steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (glucocorticoids) lecture 22 FIRST LECTURE FOR EXAM 4
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Inflammation
is a useful and normal process that consists of a series of events, including vascular changes and release of chemicals that help destroy harmful agents at the injury site and repair damaged tissue
increases
Vasodilation ___________ permeability of blood vessels in the early phase
additional damage to the body
Severe inflammation must be reduced to avoid ...
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs block the action of phospholipase
-Corticosteroids are hormones produced by the adrenal cortex
-Two groups of corticosteroids, the glucocorticoids and the mineralocorticoids, are clinically used
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs block the action of cyclooxygenase
what are the two main groups of anti inflammatory drugs
action of phospholipase
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs block the...
action of cyclooxygenase
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs block the ....
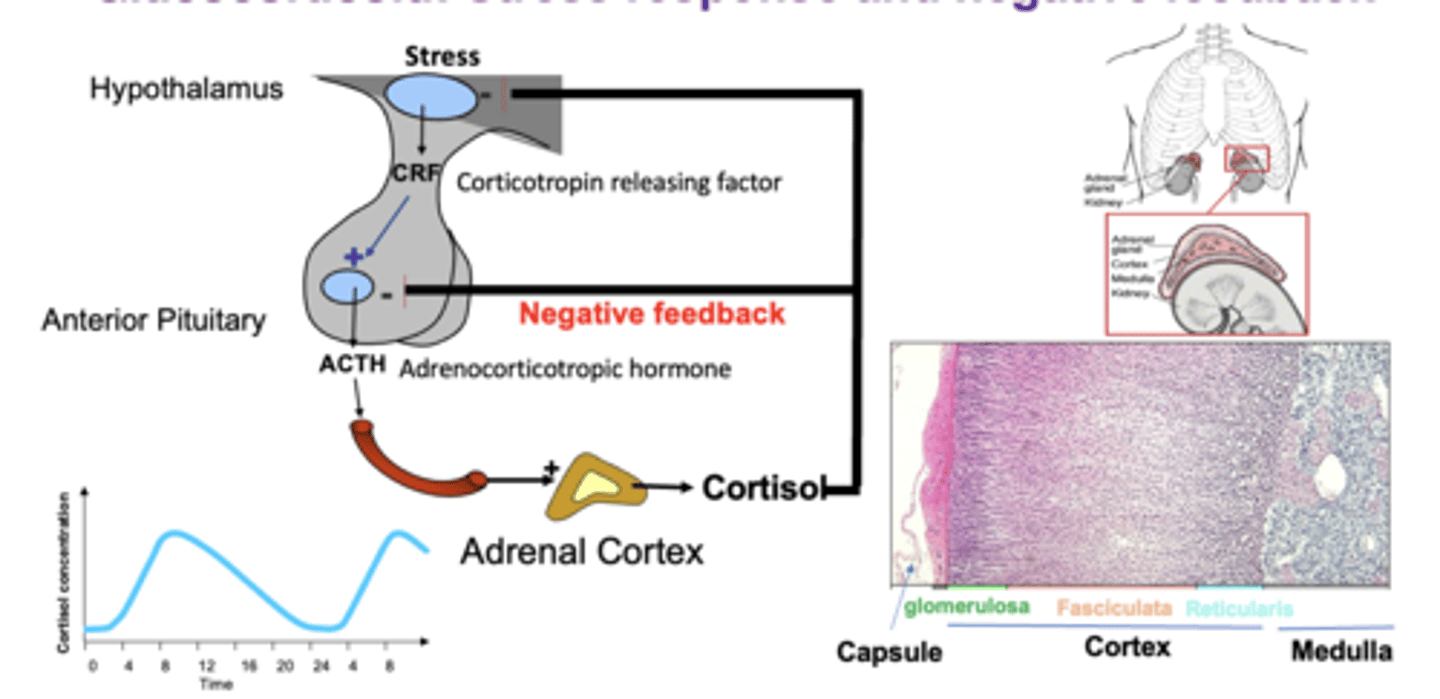
glucocorticoid: stress response and negative feedback
glucocorticoid: stress response and negative feedback
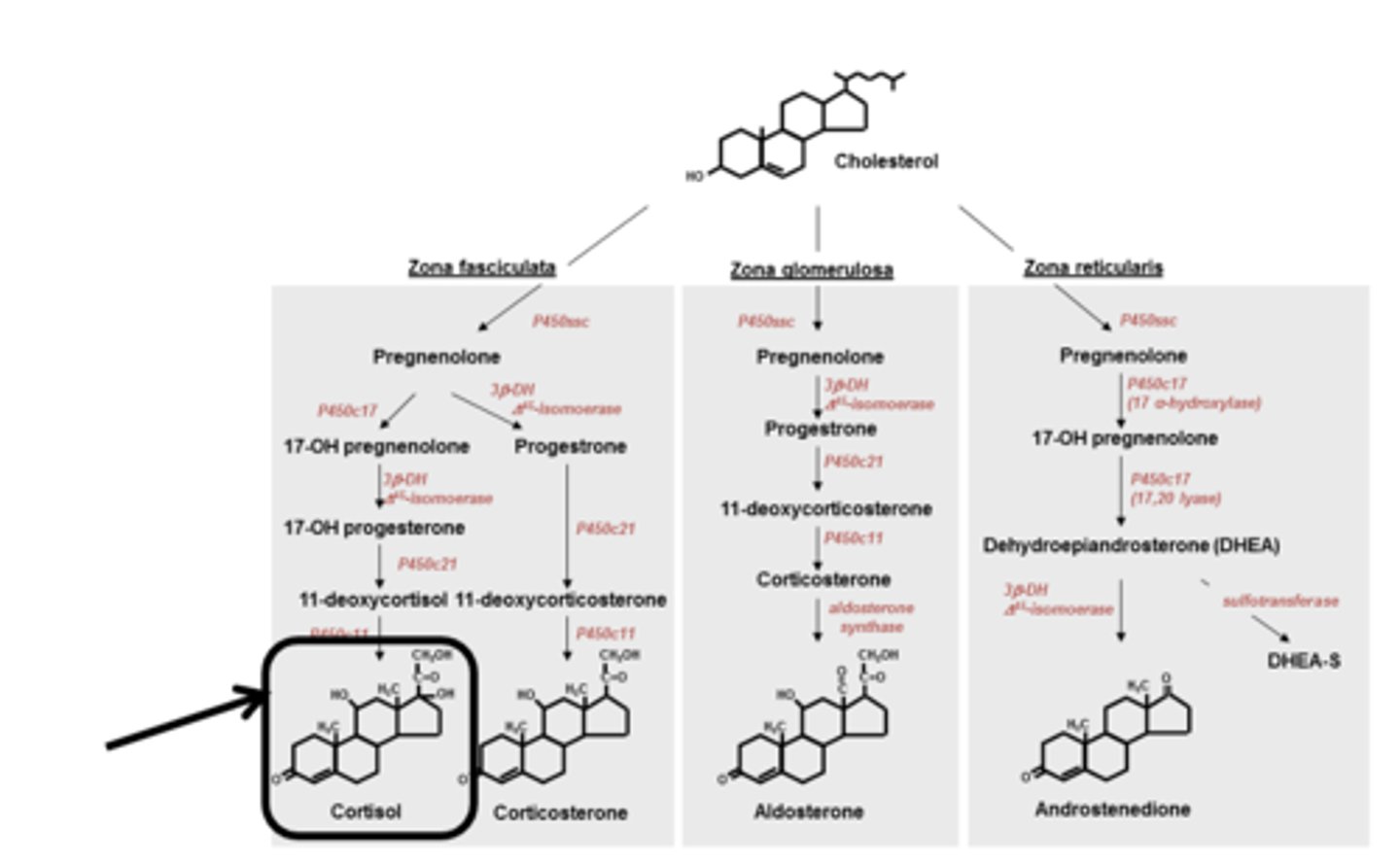
adrenal cortex: hormones
adrenal cortex: hormones
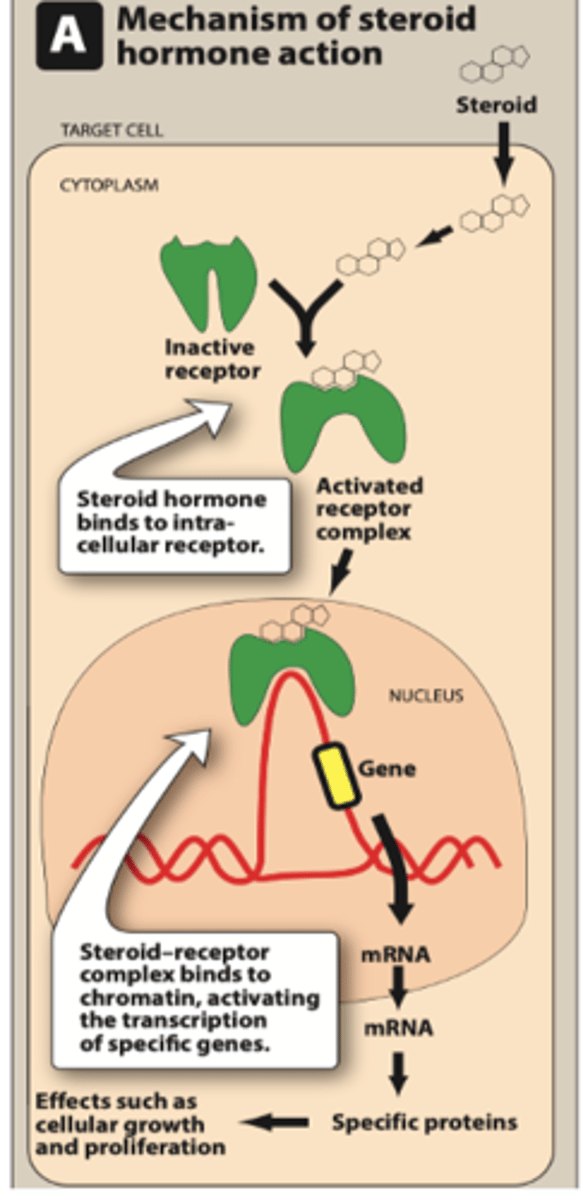
1. ligand
2. DNA
3. activated
4. proteins
5. widely distributed
GLUCOCORTICOID MOA:
1. ________ binds (steroid/glucocorticoids) to the cytosolic receptor
2. Ligand/receptor complex translocates to the nucleus and binds to ______
3. Transcription of mRNA is ____________
4. __________ are translated that induce biological effects of Glucocorticoids
5. Glucocorticoid receptor is __________ __________
1. promote normal intermediary metabolism
2. increase resistance to stress
3. alter levels of circulating blood cells
4. anti-inflammatory actions
5. effects on other endocrine hormones
what are the 5 effects of glucocorticoids
Promote normal intermediary metabolism - utilize other substance to make glucose
liver: anabolic:
