SUPA Econ: Chapter 6 (Power of the Invisible Hand)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
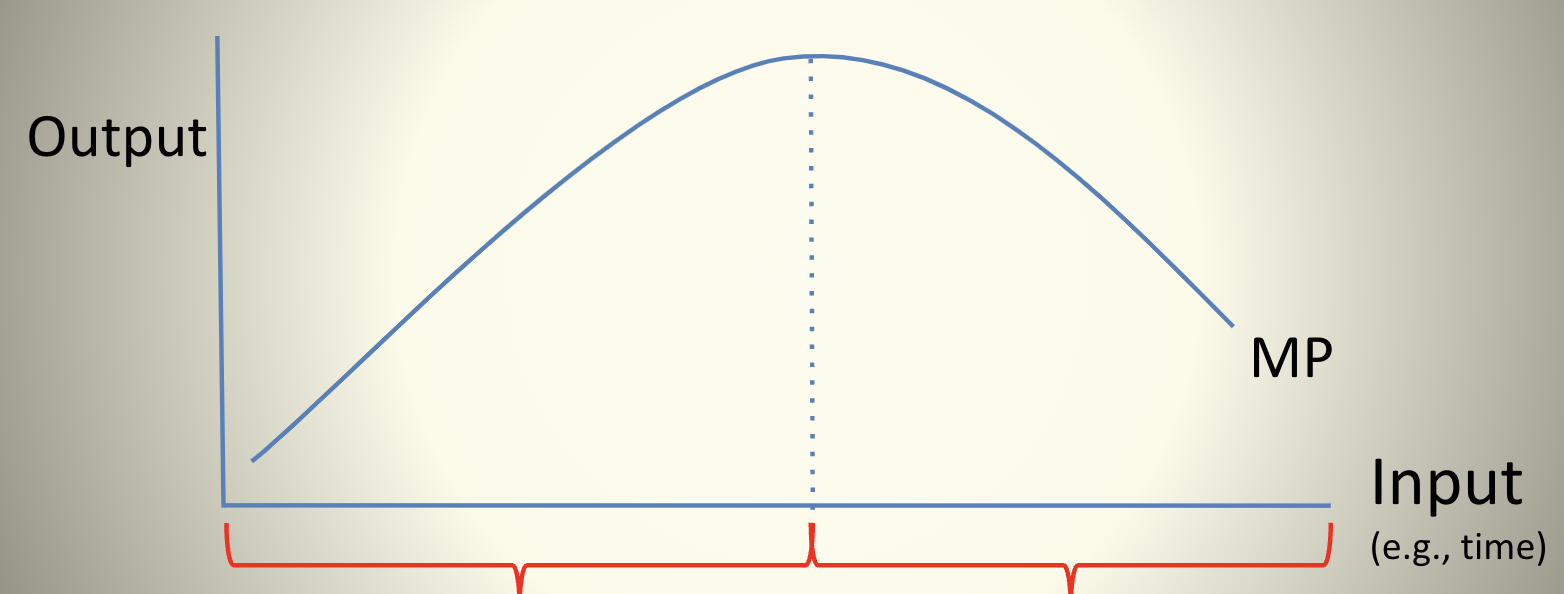
Successive units of input are more productive, so successive units of output
cost less (MC↓)
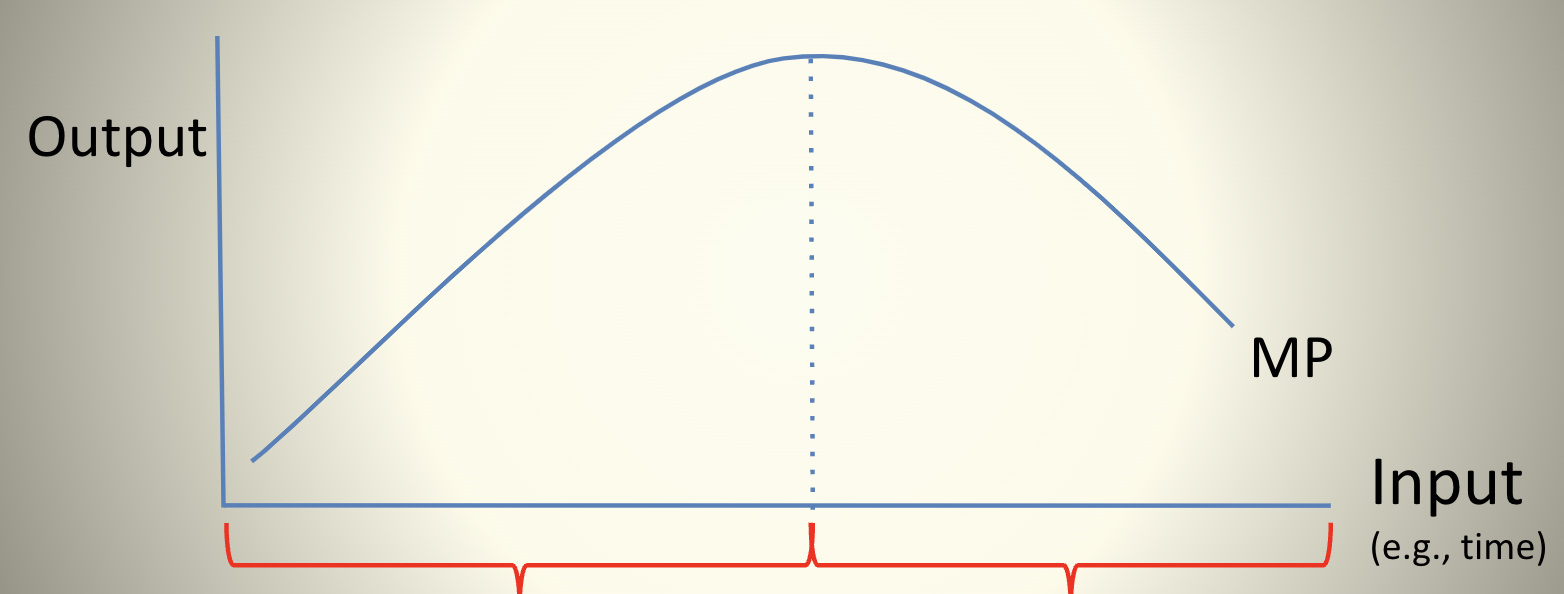
Successive units of input are less productive so successive units of output
cost more (MC↑)
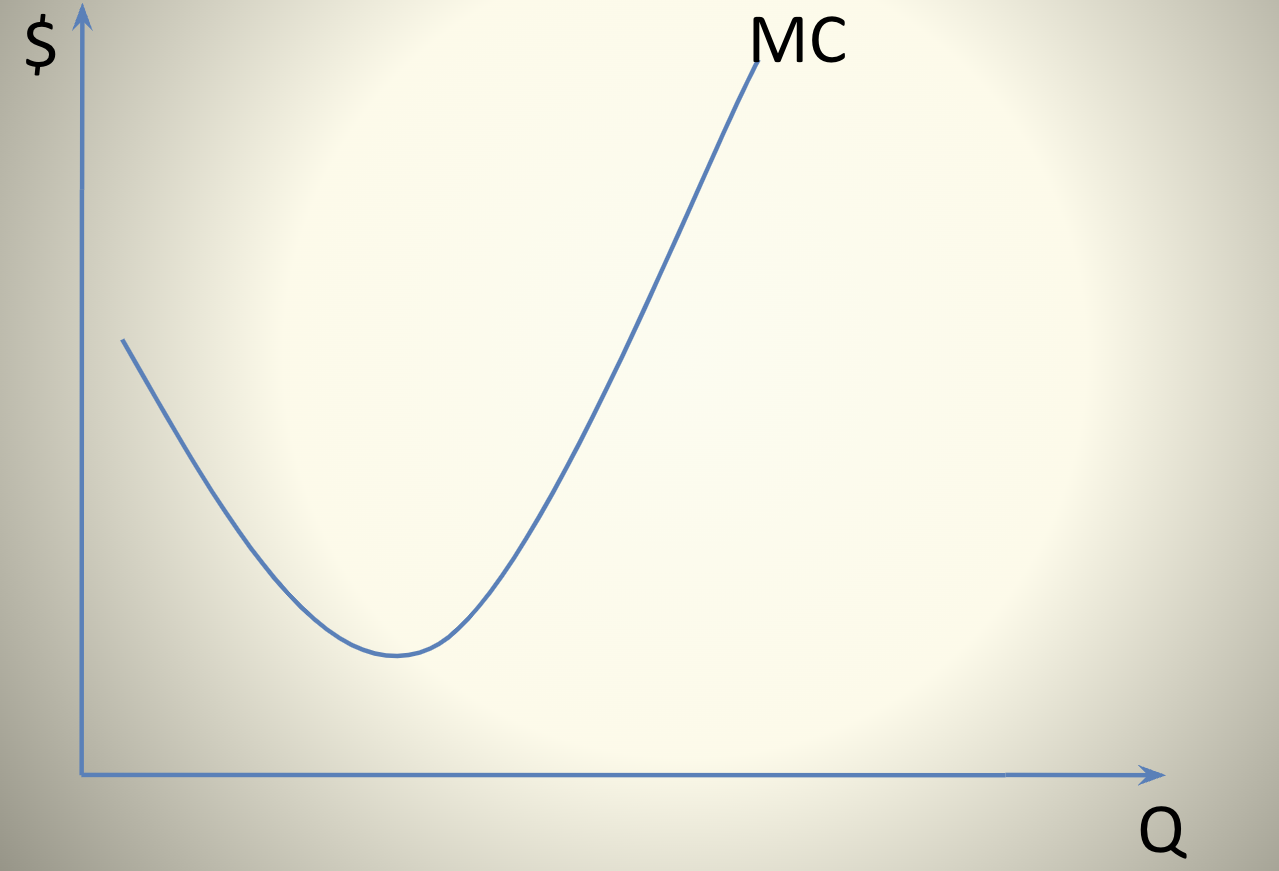
The Firm’s Cost Structure
the MC falls then rises
The ____ sets the price
market
Firm is a ______ _______
