biology unit 1 test - diversity of living things
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
3 Domains
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
6 Kingdoms
Bacteria, Archaea, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
Bacteria - Kingdom Characteristics
Prokaryote
Unicellular
Peptidoglycan
Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Cyanobacteria (some bacteria contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis)
Asexual
Archaea - Kingdom Characteristics
Prokaryote
Unicellular
Not peptidoglycan, occasionally no cell wall
Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Methanogenesis (produces methane unique to archaea)
Asexual
Extremophiles (live in extreme environments)
Fungi - Kingdom Characteristics
Eukaryote
Mostly unicellular
Chitin cell wall
Autotrophs and heterotrophs
Sexual
Animalia - Kingdom Characteristics
Eukaryote
Multicellular
No cell wall
Heterotrophs
Sexual
Protista - Kingdom Characteristics
Eukaryote
Unicellular and multicellular
Cellulose in some cell walls, occasionally no cell wall
Autotrophs and heterotrophs
Asexual and Sexual
Plantae - Kingdom Characteristics
Eukaryote
Multicellular
Cellulose
Autotrophs and heterotrophs
Sexual
8 Levels Biological Classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
broad to specific
Binomial Nomenclature
A system of naming organisms using two terms, the genus name followed by the species name, developed by Carl Linnaeus.
Eukaryotic Cell
Has a nucleus
DNA in nucleus
Has organelles
Bigger in size
Sexual reproduction common
By mitosis (asexual) and meiosis (sexual)
Most are multicellular
Needs oxygen to perform cellular respiration (aerobic)
Prokaryotic Cell
No nucleus
Most ancient cell type
Smaller size
Circular DNA
Not by mitosis or meiosis
Asexual reproduction (binary fission)
Unicellular
Does not need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (anaerobic)
3 Species Concepts
Morphology
Focuses on the physical structures (body shape, size, etc.)
Biological
Concept whether two organisms can produce attainable offspring
Phylogeny
Based on the evolutionary history of the organism
Biologists determine shared phylogeny by looking for a “common ancestor”
3 Types of Evidence to Show Relationships Between Species
Anatomical
Study morphology / structure of organisms (both living and extinct)
Physiological
Studying the functioning of organisms (how they work)
DNA
Comparing genetic sequences from various organisms
Species definition
A group of organisms that can interbreed in nature, and produce fertile offspring (babies)
Bacteria (gram positive)
Thick cell wall
30 layers of peptidoglycan
Cell wall surrounds monoderm (a single plasma membrane)
Remains purple with crystal violet stain
The stain detects peptidoglycan from the cell wall
Bacteria (gram negative)
Thinner cell wall
Single layer of peptidoglycan
Sandwiched between two lipid bilayer membranes called diderms
High antibiotic resistance
Stained pink with crystal violet stain
The stain detects peptidoglycan from the cell wall which gram (-) lacks
Peptidoglycan
A polymer that forms a mesh-like structure in the cell walls of bacteria, providing strength and rigidity.
