Comprehensive Guide to Science, Technology, and Society: Key Concepts and Historical Developments
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY
Is the study of how social, political and cultural values affect scientific research and technological innovation, and how these in turn affect society, politics and culture.
SCIENTIFIC METHOD
Systematic framework for investigation that emphasizes observation, experimentation, hypothesis testing, and evidence-based conclusions.
HYPOTHESIS
It is an educated guess based on observations and your knowledge of the topic.
SCIENTIFIC WORK IS TRANSPARENT AND OPEN TO CRITIQUE
New knowledge is disseminated and vetted through peer review and publication.
SCIENCE
A system of acquiring knowledge based on the Scientific Method.
NULLIUS IN VERBA
Latin for 'see for yourself', meaning trust the word of the scientists.
EXPERIMENTS AND VARIABLES
A variable is anything that can change during an experiment.
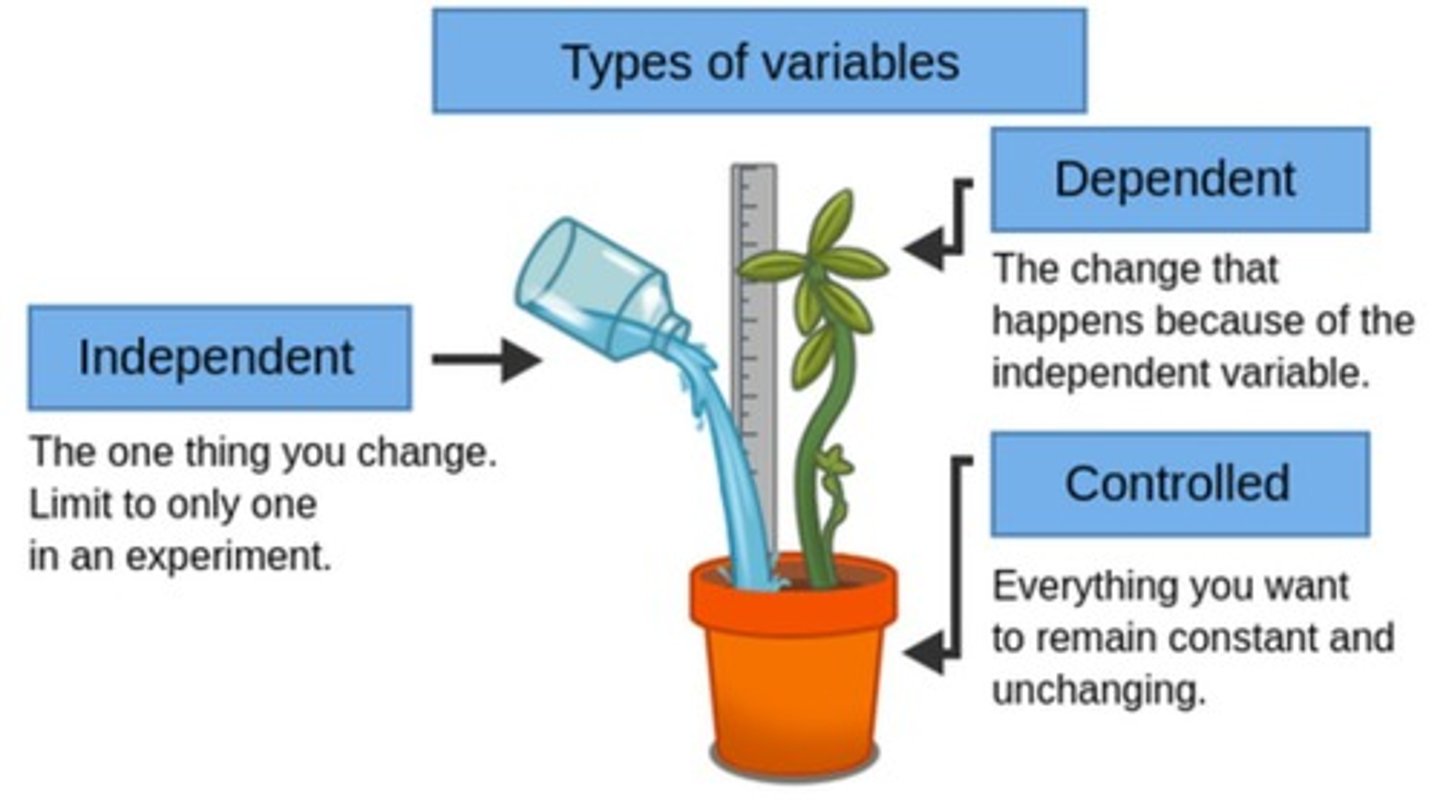
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
Can be manipulated by the experimenter.
