C6 - Color Vision Testing
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
True or false: There is only one single point on the CIE chromaticity diagram that represents "white".
false
(there is a RANGE of different shades of "white" - exemplified by different colors of "white" light bulbs)
Theoretical source of electromagnetic radiation whose spectral energy distribution is a function of both temperature and wavelength
Black tube is heated up to a certain temperature, than a spectrophotometer measures what is radiated off of that tube
Black body radiator
Collection of points on the CIE chromaticity diagram representing blackbody radiation of various temperatures - this is why "white" is represented by several points representing different standard illuminants
Planckian locus
Description of the "color" of a light source measured by the Kelvin temperature scale; can change the appearance of the object being illuminated
**the different points along the Planckian locus represent this aspect of white light
Correlated color temperature
What makes it easier for color deficient patients to pass color vision tests: standard or non-standard illuminants?
Non-standard
Out of the 4 well-known standard illuminants (A-D) published by the CIE, which is best to use for color vision testing?
for reference:
A: Average incandescent light (2856 K)
B: Direct sunlight (4874 K)
C: Average daylight (6774 K)
D: Phases of daylight
Average daylight (6774 K)
What does standard illuminant C represent?
Average daylight (6774 K)
What does standard illuminant D represent?
**can also be used for color vision testing if standard illuminant C is not available
Phases of daylight
Gold standard light for testing color vision: tungsten bulb with blue filter to mimic daylight
Gave us standard illuminant C (6774 K)
Macbeth light
Light used for testing color vision that mimics daylight illumination at 6500 K (not 6774 K)
true daylight illuminator
Measurement showing effect of a light source on the color of objects based on a 0 to 100 scale; shows differences in chromaticity (wavelength + colorimetric purity) in 8 color samples from light source vs. standard illuminant
**reference for how accurately a light source displays color
Color rendering index (CRI)
The higher the CRI number, the better or worse the color rendering ability of the light source?
Better
Do we want a light source that has a lower or higher CRI number?
**look at CRI in combination with color temperature (in K) to figure out the best option when buying a bulb
Higher
(closer to 100)
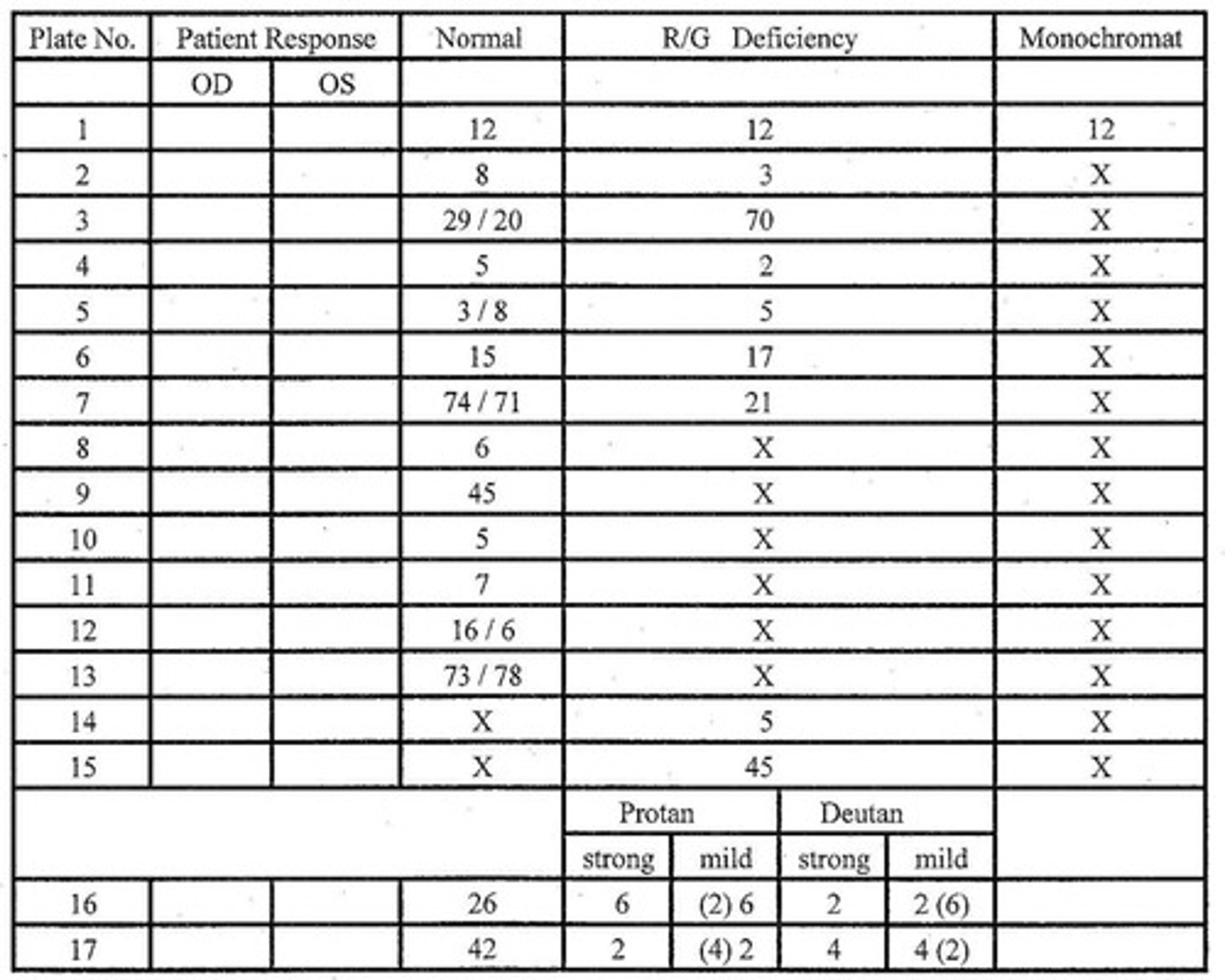
What general type of color testing books do we use in clinic?
Pseudoisochromatic (PIC) plates
Three main brands of PIC plates to test color vision in a clinical setting
HRR, Ishihara, Color Vision Made Easy
What is the visual acuity requirement for testing color vision with HRR PIC plates?
20/200 or better
What kind of color discrimination ability is required to "pass" PIC plates in color testing?
wavelength based discrimination
(also utilizes colorimetric purity, luminance, and chromaticity)
REVIEW: What is the neutral point for someone with protanopia?
(point at which color seen is perfect white)
493 nm
REVIEW: What is the neutral point for someone with deuteranopia?
(point at which color seen is perfect white)
498 nm
REVIEW: What colors does the major confusion axis for protanopia extend between?
**all colors along the line appear gray, black, or white and colors look the LEAST saturated
Bluish green to red
REVIEW: What colors does the major confusion axis for deuteranopia extend between?
**all colors along the line appear gray, black, or white and colors look the LEAST saturated
Green to purplish red
True or false: HRR testing tests for R/G defects only.
False
What kind of color defect do HRR plates test for?
R/G and B/Y
(congenital & acquired)
When administering HRR, how are we supposed to mark on the recording sheet? (correct vs. incorrect)
Put check next to correct response, leave blank if incorrect
What indicates color normal in HRR color testing?
Patient gets all screening plates correct
At what point in HRR color testing do we move on from the screening plates to the corresponding diagnostic plates?
if they miss any of the screening plates
Your patient gets 5/6 screening plates correct. You move on to the diagnostic plates, and then the patient gets all of those correct. Now what do we do?
Repeat the screening plates
(color normal if pt now gets them all correct)
What would categorize someone as having an undetermined color deficiency?
There are equal checks in both the proton and deutan boxes (or both tritan and tetartan) OR error in screening plates only when repeated after getting all diagnostic plates correct
Does someone get credit for a plate if they say they see a second symbol when there isn't actually one there?
No
How do we decide protan vs deutan or tritan vs tetaran with HRR?
Whatever column has the most checks
How do we determine the extent (i.e., severity) of the defect? (mild, moderate, severe)
most severe plate category in which an error occurs
(where the last blank in that column is)
Example: An HRR scoring sheet shows 7 checks in the protan column and 4 checks in the deutan column. The last error in the protan column occurs in the mild category, and the last error in the deutan column occurs in the moderate category. What is the defect & severity?
Moderate protan
How is someone with an HRR-determined mild color deficiency likely to see colors?
There is a lot of variability, but most likely to be able to name surface colors with occasional error
If the symbol they don't see on an HRR plate is a bluish green, what kind of deficiency does this represent? Why?
Protan - bluish green is on a protan's major confusion axis
(so a protan won't see the triangle in this image)
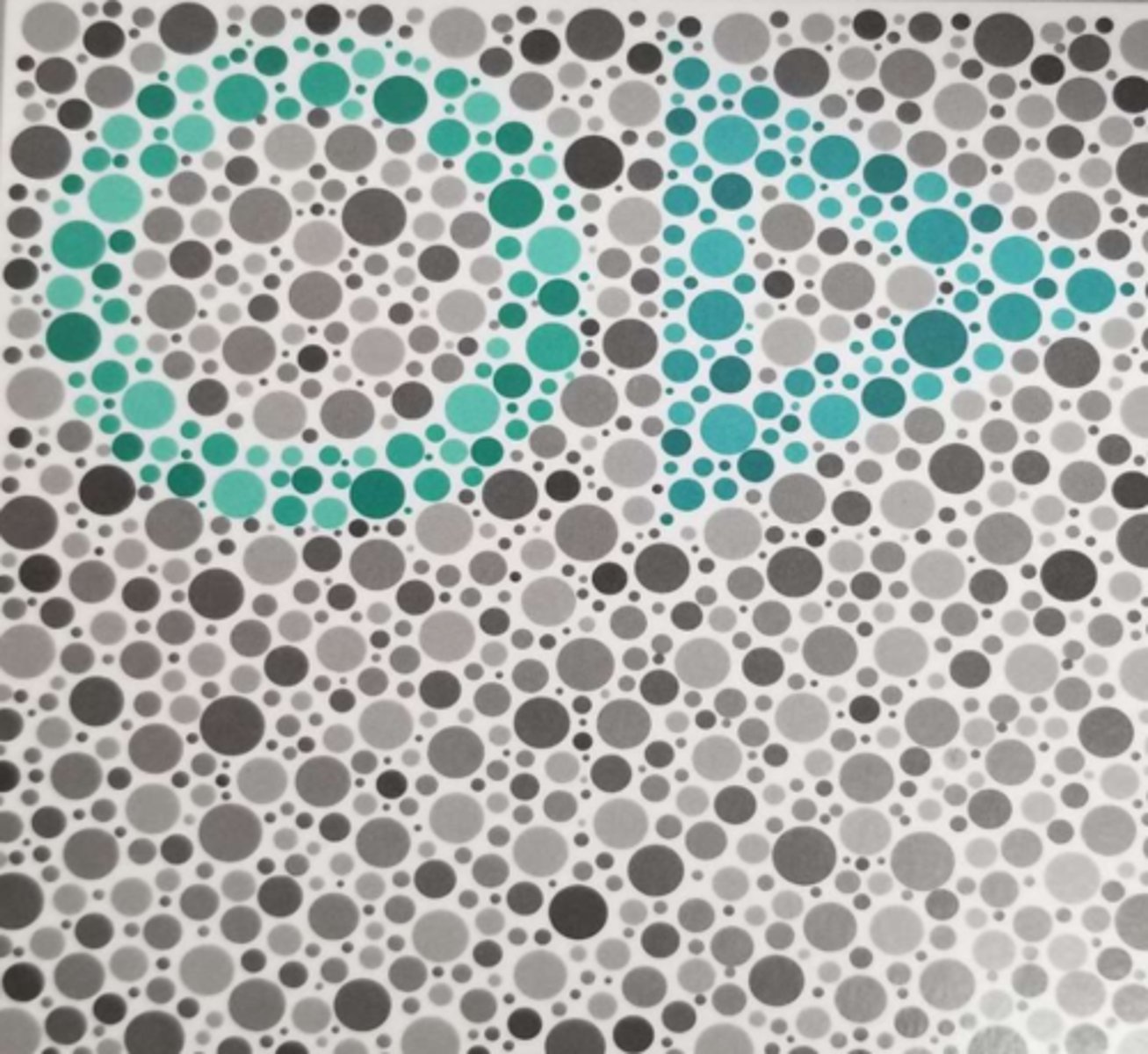

If the symbol they don't see on an HRR plate is a regular green, what kind of deficiency does this represent? Why?
Deutan - green is on a deutan's major confusion axis
(so a deutan won't see the circle in this image)

If the symbol they don't see is a purplish red, what kind of deficiency does this represent? Why?