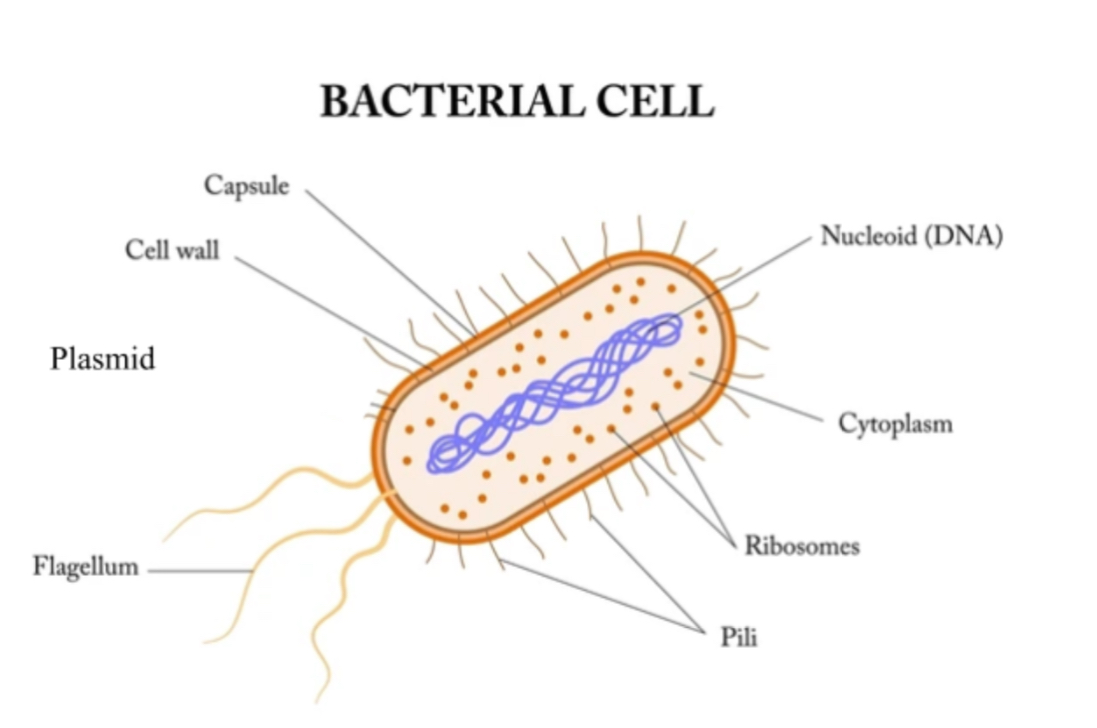
Bacteria - Capsule Function
Layer outisde cell wall
Pilus Function
For transfer of genetic material
Carries genes that can be shared during conjugation
Flagellum Function
Assists with cell movement
Nucleoid region
Contains bacterial DNA, controlling cell activities
Mesosome Function
Helps with cell division and aerobic cellular respiration
Plasmid
One circular piece of DNA
Coccus
Circular
Bacillus
Rod shaped
Spirillum
Spiral shaped
Prefix : Strep
Chain
Prefix: Staphlo
Clusters
Binary Fission
Plasmid replicate and cell divides (asexual)