DEPENDENT VARIABLE
Might be affected by the change in the independent variable.
CONTROLLED VARIABLE
The group that is not exposed to the independent variable, also called constants.
INDUCTIVE REASONING
Bottom-up approach; generalizing from data.
DEDUCTIVE REASONING
Top-down approach; applying known rules.
INDUCTIVE REASONING EXAMPLE
Observation: The sun has risen in the east every morning for my entire life. Conclusion: Therefore, the sun will rise in the east tomorrow.
DEDUCTIVE REASONING EXAMPLE
All dogs have ears; golden retrievers are dogs, therefore they have ears.
STEPS OF THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD
Provide an organized method for conducting and analyzing an experiment.
SCIENTIFIC METHOD PROCESS
It is a process that is used to find answers to questions about the natural world around us.
SCIENTIFIC METHOD PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
They all begin with the identification of a problem or a question to be answered based on observations.
SCIENCE IMPACT ON SOCIETY
Science's impact on society grew exponentially over time.
TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENTS
Have propelled science to even greater heights in recent decades.
SCIENCE AS A DYNAMIC PROCESS
Dynamic process that evolves with the accumulation of knowledge.
SCIENCE DISCIPLINES
It encompasses a vast array of disciplines, from physics and biology, to psychology and astronomy.
FORMULATION OF QUESTIONS
Formulation of questions that drive exploration and inquiry.
TECHNOLOGY
Application of scientific knowledge, laws and principles to produce services, devices, materials, tools and machines aimed to solving real world problems.
TECHNOLOGICAL TOOL
Something that takes a human's sense or ability and augments it and makes it more powerful.
Augmented Reality
Can provide real-time directions by overlaying arrows and information onto the user's view of the street.
SOCIETY
A large group of people who live together in an organized way, making decisions about how to do things in sharing the work that needs to be done.
societas
Came from the Latin word meaning a friendly association with others.
CUNEIFORM
First writing system that utilizes word, pictures and triangular symbols which are curved on clay wedge instruments and then left to dry.
ANCIENT WHEEL/POTTER'S WHEEL
Refers to early versions of the wheel that were used in various ancient civilizations.
3,500 BCE
Dating back to around this time in Mesopotamia for the invention of the wheel.
WIG
Used to protect the shaved heads of the wealthy Egyptians from the harmful rays of the sun.
SHADOOF
Ancient irrigation tool used to lift water from a well or a river to irrigate fields.
ROADS
The Sumerians develop the first roads to make the flow of traffic faster and more organized.
ANTIKYTHERA MECHANISM
Ancient Greek analog computer designed to predict astronomical positions and eclipses for calendrical and astrological purposes.
PAPER OF PAPYRUS
An ancient writing material used primarily in Egypt and other parts of the Mediterranean region.
AEOLIPILE
Also known as the hero's engine, is an ancient steam-powered device used to demonstrate the principles of steam pressure and propulsion.
MEDIEVAL/MIDDLE AGES
Historical era in Europe that spans roughly from the fall of the Western Roman Empire around 476 CE to the beginning of the Renaissance.
INK
Egyptians invented ink by combining soot with different chemicals to produce inks of different colors.
cosmetic industry
At present, the cosmetic industry is a booming multibillion industry.
cleaner than natural hair
Wearing a wig was considered cleaner than natural hair because it prevented the accumulation of head lice.
transportation
The wheel was one of humanity's most significant inventions, enabling advancements in transportation, technology and machinery.
pottery making
The ancient wheel was used for pottery making rather than transportation.
Nile Delta
The papyrus plant, used to make paper, grows in this region.
HEAVY PLOUGH
One of the most important technological innovations during the middle ages.
GUNPOWDER
One of the most interesting inventions in China.
COSMETICS
The Egyptians invented the use of cosmetics.
TELEPHONE
Invented by Alexander Graham Bell.
MECHANICAL CLOCK
The sophistication of clockwork technology of the mechanical clock drastically changed the way days were spent and work patterns were established.
CALCULATOR
Faster way to compute more complicated equations.
ENGINE-POWERED AIRPLANE
Invented by the brothers, Orville Wright and Wilbur Wright.
MODERN AGES
Refers to the period in history following the Middle Ages and extending to the present day.
TELEVISION
Invented by John Logie Baird.
MICROSCOPE
Zacharias Janssen was able to develop the first compound microscope.
PHILIPPINE INVENTION
Philippines also contributes to the global advancement of science and technology.
TELESCOPE
An optical instrument that helps in the observation of remote objects, was a great help for navigators during this time.