Deutan - purplish red is on a deutan's major confusion axis
(so a deutan won't see the circle in this image)
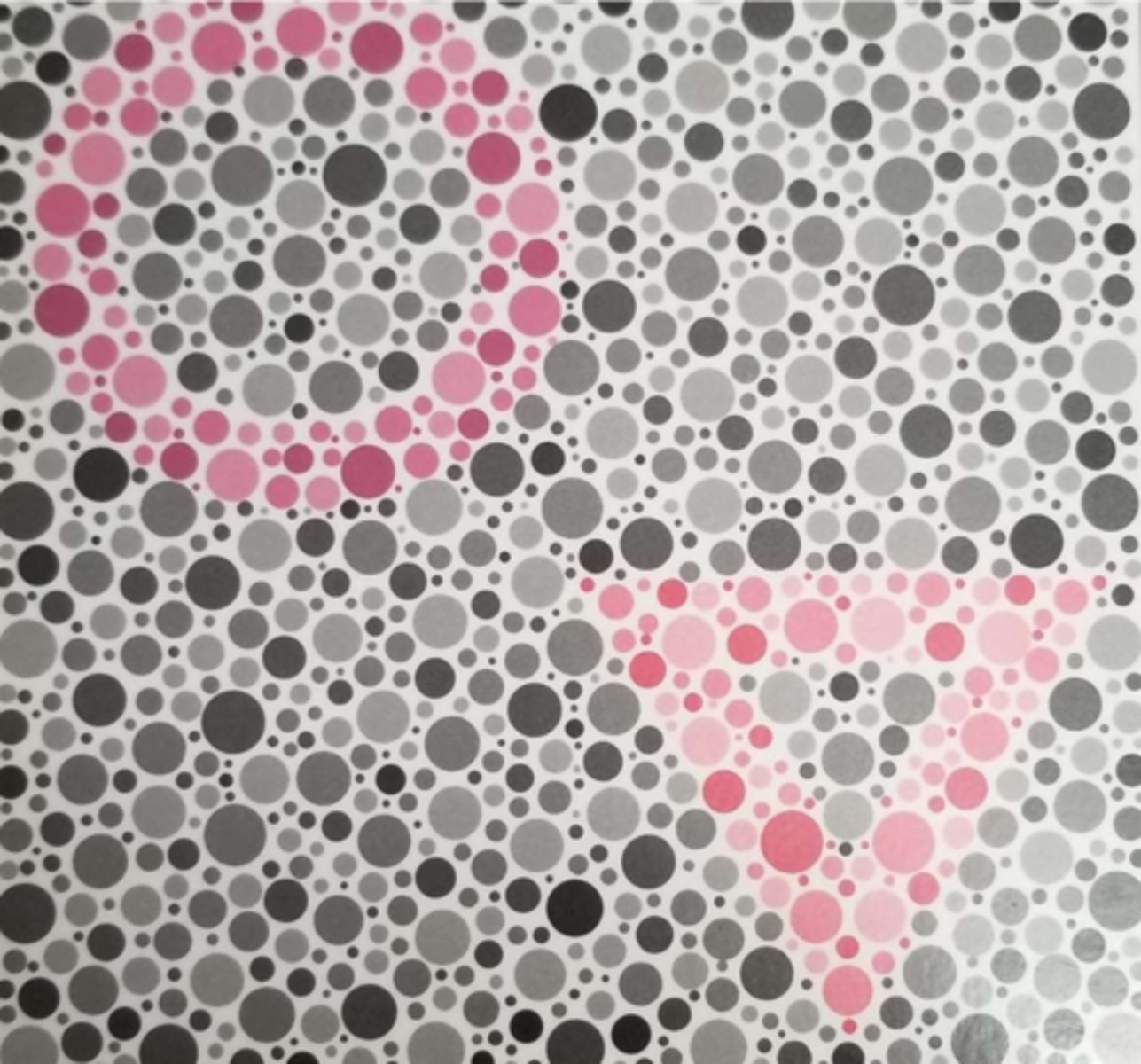

If the symbol they don't see is more of a red color, what kind of deficiency does this represent? Why?
Protan - red is on a protan's major confusion axis
(so a protan won't see the triangle in this image)
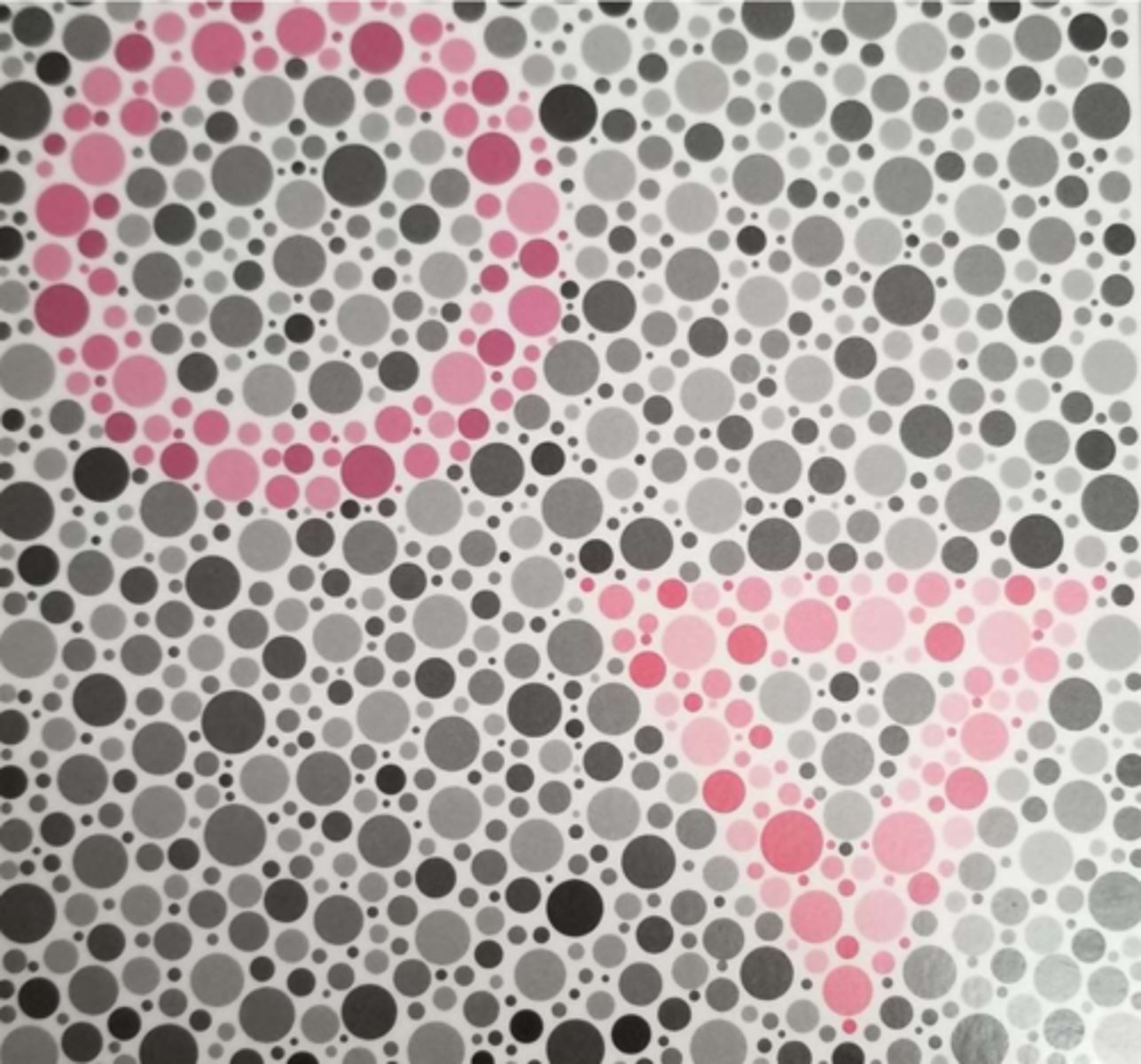

Why do the color plates vary from less saturated to more saturated?
Distinguishes severity
The less saturated color plates evaluate a patient's ability to see what special type of color pairings?
****requires more figure-background discrimination ability
Metameric matches
Which kind of color defect is associated with issues with less saturated colors only: dichromacy or anomalous trichromacy?
Anomalous trichromacy
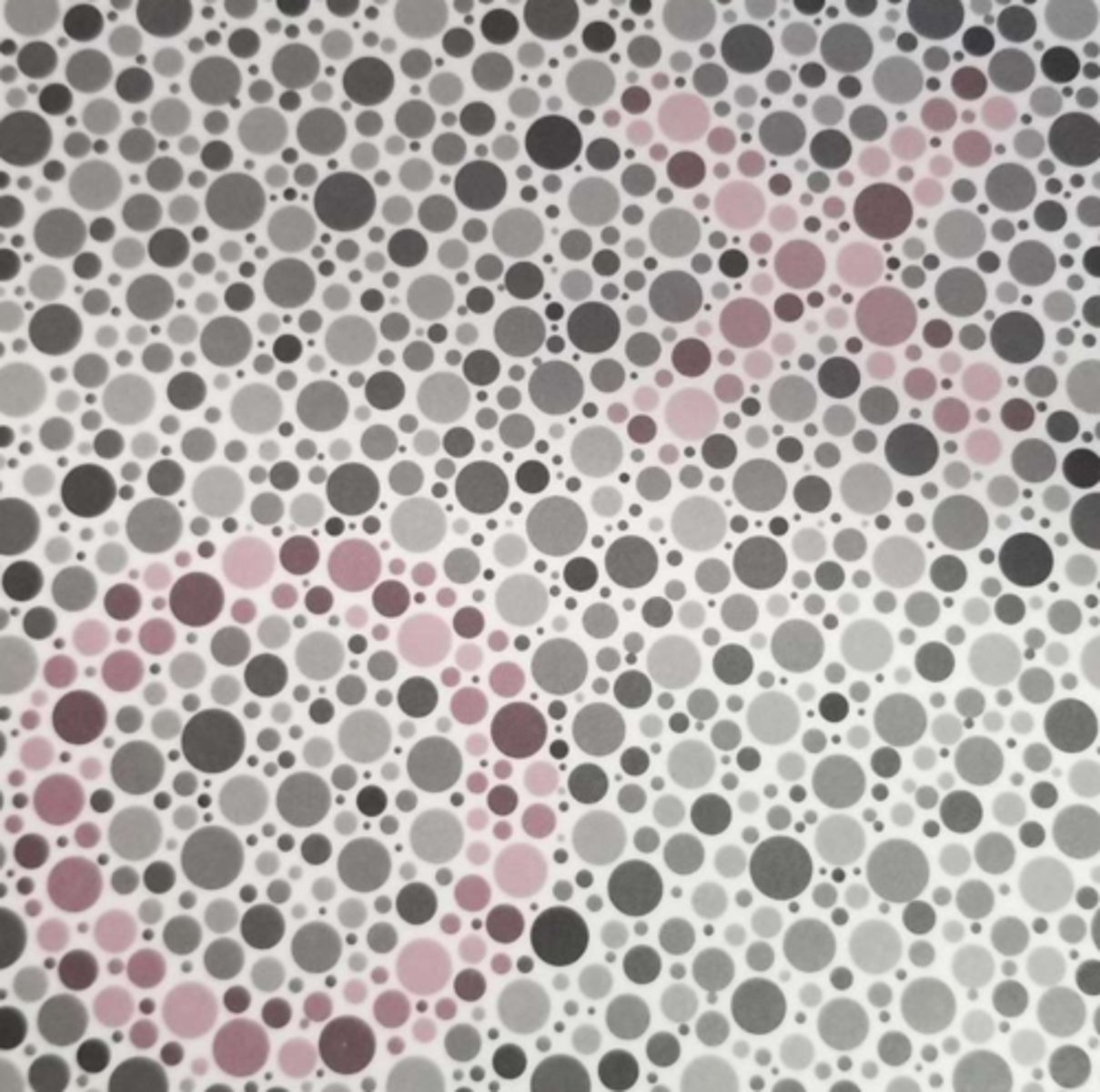
Which kind of color defect is associated with issues with both less and more saturated colors: dichromacy or anomalous trichromacy?
Dichromacy
What kind of color defect do Ishihara plates test for?
R/G only
(hereditary)
How are the figure-background plates designed in Ishihara testing to distinguish a protan vs. deutan defect?
Colors lie on specific color confusion lines
What is the purpose of the Ishihara diagnostic plates?
Diagnose protan vs. deutan and determine severity
Should we use Ishihara to diagnose monochromacy/achromatopsia? Why or why not?
No - there are much better tests specifically for this
How do we score an Ishihara color test when using numbers?
Write down patient's response in each eye, count up how many plates are correct according to scoring sheet
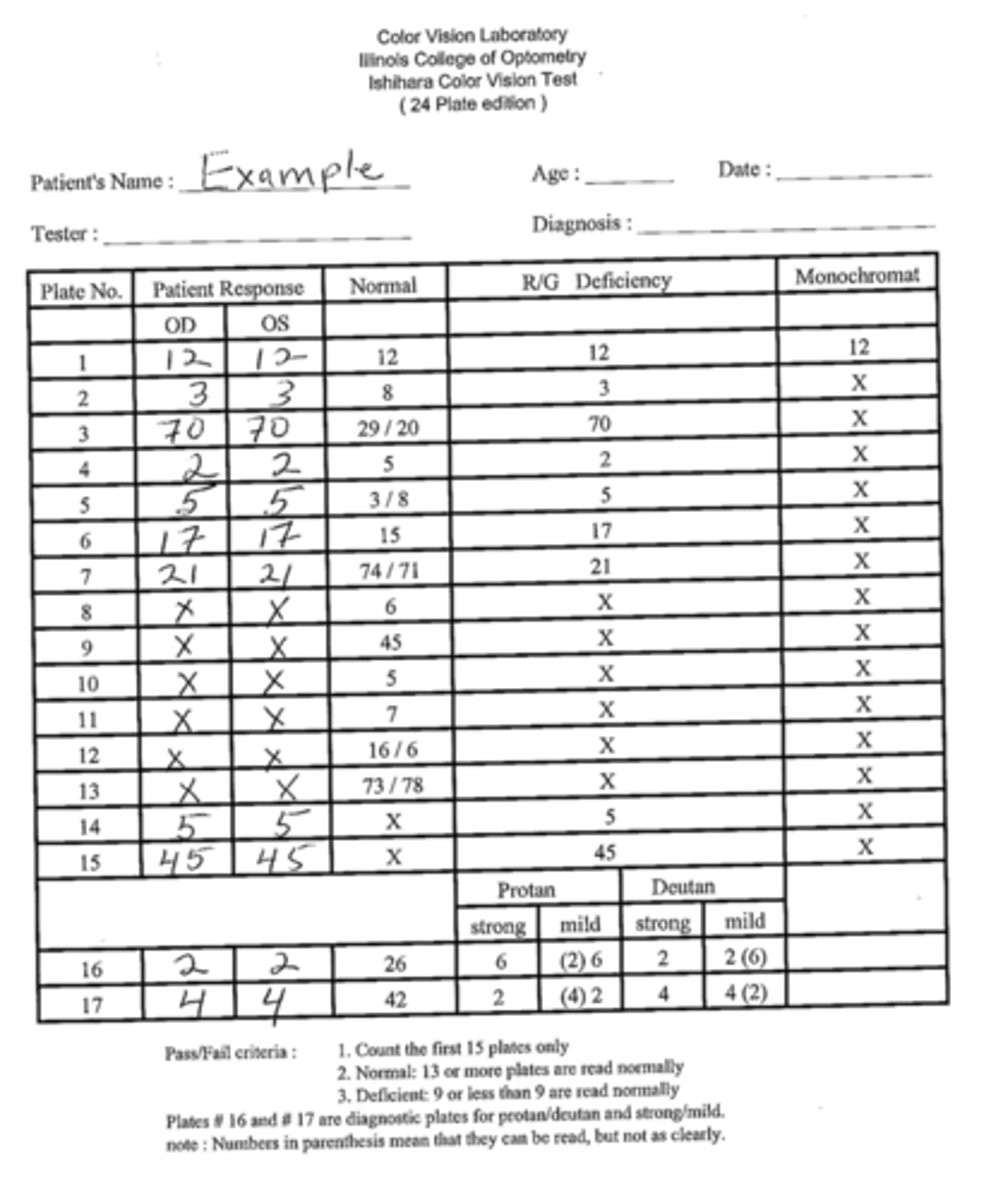
On Ishihara transformation # plates, what should a color normal vs. deficient patient see?