Conjugation
A process where bacteria transfer DNA through the pilus
Produces cells and new genetic combinations
Fungi Structure
Cap, Scales, Gills, Ring, Stem, Cup, Mycelial threads
Fungi Nutrition
Heterotrophic: they rely on other food sources in their environment for nutrients
Ex. animal waste, plant matter, and organic carbon
Fungi Reproduction
Spore: Reproductive cells that can develop into new organisms
Basidia: The reproductive organs of fungi
Virus
No cellular structure, cannot reproduce on its own, needs a host cell to replicate, has RNA or DNA
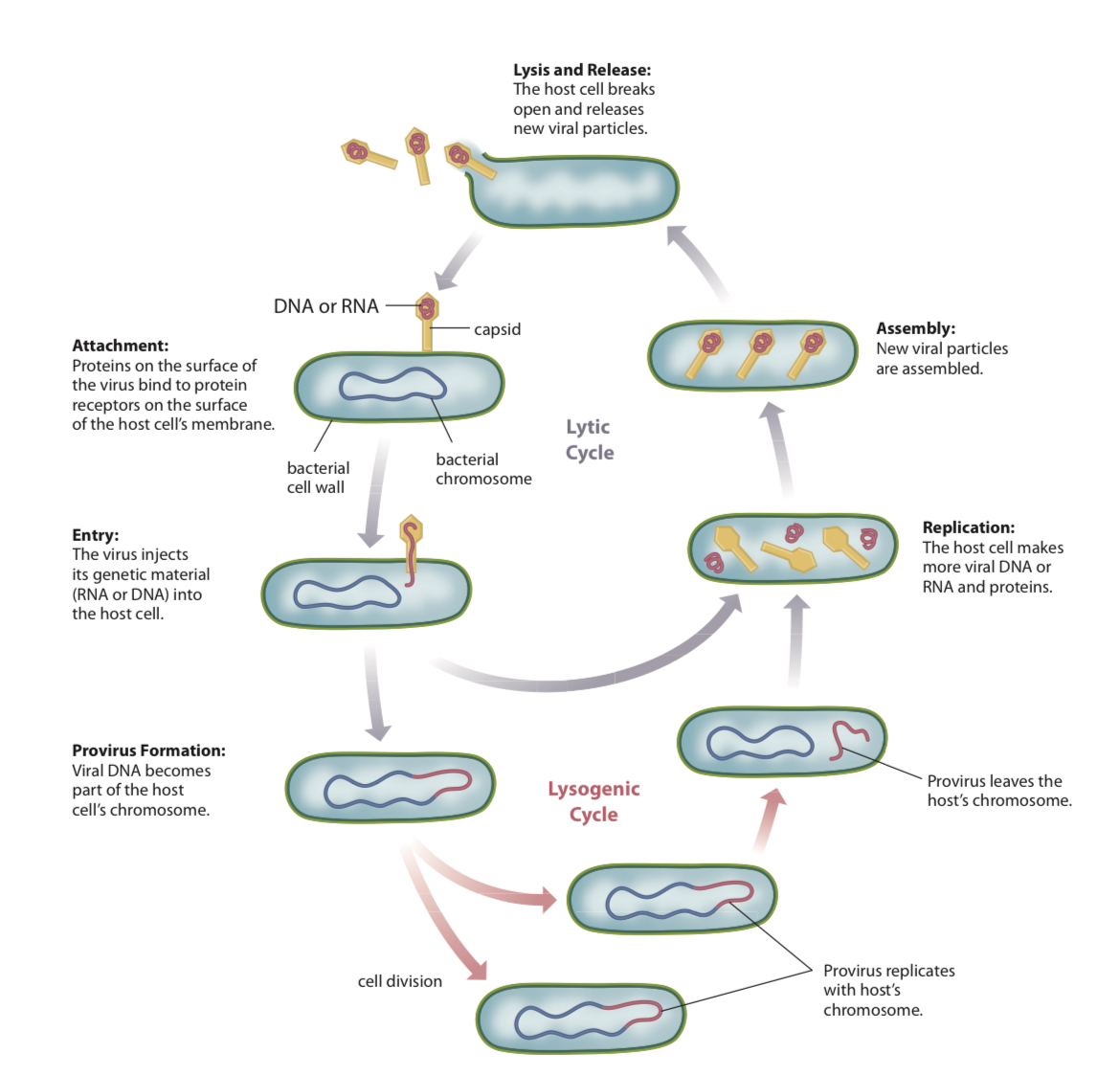
Virus - Lytic Cycle
The replication process in viruses in which the virus’s genetic material uses the copying machinery of the host cell to make new viruses
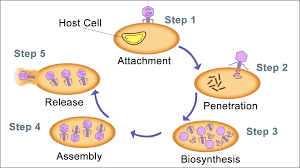
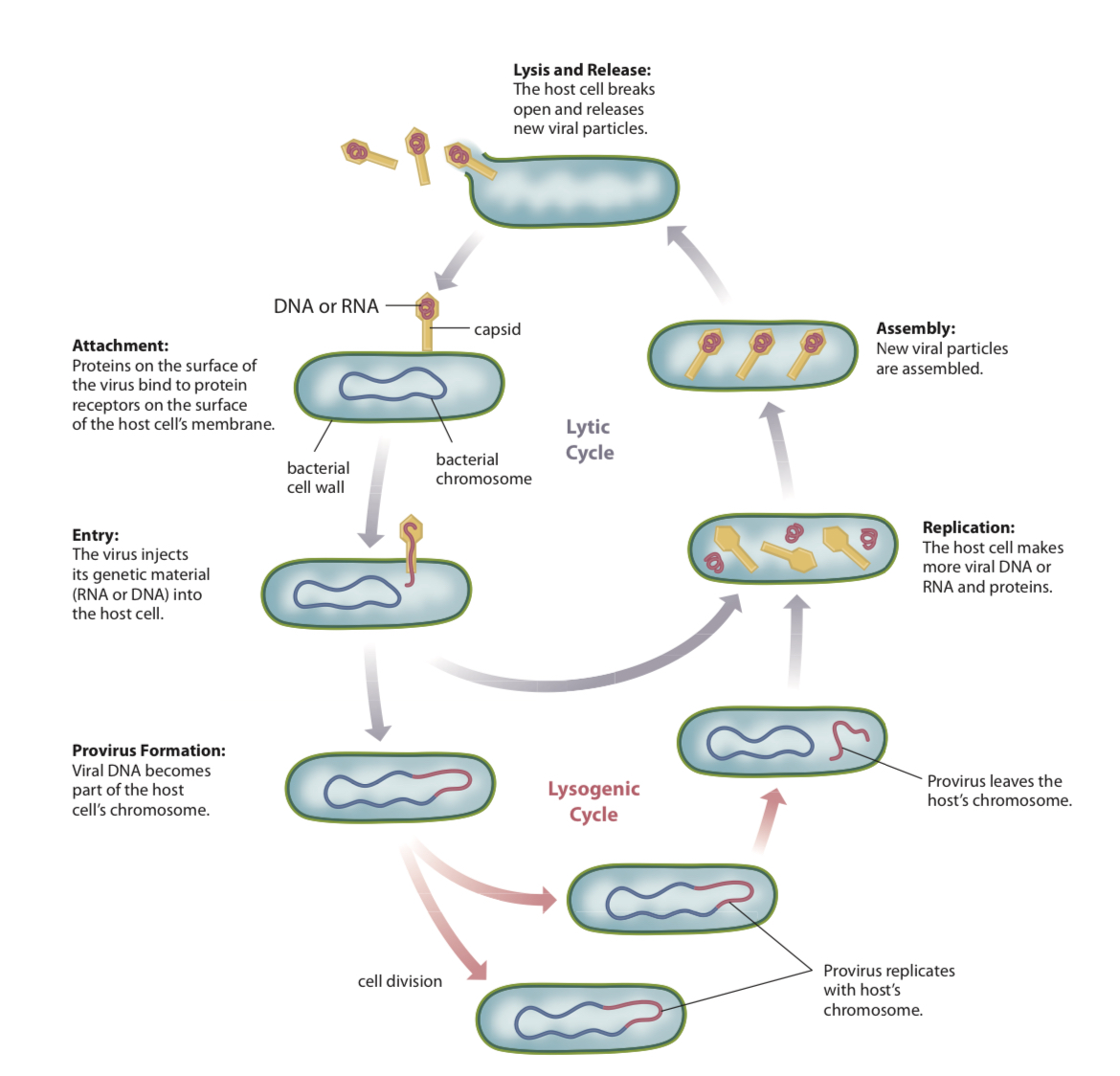
Virus - Lysosome Cycle
Virus injects DNA into a host cell and hides there, allowing the virus to be copied when the host cell divides
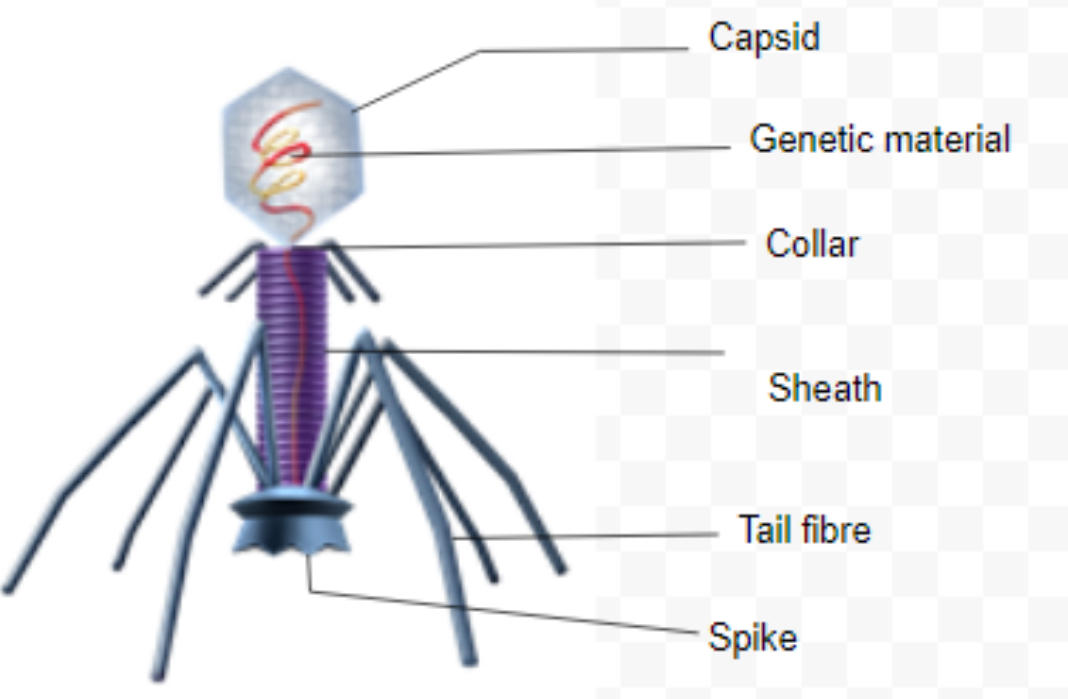
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
Attaches to bacteria cell and injects genetic material
Lysis
The breaking open of a cell
