Population Growth and Regulation
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ecology exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Intrinsic Growth Rate
“r”
-highest growth rate per capita
=births-deaths
exponential growth equation
N(t) = N₀e^(rt)
-for ideal conditions and consistent breeding
Observed rate formula
dN/dt=rN
rate of growth at a specific moment in time
-use when given population and intrinsic rate of growth
Negatively growing population
more deaths than births
geometric growth model
N(t) = N(0) * λ^t
-used for species with a breeding season
λ
discrete population growth rate used for breeding seasons
λ = N(t)/N(t-1)
link two models
λ = e^r
convert between r and λ
r=ln λ
doubling time
-time for population to double in size
doubling time exponential model
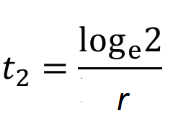
doubling time geometric model
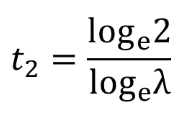
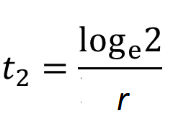
what does log e mean?
ln
density independent factor
mostly abiotic, like storms
-geometric and exponential models are density independent
Is indefinite growth possible?
No because of limited resources and abiotic factors
density dependent factors
are often biotic, like limited food resources and disease
negative density dependence
high population causes negative population growth
positive density depedence
low density causes decreased population
-difficulty finding mates or hunting in groups
“Allee effect”
carrying capacity “K”
-maximum population the ecosystem can support
-going over capacity starts reducing the population
-overshoot causes population collapse
logistic growth model
-early growth is exponential, then slows as it approaches K
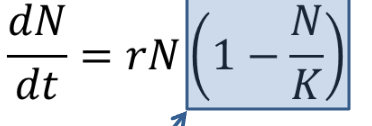
logistic graph
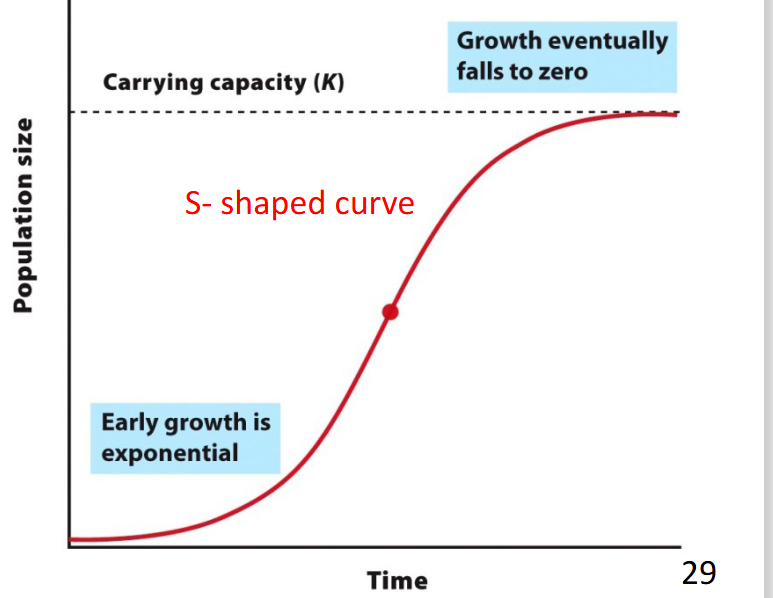
inflection point
-point at which growths stops being exponential and starts to slow
-when N=K/2