Immuno kill me
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
death
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Neutrophils
1ST RESPONDERS THAT INGEST BACTERIA AND FUNGI
Phagocytes and granulocytes
Ingest and destroy bacteria and fungi using reactive oxygen species and enzymes (e.g. in granules)
Form pus; major cells in acute inflammation.
Short-lived, but crucial for initial defense (deficiency leads to recurrent bacterial/fungal infections)
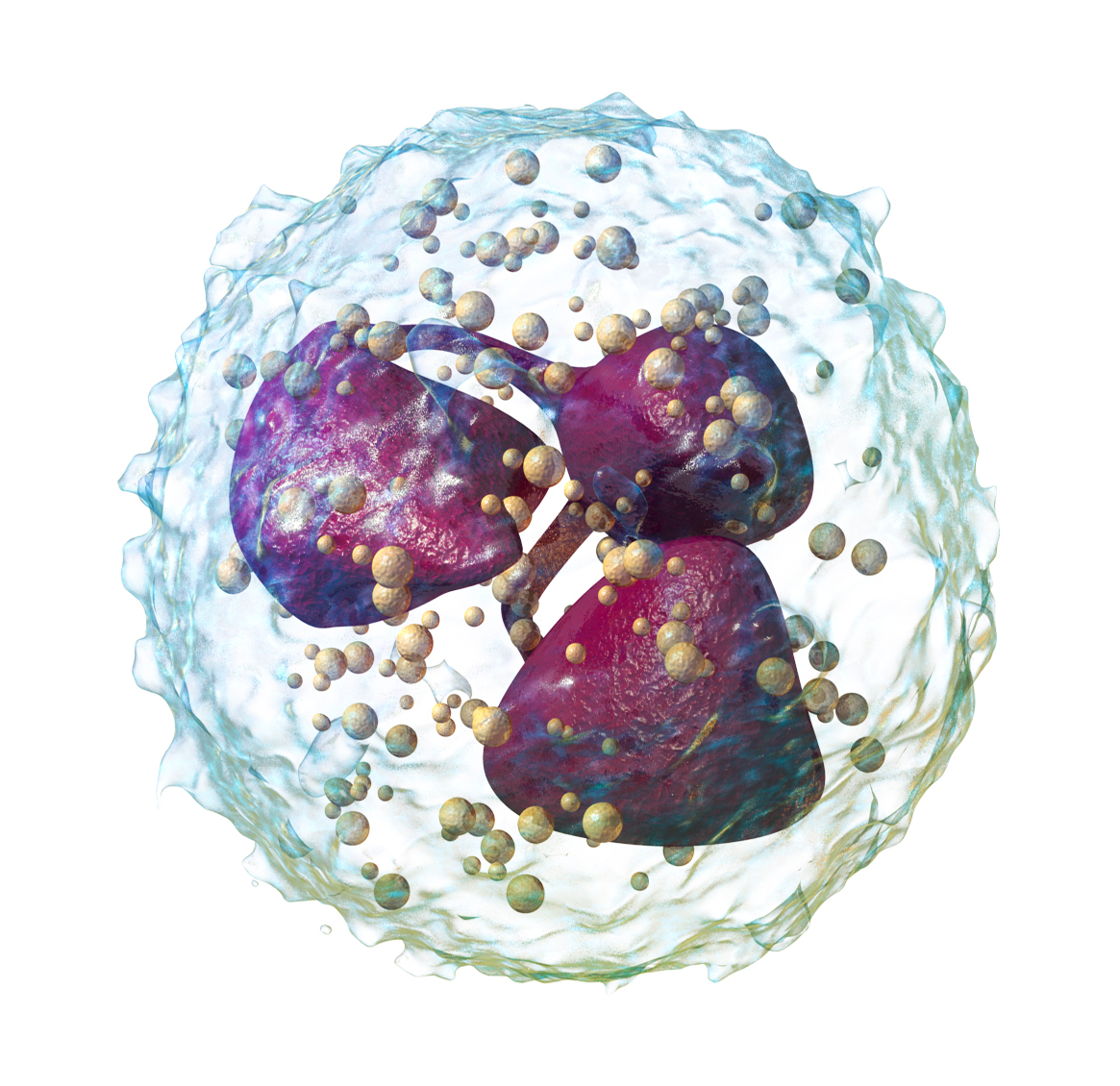
Eosinophils
FIGHT HELMINTHS AND TAKE PART IN ALLERGIC RESPONSES
Phagocytes and Granulocytes
Attack parasites (especially helminths) too large to phagocytose by releasing toxic granule proteins (e.g., major basic protein) and ROS.