Releases new virus particles
Retrovirus
A virus with RNA as its genetic material
Virus - Prion
Infectious protein
Antibiotics
Treats bacterial infections
How do people misuse antibiotics?
Taking to cure infections (ex. colds)
Not completing prescribed course
Overuse or self-prescribing
Current problems with use of antibiotics in livestock feed
Leads to antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistant bacteria can spread to humans
Reduces the effectiveness of antibiotics
4 Stages of Typical Growth Curve for Bacterial Colony
Lag phase
Bacteria adjust to its environment, preparing for growth
Log (exponential) phase
Bacteria start dividing quickly, size increases
Stationary phase
Growth slows
Death phase
Bacteria die due to lack of resources and space
What temperature promotes optimal growth for colonies?
~37 degrees celsius
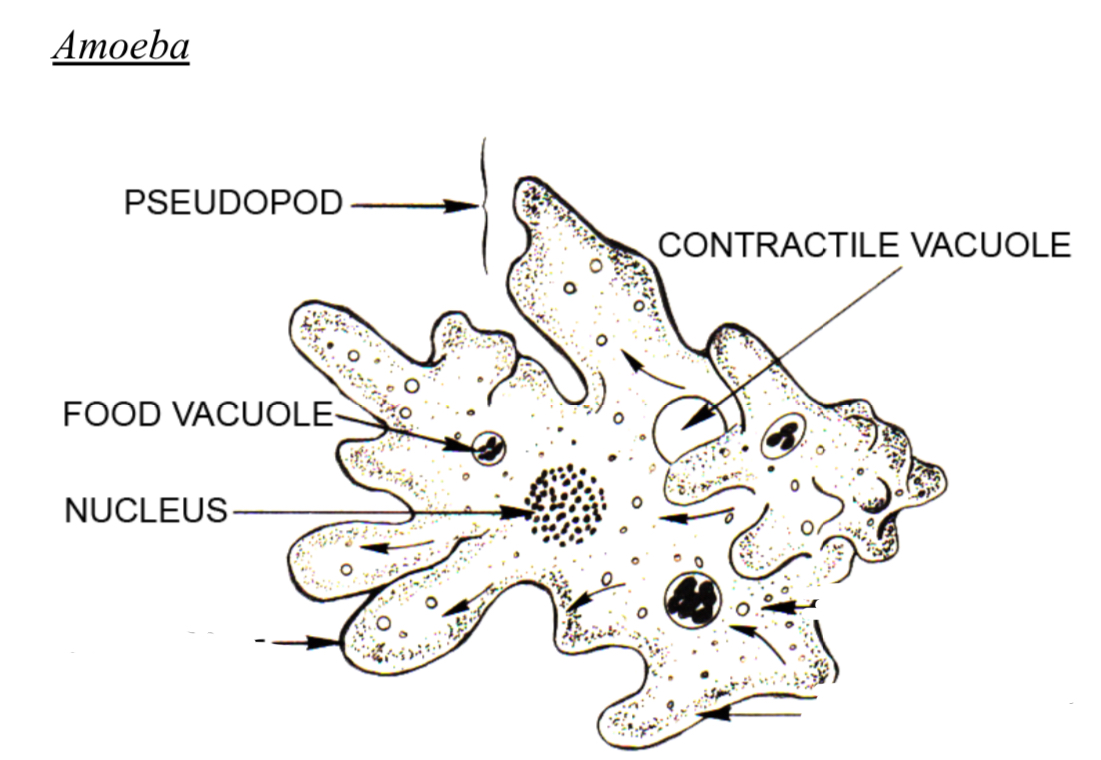
Protist - Pseudopods Function
Amoebas use for feeding and movement
Protist - Cilia Function
Feeding purposes, and locomotion
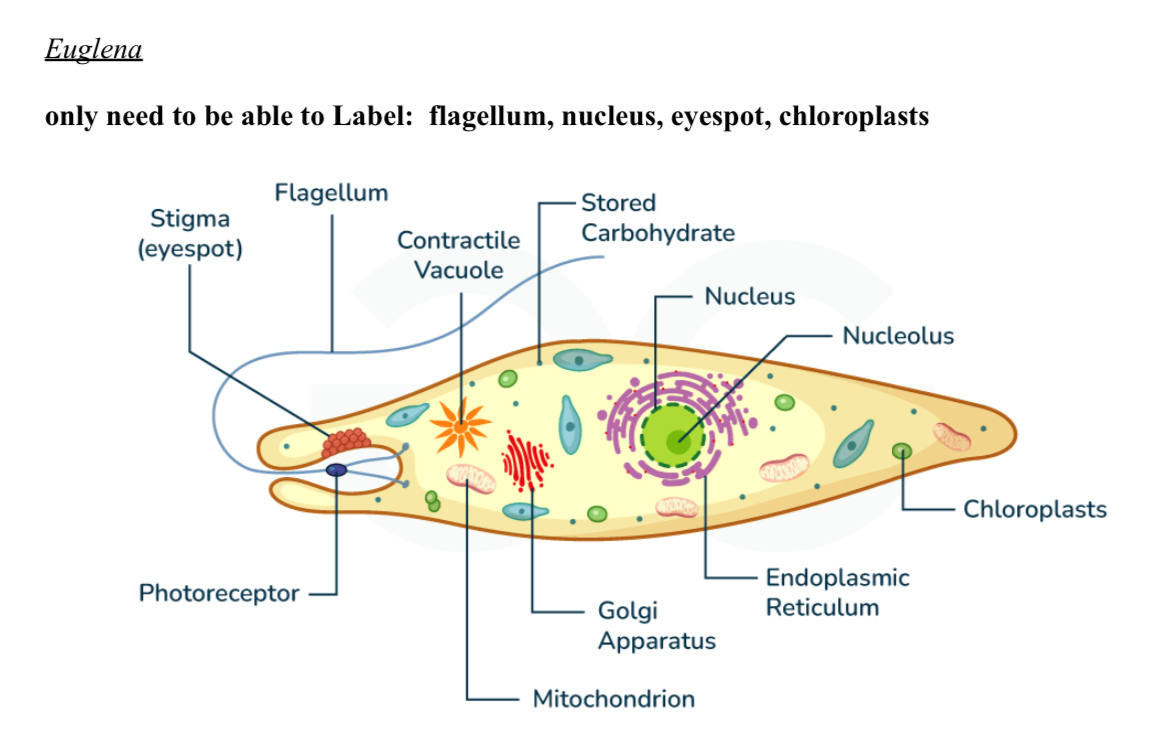
Protists - Eyespot
Helps find light to make food through photosynthesis
Protists 3 Main Groupings
