Lecture 2 - Functional Neuroanatomy
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
caudal
towards the tail
rostral
towards the nose
ventral
towards the belly
dorsal
towards the back
ipsilateral
same side
contralateral
on the opposite side
unilateral
applies to one side of the brain
bilateral
applies to both sides of the brain
proximal
brain regions near
distal
brain regions far
medial
closer to the midline
anterior/posterior axis
front and back
ventral and dorsal axis
top and bottom of the brain, front and back of the body
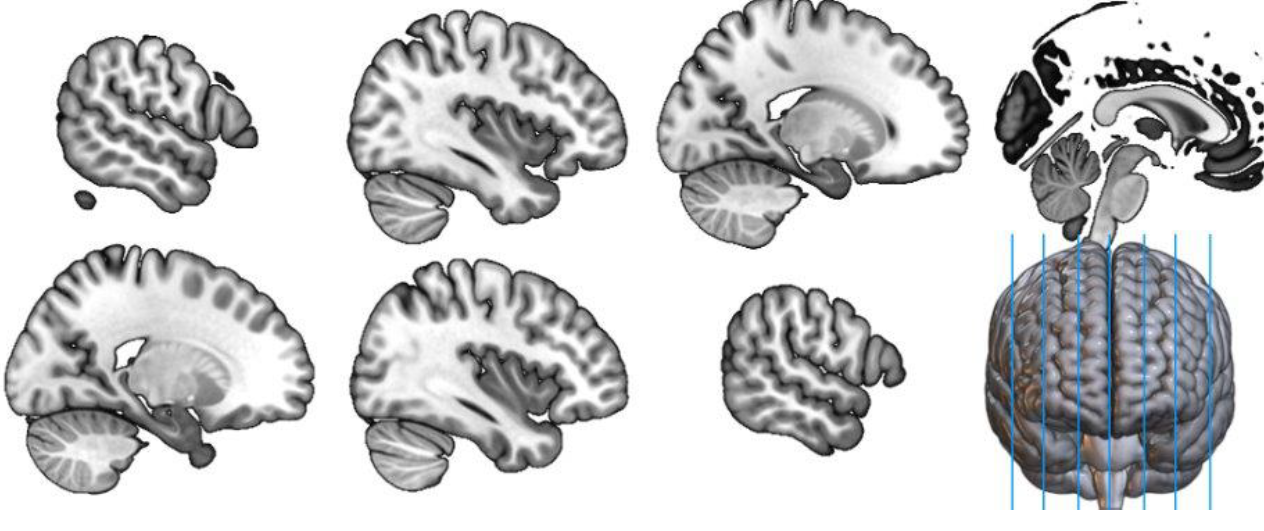
sagittal plane
split brain into left and right hemisphere, the corpus callosum connects them, also brainstem, closer to the midline
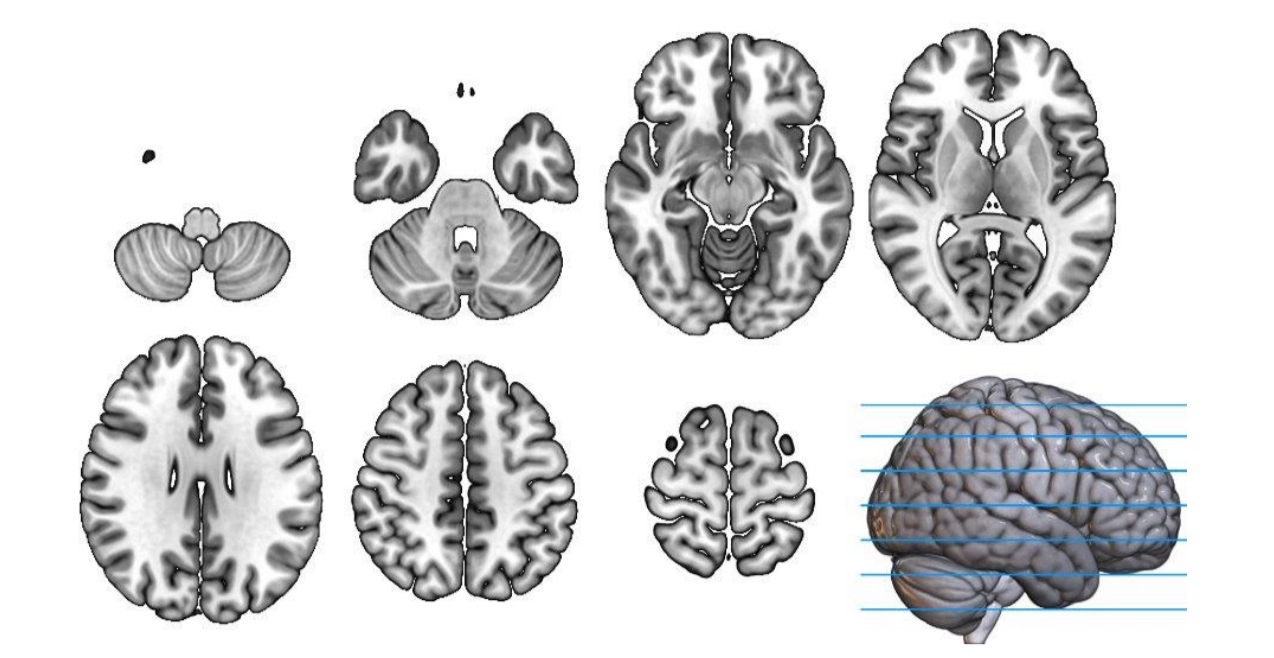
coronal plane
split brain into front and back, shows the brain as if looking at the person straight on
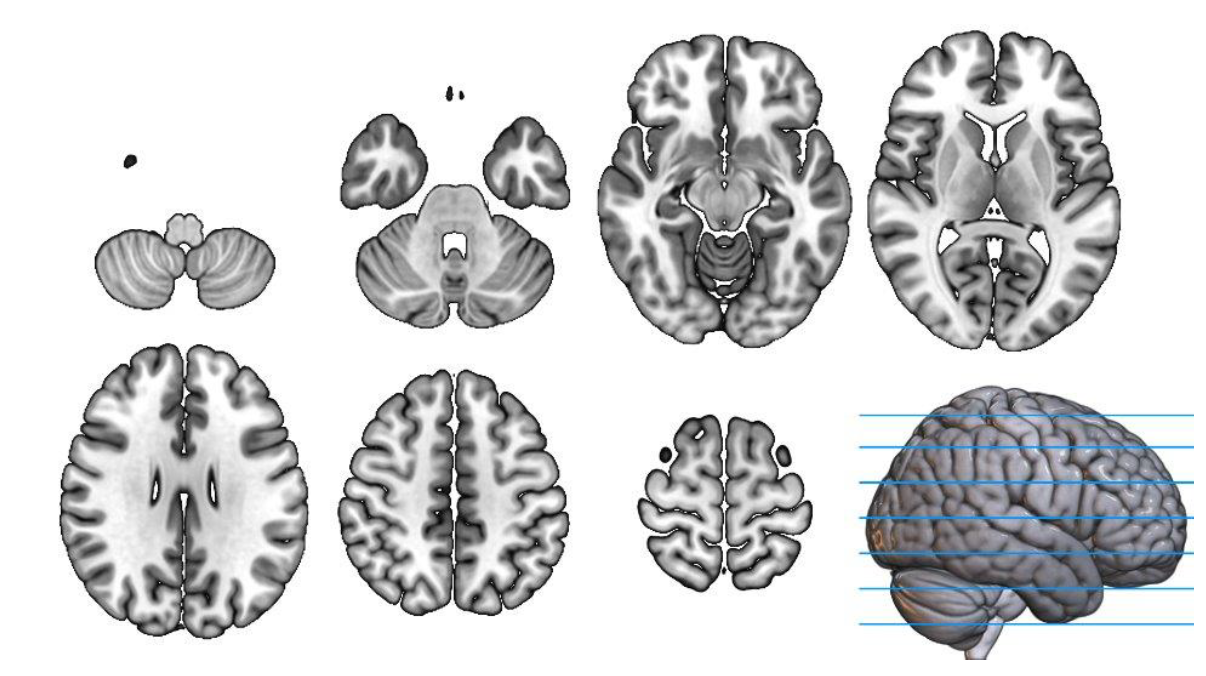
horizontal/axial plane
splits brain into top and bottom, parallel to the floor, useful for birds eye view from below to the top
what plane would you use for basal ganglia?