Displayed # if normal, different # (or no #) if deficient
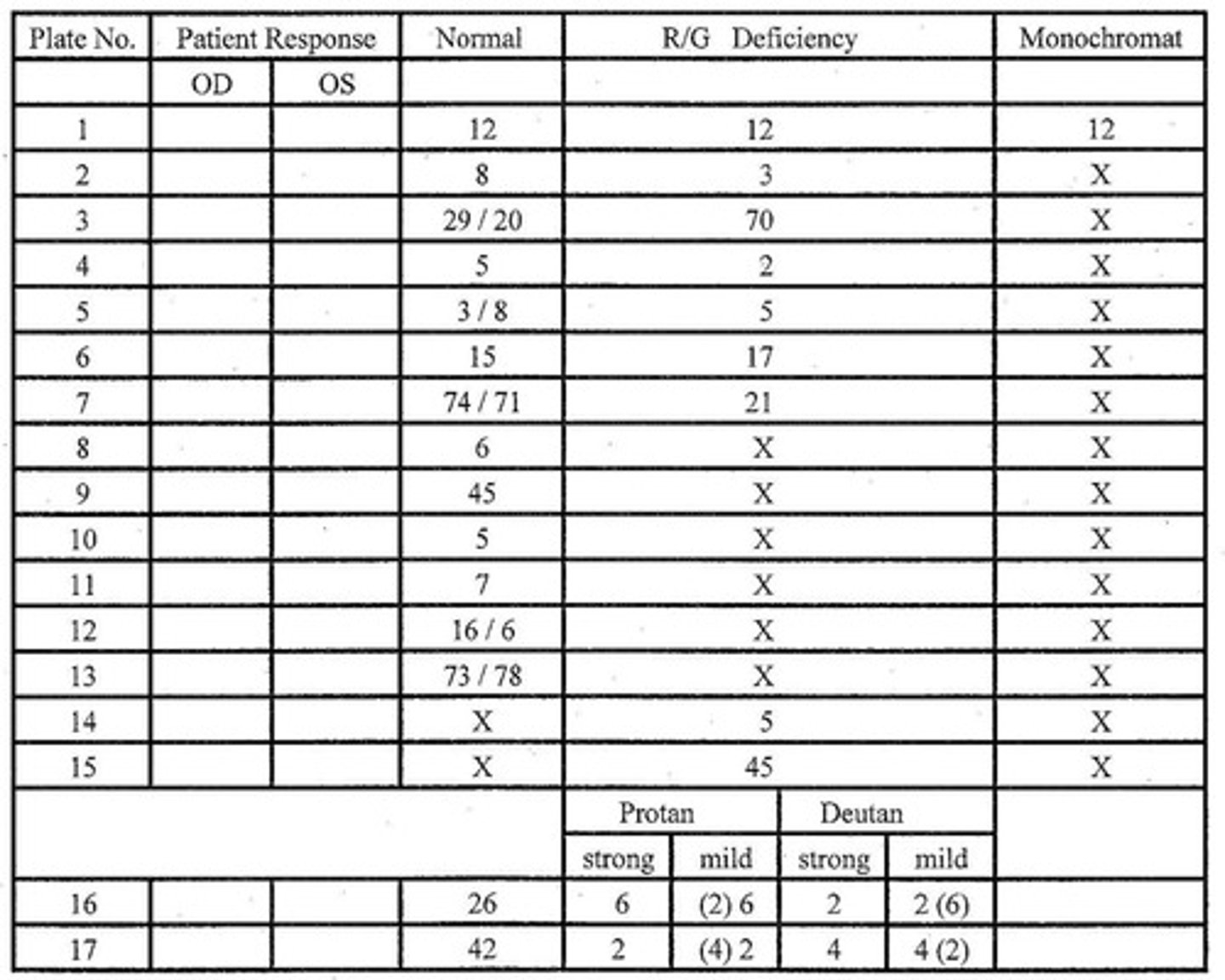
On Ishihara vanishing # plates, what should a color normal vs. deficient patient see?
some # if normal, no # if deficient
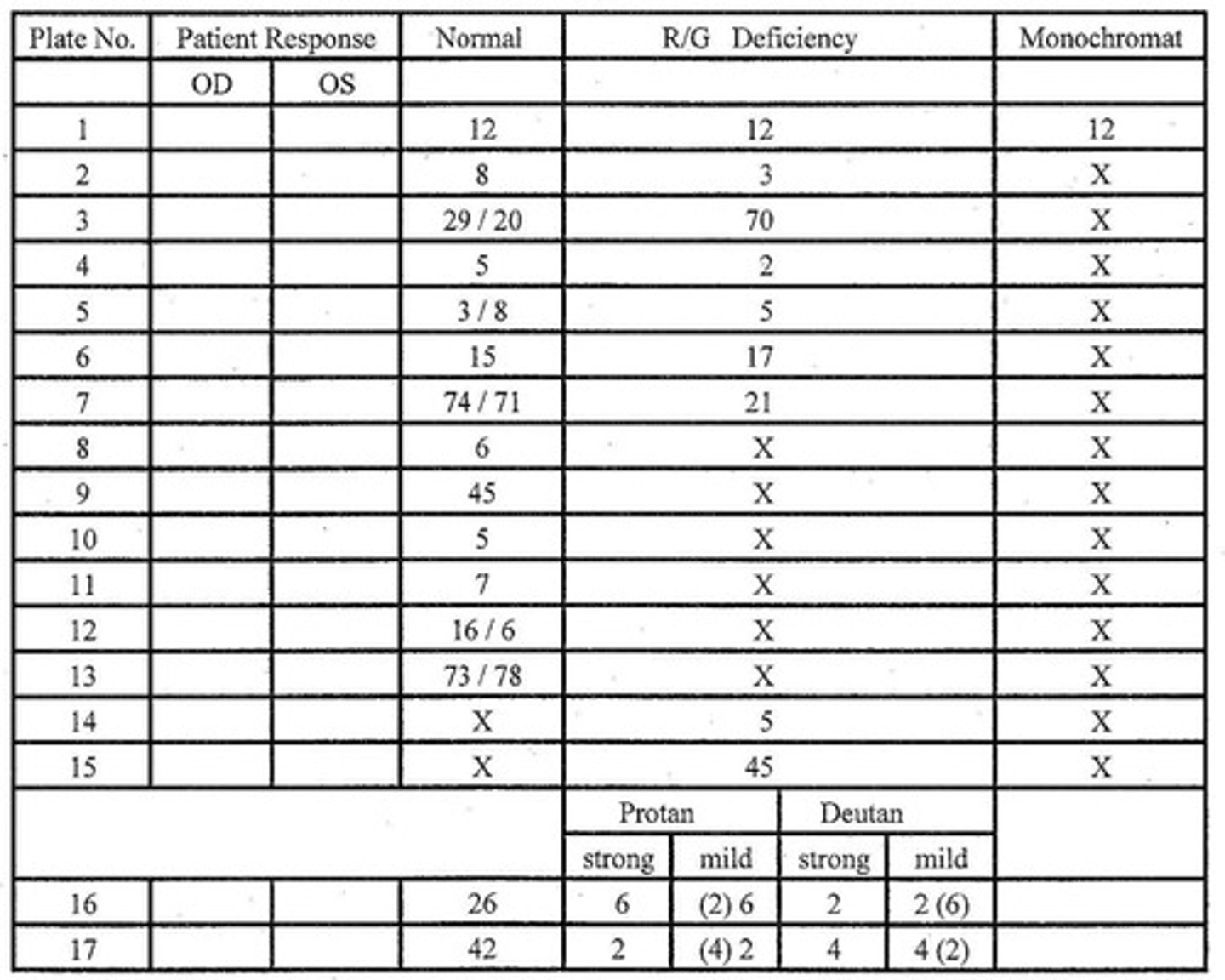
On Ishihara hidden digit # plates, what should a color normal vs. deficient patient see?
no # if normal, may be malingering if deficient
What is another color vision test that is similar to the Ishihara color plates?
Color Vision Testing Made Easy
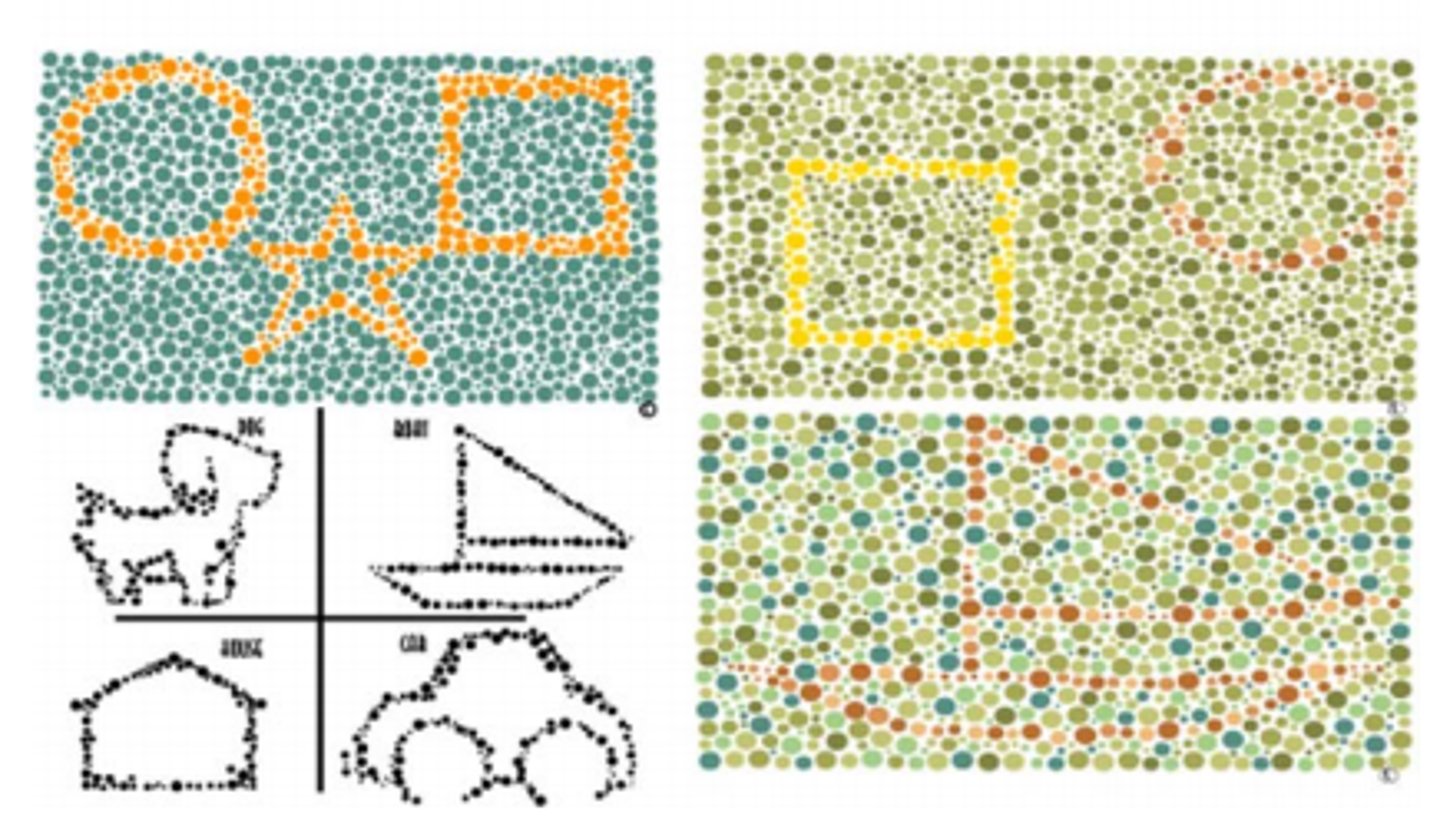
Who is Color Vision Testing Made Easy designed for?
kids age 3+ and those with cognitive delays
What kind of color defect do Color Vision Testing Made Easy plates test for?
R/G only
What makes CVTME so easy?
only has symbols and shapes
What is unique about CVTME compared to HRR and Ishihara? (2)
has demonstration and test plates on the same plate
also does not distinguish severity, only identifies presence/absence of a R/G defect
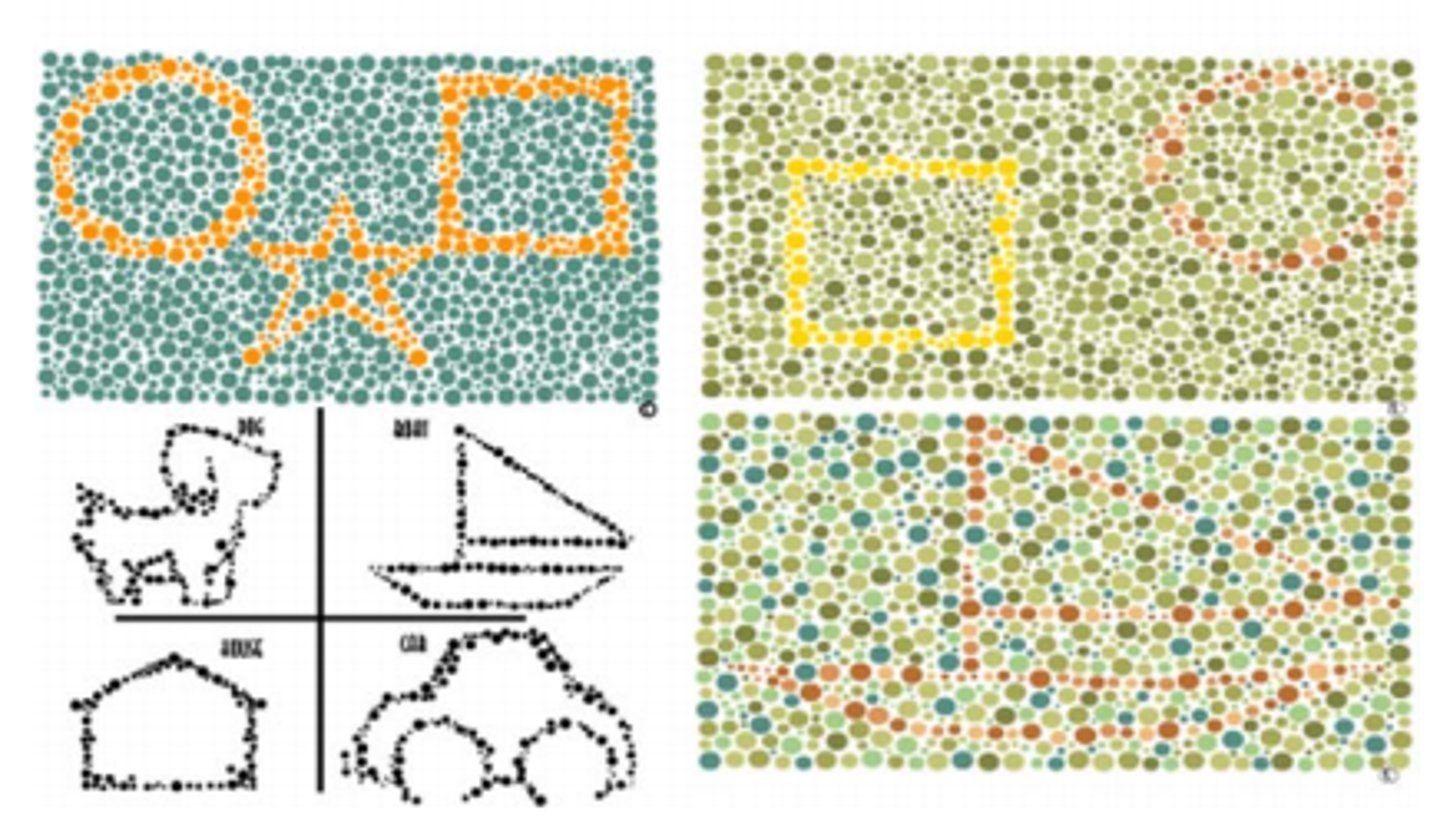
What if a patient sees no shapes on the CVTME page?
