1.5 Sleep and Dreaming - AP Psychology
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Consciousness
Awareness of environmental and cognitive events around a person
Biological Rhythms
Fluctuations in energy level and alertness across the span of the day
Circadian Rhythm
Sleep-wake cycle, occur once every 24 hours
Alpha Waves
Awake but resting, eyes closed, not mentally concentrating on any subject or task
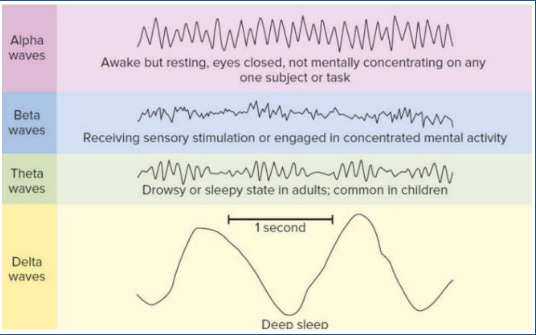
Beta Waves
Receiving Sensory Stimulation or engaging in concentrated mental activity
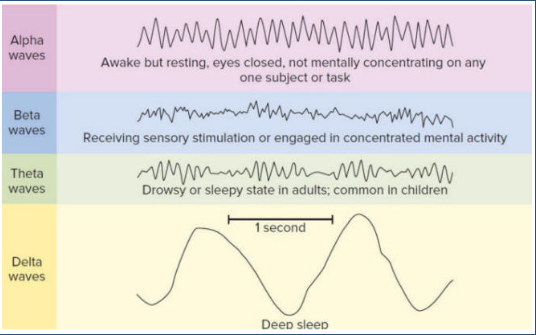
Delta Waves
Deep sleep, stage 3
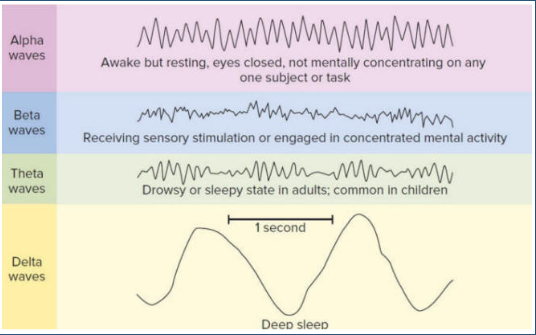
Hypnagogic Hallucination
Transitional state from wakefulness to sleep, also defined as the waning state of consciousness during the onset of sleep
NREM1
Stage 1, Falling Asleep, Alpha Waves, transition from wakefulness to sleep
NREM2
Stage 2, Clearly Asleep, Sleep Spindles, K-Complex Waves
Sleep Spindles
Burst of rhythmic brain activity
K-Complex Waves
Shows the person is about to transition to Stage 3
NREM3
Stage 3, Deep sleep, Slow wave sleep, no memory, Delta waves
REM Sleep
Paradoxical Sleep, motor cortex active and stem blocks movement, DREAMS, closely resembles Waves of stage 1 sleep
REM Rebound
Increased frequency, depth, and intensity of rapid eye movement
REM sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD)
Acting out of dreams, muscles don’t paralyze
Sleep Apnea
Temporary cessation of breathing during sleep and consequent momentary reawakening
Narcolepsy
Uncontrollable sleep attacks, may lapse directly into REM sleep
Insomnia
Recurring problems in falling asleep or staying asleep
Somnambulism
Sleepwalking
Nightmares
Memory of the dream,
Night terrors
No memory of dream
Memory consolidation theory
Dreaming is influenced by the consolidation of memory during sleep
Activation synthesis theory
Suggests that brain is in a lot of neural activity that is random in dreams
Pineal gland
Light triggers SCN to decrease melatonin (morning) from pineal gland
Manifest content
The actual plotline of the dream
Latent content
The symbolic, unconscious meaning of the dream
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
Triggered by light to increase or decrease melatonin
Ultradian Rhythm
90 MInute sleep cycle
The Restorative Sleep Theory
Sleep is crucial for the body’s physical health. Facilitates muscle growth, tissue repair, protein synthesis, and growth hormone release.
Adaptive Theory of Sleep
Suggests sleep is an evolutionary adaptation.
Cognitive Neuroscience
Scientific study of how the brain enables the mind, or the biological basis of mental processes
Dual Processing
Theory that describes how mental processes and behaviors can be influenced by two different processes, which can occur simultaneously or compete with each other
Parallel processing
The brains ability to process multiple stimuli simultaneously
Sequential processing
Mental process that involves organizing and carrying out tasks in a specific order
Sleep
Recurring state of consciousness that involves reduced response to environment
Jet Lag
Common sleep problems from traveling through time zones
EEG patterns
Recording of brain wave patterns that can be used to study normal brain function