(10)Linear Kinetics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Overview
Newton’s Laws of Motion
Law of Inertia
Law of Acceleration
Law of Reaction
Ground Reaction force
Law of Gravitation
Weight
Friction
Momentum and Impulse
Momentum-impulse relationship
Mechanical work, power and energy
Work-energy relationship
1st Law: Law of Inertia
A body remains at current state of motion (constant velocity) unless acted upon by an external force
1st Law: Inertia (statics)
the tendency of an object to keep the current state of motion
Difficulty in changing the state of motion
Proportional to mass of the object
Mass=measure of inertia in linear motion
2nd law: Law of Acceleration
An external force applied to a body causes acceleration
F=ma
2nd Law: Acceleration
Acceleration
proportional to force
inversely proportional to mass (linear inertia)
a=F/m
Direction of a= Direction of F
If F=0 —→ a=0
constant v
no change in state of motion
law of inertia
a= F/m=0
3rd Law: Law of Reaction
For every force (action), there is an equal and opposite reaction
3rd law: Reaction & Examples
Reaction
Same magnitude
opposite direction
Examples
Bullet vs Gun
Fist Fighting
Propulsion in swimming
Hockey Players
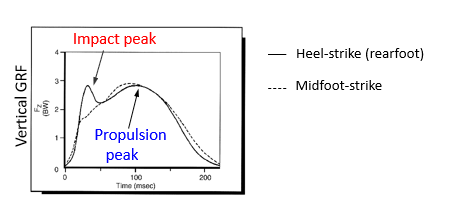
Ground Reaction Force
GRF
reaction supplied by the ground
passive force
Important for human motion
major external force that accelerates the body
speeds up
slow down
the only external force one can voluntarily control
weight is always constant and downwards
Examples of GRF
High jump
ax=Fx/m < 0
slow down of rightward (+) Velocity
ay=Fy/m>0
slowdown of downward (-) velocity
speed up of upward (+) velocity
Running
Law of Gravitation
All bodies are attracted to one another due to their masses
G= Gravitational constant= 6.672×10-11 Nm2/kg2
Gravitation
proportional to masses
inversely proportional to (separation distance)2
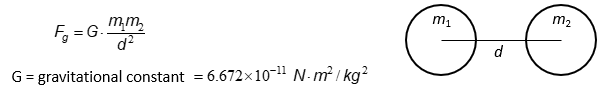
Weight
Gravity Exerted to a body by the earth
Weight= (mass)(gravitational acceleration)= mg
Direction- downward
passes through the COM of the body
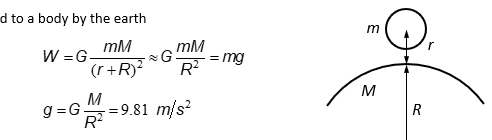
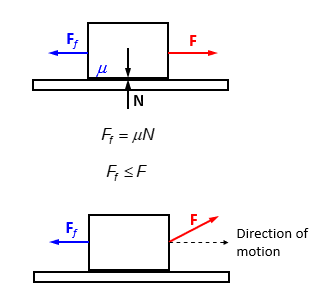
Friction
Friction
force acting at the area of contact between two surfaces
Source of horizontal GRF
Magnitude
proportional to
normal reaction force (N)
friction coefficient (Mu)
Cannot exceed your force
Direction
opposite that of motion or motion tendency
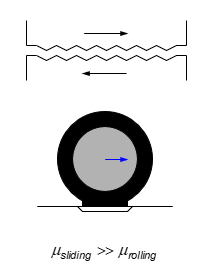
Sliding vs Rolling Friction- Nature of interaction
Sliding friction
friction due to relative motion of the surfaces
Rolling Friction
friction due to temporary deformations of the surfaces
Sliding vs rolling
sliding friction>> rolling friction
Beneficial to convert sliding to rolling for smaller friction
EXAMPLES
Wheels
how they built the pyramid of giza (rolling the stones over logs to get to the location
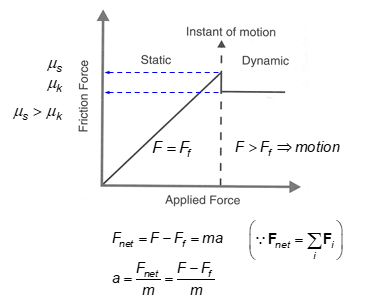
Static vs Kinetic (Dynamic) Friction — State of motion
Static Friction
Ff experienced with no motion (F=Ff)
Max Static friction= force required to initiate motion
Kinetic (Dynamic) friction
Ff experienced during motion (F>Ff)
force required to maintain motion once initiated
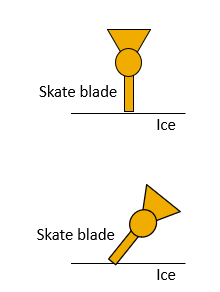
Friction Strategies
Minimize friction as resistance
Lubrication- synovial fluid (mu=0.01)
Skating-gliding
tire inflation and paving
Maximize friction as source of propulsion
source of horizontal GRF
cleats: Prevent slipping
Skating: Push off
Momentum
Amount of motion
(inertia)(velocity) M=mv
important in giving and receiving impact, collision, etc
Vector quantity
direction=direction of velocity
Unit: kg*m/s
Principle of momentum conservation
If no external force, total momentum remains constant
a=Fnet/m = 0
a=delta v/ delta t= 0
v= constant M=mv= constant
from netwons first law
example: Hockeyplayer
Impulse
The accumulated effect of force exertion over a period of time I=F(bar)*delta t
vector quantity: direction=direction of force
Unit: Ns (same as momentum)
causes change in Momentum
momentum impulse relationship
I= Delta M= M2-M1=mv2-mv1= m(v2-v1)= m*delta v
Impulse strategies
Giving impulse ( Batting, throwing, etc.)
maximize impulse by maximizing the momentum of the apparatus (batting)
elongating elapsed time (throwing)
I=F(bar)*delta t= delta M apparatus
receiving impulse (landing, catching, etc.)
reduce impulse if possible
reduce impulse force/pressure by increasing time/area
F(Bar)= I/delta t P(bar)= F(Bar)/A
Mechanical Work
Force applied against a resistance
accumulated effect of force exertion over a displacement
work=(force)(displacement)
W= F(bar)*d*cos theta
Scalar
Unit: J (joule)=Nm