questionable result, maybe isn't a good test for them
(since the deficient color vision column shows the demonstration shape that everybody should be able to see)
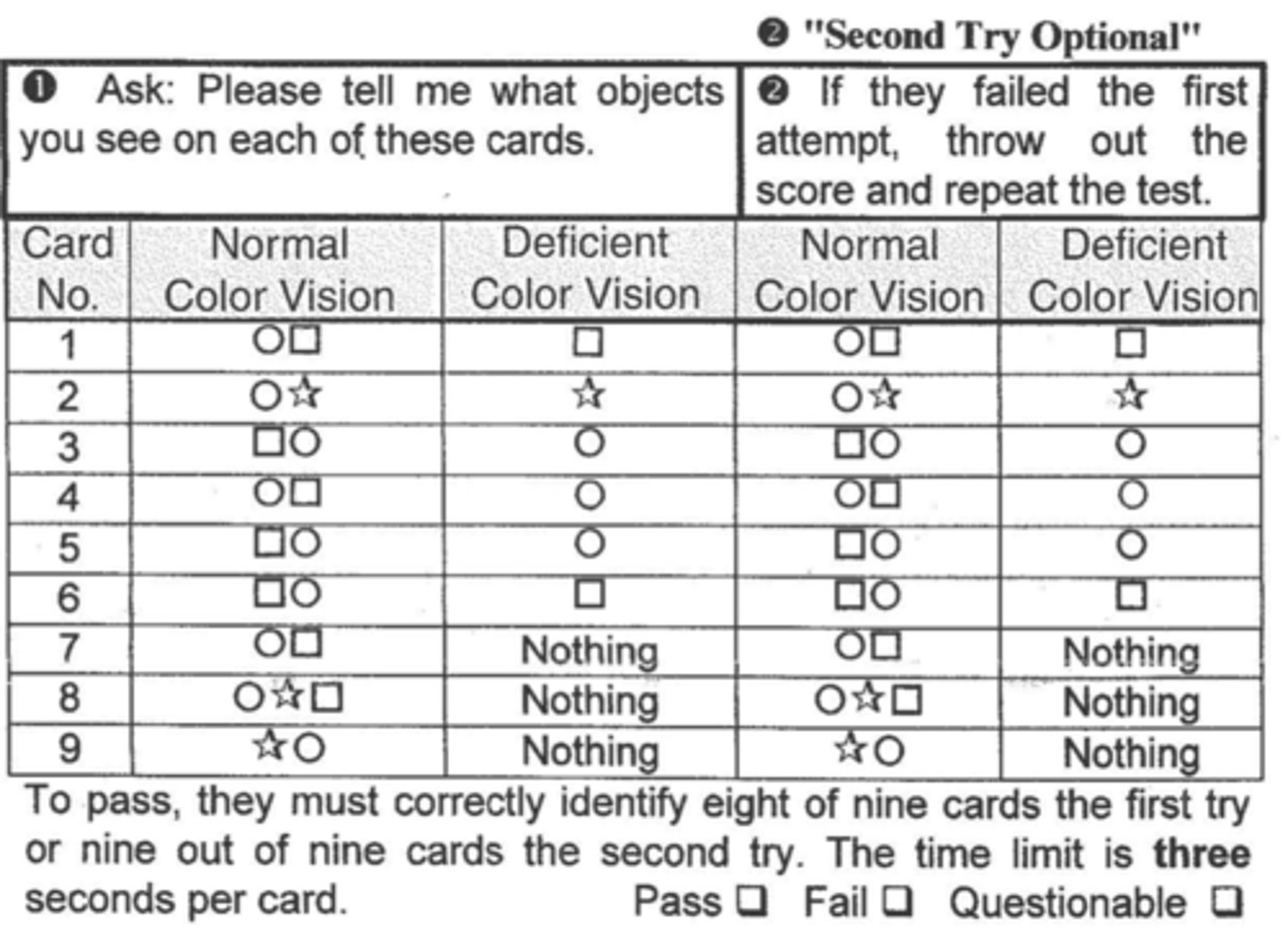
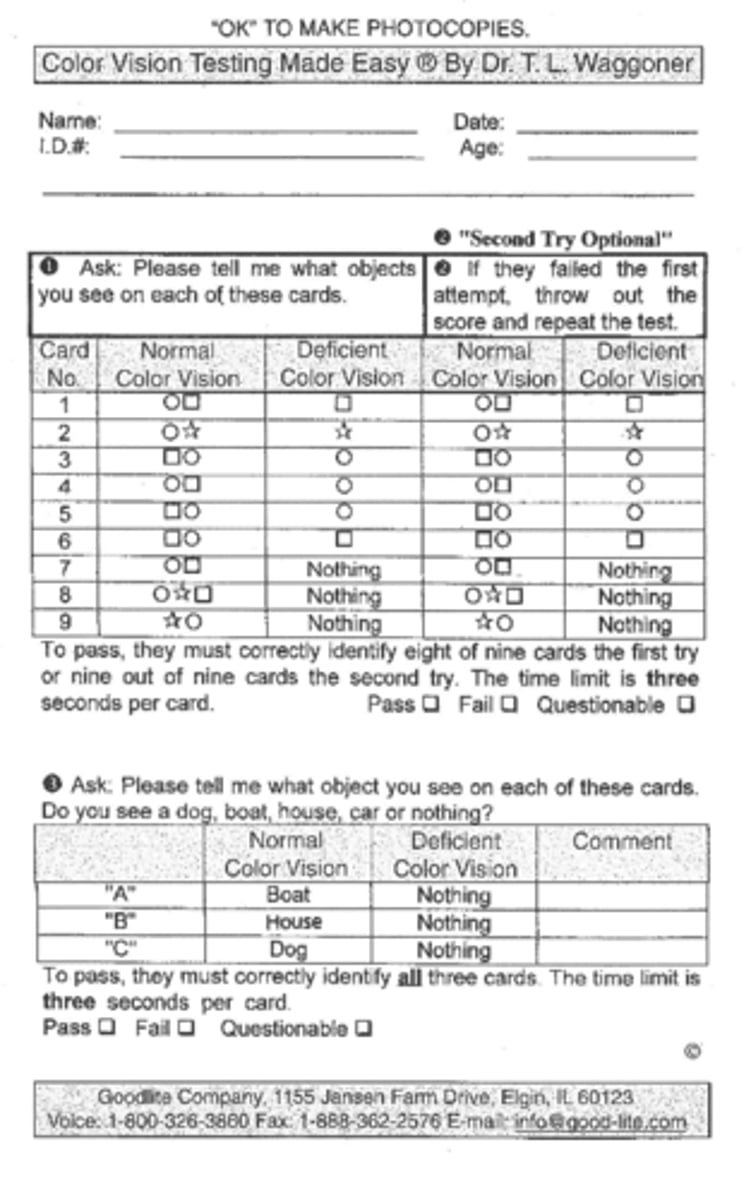
How many shapes does a patient have to get right to pass CVTME?
8/9 on first attempt or 9/9 on second attempt
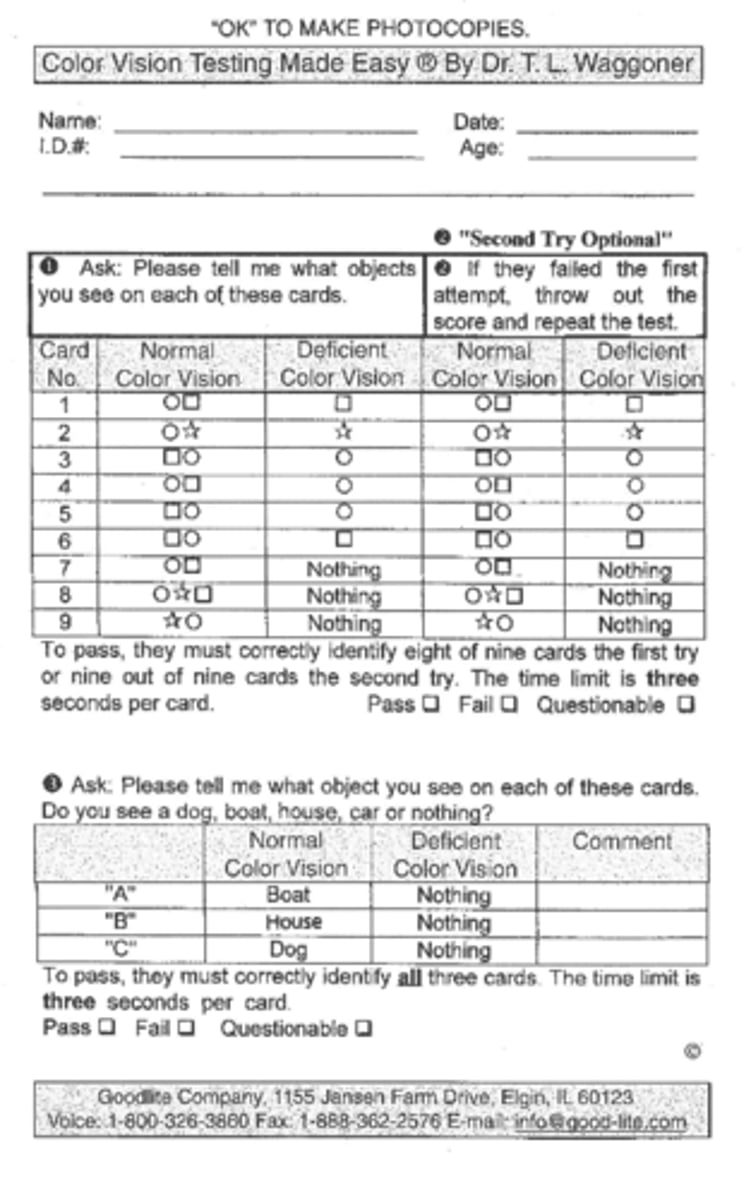
How many symbols does a patient have to get right to pass CVTME?
all 3 of them
Out of HRR, Ishihara, and Color Vision Testing Made Easy, which color test is the only one that can test for B/Y defects in addition to R/G?
A. HRR
B. Ishihara
C. CVTME
A
What are 2 other pseudoisochromatic plate books besides HRR, Ishihara, and CVTME?
Dvorine, Waggoner
(can also use: online software, iPad apps, and VA monitors)
Another color vision test we can use is the arrangement test, which comes in what two forms?
Farnsworth dichotomous test, Munsell 100 hue test
The Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test identifies those with what type/severity of color deficiency?
moderate to severe R/G or B/Y deficiency
True or false: The Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test is useful as a screening tool.
false
If the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test is not useful as a screening tool, then when do we use it?
after pt fails pseudoisochromatic plates
(used for diagnosis)
The Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test was developed using what conceptual markings on the CIE chromaticity diagram?
color confusion lines
(NOT the major confusion axis like with PIC plates)
The Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test consists of 15 small discs and is not timed. What are the instructions we give the patient?
take your time and arrange the colored buttons in order by color, making changes as necessary
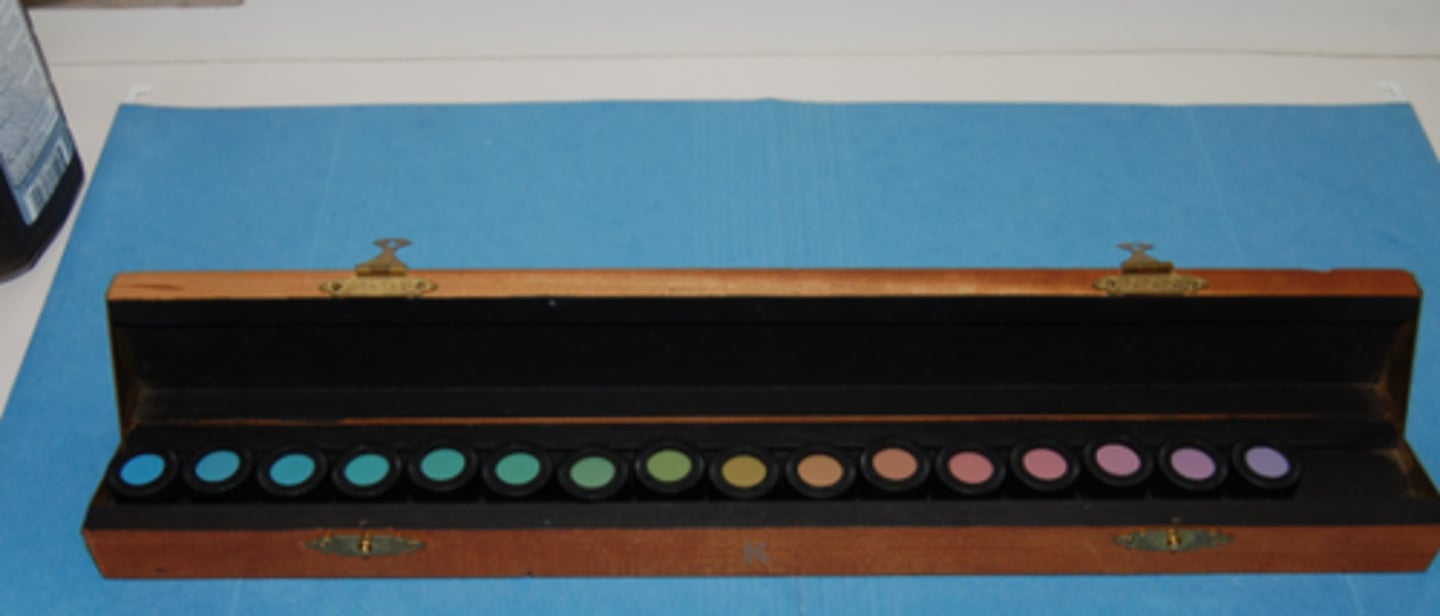

How do we record the results of the Farnsworth dichotomous test?
