BI403 Molecular Genetics
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is DNA
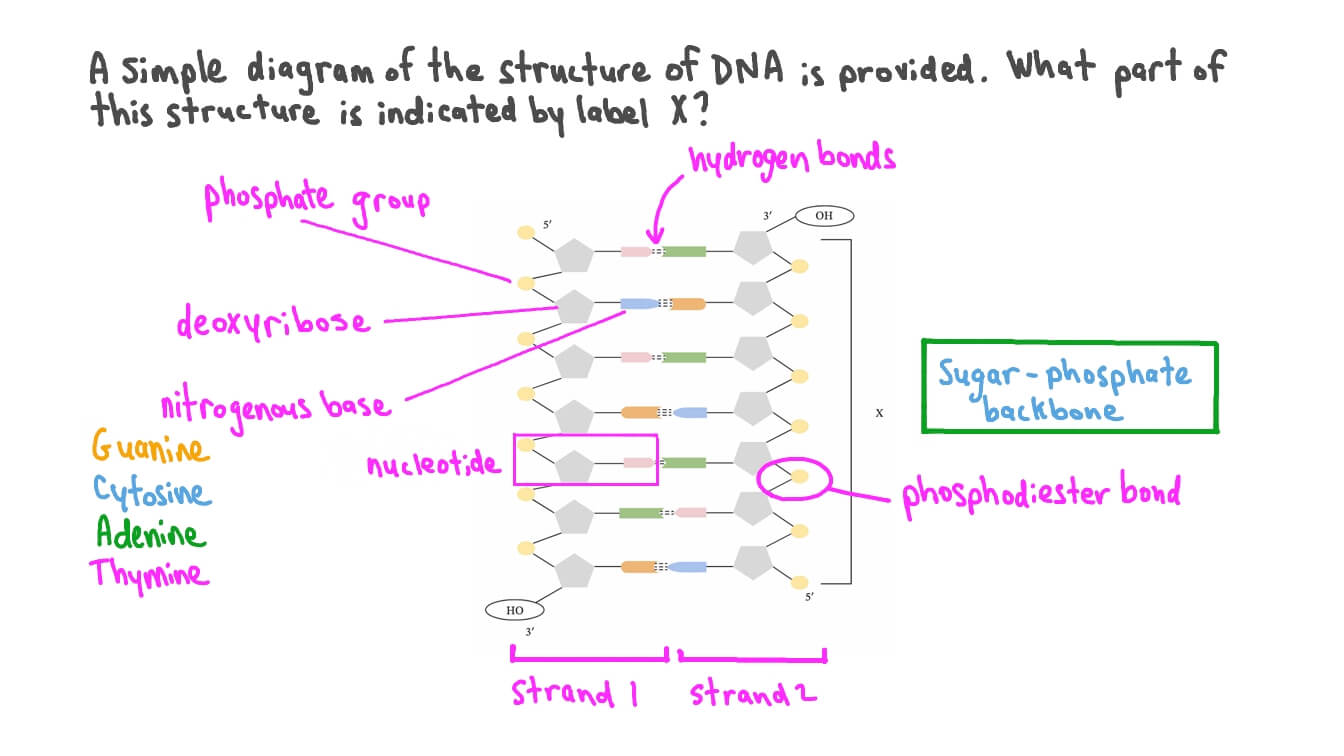
DNA is a double helix, comprising two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by
hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs, each nucleotide is made up of a sugar, a phosphate group and one of four different bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, thymine; the concept of phosphodiester bond is required).
Differentiate DNA and RNA
DNA (deoxyribose, adenine thymine guanine cytosine, double stranded, 1:1) RNA (ribose, adenine uracil guanine cytosine, single stranded, no fixed ratio)
Nucleotide
It’s is the basic building block of DNA made up of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
Distinguish between DNA, gene and chromosome
DNA is a polynucleotide.
Genes are small/short segments of DNA Chromosomes are made of long strands of DNA
Define gene
A gene is a sequence of DNA nucleotides that controls the formation of a single polypeptide.
Describe the structure of a DNA
Anti parallel strands, nucleotide bonds, complementary base pairing, nitrogenous bonds
Where does transcription occur
Nucleus
Where does translation occur
Cytoplasm
Define transcription
Transcription is the process by which the DNA template is used to make a single-stranded molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA).
mRNA has a base sequence complementary to that of the DNA template.
Process of transcription
RNA polymerase (an enzyme) binds to the DNA at the start of a gene and moves along the gene causing the DNA double helix to unwind and separate into 2 strands.
only on strand, template strand is used for the synthesis of a complementary mRNA molecule. This DNA strand is known as the template strand. The other DNA strand that has the complementary base sequence is known as the non- template strand
Transcription is the process by which the DNA template is used to make a single-stranded molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA).
mRNA has a base sequence complementary to that of the DNA template.
Free RNA nucleotides pair up with complementary bases on template strand of the DNA. There is no thymine in RNA, so uracil pairs with adenine via complementary base pairing.
RNA polymerase catalyses the formation of covalent bonds (phosphodiester bonds) between RNA nucleotides on the mRNA strand.
When transcription is completed, both the RNA polymerase and the newly synthesized mRNA molecule separate from the DNA.
mRNA moves to the cytoplasm for translation.
Define translation
Translation is the process by which the sequence of mRNA codons is used to make a polypeptide.
Translation process
Translation occurs in the ribosomes found in the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell. Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis in a cell.
There are 3 binding sites on a ribosome (E, P, A )
mRNA leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pore.
mRNA enters the cytoplasm and attaches itself to a ribosome.
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is a molecule that carries different amino acids to the ribosomes.
Each tRNA has one end that has three bases known as anticodon. The bases are complementary to the codon on the mRNA. On the opposite end of the tRNA is an amino acid.
As the two tRNA molecules can bind to the ribosome at the same time. The ribosome will join the amino acids together by peptide bonds.
The tRNA then detaches itself from both the mRNA and amino acid.
As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, the polypeptide produced gets longer as more amino acids are joined together.
At the end of the mRNA strand, the ribosome detaches from the mRNA and the polypeptide is released