Price taker
The Firm under Perfect Competition
No market failure, no market power, Market determines price - firm is a “price taker” It's demand line is perfectly elastic at the market price
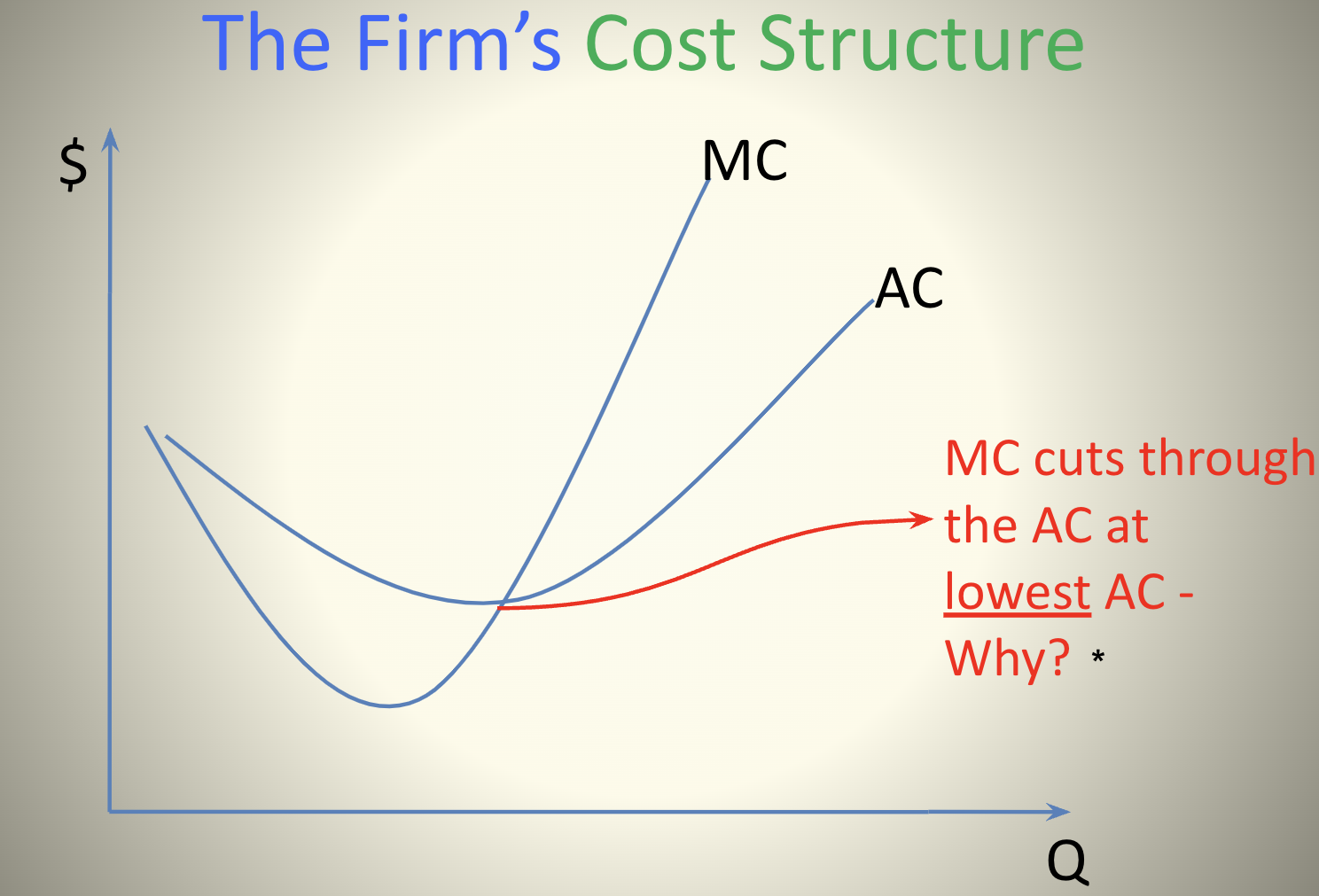
Relationship of Average and Margin
The margin always pulls the average in its direction. If the margin is above the average, it pulls the average up. If the margin is below the average, it pulls the average down
Marginal Cost (MC)
How much it costs to make the next unit
Average cost (AC)
generic measure of cost, total cost of production divided by the total units produced
You average 27 hits a season. This year (at the margin) you hit 35. What happens to the average?
it increases
Total Revenue
Price X Quantity (pXQ)
Total Cost
Average Cost X Quantity (ACxQ)
You get profit when
Total Revenue (TR) > Total Cost (TC)
You have a loss when
Total Revenue (TR) < Total Cost (TC)
Variable Costs
costs that change depending on how much you produce (ex. flour, cheese (for pizzas))
Fixed Costs
Costs that generally remain the same, no matter how much you produce (ex. Pizza Ovens)
Profit
Total Revenue (TR) - Total Cost (TC)
Total cost includes a
normal return (a sufficient return to make it worth staying in business)
any positive profit is good, but
not necessary to stay in business
Dynamics of Perfect Competition
Profit attracts competitors, Competitors enter market, Market Supply increases, Market price falls, Falling market price squeezes firm’s profit. This dynamic continues so long as there is any profit to attract competitors.
