population and the environment- Japan and the demographic transition model單詞卡 | Quizlet
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Demographic Transition Model
A model to suggest that a country's total population growth rate cycles through stages as that country develops economically. Each stage is characterized by a specific relationship between birth rate (number of annual births per one thousand people) and death rate (number of annual deaths per one thousand people).
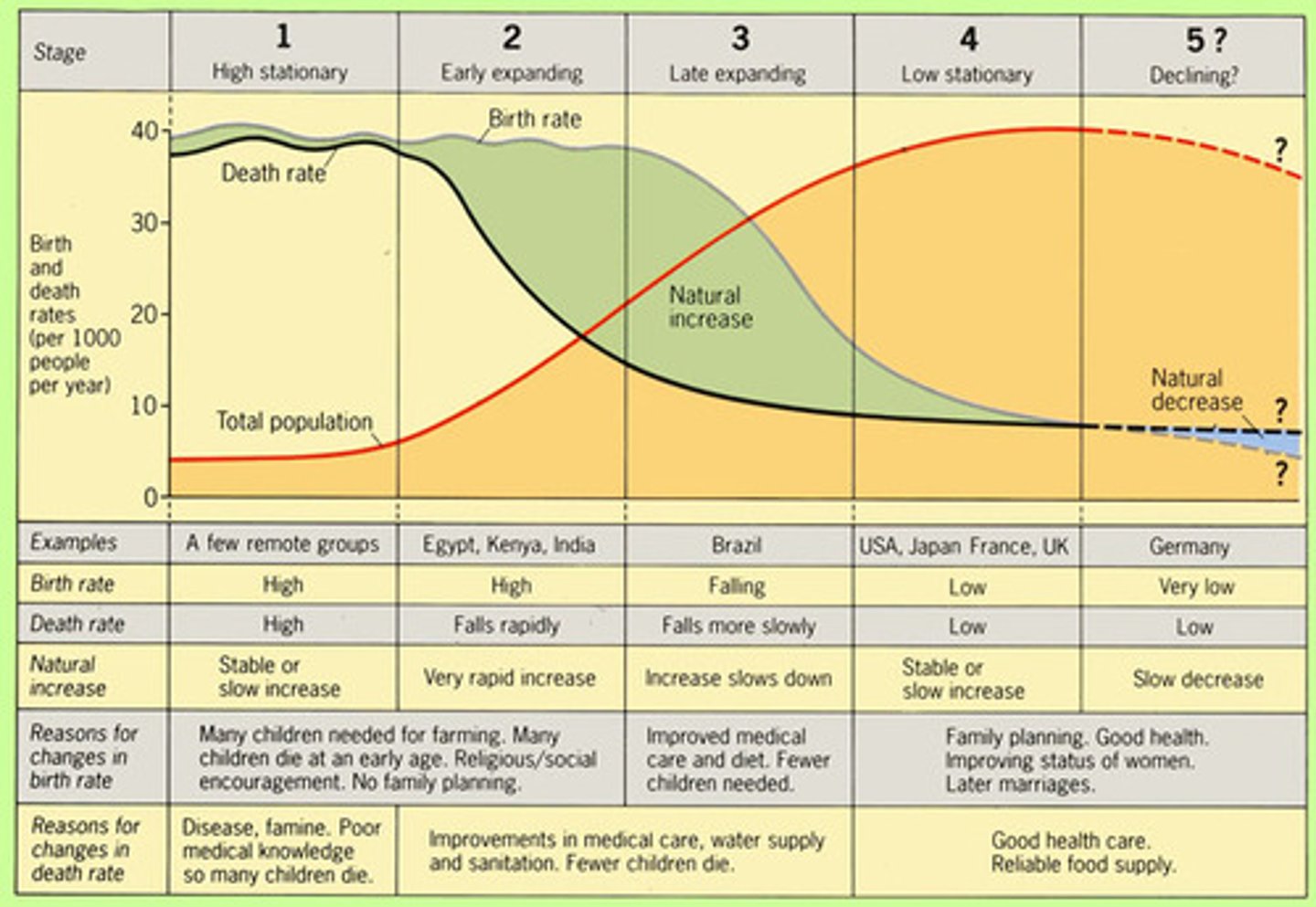
why does the demographic transition model fluctuate in stage 1
stage 1 would be populations like tribes
there may be events like famine or drought, leading to a higher death rate
the higher birth rate fluctuations could be due to the inability to access contraception
how many children would someone have to have on average to maintain the population in Japan
2, however the population average is only 1.4
there could be a projected population drop of 1/3
what are the social causes of a declining birth rate in Japan
there is increased education and wealth, more women are in careers, and do not want to give up their job to have children (also economic)
very little support should you have a child e.g there is very little maternity leave (some is paid, some is unpaid) and runs from 6 weeks before the birth to 6 weeks after the birth and is adjusted based on how many children will be born (like in the case of twins)
it is harder for people who are not Japanese to migrate to the country- 1/60 in japan are not Japanese than compared to 1/8 in UK
fewer people are getting married, generally people are not born out of wedlock (also a cultural cause). only 2% are compared to the 50% in the UK
what are the economic causes of a declining birth rate in Japan
employment- 53% of women in Japan are employed, and many of these women are choosing not to have children.
child allowance is only 10000 yen a month (£50) compared to Denmark which is DKK 1,548 (£177) and Denmark also offers subsidised childcare.
