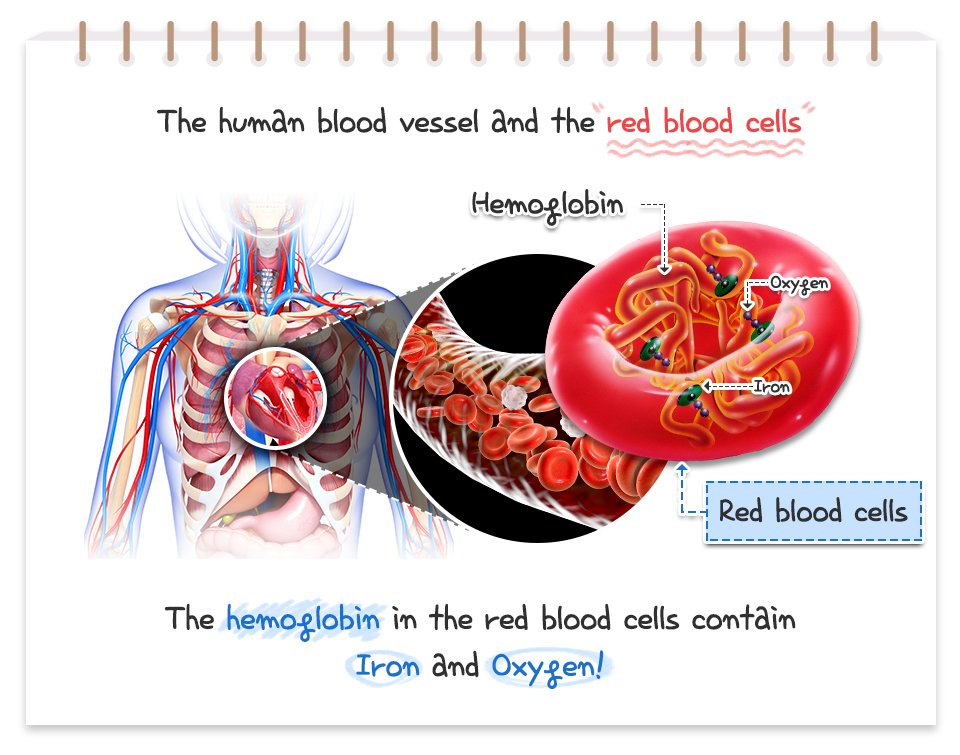
Where is most iron in the body found?
attached to hemoglobin in the RBCs (carries oxygen from lungs to tissues).
Who is at the highest risk of iron deficiency?
Women and children
Where is iron found?
Heme: meat, poultry, fish (higher bioavailability). Non-heme iron: plants and dairy.
What is the absorption of iron dependent on
Dose and affected by other nutrients (vitamin C is an enhancer of non-heme iron absorption).
Most important function of iron in the human body
Oxygen transport (also enzyme systems -> regulation of cell growth and differentiation and immune function).
Iodine is found where
Seaweed and seafood, iodized salt, yogurt, fruits and veggies (soil dependent).
