Myocardial Ischaemia and Acute Coronary Syndrome part 1
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
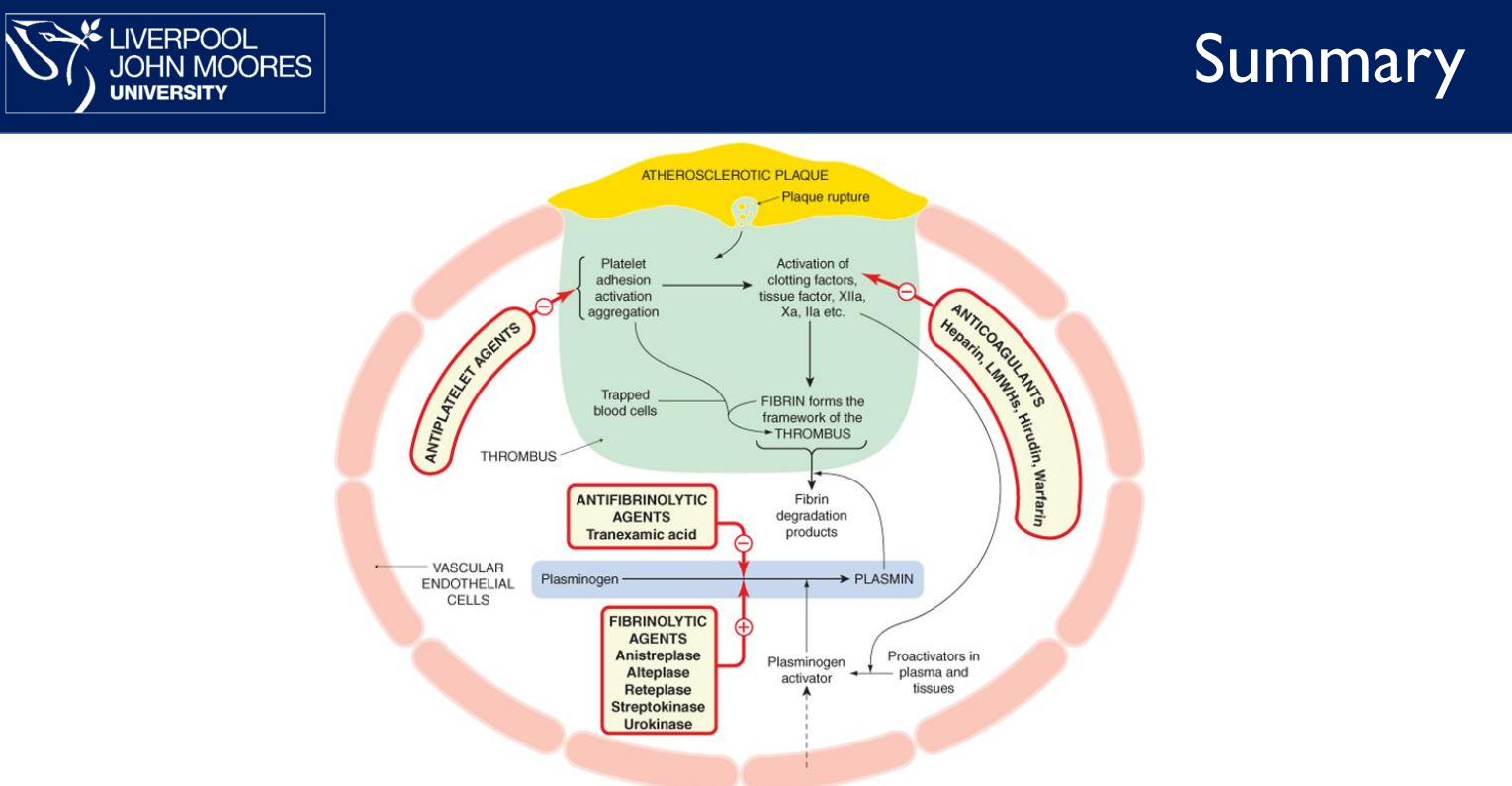
What are the 3 main classes of antithrombotic drugs? (3 points)
1. Anticoagulants
2. Antiplatelets
3. Thrombolytics
What are common anticoagulant drugs? (6 points)
1. Warfarin
2. Heparin
3. Apixaban
4. Rivaroxaban
5. Edoxaban
6. Dabigatra
Q: What are common antiplatelet drugs? (5 points)
1. Aspirin
2. Clopidogrel
3. Ticagrelor
4. Prasugrel
5. Tirofiban (short-term, hospital use)
What are common thrombolytics? (4 points)
1. Streptokinase
2. Alteplase
3. Reteplase
4. Tenecteplase
What are key uses of antiplatelets? (5 points)
1. Acute coronary syndromes
2. Chronic coronary syndromes
3. Ischaemic stroke
4. Transient ischaemic attack
5. Peripheral arterial disease
How do antiplatelets work in platelet aggregation? (3 poin
1. Aspirin inhibits COX-1 and blocks thromboxane production
2. P2Y12 inhibitors (clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor) block ADP binding to P2Y12 receptor
3. Tirofiban blocks fibrinogen binding to GPIIb/IIIa receptors
What are the primary uses of anticoagulants? (5 points)
1. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
2. Pulmonary embolus (PE)
3. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation
4. Clotting during dialysis
5. Acute coronary syndrome
What is the mechanism of action of warfarin? (3 points)
1. Blocks Vitamin K reductase
2. Prevents synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X
3. Requires monitoring via PT and INR
What are the key monitoring parameters for warfarin? (2 points
1. Prothrombin Time (PT)
2. International Normalised Ratio (INR)
How does heparin work? (3 points)
1. Binds to and activates antithrombin III
2. Inhibits Factor Xa and thrombin
3. Prevents conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
hat types of heparin are there? (3 points)
1. Unfractionated Heparin (UFH)
2. Low Molecular Weight Heparins (LMWHs): enoxaparin, dalteparin, tinzaparin
3. Synthetic pentasaccharide (fondaparinux)