record the numbers from the buttons in the order that the patient arranged them
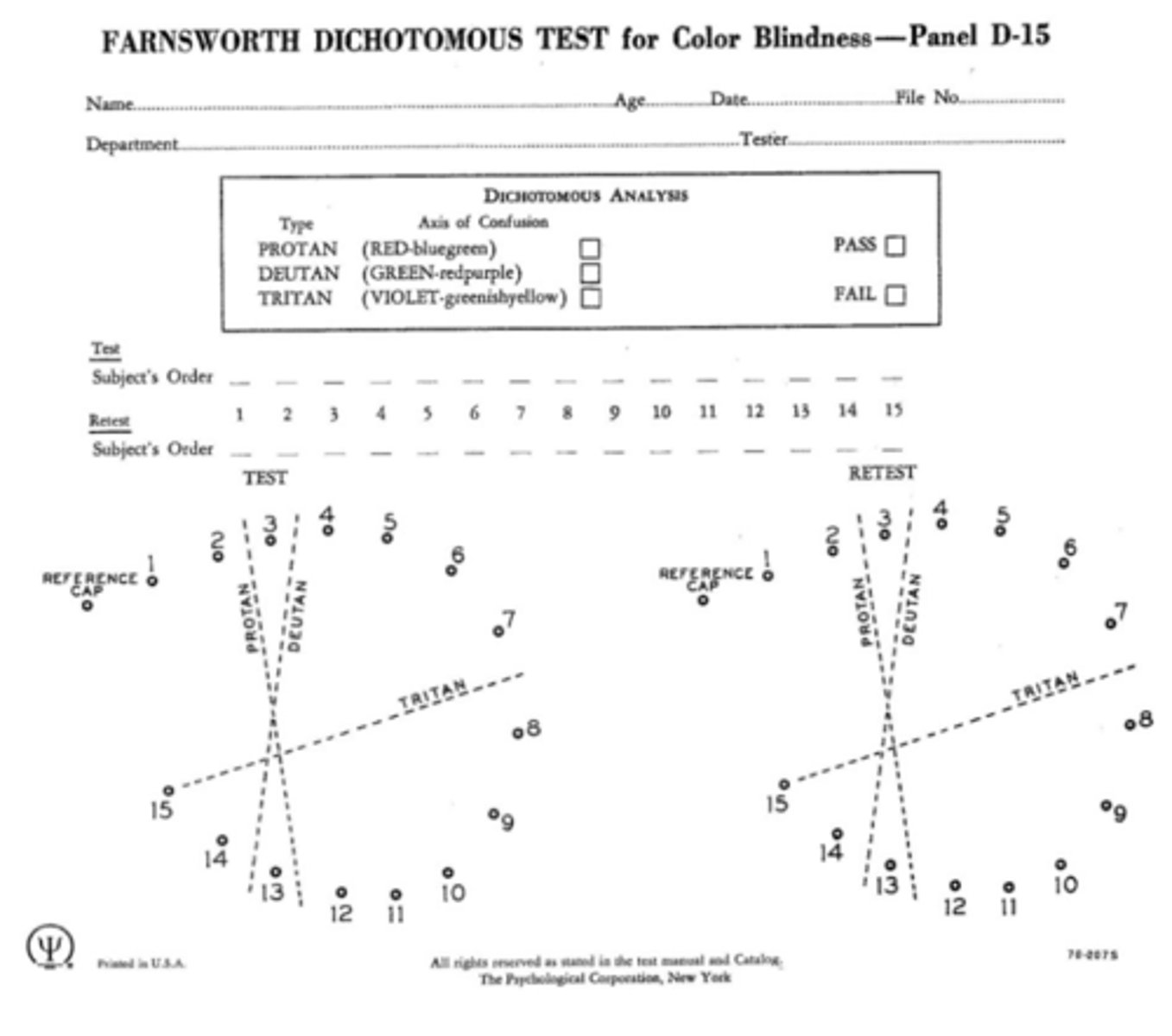
If someone passes the Farnsworth dichotomous test, does this automatically mean they are color normal?
no - it means they may be color normal or have a mild anomalous trichromatic defect
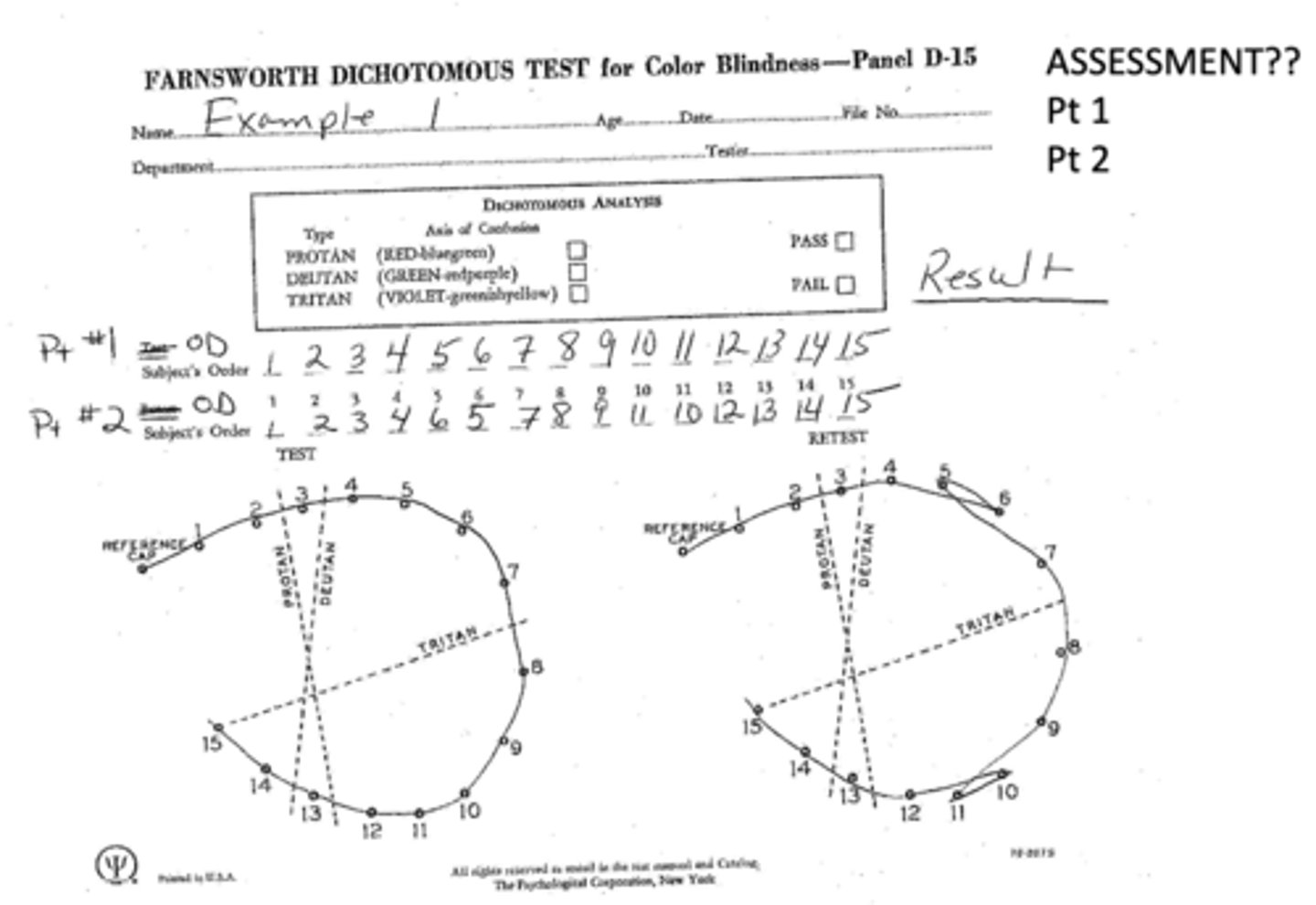
What is considered a "questionable" result from the Farnsworth dichotomous test?
1 major crossover (inversion of colors)
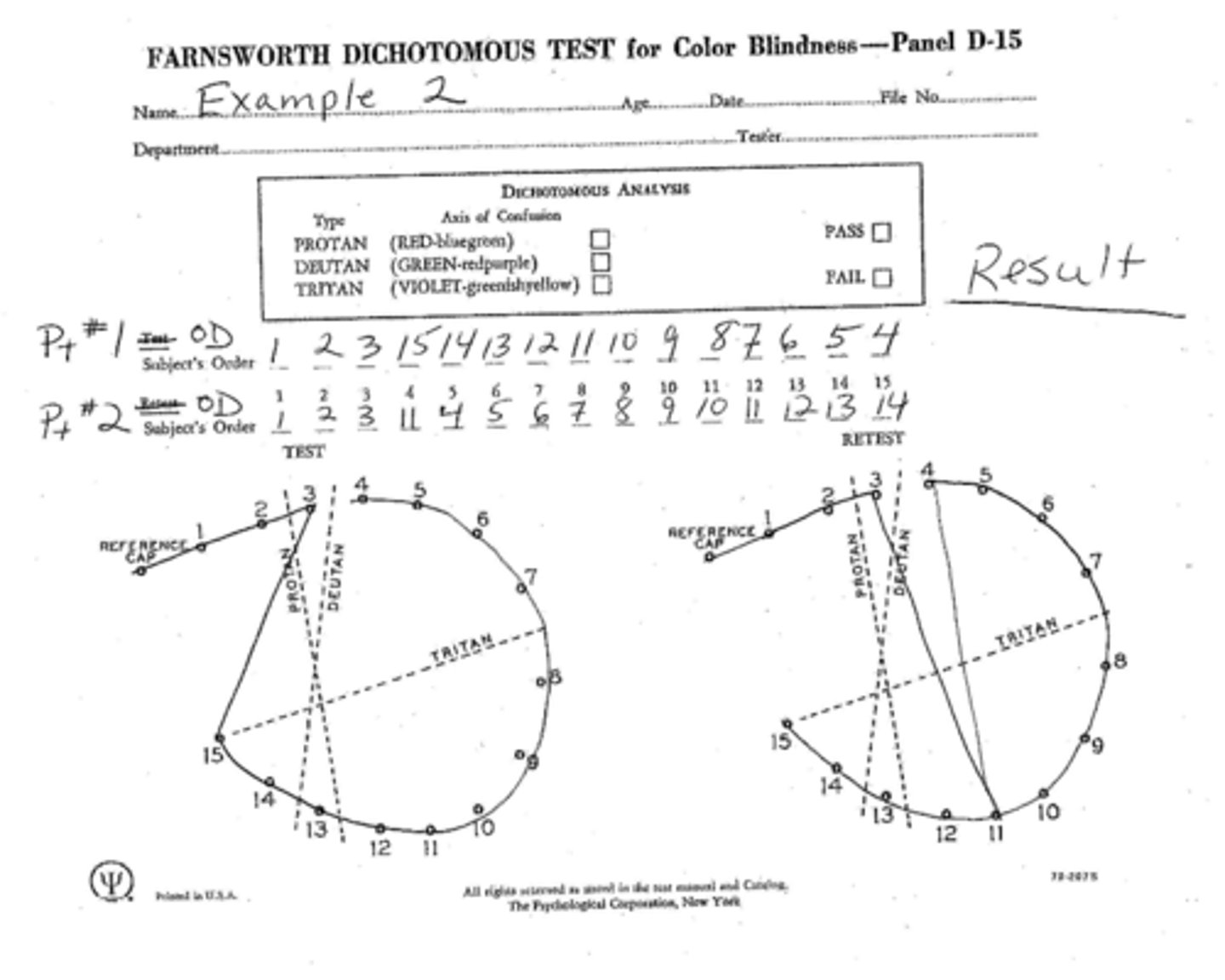
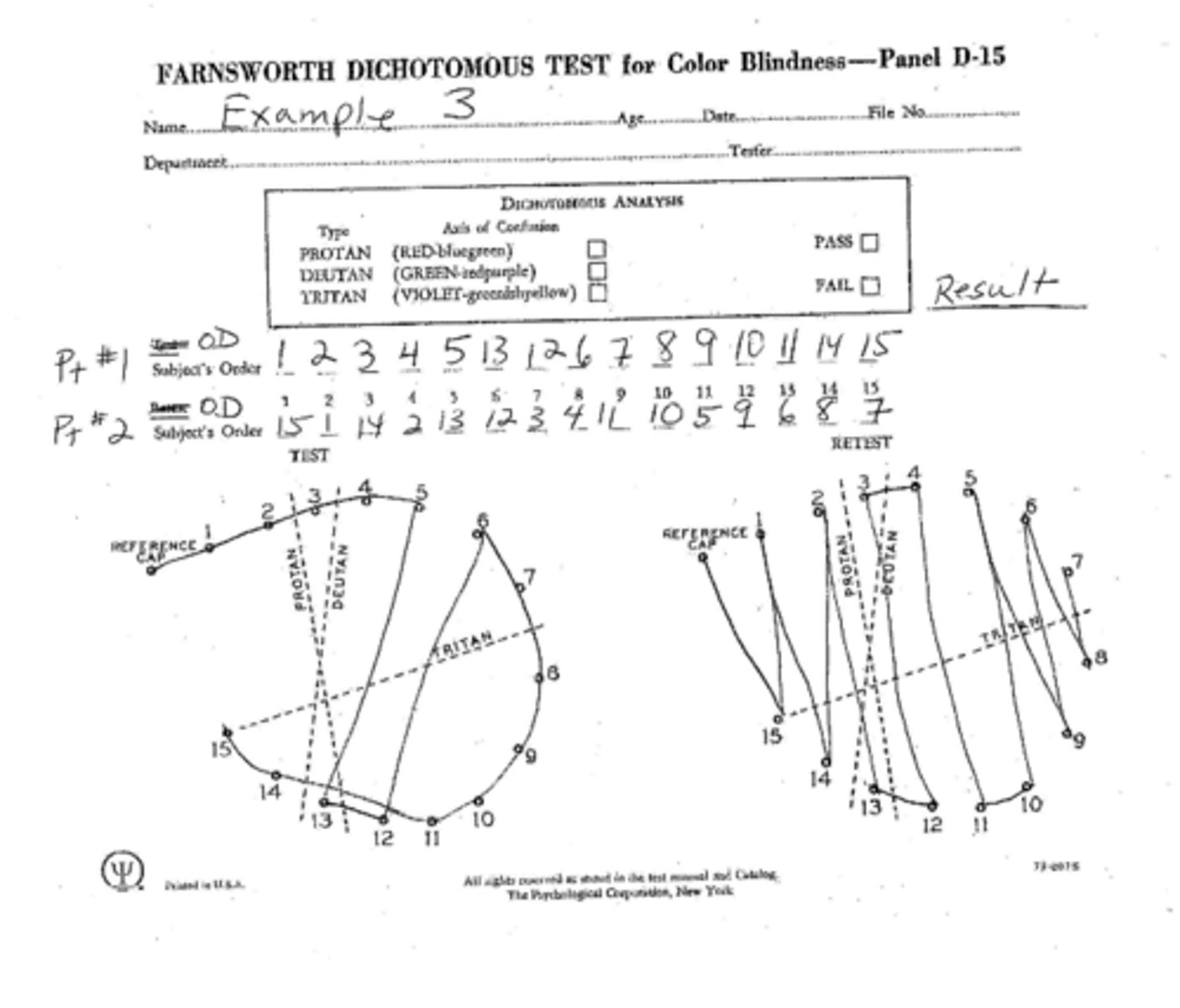
What is considered a "failing" result from the Farnsworth dichotomous test?