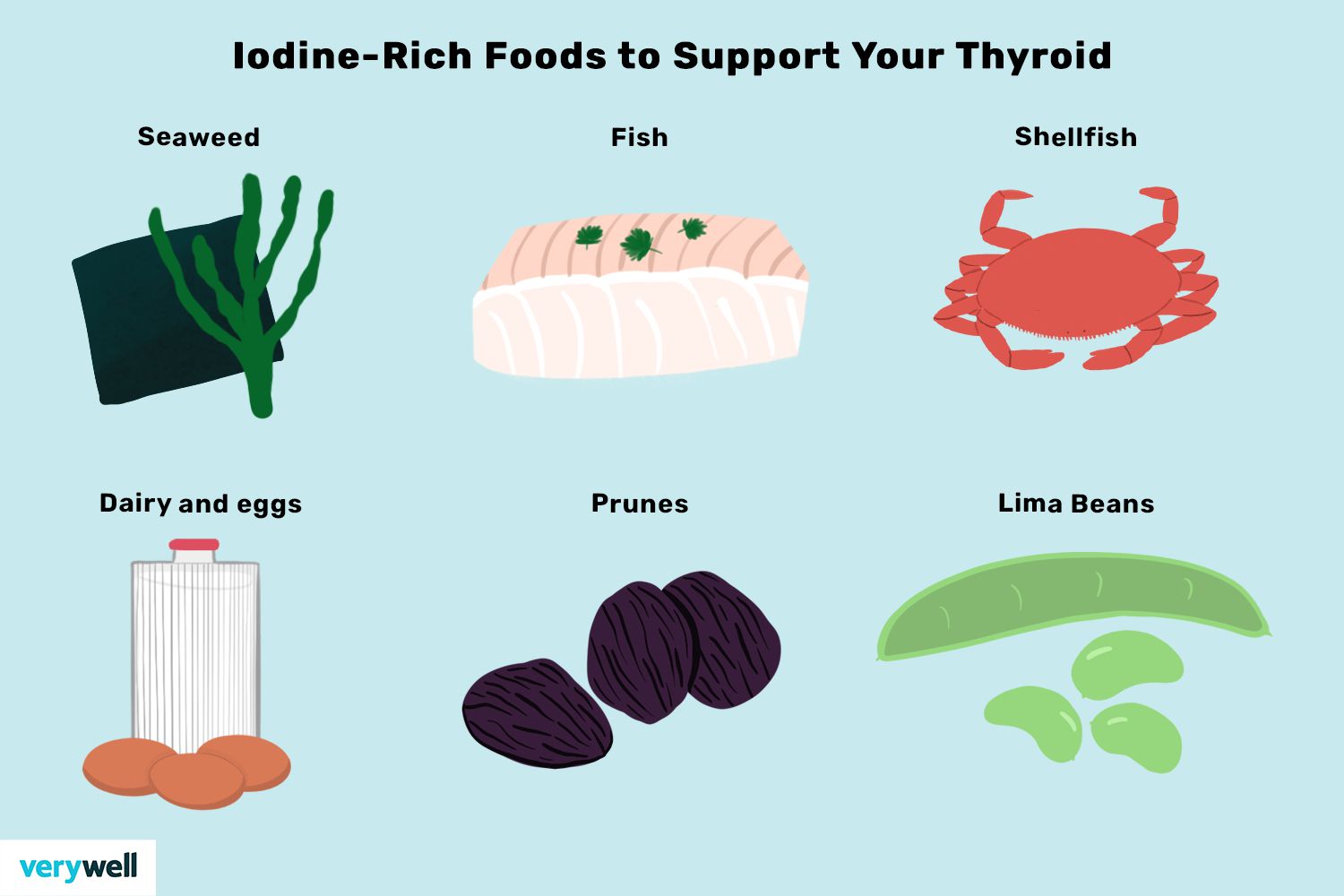
Iodine function
component of thyroid hormone (T3 &T4).
Why are thyroid hormones important?
essential to proper development and differentiation of almost all cells of the human body.
control of basal metabolic rate, macronutrient metabolism, heat regulation, growth & body's sensitivity to catecholamines (such as adrenaline).
Consequences of iodine deficiency
Mental retardation (cretinism) goiter (visibly enlarged thyroid gland), hypothyroidism, impaired growth and development
What deficiency is the leading cause of preventable cognitive impairment?
Iodine
Where is zinc found?
Bioavailability is best in animal sources (beef, poultry, oysters, crab meat).
Plant sources: beans, nuts, whole grains, fortified breakfast cereals, & dairy; however phytates— found in whole-grain breads, cereals, & legumes—bind to zinc and inhibit absorption lowering bioavailability from plant foods.

Zinc function
component of >100 enzymes
essential in cell growth and differentiation
essential for immune system and the gastrointestinal tract
Zinc supplementation is part of WHO guidelines to treat what disease?