Involved in allergic responses (eosinophilia seen in allergies)
Secretes inflammatory mediators and cytokines
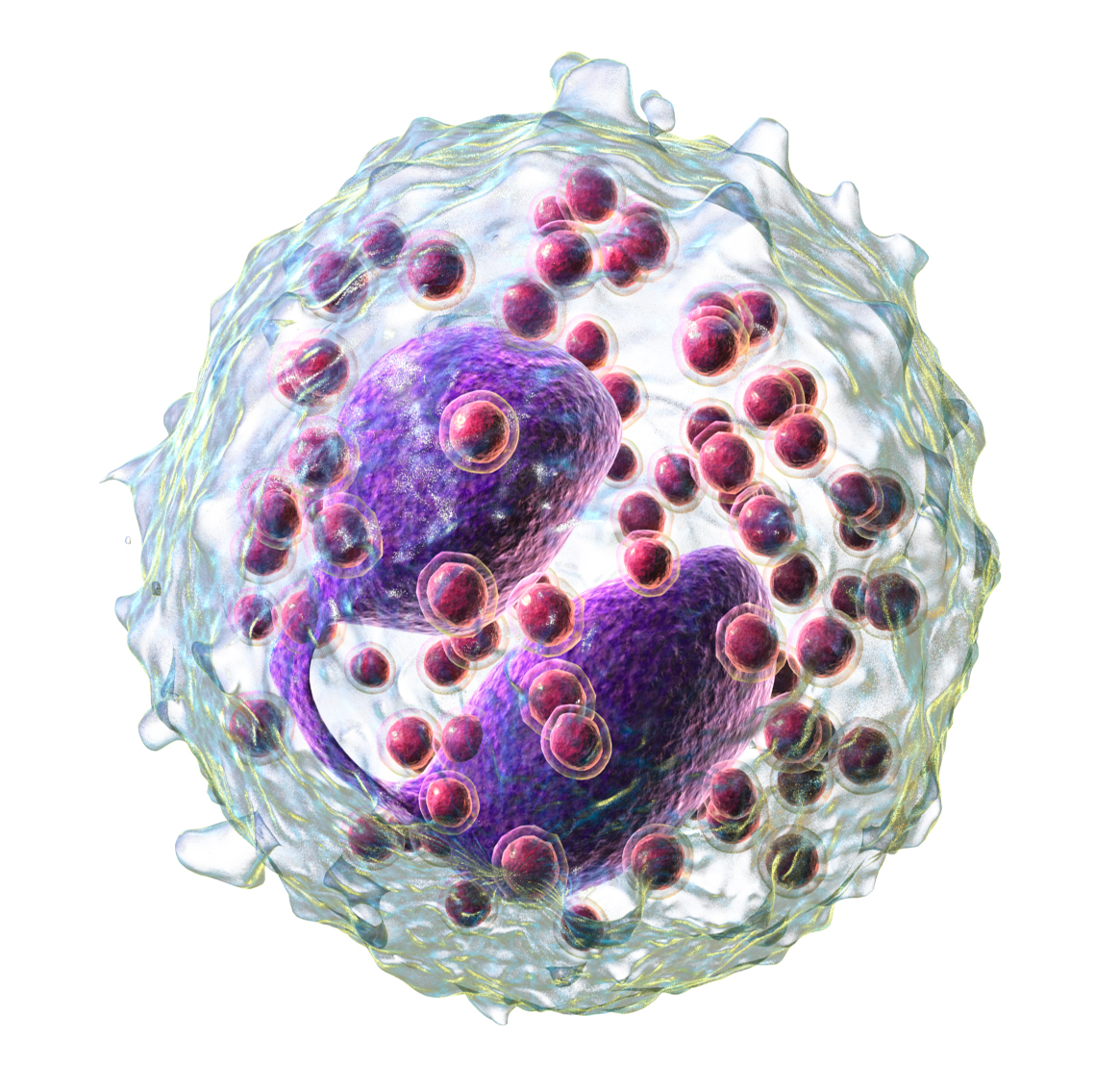
Basophils
MEDIATE IgE-driven reactions
Phagocytes and granulocytes (LARGEST of the granulocytes)
Circulating and rare (0.5-1% of WBC), similar function to mast cells
Important for parasitic infections
Contains heparin (anticoagulant)
Bear high-affinity IgE receptors, upon IgE cross-linking (e.g in allergic rxns), release histamine, serotonin, and other mediators, causing inflammation
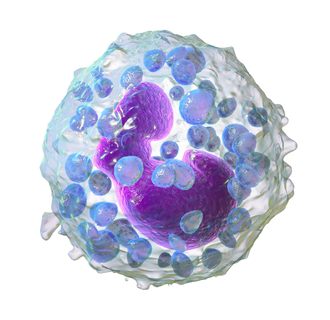
Mast Cells
MEDIATE IgE-driven reactions
Two types (Connective tissue and Mucosal)
Granulocytes
Tissue-resident cells (in mucosa, connective tissue) are analogous to basophils
Trigger acute inflammation and allergic rxns by degranulating (histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins) that cause vasodilation, bronchospasm, and increased vascular permeability
Key effectors in allergies (atopic rxns) and in parasite defense
Monocytes
PHAGOCYTES AND CYTOKINE SOURCES
Monocytes (fast): short-lived and rapidly recruited
Monocytes circulate in the blood and differentiate into macrophages in tissues
Functions imprinted in the bone marrow
Homogeneous in the steady state, yet it can arise from distinct precursors.
Macrophages
PHAGOCYTES AND CYTOKINE SOURCES
Long-lived phagocytes that engulf and digest microbes and debris
Act as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and secrete cytokines (like IL-1, TNF) to orchestrate inflammation.
Can be tissue-resident or monocyte-derived (arise from monocytes that invade tissue in response to infection/cancer)
Dendritic Cells (DCs)
PROFESSIONAL APCS (antigen-presenting cells) found in tissues; capture antigen (via phagocytosis or pinocytosis) and migrate to lymph nodes to present peptides to T cells.
Phagocytes
Bridge innate and adaptive responses by innate sensing of pathogens and displaying their antigens to T cells of the adaptive system
Plasmacytoid DCs also produce large amounts of type 1 interferons to antiviral responses.