2+ major crossovers
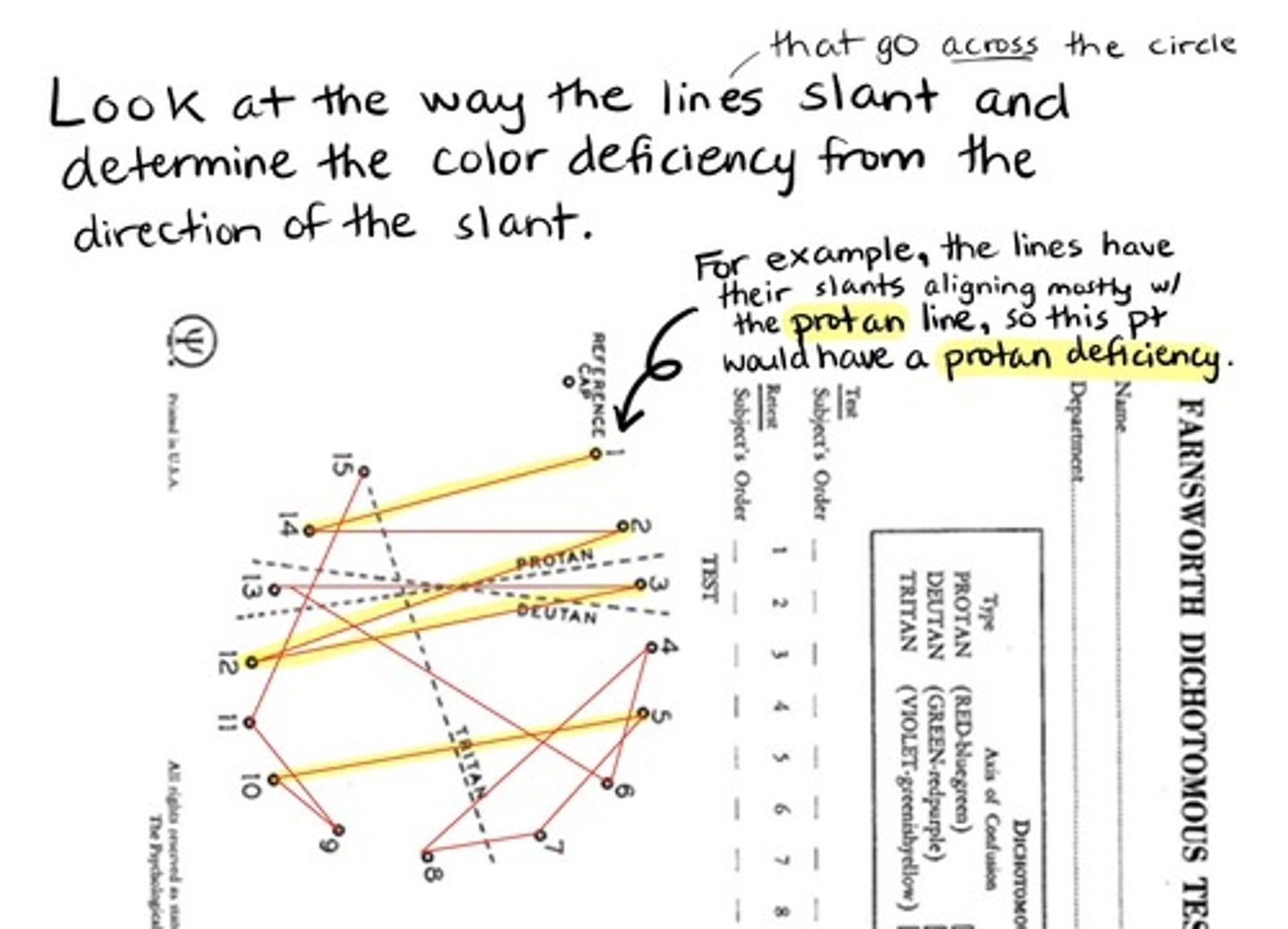
How do we determine if a crossover corresponds to a protan, deutan, or tritan deficiency?
look at the way the crossover lines slant and determine the color deficiency from the direction of the slant
Ultimately, what specifically could it mean for someone to PASS the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test?
they have normal color vision or a mild color vision loss, likely an anomalous trichromacy
Ultimately, what specifically could it mean for someone to FAIL the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test?
they have dichromacy or a strong anomalous trichromacy
The purpose of the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test is to assess if someone can correctly identify surface colors. However, if you PASS the D-15, can you still have color naming difficulty?
possibly
The purpose of the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test is to assess if someone can correctly identify surface colors. However, if you FAIL the D-15, would you definitely have color naming difficulty?
likely yes
A "pass" on the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test can be equivalent to what result with HRR PIC plates?
mild color deficit
(meaning there may be some degree of color vision impairment)
Why would we use large discs for the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test instead of the standard small ones? (3)
if patients are visually impaired, have poor dexterity, or are developmentally delayed
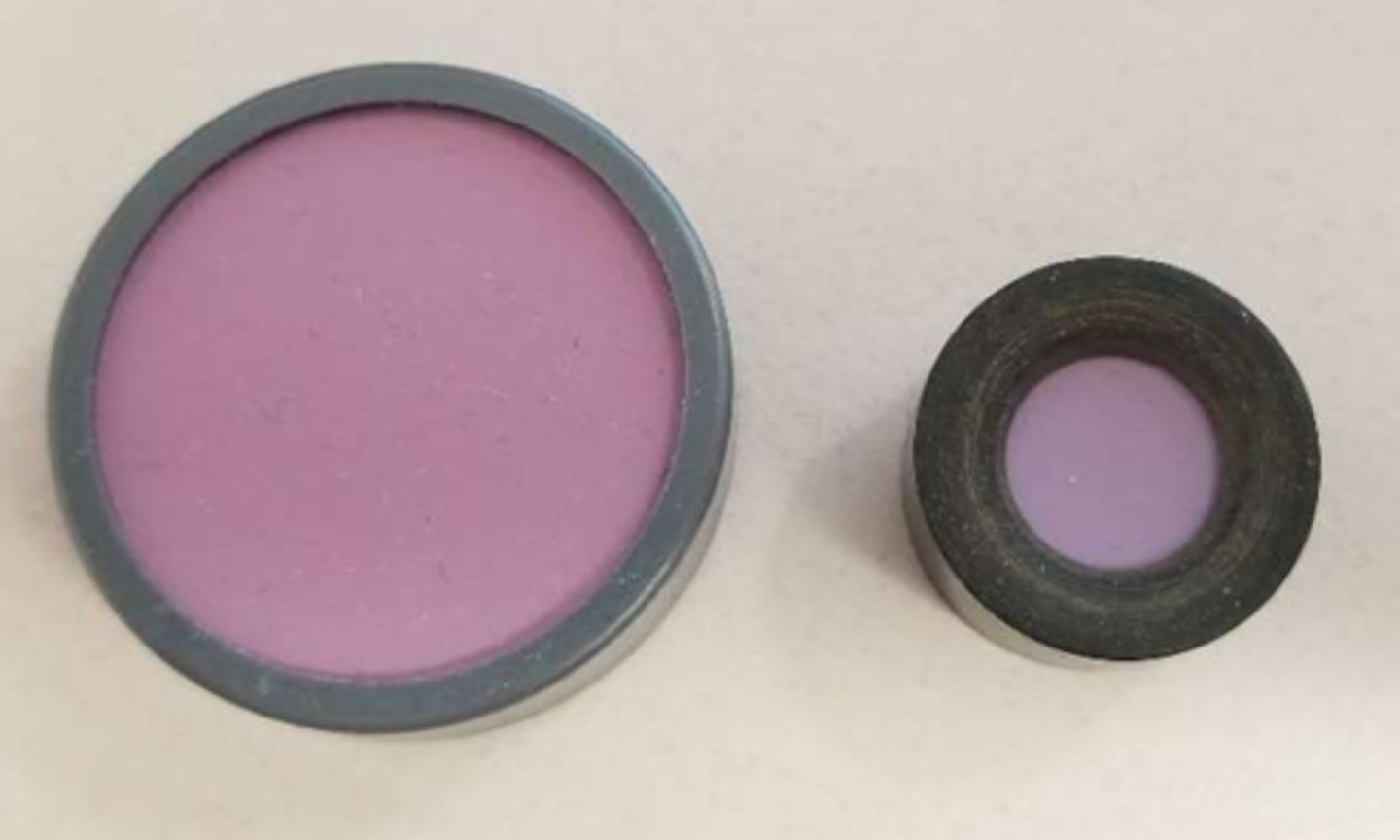

Why should we use caution with administering the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test with large discs?
they subtend a larger retinal area, so pt may pass large D-15 while failing the standard
How can we distinguish between someone who is color normal and mildly color deficient with the Farnsworth D-15 dichotomous test?
**pretty much only used with certain careers that require more specific testing
desaturated discs

The Munsell 100 hue test involves what 3 psychological properties of color?
hue, chroma, value
The Farnsworth Munsell 100 hue test is similar to the D-15 test. However, how is it more specific/general?
involves way more discs to separate people with normal color vision by their discrimination abilities
(also measures the zones of color confusion of color deficient patients)
When scoring the Munsell 100 hue test, we need a score for each disc. How do we find each cap score?
difference between cap number and value of cap to the right + difference between cap number and value of cap to the left
(then plot the score for each cap!)
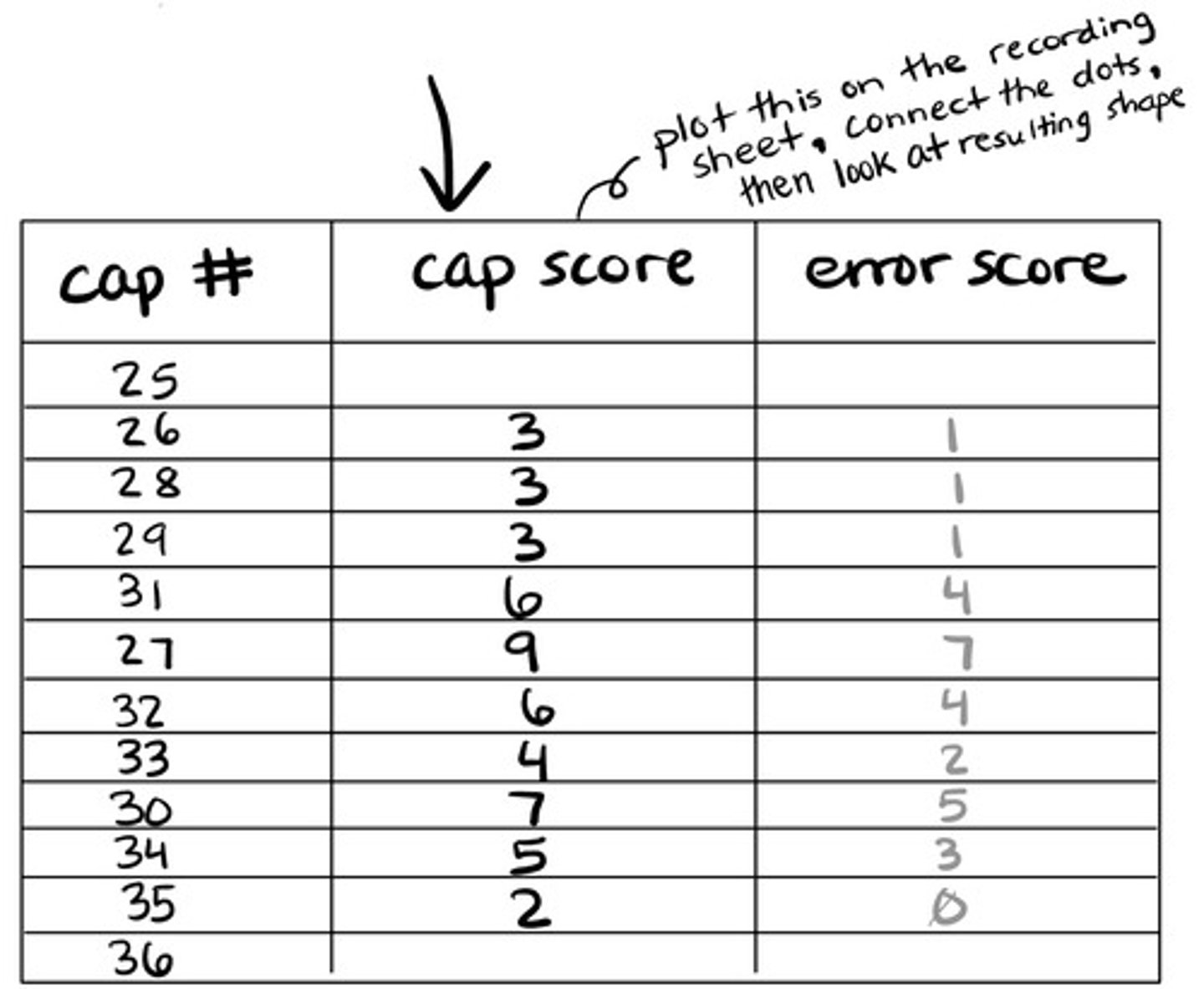
Example: When scoring the Munsell 100 hue test, three caps with numbers 46, 56, and 51 are in a row. What is the cap score for disc #56?