Diarrhea
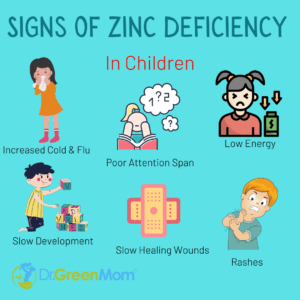
Consequences of Zinc deficiency
Shiraz dwarfism in extreme cases (delayed growth and sexual development).
Poor growth, weight loss, poor immune function, poor wound healing.
Vitamin a importance
Essential for vision
cell function for growth
epithelial cellular integrity
immune function and reproduction
Vitamin A deficiency is the leading cause of...
...preventable childhood blindness. Also causes reversible night blindness, and increases the risk of death from common childhood illnesses such as diarrhea
T/F: globally, 1/3 of children aged 6-59 months were estimated to be vitamin A deficient
True! Between 100 and 140 million children are deficient.
Highest rates in sub-Saharan Africa (48 per cent) and South Asia and South Asia (44 per cent).
Vitamin Supplementation reduces...
...all-cause mortality by 12-24%
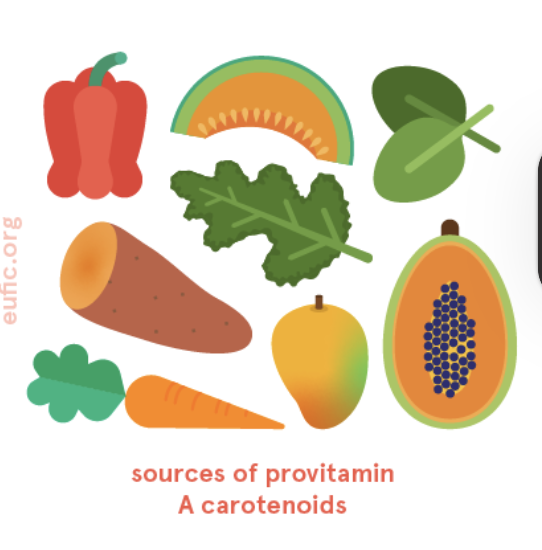
sources of preformed vitamin A (retinol)
animal sources (liver, kidney)
cream, butter, egg yolk
more bioavailable

sources of provitamin A carotenoids (need to be converted into vitamin A)
Found in plants (dark green, yellow, and red fruits/veggies). Beta carotene is found in mangos, yellow sweet potatoes, and carrots.
Many B-complex vitamins work in tandem in several bodily processes...
...energy release, energy formation, RBC formation, oxygen transport and delivery, protein metabolism
citric acid cycle
release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy (ATP).
Folate (B9)
Water-soluble B vitamin that occurs naturally in food (Latin = folium = leaf)
Folic acid
synthetic form of folate found in supplements/fortified foods
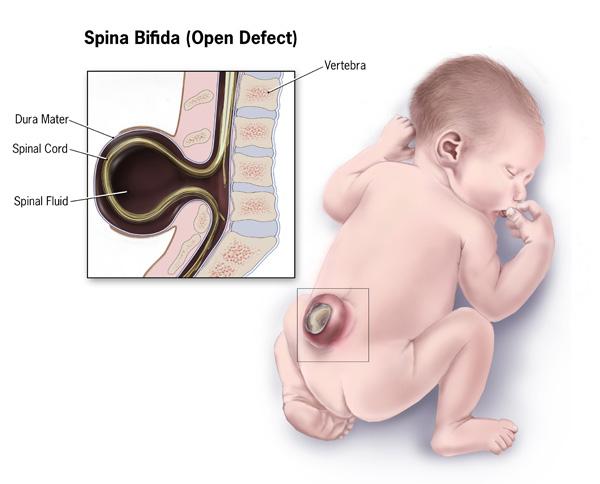
Folate deficiency
megaloblastic anemia, neural tube defects (defects of brain, spine, spinal cord) (spina bifida, anencephaly)
Prevention of folate deficiency
Mandatory flour fortification, folic acid supplements for women capable of being pregnant