Increasing gluconeogenic enzymes and amino acid uptake by the liver and kidney
Promote normal intermediary metabolism - utilize other substance to make glucose
Extrahepatic tissue:
Stimulate protein catabolism to provide energy needed for glucose synthesis
Increase activity of hormone-sensitive lipase to generate fatty acid fuel
Increase resistance to stress
Elevated glucose levels provide energy required to combat stress: trauma, disease, fight or flight
Can cause a modest rise in blood pressure (mineralocorticoid effects)
Adrenal insufficiency: individuals may become hypotensive during severe stress
alter levels of circulating blood cells
Decreases eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes by redistributing them from circulation to lymphoid tissue
Increases the levels of hemoglobin, erythrocytes and platelets in the circulation
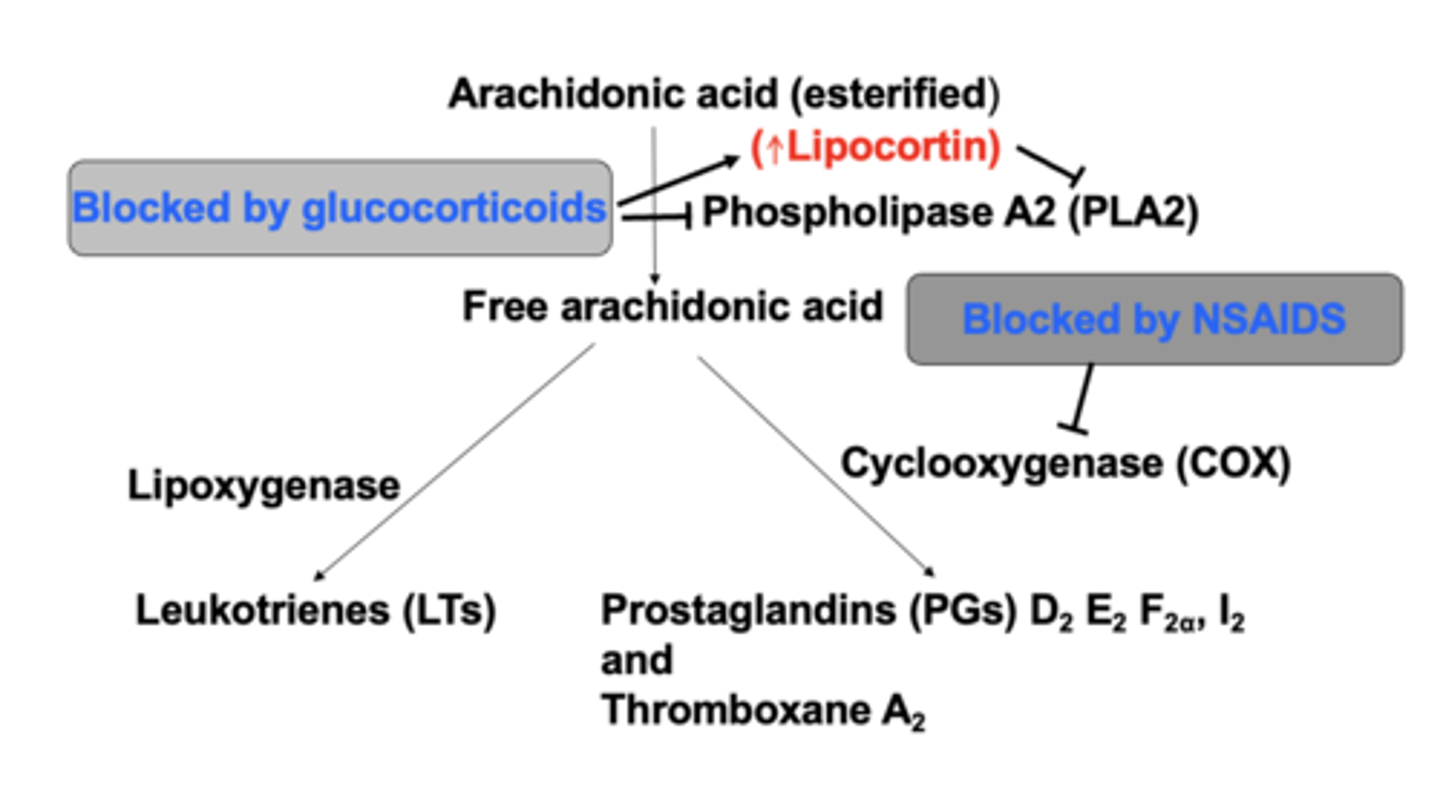
anti-inflammatory actions
Inhibits NF-𝜅B, a transcription factor considered the master regulator of inflammatory responses
Inhibits phospholipase A2, via activation of Lipocortin
Decreases activity of peripheral lymphocytes and macrophages
Interfere in mast cell degranulation resulting in decreased histamine and bradykinin to reduce capillary permeability
want to reduce redness and reduce pain
glucocorticoid : inflammation
glucocorticoid : inflammation
Effects on other endocrine hormones
Negative feedback inhibits further glucocorticoid synthesis
Reduces thyroid-stimulating hormone
Production of growth hormone is increased
important points
What is the mechanism of action of glucocorticoids at the cellular level?
What are the mechanisms that glucocorticoids inhibit the inflammatory response?
What is the effect of glucocorticoids in the liver vs extrahepatic tissues, on the metabolism of carbs, lipids, and proteins?
90%
____% Cortisol is bound to plasma proteins
- Corticosteroid binding globulin (75%)
- Albumin (25%)
Remaining 10% is free and accounts for activity
albumin
Synthetic corticosteroids are bound primarily by ...
hepatic dysfunction
Glucocorticoid therapy should be monitored in individuals with ....