Natural Killer (NK) Cells
KILL STRESSED OR MHC-I LOW CELLS
Innate lymphocytes that kill virus-infected/tumor cells lacking normal MHC I expression
Release cytotoxic granules (perforin and granzymes) to induce apoptosis of targets
Activated by cytokines (IL-12, IFN-a/B) and have inhibitory receptors for MHC I to prevent attacking healthy cells
Mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) via CD16 binding to IgG-coated targets
B Lymphocytes (B Cells)
MAKE ANTIBODIES AFTER ACTIVATION
Recognize Antigens via B-cell receptor (membrane Ig)
After activation → differentiate into plasma cells that secrete antibodies (immunoglobulins)
Act as APCs (presenting antigen to TH cells) and secrete cytokines
Originate and mature in bone marrow (primary lymphoid organ)
Plasma Cells
MAKE ANTIBODIES AFTER ACTIVATION
Fully differentiated antibody-secreting factories derived from B cells
Reside in bone marrow or peripheral lymphoid tissues
Produces large volumes of antibodies specific to the antigen that stimulated the parent B cell
Extensive Rough ER (for antibody synthesis) and DO NOT typically circulate
Responsible for humoral immunity (e.g. plasma cells secreting IgA in mucosa, IgG in serum, etc.)
T Cells
CD4 HELPER AND CD8 CYTOTOXIC ROLES
Develop in the thymus and orchestrate cell-mediated immunity
Each T cell has a unique T-cell receptor (TCR) recognizing peptide antigens presented on MHC
Helper T (CD4+) cells
Provide help via costimulation and cytokines to activate B cells, macrophages, and cytotoxic T cells,
Organize immune responses
Cytotoxic T (CD8+) cells
Directly kill infected or cancerous cells by releasing perforin/granzymes (requires antigen presentation on MHC I)
Regulatory T cells (CD4 + CD25 + FoxP3+)
Suppress immune responses to maintain self-tolerance and prevent autoimmunity
M cells (Microfold Cells) - Mucosal Immunity Cell Type
Antigen transcytosis; delivery of antigens by endocytosis to lamina propria, Peyer’s patches
Initiation of adaptive immunity by delivering to DENDRITIC CELLS
Goblet Cells - Mucosal Immunity Cell type