Working Memory Model Flashcards
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards reviewing the key components and functions of Baddeley and Hitch's Working Memory Model.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is working memory (WM) according to Baddeley & Hitch's model?
A dynamic structure that stores and manipulates information using active processing, replacing the unitary view of STM.
What is the capacity and function of working memory (WM)?
Limited capacity and duration; used for cognitive functions like mental arithmetic.
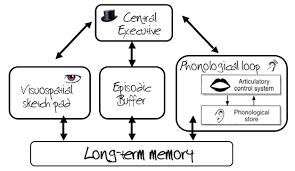
What is the central executive (CE) in the Working Memory Model?
An attentional system that filters information, prioritizes input, allocates tasks to slave systems, and links to LTM.
What is the capacity of the central executive (CE)?
It can only process one piece of information at a time.
What is the visuo-spatial sketchpad (VSS)?
A temporary memory system for storing visual and spatial information, with components for visual data and object arrangement.
What are the two components of the visuo-spatial sketchpad (VSS) and what do they do?
Visual cache (stores visual data about shape, colour etc.) and inner scribe (records object arrangement and rehearses info; rehearses/transfers information to the CE).
What is the capacity of the visuo-spatial sketchpad (VSS)?
3 or 4 objects.
What is the phonological loop (PL)?
A temporary memory system for holding auditory information in a speech-based form.
What are the two components of the phonological loop (PL)?
Phonological store (inner ear) and articulatory process (inner voice).
What is the capacity of the phonological loop (PL)?
About 2 seconds worth of speech, unless rehearsed.
What is the episodic buffer (EB)?
A temporary storage component that links LTM to the slave systems of working memory, integrating visual, spatial, and verbal information.
What is the capacity of the episodic buffer (EB)?
About 4 chunks of information.
How does the central executive handle divided attention?
The CE decides how resources are shared, switching attention between different inputs of information. The harder/newer the task, the harder the CE has to work to split it between the slave systems
What does the VSS help navigate?
Helps with navigating and Interacting with the physical environment
What does the phonological store do?
Stores speech recently heard, involved in speech perception.
What does the Articulatory Process do?
Allows for maintenance rehearsal to prevent decay or holds verbal material until it’s spoken, involved in speech perception.
How can confusion occur with the phonological loop?
The acoustic nature can mean confusion may occur with similar sounding sounds.
How does the WMM work
How is information processed in Working Memory (WM)?
Information from LTM is accessed and transferred to WM, where it is combined with new information and manipulated. WM has a limited capacity and duration. It is used when performing certain cognitive functions e.g. mental arithmetic. The information must be kept active in order to be retained, and different tasks within WM can interfere with each other.
What does the WMM look like?