Firm vs Market Graph
Firm has MC and AC while Market has supply and demand
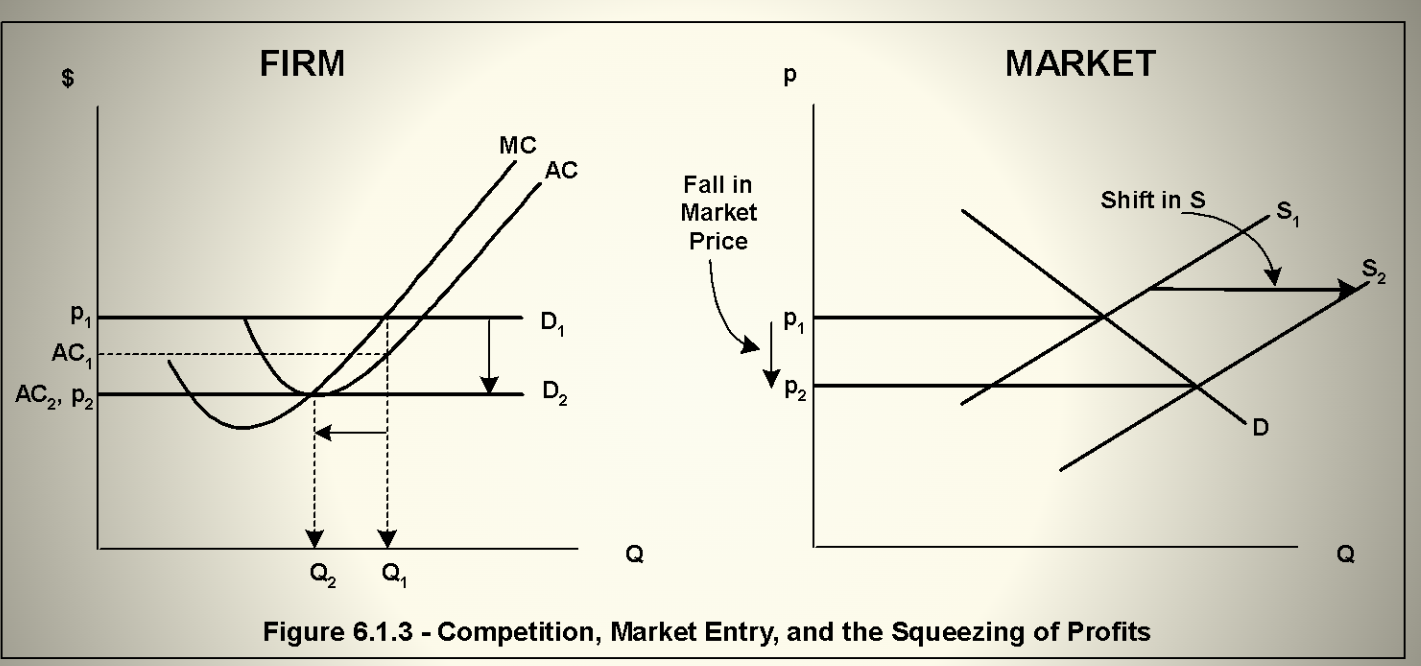
When Profit is Gone
Firms are mad (they love the profit), but society is served
All firms are forced to
produce at the lowest average cost, the most efficient method production
Firms don’t choose efficiency. They are force to be efficient by
Perfect Competition
How does an entrepreneur get back to a profit-making condition without cheating?