coronal because its a deep brain structure
foramen magnum
hollow region, where the brainstem exits the skull and connects to the spinal cord
what slice would you use for the cerebellum?
an axial/horizontal slice because it separates the two areas in the posterior region of the brain
optic radiations
connects the thalamus to the occipital cortex
ventricles
they have a C like shape
temporal lobe
located at the anterior ventral part of the brain, responsible for hearing and language
occipital lobe
located at the posterior ventral part of the brain, responsible for vision
parietal lobe
located at the posterior dorsal part of the brain, responsible for motor movement, sensory information, orientation/grasping something
frontal lobe
located at the anterior dorsal part of the brain and responsible for executive functions, cognition, decision making and planning
rostrolateral frontal cortex
front and outer part of the frontal cortex
dorsolateral frontal cortex
top and outer part of the frontal cortex
ventromedial hypothalamus
bottom, middle part of the hypothalamus
posteromedial hypothalamus
back, middle part of the hypothalamus
anatomical divisions
divisions for physical structure, landmarks in the brain/cytoarchitecture (ex; frontal lobe, brodmann area 17)
functional divisions
divisions based on the area’s function so patterns of activity and role in cognitions (ex; primary motor cortex and broca’s area)
broca’s area
responsible for the expression of language, when damaged ppl can’t produce speech but they can understand it
telencephalon
includes the cerebral cortex and subcortical nuclei, this is also know as the forebrain which includes the outer layer of the brain, it is covered by meninges and floats in CSF, it is included in limbic system structures
diencephalon
includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, lateral geniculate and medial geniculate
mesencephalon/midbrain
includes the tectum and tegmentum
metencephalon
includes the cerebellum and pons
myelencephalon
includes the medulla, it is important for sensory information/incoming tracts and motor information/outgoing tracts
forebrain
telencephalon and diencephalon
hindbrain
metencephalon and myelencephalon
cerebral ventricles
hollow regions filled with CSF, there are two c shaped lateral ventricles, third ventricle in the midline and the fourth is between the cerebelum and brain stem connected to the third ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
connects the 4th ventricle to the 3rd one
central nervous system (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord encased in bone, skull and vertebrae respectively
peripheral nervous system
everything outside of the CNS, includes somatosensory (afferent) nerves, motor (efferent) nerves and the autonomic nervous system
somatosensory (afferent) nerves
arrives, signals going into the system
motor (efferent) nerves
takes info out of the nervous system to cause action into the muscles
enteric nervous system
involved in the contraction of smooth muscles and other internal organs
microglia
involved in synaptic pruning and secretion, they are immune cells that eat up excess debris and by products of the cellular system
oligodendrocytes
provide trophic support, responsible for presynaptic regulation, provide the myelin sheath that helps with conduction of electrical information
astrocytes
involved in neurotransmitter release, extracellular environment regulation, and synapse engulfment, they modulate responses, and they are involved in regulating the blood-brain barrier
OPC (NG2) glia
responsible for bidirectional synaptic communication, synapse elimination and secretion
sensory neurons
usually unipolar or bipolar, processes are extensions from the cell body to determine the polarity
gray matter
cell bodies of the neurons in the CNS
white matter
axons carrying info from one region to another in the PNS, they are information highways consisting of axons and neurons, they connect different regions to one another
neurons
excitable cells that generate and conduct electrochemical signals
dendrites
detect neurotransmitters and generate post synaptic potentials
cell body
contains organelles for sustaining function and creating new proteins
axon hillock
location where potentials from dendrites is integrated
axon
response for action potential transmission
axon terminal
sends neurotransmitter to subsequent cell
transmission of information