E-JEEPNEY
Dominated the Philippine streets and is considered as the primary mode of transportation of most Filipinos.
electric jeepney (eJeepney)
An environment-friendly vehicle that does not emit any smoke and noise.
SALAMANDER AMPHIBIOUS TRICYCLE
A vehicle that can cross flooded streets, rivers, and lakes, useful for traveling between islands in the Philippines.
JACQUARD LOOM
A type of weaving loom that uses a series of punched cards to control the pattern being woven.
Joseph Marie Jacquard
The developer of the Jacquard loom in the early 19th century (around 1801).
PRE-COLONIAL PERIOD
A time characterized by the use of plants and herbs as medicines, farming, animal-raising, and the development of various transportation modes.
rice terraces
A complicated engineering feat built by the natives of the Cordilleras to cultivate crops on mountain sides in cold temperatures.
irrigation system
A system that uses water from forests and mountain tops to support an elaborate farming system.
MEDICAL INCUBATOR
An invention by Dr. Fe del Mundo, made from indigenous materials that did not run on electricity, using a native laundry basket for warmth.
ERYTHROMYCIN
A broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat and prevent a wide range of infections, discovered by Abelardo Aguilar.
COLONIAL PERIOD
A period marked by colonization by the Spaniards, which introduced modern construction methods and health and education systems.
BANANA KETCHUP
A condiment first mass-produced commercially in 1942 by Filipina food technologist Maria Y. Orosa.
Ferdinand Marcos
A leader who ushered in advancements in science and technology in the Philippines.
Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA)
An agency established in place of the abolished Weather Bureau during Ferdinand Marcos' administration.
National Academy of Science and Technology (NAST)
An institution established during Ferdinand Marcos' administration to promote science and technology.
Department of Science and Technology (DOST)
An agency established on June 13, 1987 (R. A. 7356) during Corazon Aquino's administration.
Presidential Task Force for Science and Technology
An initiative created by Corazon Aquino that developed the first Science and Technology Master Plan (STMP).
American occupation
A period that modernized almost all aspects of life in the Philippines and established the Bureau of Science.
Bureau of Science
A government agency established during American occupation to nurture development in science and technology.
Filipino pediatrician
Dr. Fe del Mundo, the first Asian woman admitted into Harvard Medical School.
hot water bottles
Used in the medical incubator to provide warmth between the baskets.
complex patterns
Patterns that the Jacquard loom allowed for automatic production in the textile industry.
indigenous materials
The materials used to construct the medical incubator by Dr. Fe del Mundo.
engineering skills and tools
The advancements brought by the Spaniards that facilitated modern construction in the Philippines.
New Industrialized Country (NIC)
A status the Philippines could attain through science and technology.
Science and Technology Agenda for National Development (STAND, 1993)
Programs established that were significant to the field of science and technology.
Philippine Clean Air Act of 1999 (R.A. 8749)
Legislation designed to protect and preserve the environment and ensure sustainable development of natural resources.
Electronic Commerce Act of 2000 (R.A. 8792)
Law that outlaws computer hacking and provides opportunities for new businesses in the Internet-driven economy.
Filipinovation
A coined term used to help the Philippines become an innovation hub in Asia.
Access to Information
Provides access to educational resources and platforms, improving literacy rates and educational outcomes.
Research and Development
New discoveries and technologies that drive further advancements in various fields.
E-Governance
Streamlines government operations, improves transparency, and makes public services more accessible and efficient.
Data Management
Collects, analyzes, and uses data for better decision-making and policy formulation.
Renewable Energy
Sources like solar, wind, and hydro power that reduce dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Conservation
Science aids in understanding and preserving ecosystems, managing natural resources, and developing sustainable practices.
Advanced Technologies
Innovations in cybersecurity, surveillance, and defense systems that help protect national security.
Disaster Management
Technologies such as early warning systems and emergency response that improve disaster preparedness and resilience.
Communication
Enhances communication and connectivity, fostering social interactions and cultural exchange.
Entertainment and Media
Development of media and entertainment technologies that enrich cultural life and provide platforms for creative expression.
Intellectual Revolution
Periods of significant transformation in thought that have profound impacts on society.
Paradigm Shift
A fundamental change in the way that people view the world around them.
Innovation and Industry
Drives innovation, leading to new industries and modernization of existing ones, creating jobs and boosting productivity.
Efficiency and Productivity
Improves efficiency in agriculture, manufacturing, and services through automation and modern techniques.
Transportation Infrastructure
Development of better transportation infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and railways, essential for economic activity.
Utilities Innovations
Improvements in energy, water management, and waste treatment that enhance the quality and reliability of essential services.