Pharmacokinetics (PK)
Pharmacokinetics (PK)
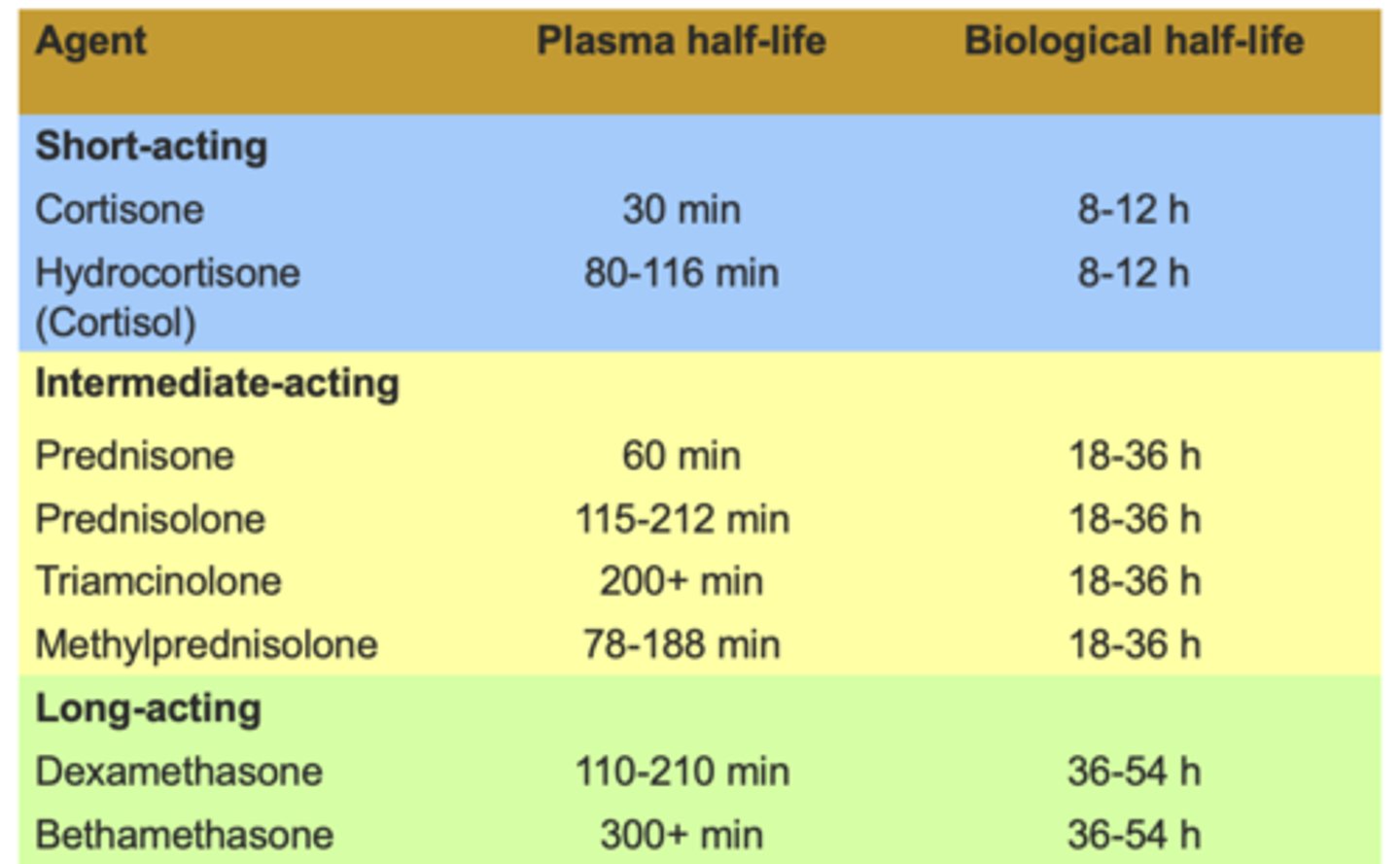
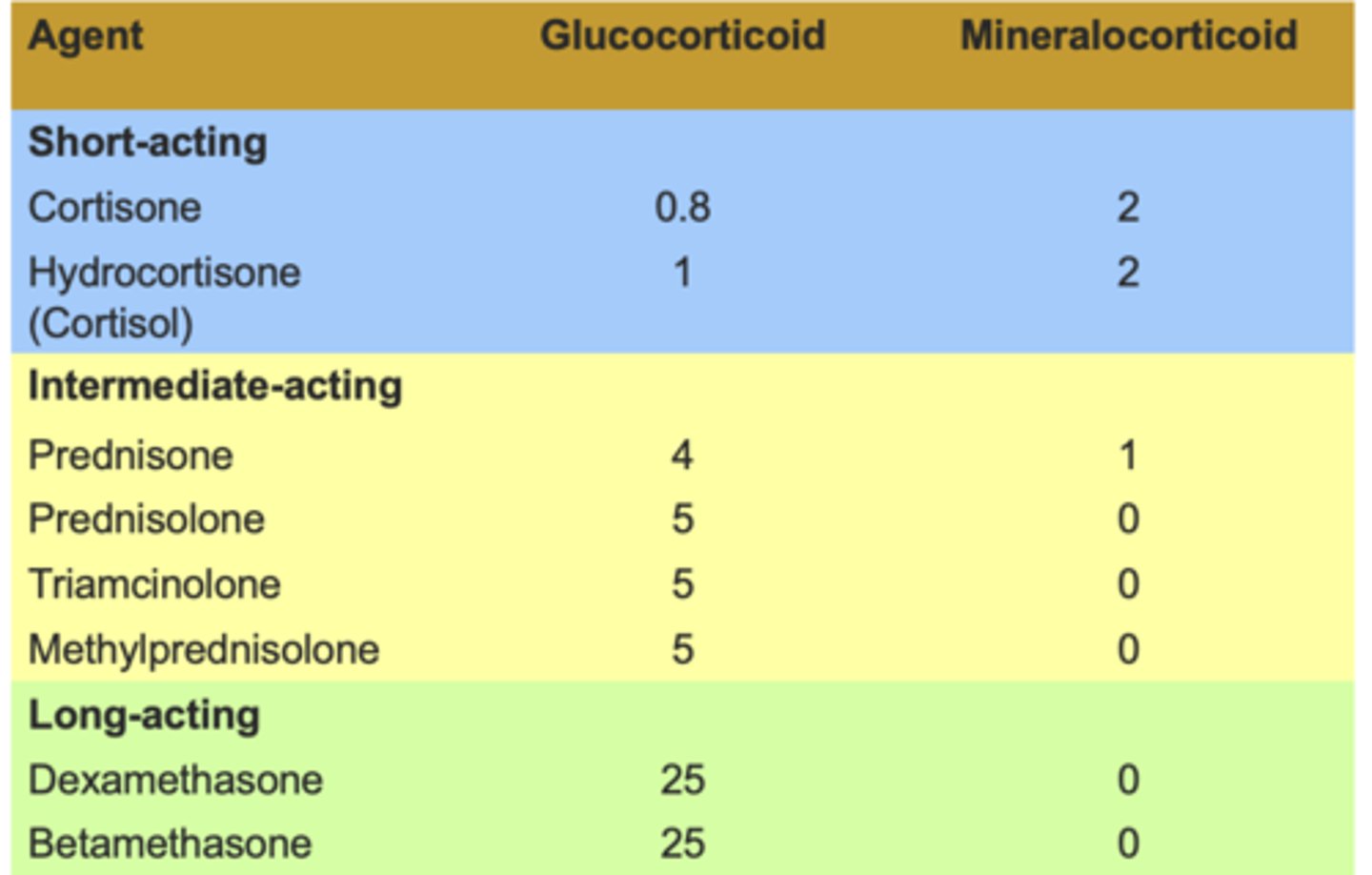
Relative Potencies
Relative Potencies
1. Orally (tablets or liquids)
2. Intravenously or intramuscularly
3. Topically (creams, ointments)
4. Inhaled (for respiratory conditions)
5. Local injections (e.g., joint injections)
6. When possible, local treatments are preferred over systemic administration to reduce the risk of side effects
Glucocorticoid can be administered in various ways:
alter circulating glucose, and minor mineralocorticoid effects
Glucocorticoid effects are measured by the ability to ...
Aldosterone
The primary mineralocorticoid is ..
Mineralocorticoids
promote sodium retention in the Kidney and affect blood pressure
salt retention
Mineralocorticoid effects based on ...
1. Glucocorticoid vs. mineralocorticoid activity
2. Duration of action
3. Time of day that steroid is administered - cortisol is highest in the morning, so give drug in morning to lower cortisol
what are 3 important dosage points
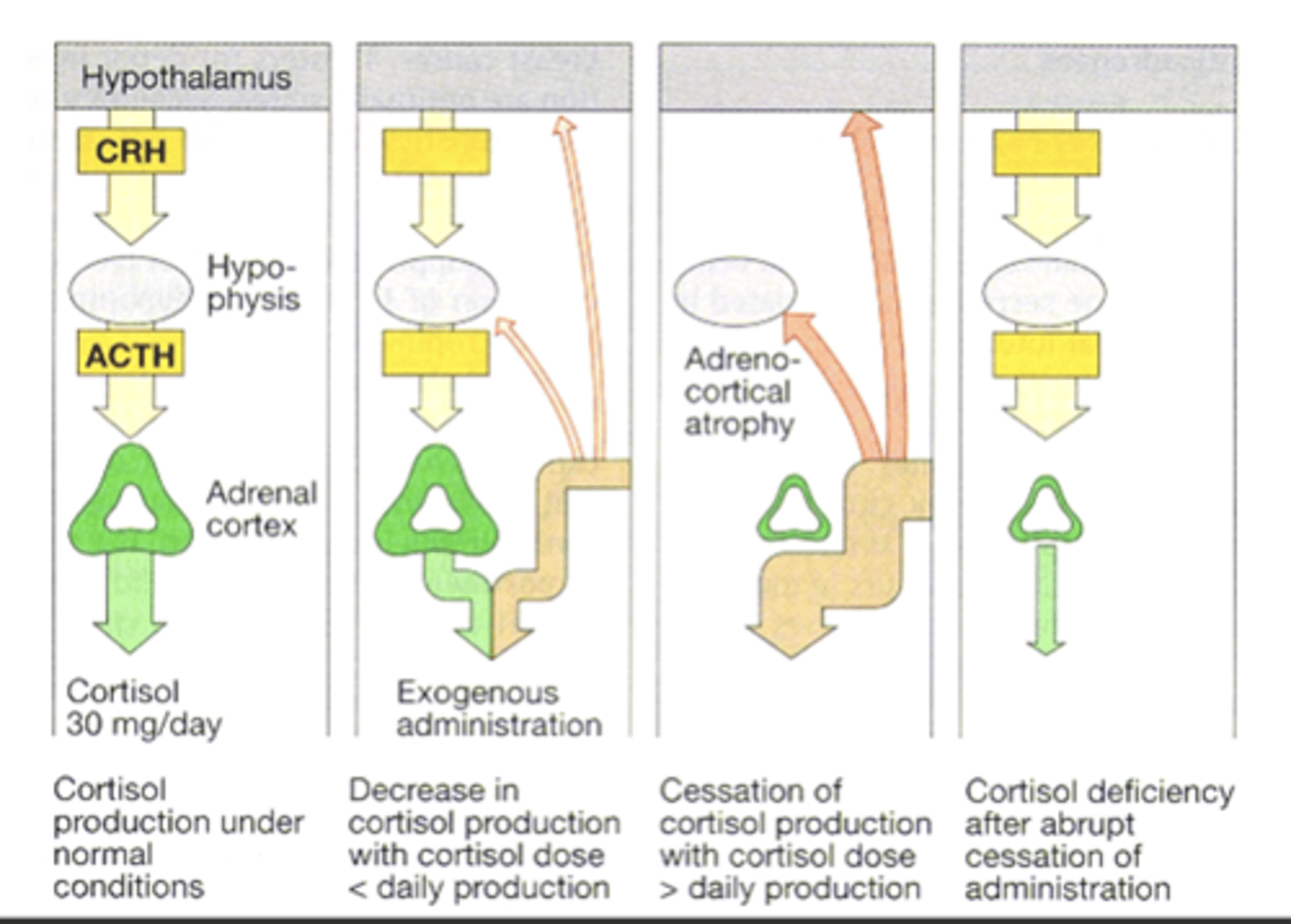
suppression of the HPA axis