the action potential drives synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane, then the neurotransmitter inside the vesicles spills out into the space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron (dendrite), the neurotransmitter interacts with the receptor on the postsynaptic neuron, this interaction induces a PSP, and they combine with others to encourage or discourage potential firing
lock and key
the idea that certain receptors are needed for certain molecules to be recognized
amino acids
class of neurotransmitters that include glutamate (GO) and GABA(STOP)
systems neurotransmitters (modulators)
a class of neurotransmitters that includes serotonin, acetylcholine, dopamine and noradrenaline
serotonin (5HT)
involved in regulating mood, sleep and pain, implicated in depression and anxiety
acetylcholine (Ach)
supports learning, memory and attention
dopamine (DA)
involved in reward, motivation and reinforcement learning, involved in parkinson’s and addiction
noreadrenaline (NE)
enhances attention and arousal
cortex
mostly made of gray matter, the outer layer of the cells are called bark, highly wrinkled and thin in humans, made of gyri (bumps) and sulci (folds)
longitudinal fissure
divides the hemispheres
central fissure
frontal (located at the precentral gyrus before the fissure) and parietal (located at the postcentral gyrus after the fissue) lobes
lateral fissure
separates the top half (frontal and parietal) from the bottom half (temporal) of the brain
insula
this is a cortical region located between the temporal and frontal lobe deep within the lateral (sylvian) fissure, it is responsible for taste, pain and salience, it is important for emotional responses like disgust
neocortex
makes up 90 % of the cortex, made of 6 layers, it is more evolved and explains the majority of higher order behaviors, it enables us to have certain higher order cognitive abilities
allocortex
makes up 10% of the cortex, made of 3 layers
basal ganglia
a subcortical region of the brain, its a group of brain structures that play an important role in motor control, executive functions and reward learning, it plays a role in parkinson’s and huntington’s disease as well as addiction
ventral striatum
involved in habit control and learning, part of the nucleus accumbens, relevant to addiction
caudate and putamen
dorsal striatum as well as globus pallidus, important for movement
the limbic system
includes the cingulate cortex, the hippocampus, amygdala, mamillary body and the septum, it has many functions like emotion regulation, memory formation, motivation and reward, autonomic regulation and olfaction
hippocampus
located in the medial temporal love, responsible for forming new episodic memories and the rich retrieval of those memories, if disrupted it can cause anterograde amnesia, alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy and spatial disorientation
amygdala
it plays a role in emotion, arousal, reward, decision-making, memory (modulation), anxiety, fear and decision making, it plays a significant role in mood disorders
bilateral amygdala damage
in the case of patient SM, they were unable to recognize fear in facial expressions
anterograde amnesia
when you can’t form new memories after onset of the region
thalamus
all senses have to go through it except for olfaction
medial geniculate
responsible for auditory info going into the thalamus
lateral geniculate
responsible for visual info going to the thalamus
brainstem
includes the medulla, pons and midbrain, it is responsible for basic bodily functions like respiration, heart rate, thirst, hunger and sleep/wake cycle
superior colliculus
the vision related area of the midbrain
inferior colliculus
the auditory related area of the midbrain
substantia nigra
the area of the midbrain responsible for motor coordination
ventral tegmental area
the area of the midbrain responsible for reward and dopamine
reticular formation
the area of the brain responsible for arousal
periaqueductal grey area
the area of the brain responsible for nociception/pain
cerebellum
part of the metencephalon, plays a major role in cognition
commissural fibers
connects from side to side
projection fibers
connects from top to bottom
association fibers
connects within the same lobe different cortical regions
MS lesions
can be very widespread and leads to overall slower processing and cognitive dysfunction, causes deficit in processing speed
arcuate
connects the temporal and frontal lobe, involved in language (the regions in the broca’s area are in the left inferior frontal lobe)
uncinate
connects the temporal and frontal lobe but involved in memory and emotion
inferior longitudinal
connects the occipital and temporal lobes for object recognition