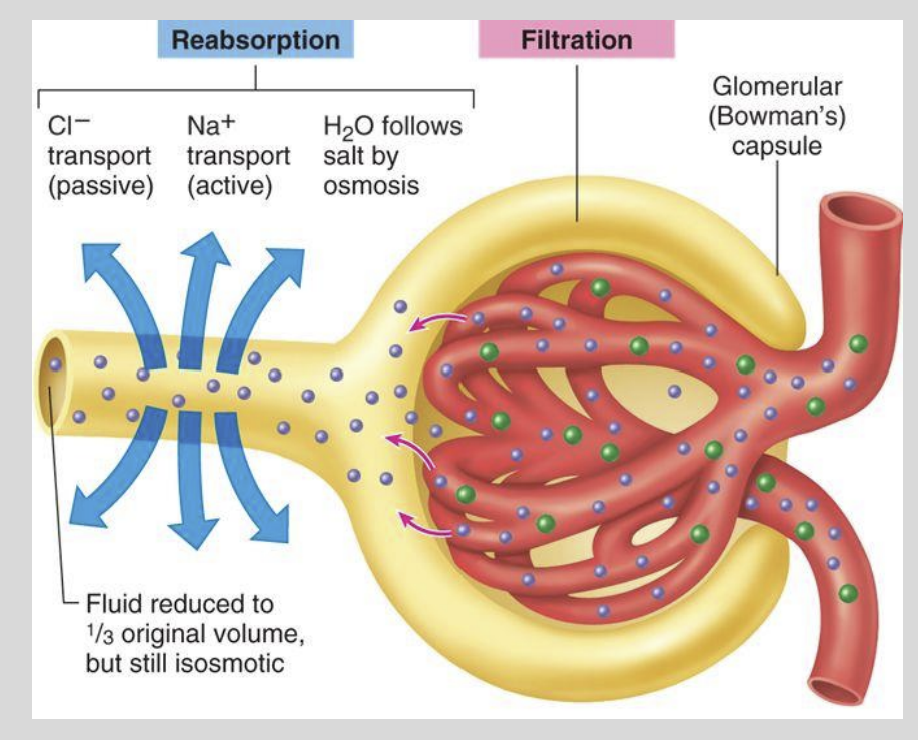
4: Reabsorption of Salts and Water
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
The reabsorption of water from the nephron occurs?
Passively through Osmosis
What allows the passive reabsorption of Water From the Nephron?
the transportation of Na+ and Cl-
across the tubule wall
The proximal tubule and loop of Henle reabsorb the majority of?
Water & Salt from the Filtrate
however only 1-2L of?
Urine is produced daily
Epithelial cells line the inner?
Inner wall of the Nephron
Epithelial cells that line the Inner Nephron wall serve to filtrate?
the lumen from the underlying connective tissues and vasculature.
epithelial membrane functions to?
Reabsorb the Filtrate
The proximal tubule and nephron loop of Henle reabsorb ….%? of the filtrate?
85 of the Filtrate
In what Fashion do the Proximal Tubule and Nephron loop of the Henle absorb?
constant unregulated fashion
What does “Constant Unregulated Fashion” mean?
This means reabsorption happens at a constant rate
and is not influenced by hormones or the autonomic nervous system etc.
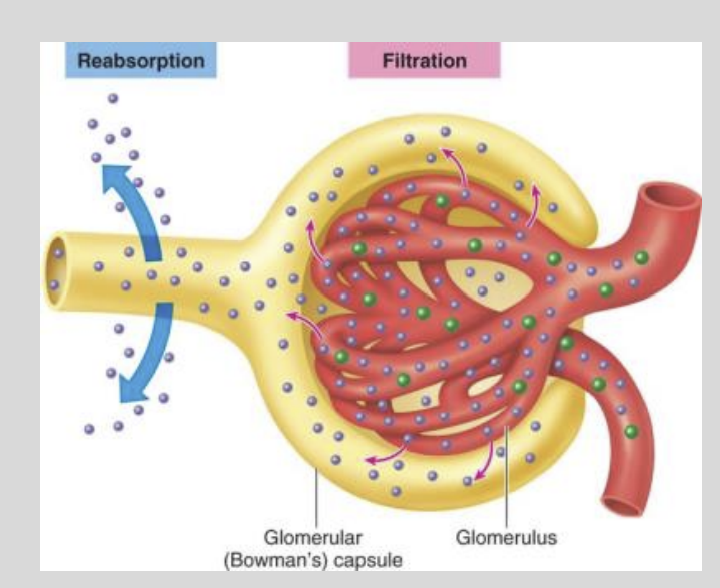
Nephron Reabsorption Diagram
In cases of severe dehydration when the body needs to conserve water, only ?ml of urine is produced per day.?