15
(56-46=10, 56-51=5, 10+5=15)
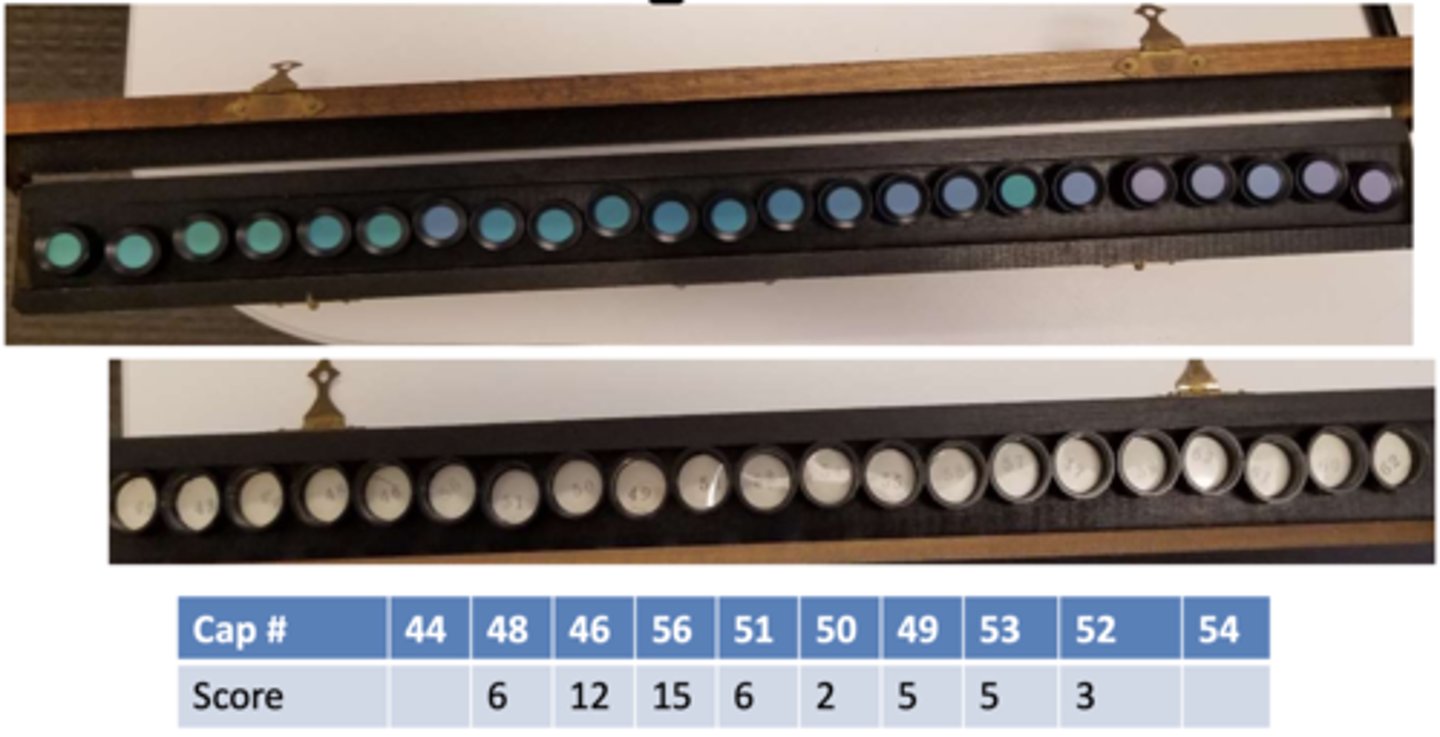

When scoring the Munsell 100 hue test, we also need the total error score. How do we calculate this?
each cap score - 2, then sum all error scores
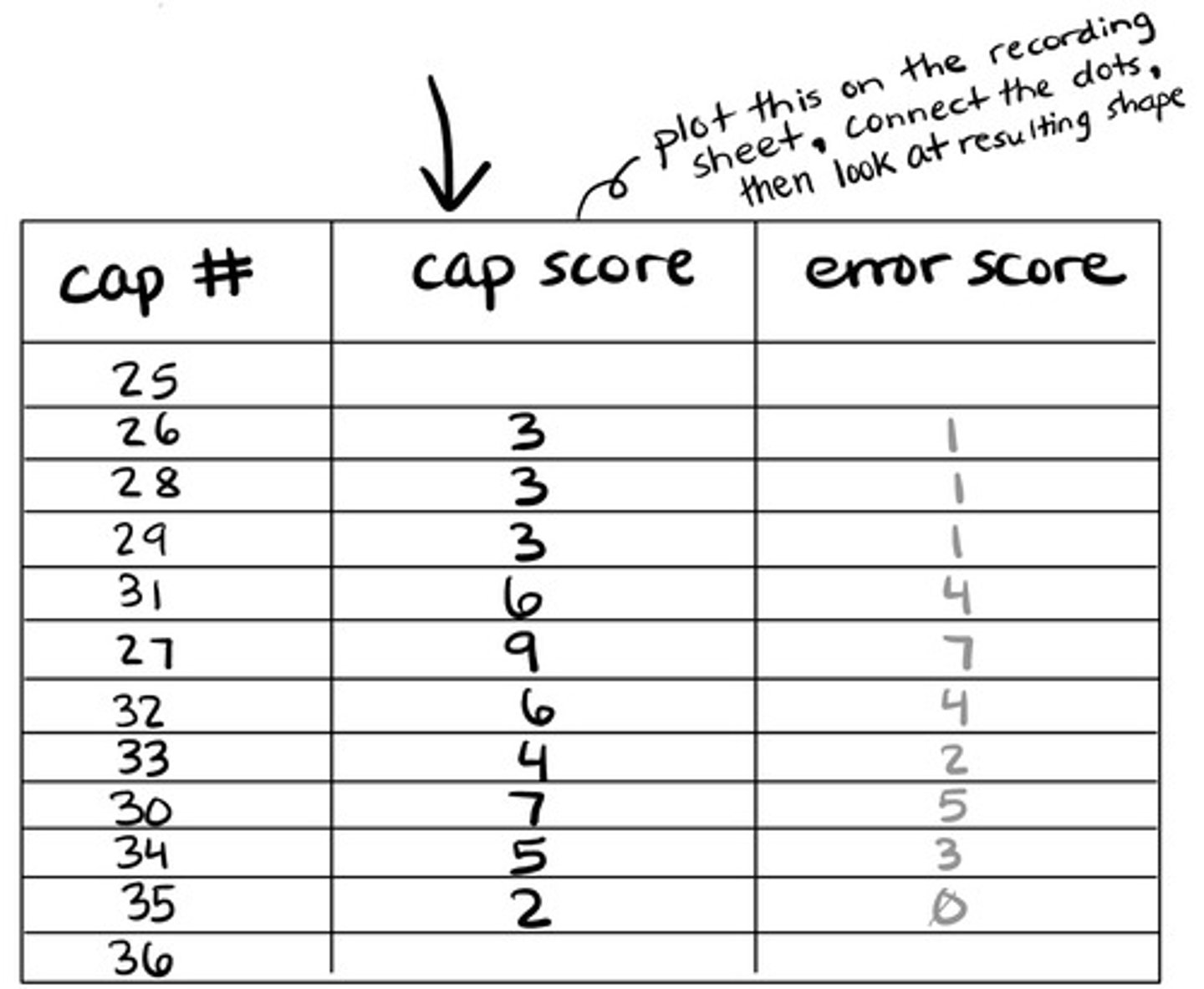
What does the total error score tell us?
accuracy of an observer's ability to arrange caps
Who would have the highest mean total error score?
<10 year olds
Who would have the lowest mean total error score?
18-30 years old
If the lowest mean total error score is found in ages 18-30, then what happens to the mean score with age over 30?
gradual increase
What total error score distinguishes color normal vs. color deficient?
no one defining score, maybe <100
(since it is so age dependent)
True or false: Someone who is R/G color deficient has different trends in the total error score as someone who is B/Y color deficient.
false
(same trend in scores whether R/G or B/Y deficiency)
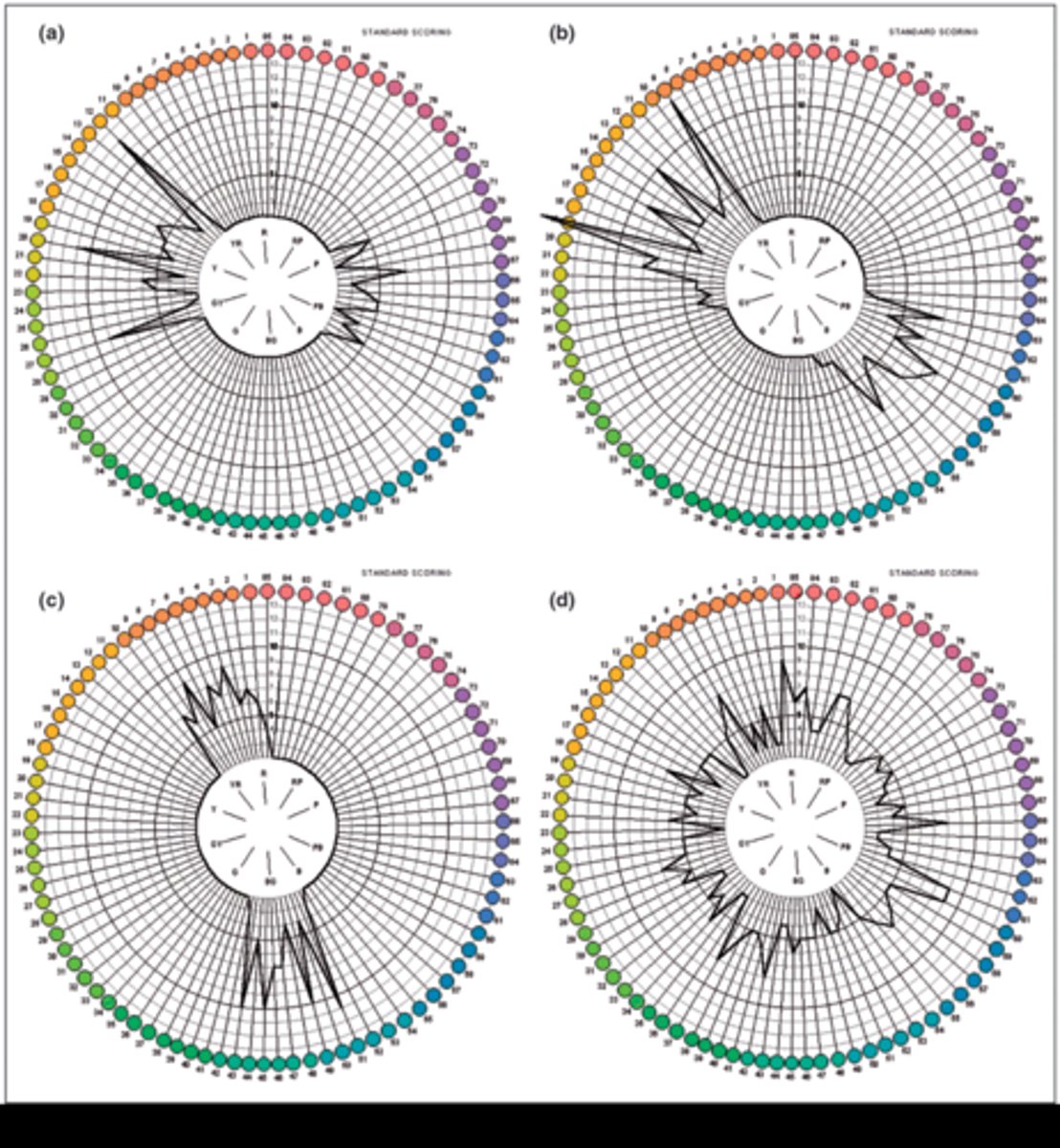
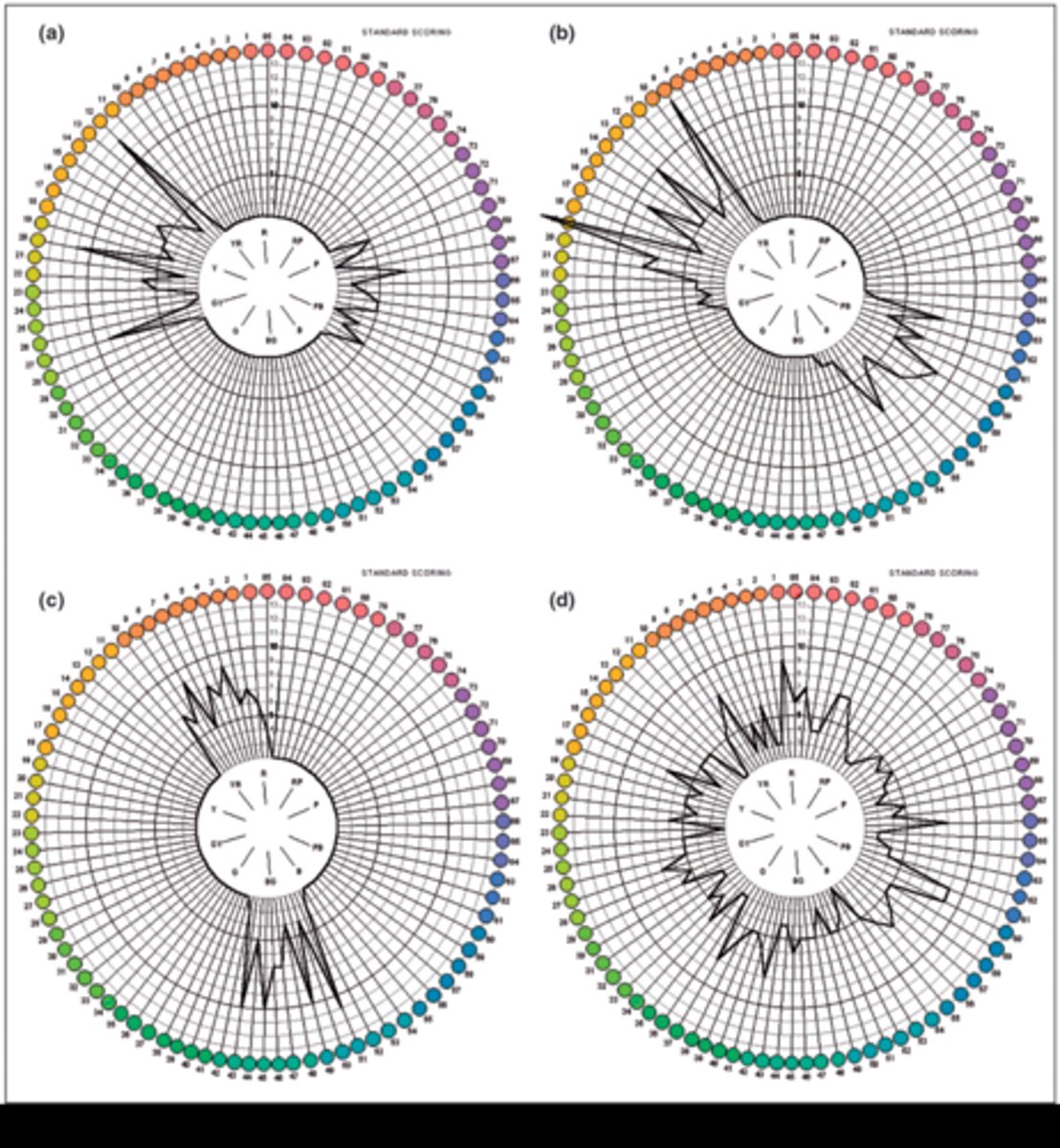
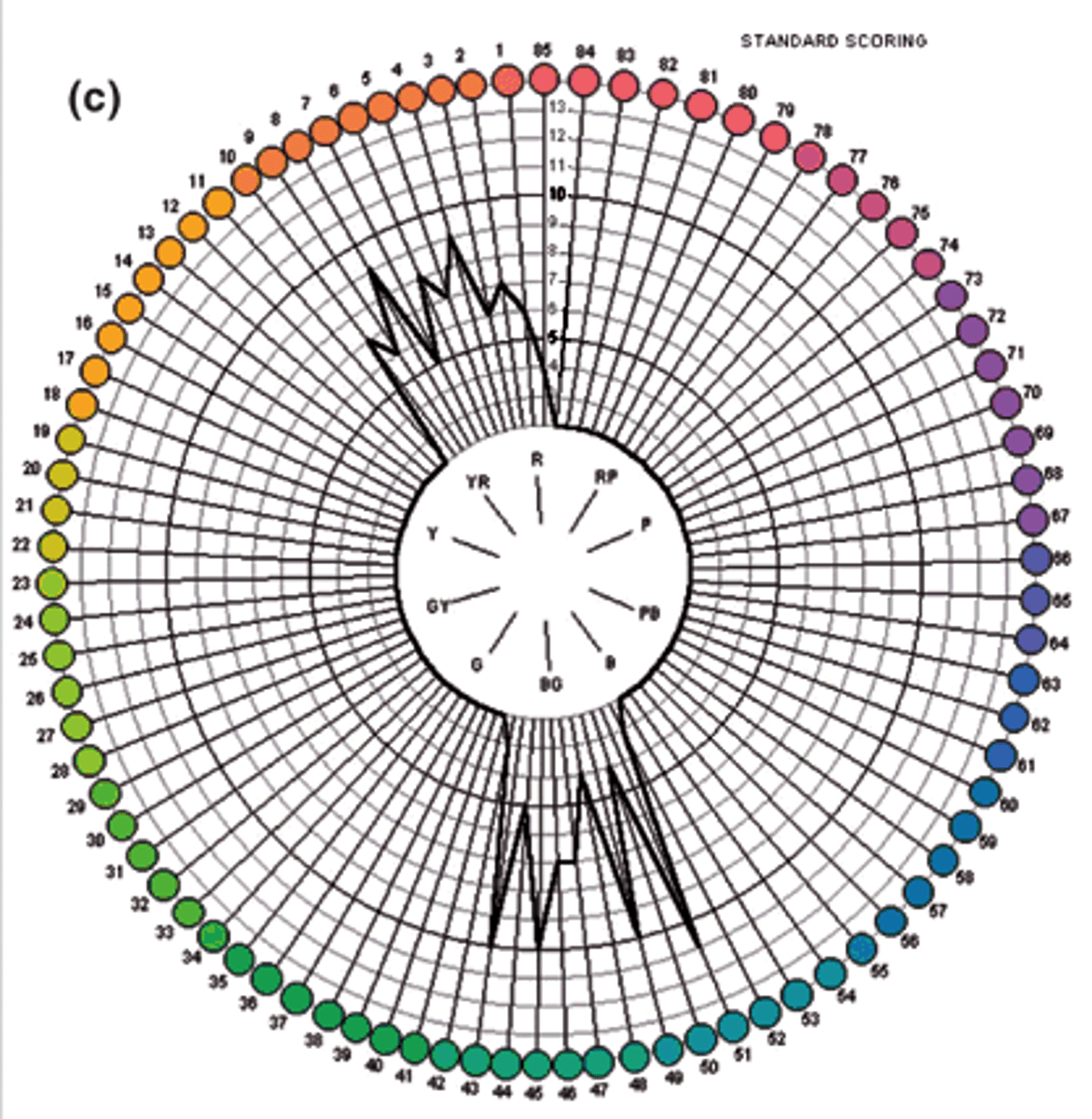
Once we get the error score for each cap, how can we visualize the results?
plot on a circular graph
What is the characteristic graph shape for someone who is color normal but with bad discrimination ability?
evenly distributed spikes
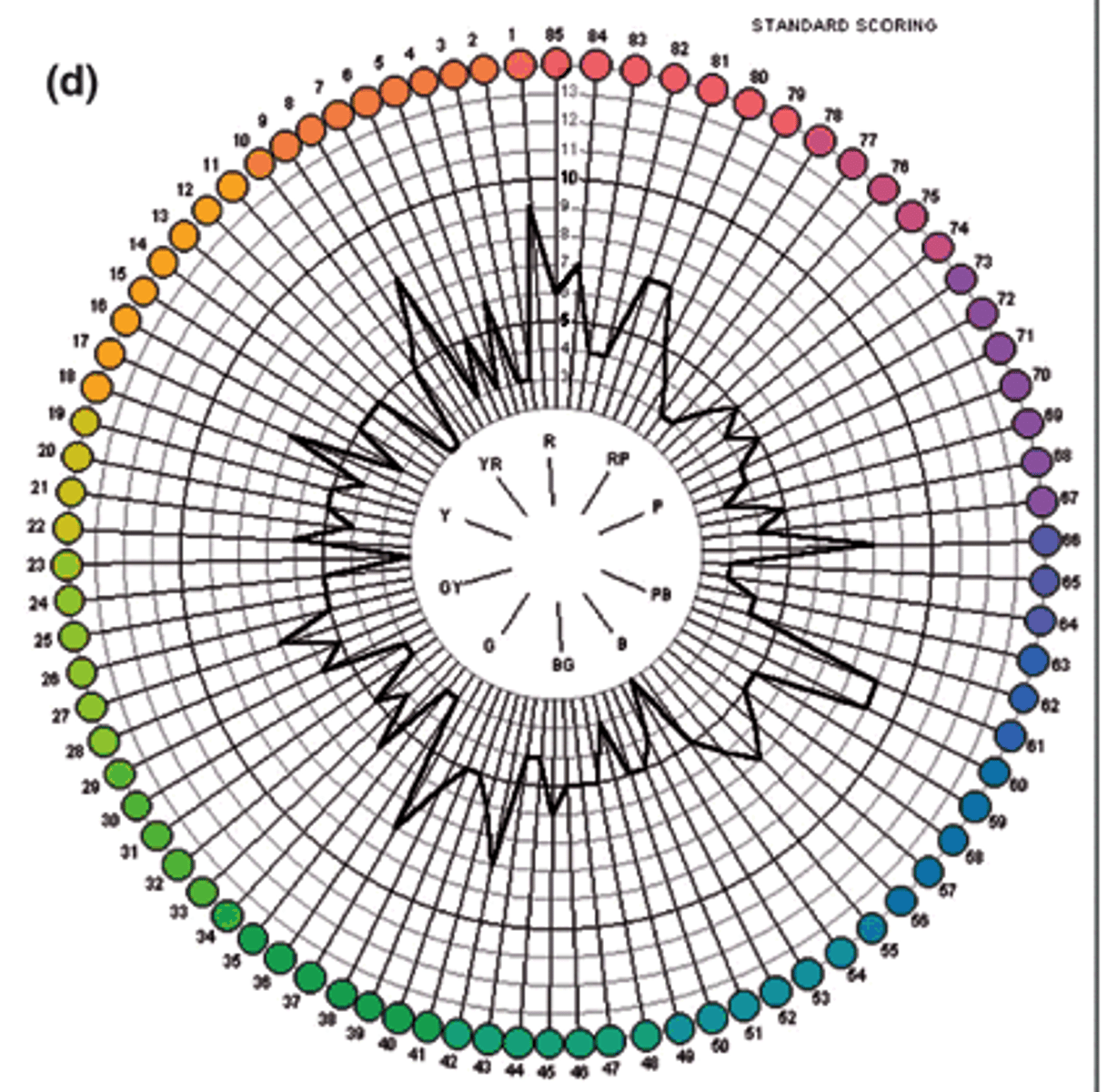
What is the characteristic graph shape for someone who is color deficient?
spikes on opposite sides