Large doses over an extended period of time can cause ...
recover on days that the hormone is not taken
A regimen of alternate day therapy is useful, in allowing the HPA axis to ....
important points
How much cortisol is bound to proteins and why is this important?
What is the difference between the plasma and biological half life?
How glucocorticoid may have mineralocorticoid characteristics?
Inflammatory diseases
-Skin: eczema and dermatitis
-Rheumatic: Arthritis, bursitis, tenosynovitis
-Bowel: ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease
-Respiratory diseases: Asthma, COPD
what are the therapeutic uses: anti-inflammatory
- Autoimmune diseases
- Organ transplants
- During surgery
- Allergic conditions
- Lupus
what are the therapeutic uses: inhibition of the immune system
- Cerebral edema
- Premature delivery: reduces respiratory stress and neonatal mortality
- Eye injury (Inhibit fibrosis)
- Replacement therapy (Addison's disease)
what are some other therapeutic uses
adverse effects
BE CAREFUL WITH DIABETES/HYPERTENSION PATIENT
Increased protein catabolism: decreased growth in children, Osteoporosis, impaired wound healing, muscle wasting…
Disturbed lipid metabolism: centripetal distribution of body fat-fatty belley, buffalo hum, moon face…
Increased hepatic gluconeogenesis: hyperglycemia, cataract…
Suppressed immune response and reduced WBC: increased risk of infection…
Disturb ion balance: negative calcium balance, hypokalemia…
Increased gastric acid secretion: appetite, ulcer…
Emotional disturbances: euphoria, depression…
Weak mineralocorticoid action: Peripheral edema, hypertension…
Androgenic activity: hirsutism
adrenal suppression
adrenal suppression
addisons disease - adrenal gland malfunction
Etiology: Insufficient Glucocorticoid production
Primary adrenal insufficiency
-- Autoimmune
-- Infections (Tuberculosis)
Secondary adrenal insufficiency
-- ACTH deficiency
Can develop after cessation of treatment with Glucocorticoids
addison's disease - adrenal gland malfunction
Symptoms
- Chronic fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
Treatment
- Replacement therapy with Glucocorticoids
alternate date therapy - adrenal gland malfunction
dont give every day
Greater reduction in side effects than can be achieved by dose reduction alone:
-- 200 mg given every other day has the same efficacy as 90 mg given every day
-- 200 mg given every other day produces the same adverse effects as 25 mg per day
Used with intermediate acting glucocorticoids
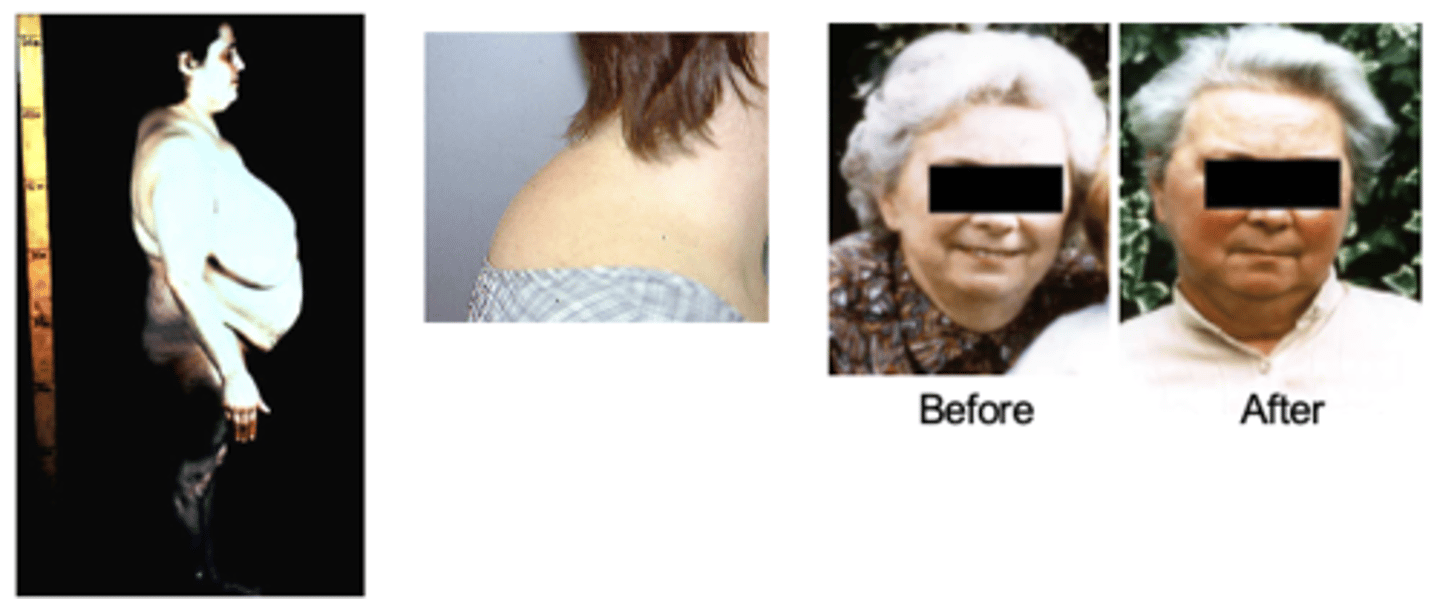
cushing's syndrome - adrenal gland malfuncition
Etiology: Excess glucocorticoids
-- Adrenal cortex tumor (Primary)
-- Cushing’s disease: Pituitary over-secretion of ACTH (Secondary)
-- Ectopic secretion of Cortisol
Long term treatment with Glucocorticoids can mimic Cushing’s Syndrome
cushing's syndrome - adrenal gland malfuncition
Clinical features:
-- Rapid weight gain in trunk, and face, and growth of fat pads along the collarbone
-- Central obesity; buffalo hump; moon face
-- Easy bruising, skin atrophy and thinning
-- Acne
-- Hirsutism
important points
What is the cause and treatment for Addison's Disease?
What causes Cushing's Syndrome?
Primary vs Secondary: Cushing's Syndrome vs Cushing's disease
summary : know moa and side effects as well as info on glucocorticoids
summary : know moa and side effects as well as info on glucocorticoids