Q: What is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)? (3 points)
1. Rare but serious adverse effect of heparin
2. Causes immune-mediated platelet activation
3. Leads to thrombosis despite low platelet count
Q: What are Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants (NOACs)? (4 points)
1. Factor Xa inhibitors: Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Edoxaban
2. Direct thrombin inhibitor: Dabigatran
3. Inhibit clotting by blocking key enzymes
4. Used for stroke prevention, DVT/PE treatment
Q: What are the reversal agents for anticoagulants? (4 points)
1. Warfarin - Vitamin K
2. Heparin - Protamine
3. Dabigatran - Idarucizumab
4. Apixaban/Rivaroxaban/Edoxaban - Andexanet alfa
What are the uses of thrombolytics? (5 points)
1. Acute myocardial infarction (if PCI not available)
2. Acute thrombotic stroke
3. Clearing thrombosed shunts and cannulae
4. Pulmonary embolism (PE)
5. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT
Q: How do thrombolytics work? (2 points)
1. Convert plasminogen to plasmin
2. Plasmin breaks down fibrin strands in clots
What is the difference between streptokinase and tissue plasminogen activators (tPAs)?
(2 points)
1. Streptokinase forms complex with plasminogen to activate it
2. tPAs (Alteplase, Reteplase, Tenecteplase) directly convert plasminogen to plasmin
Coagulation Pathway Summary with Key Drugs
Pathways:
Extrinsic: Triggered by tissue damage → activates Factor VIIa → leads to Factor Xa.
Intrinsic: Triggered by contact → activates Factors XII → XI → IX → Xa.
Common: Factor Xa → converts Prothrombin (II) → Thrombin (IIa) → Fibrin clot.
💊 Anticoagulants & Actions:
Vitamin K antagonists (e.g., Warfarin) → inhibit Factors II, VII, IX, X
Heparin → indirectly inhibits Xa & IIa via antithrombin
Direct Factor Xa inhibitors (Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Edoxaban) → inhibit Xa
Direct Thrombin inhibitor (Dabigatran) → inhibits IIa (Thrombin)
🛑 Reversal Agents:
Vitamin K → reverses warfarin
Protamine → reverses heparin
Andexanet alfa → reverses Xa inhibitors
Idarucizumab → reverses dabigatran