Animal like protists
Fungus like protists
Plant like protists
Chordata
Have a spine, vertebrate (ex, humans, monkey, shark)
Mollusca
Soft body enclosed in a shell, strong foot for movement, water can pass them (ex. snail, clam)
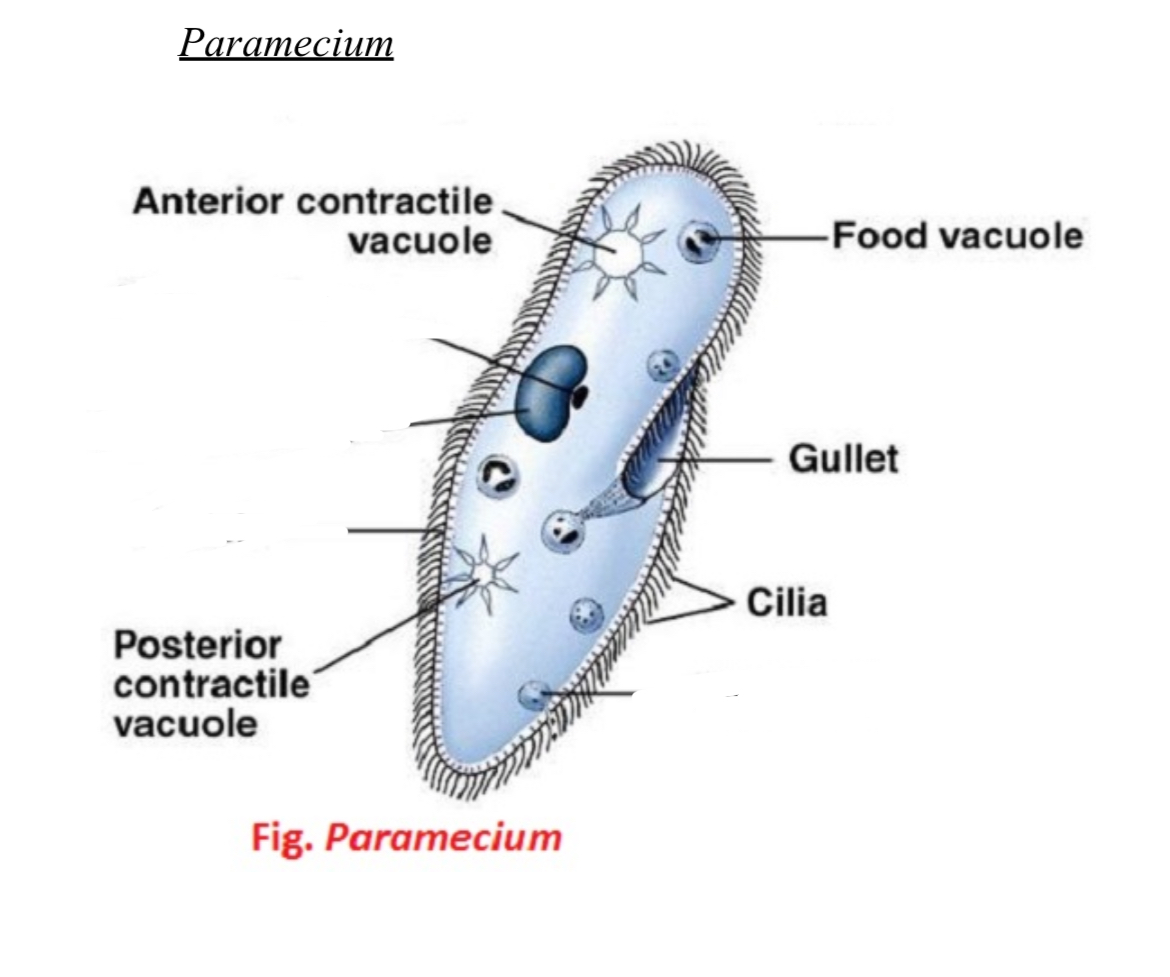
Paramecium diagram
Amoeba diagram
Euglena diagram
Virus diagram
RNA or DNA surrounded by a protective protein coat
Bacteria cell diagram
Mesophile definition
An organism that lives/habitats in moderate conditions
Endospores function
Protect genetic material of an organism. Not found in archaea