By being imaginative and innovative, lowering cost structure by coming up with a more efficient way to produce
When firms are experiencing a loss
someone has to go (and someone will)
Firms exiting from the market
shifts market supply left and raises price
Price will rise until
all losses are gone and remaining firms are simply making a normal return
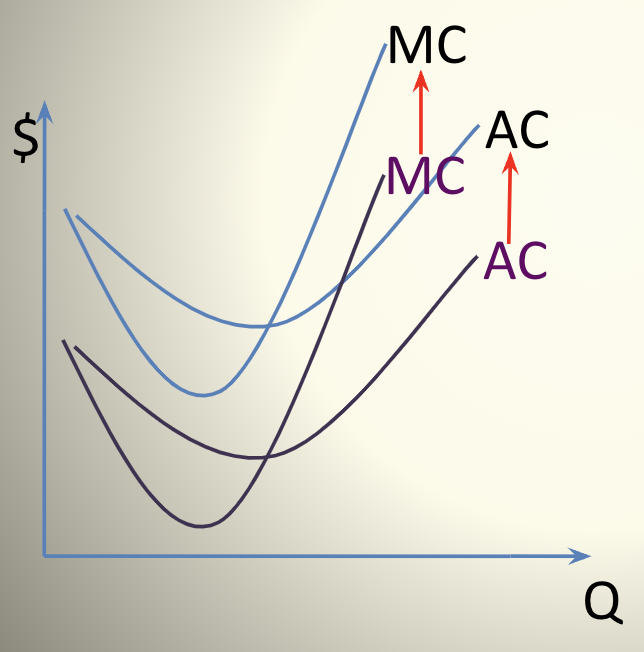
If the cost of inputs go up or the technology gets worse, then
at any given quantity (Q) the MC and AC will go up raising the cost structure
If the cost of inputs go down or the technology improves then
at any given quantity (Q) the MC and AC will go down, lowering the cost structure
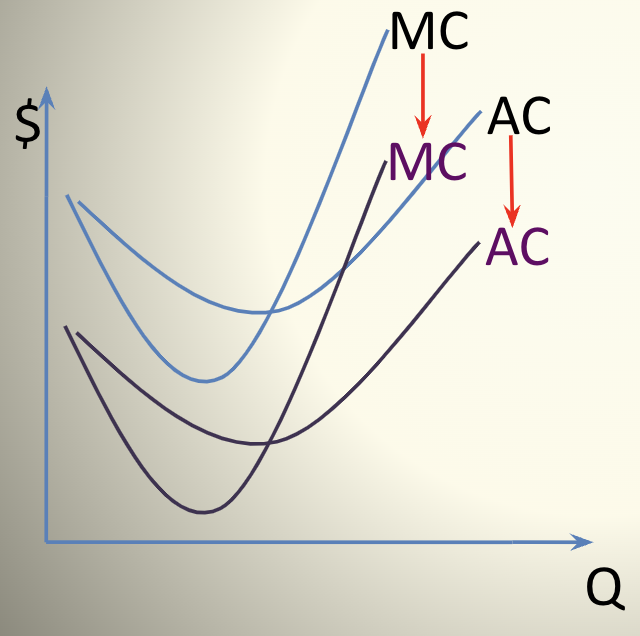
Leader firm with lower cost structure
will enjoy a profit until others figure out the new more efficient production technique
The leader’s profit is ephemeral (lasting for a very short time). Competitors will figure out and copy the innovations. So to stay ahead and continue to enjoy a profit requires ever more
innovation
Perfect Competition drives all firms to not only be most efficient but to become
ever more efficient
From a given set of resources we get an
ever growing output (a bigger societal pie)
PC requires __________ _______ to ensure a fair, keen competition (ex: no market power)
Commutative Justice
Does PC ensure Distributive Justice
No. One will get a share proportional to one’s share of the initial endowment, and this initial distribution can be quite unjust. This is a moral, not an economic question.
When profits have been driven to zero by competition
Price = MC = AC (At the bottom of the AC line [includes normal returns] This is the most efficient point)
The self-interested behavior of seeking profits leads to the
most efficient outcome
Markets encourage
creativity and innovation/inventiveness
If you have negative cross-price elasticity, and we lower the price of hamburgers, what happens?
If you have a negative cross-price elasticity and lower the price of hamburgers, the demand for the complementary good (like french fries or soda) will also increase
Total Cost
Total Costs = Variable Cost + Fixed Cost