color vision tests involving recognition of red, white, and green signal lights (no blue/yellow), but does not diagnose the type or severity of a R/G defect
lantern tests
What kind of color deficiency is evaluated with a Farnsworth lantern test?
R/G only
What is the gold standard for R/G color vision testing?
pretty much just used in research and DOES NOT test for B/Y defect!
anomaloscope
True or false: The anomaloscope can test for a B/Y defect in addition to R/G.
false
(R/G only)
Why does a color normal trichromat function as a dichromat with an anomaloscope?
S cones don't absorb any light at the wavelength tested
How do we use the anomaloscope to test color vision?
use a test field of yellow (590 nm) on the bottom with a mixture field containing red (670 nm) and green (546 nm) on the top
adjust color of top half to match bottom yellow and brightness of bottom half to match top mixture
(we are finding the proportional amount of spectral red and green required to match spectral yellow via the Raleigh match/equation - it should be 50% red and 50% green, which is where a color normal pt will correctly identify that it matches the bottom)
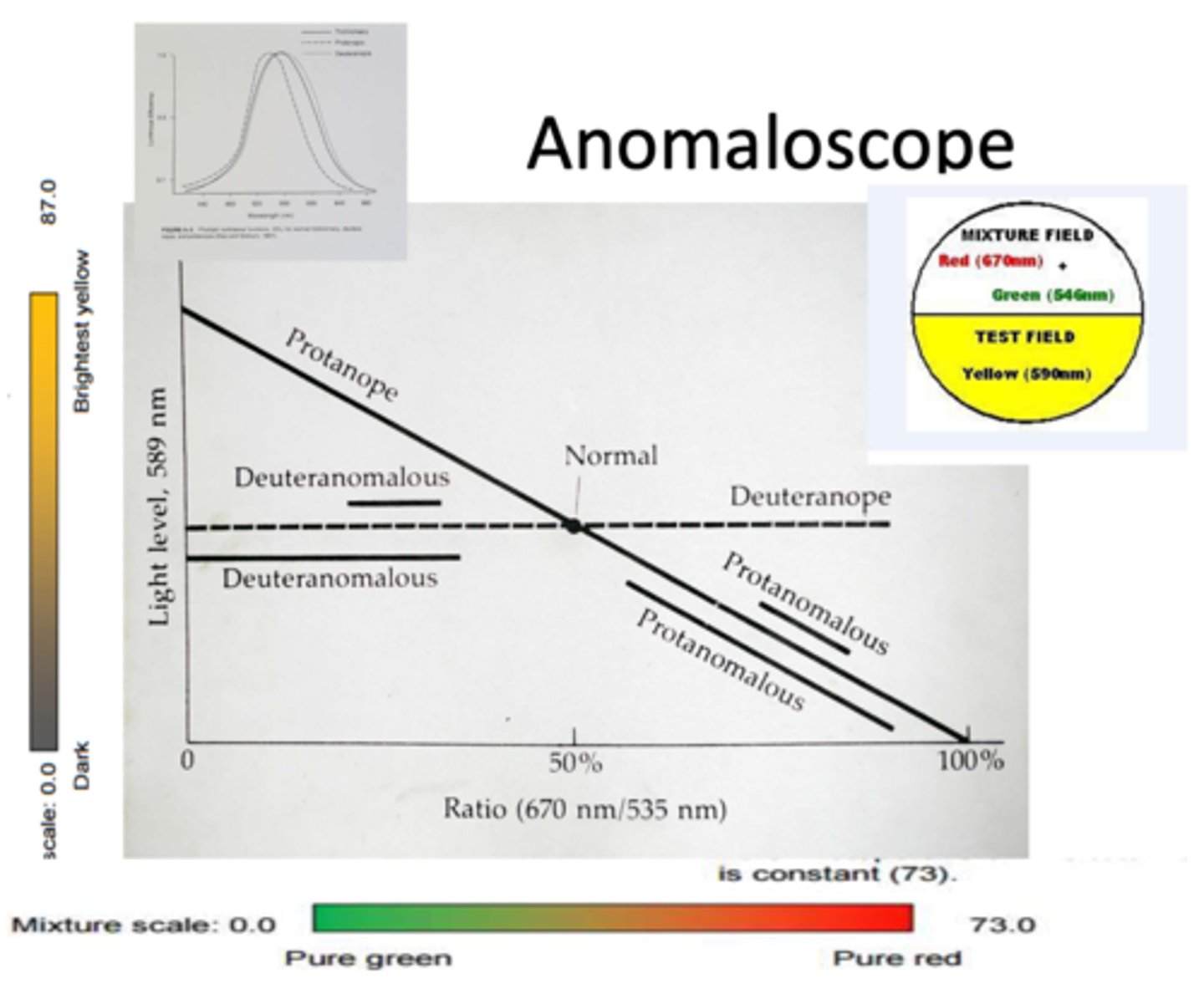
What is the first match made on the top half of the anomaloscope?
match top/bottom color
(top can be adjusted to be more red or more green)
What is the second match made on the bottom half of the anomaloscope?
match top/bottom brightness
(bottom is set at yellow, but brightness can be adjusted)