400ML
This is the minimum needed to excrete Metabolic Waste
The composition of the glomerular filtrate is almost identical to that of the?
Of Blood Plasma
Besides Plasma Proteins & Cells
The filtrate has an osmolarity of?
300 mOsm
The Filtrate and Blood Plasma are?
Isomotic
Reabsorption of the filtrate cannot occur?
Passively by Osmosis
Why can’t the Reabsorption of Filtrate occur passively by Osmosis?
As very little concentration gradient exists between
the filtrate and blood plasma
The Reabsorption of Filtrate thus requires what ?
Active Transport of Na+
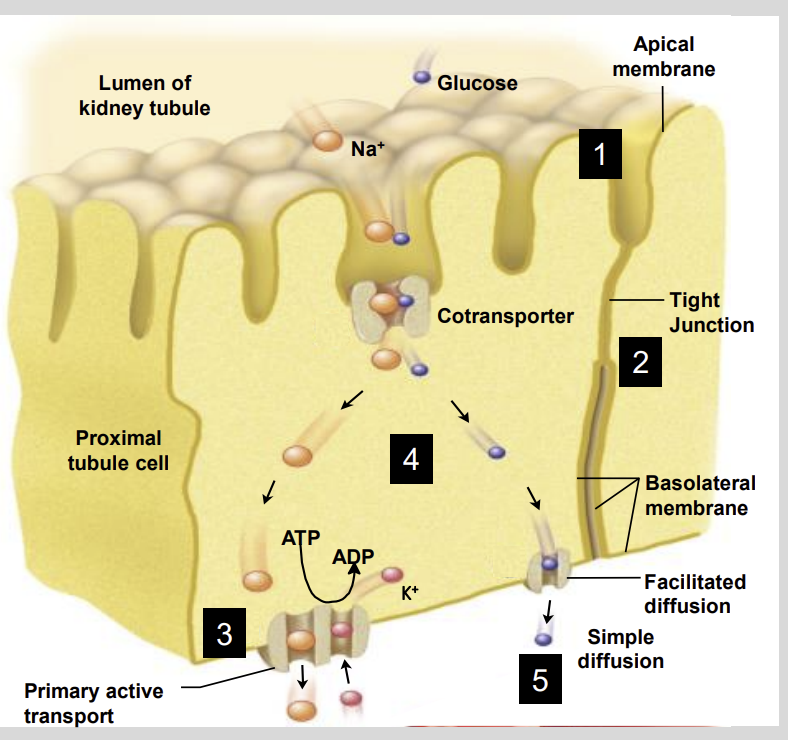
Proximal Tubule Reabsorption DIagram
Since the concentration of Na+ , K+ , glucose etc. in the filtrate of the nephron tubule is the same as the blood plasma what is required?
Active Transports
necessary to create a concentration gradient between the two fluid compartments
The apical surface of the epithelial cells contain?
Microvilli
These microvilli function to?
Increase the surface area of the Apical Membrane
In contact with the filtrate of the proximal tubule
Microvilli allow?
This allows for the greater diffusion of solutes across the apical plasma membrane
Apical Surface means?
Surface facing the lumen.
The cytoplasm of proximal tubule epithelial cells has low?
Na+
Due to the Sodium Potassium Pumps on the basolateral membranes
The movement of Na+ down its concentration gradient drives?
Reabsorption of Other Molecules
The movement of Na+ creates electro…?
Electrostatic Gradient
for transport of Cl- , so Cl follows Na+
The tight junctions of the proximal tubule are permeable to?
To CI-,
so not a lot of CI enters the Epithelial cell.
The majority of Clis reabsorbed from the filtrate by a?
Paracellular Route
Glucose is able to enter the epithelial cells of the proximal tubule through the?
Na+ -glucose cotransporters via a piggy-back mechanism
The Na+ -glucose is what type of Transport?
Secondary Transport
glucose can only enter the cell because of the Na+ concentration gradient created by?
the Na+ /K+ ATPase pumps
Approximately 65% of all water & salt in the filtrate is reabsorbed in the?
Proximal Tubule
At constant and unregulated rate
Glucose is only absorbed in the?
Proximal Tubule