(Denmark has an increasing birth rate, increasing by 7.6% since 2013)
what is otaku culture
a Japanese word used to describe devoted fans, usually of manga, anime, or video games.
what are the cultural causes of a declining birth rate in Japan
very traditional views, only 2% of people are born out of wedlock compared to the 50% in the UK.
Couples in Japan are having less sex (also could link to the otaku culture)
Otaku culture. Some people, particularly men have online girlfriends and in some cases are not interested in meeting a 'real' person to potentially marry. A lot of men see their school days as 'comforting' as a way to escape their adult jobs.
Some men would want the women to revert to stereotypical roles, the women as housewives. Some women want to still work if they have children, but along with the hard working culture of the country, some women would see themselves as a burden to the company after they have had a child
what are the political causes of a declining birth rate in Japan
there is an increasing focus on encouraging women back into the workforce. 'womenomics'
Some people seem to resist mass immigration, so less people are moving to japan and starting families. They do not wish to relax them as it allows them to keep cultural customs and traditions.
Social consequences of a declining birth rate in japan
Yubari population has plummeted from 100,000 to less than 10,000
there was once 21 primary schools, now there is just 1
Economic consequences of a declining birth rate in Japan
Maternity unit is closing down in some hospitals e.g in Yurabi city- potentially less jobs
Elderly people are living longer and so still expect to receive a pension, however less people are working and so less money is made through taxes.
The retirement age has been increased to 70
the government have raised taxes. E.g the consumption tax (like VAT) has risen 5% and is expected to raise another 5%
cultural consequences of a declining birth rate in japan
Many men have expectations of women that are following stereotypical gender roles, which is clashing with the rise of female employment
Japan has enacted a new law to promote the active engagement of women in society- this would mean men and women sharing similar roles in the home too, something that some men don't want.
Political consequences of a declining birth rate in japan
Have had to print more money, $1 trillion
what percent of Japans annual budget is spent on pensions/ social security for the elderly
25% of the Governments budget
40% of the public spending is also on the elderly
population of japan (2022)
125.1 million people
estimated population decline
population is expected to decline by about half from 124 million in 2023 to 63 million by 2100
what percentage of the japanese population are over 65
28.7%
How many people in japan are over 100
80000
What was the fertility rate of Japan as of 2020
1.34
What stage of the DTM is Japan in
Stage 5
What is the median age in Japan, what is it in the UK?
Japan: 48
UK: 40
What are some Japanese attitudes towards work
Many people don't take holidays, only 24% of Japanese employees take a weeks holiday per year
Lots of women work now but the decline in birth rate could be attributed to this- some think it isn't feasible to work and take care of children. Married working women are sometimes demonised as 'devil wives'
Lots of people work overtime- 20% of 10000 interviewed worked 80hr overtime per month
Japanese Immigration statistics and impacts
Approximately 1.7 million foreign workers as of 2022, up 13.6% from 2021
Don't offer permanent residency for foreign workers and family cannot come. The visas are also capped at 5 years.
Bankruptcy is increasing due to less employee availability
Japanese government responses to an ageing population
Raise taxes- VAT has risen 5% and expected to rise further
Retirement age is now 70
Encourages pronatal policies e.g increasing maternity leave (6wks before, 6wks after, paid) and paying for people to freeze eggs
Tax reduction of ¥10000 per month per child
What are Dementia towns
1/5 of people over 65 by 2025 are expected to suffer with dementia, with 4.6 million people who currently have dementia
'Orange Plan' 2015 was introduced with a range of initiatives e.g specialised medical staff, drug development, raising public awareness
This will help as people with dementia are at risk- number of sufferers who have went missing was 15000 in 2016
Japanese government responses to a declining birth rate
Pronatal policies
1 million yen to families moving to areas with a declining birth rate
birth rate declined from 2 million in 1970 to 800,000 in 2023
has globalisation affected japanese population?
Technology- related to otaku culture and the idea that some people may have online partners
Migration? Not so much of an effect on japanese population as 1/60 arent japanese in japan compared to 1/8 in UK
how much money are governments offering to new parents as an incentive
¥80,000 ($500)
in sweden, the birth rate is rising with the Swedish government incentivising you to have children. In 2019, the amount was 1250 SEK (~$150 USD) monthly