Suzie Chen 2: genomic library + sanger gel electrophoresis + PCR
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
if upon cleavage by Bam HI human DNA is able to ANEAL with ITSELF can the strand of DNA be replicated in bacterial cells?
NO because if the DNA is anealed (comes back together) it CANNOT BIND TO PLASMID DNA
ALSO HUMAN PURE HUMAN DNA CANNOT BE REPLICATED BY BACTERIAL CELLS (has to become apart of the bacterial DNA)
what is the ideal outcome of cleavage by BAM HI for recombinant DNA production
Human DNA and plasmid DNA of bacteria get cut by the same restriction enzyme (same bps) and come together
Recombinant DNA now able to be replicated in DNA
DO NOT BIND WITH THEMSELVES UPON CLEAVAGE ‘
what would happen if after cleavage by BAM HI, the plasmid DNA and human DNA undergo dephosphorylation by phosphatase?
will they be able to replicate in bacterial cells?
do phosphatases increase or decrease the number of empty vectors?
HUMAN DNA AND BACTERIAL VECTOR WONT BE ABLE TO COME TOGETHER THROUGH PHOSPHODIESTER BONDS
will NOT replicate
REDUCE the number of empty vectors (fewer vectors are now available to bind with human DNA bc/ they don’t have the phosphorous to bind to human sugar)
If plasmid DNA anneals to itself after cleavage by BAM HI is it still able to replicate in bacterial cells?
Does this reduce or increase the amount of empty vectors / background?
yes, it can replicate since it is the same bacterial plasma DNA fragment it was before
INCREASE the amount of empty vectors/background number (are able to be
what are empty vectors?
what reduces the number of empty vectors?
what increases the number of empty vectors?
Plasmid that has everything needed to combine with human DNA but does not
PHOSPHATASE reduces empty vectors bc/ now the plasmid doesn’t have phosphorous to bind to itself
what happens when HUMAN DNA that reacts with phosphatase upon cleavage with BAM HI is added to bacteria? Can recombinant DNA be formed?
Is this DNA able to undergo replication in bacterial cells?
Bacteria will transfer phosphate to human DNA and will still be able to create recombinant DNA and replicate in bacterial cells
after you insert a piece of foreign DNA into bacterial cells, how can you tell which bacteria have the recombinant DNA?
colony hybridization
is it easy for recombinant DNA to be replicated once inserted into bacteria?
How can this be combatted?
NO usually only a minority retain the plasmids through replication
antibiotic-resistant gene within plasmid DNA
do cells automatically have antibiotic resistance when placed into bacteria?
NO you have to grow the bacteria in a medium that has the antibiotic in it so only those that are resistant will survive
_________ _________in plasmids provide resistance to compounds in the growth media allowing rare population of bacteria (that have taken up the recombinant plasmids) to grow while PREVENTING GROWTH OF EMPTY VECTORS
selective markers
what are three examples of selective markers?
ampicillin
tetracycline
kanamycin
what are antibiotics
bacteria or fungi which inhibits a step of protein synthesis of another bacteria
in general terms what is a genomic library?
COMPLETE DNA of an organism is digested with a restriction endonuclease
EVERY SINGLE DNA FRAGMENT ARE IN VECTORS
the process of subdividing genomic DNA into clonable fragments and inserting them into vectors is called
creating a genomic library
the specific clones that carries the DNA sequences of interest of the genomic library must be _______ ___________ and __________
identified isolated and characterized
Construction of a Genomic Library :
Human DNA is cleaved with ______ ______
creating ________ of ___________ —→
Plasmids are cleaved with the same ______ ____________ as the human DNA —>
DNA fragments inserted into plasmids by _________ _______________ —→
Introduction of plasmids into ____________ —>
Genomic Library containing ALL _____ __________ of human DNA
restriction enzymes millions DNA fragments
restriction enzyme
DNA LIGASE
restriction fragments
Once you have your recombinant DNA and have transferred it into bacteria cells in a medium containing antibiotics what is the next step?
COLONY HYBRIDIZATION
what is the point of DNA hybridization?
be able to identify whether or not your gene of interest is present within a colony of DNA
probe (with the complementary strand to the gene of interest) will hybridize with the gene of interest
once you spread your colony of bacteria containing recombinant DNA in a master agar plate with antibiotics
what do you place on top of the agar?
what will happen after you place this on top of the agar plate?
what is the next step?
nitrocellulose/mylon membrane
the colony will replicate onto the membrane
remove the membrane now with new colony and soak in solutions and HYBRIDIZE W PROBE
in hybridization what do you place on top of the agar plate with the colony of bacteria?
nitrocellulose/ nylon membrane
in hybridization, once the bacteria is transfered onto the nitrocellulose/ nylon membrane and you remove it from the agar plate, what must be done to it? transfer
it must be
denatured (so probe can bind to it)
neutralized
washed
dried/ fixed
once the bacteria on the nitrocellulose membrane has been denatured, neutralized, washed, dried, and fixed
what can now be done?
bacterial DNA can be hybridized with probes (complementary strand of recombinant DNA) !
washed
autoradiographed
PROBE WILL ALLOW YOU TO SEE WHICH BACTERIA HAS RECOMBINANT GENE SO YOU KNOW WHAT TO GROW IN A LIQUID CULTURE
once a probe identifies which proteins from the membrane HAVE the recombinant DNA in them, what is then done?
the bacteria marked with probes is then purified and placed in a LIQUID CULTURE TO GROW
nitrocellulose/nylon membrane or “disc” allows DNA to be ________________ using ______/_____
THEN a single-stranded ______ of complimentary _________ RNA or DNA is added, and the strands are allowed to -________
denatured acids/bases
probe RADIOACTIVE re-anneal
DNA Hybridization
the presence of a specific _____has to be identified before it can be used for further analysis
restriction enzymes are used to reduce the DNA to smaller fragments
the DNA segments are separated by ___________ ________ ________________
to identify the fragment that contains the DNA of interest, a specific _____ is used to hybridize the DNA fragments
gene
agarose gel electrophoresis
PROBE
how can you tell which nucleotides make up your DNA?
Sanger Chain - Termination DNA Sequencing
the Sanger DNA sequencing method uses __________ ________ to terminate DNA synthesis yielding series of DNA fragments whose sizes can be separated by electrophoresis
dideoxy nucleotides
In Sanger Sequencing we know
which dideoxy nucleotides terminated each fragment and which ____ it attached to
so we know the last _____ of each fragment and we will get EVERY SINGLE FRAGMENT
base
in gel electrophoresis do we read the bases from top to bottom or bottom to top?
bottom to top
each row you go up there is one additional base pair that did not get to go all the way down due to its larger size
the biggest fragment is at the top, as it was unable to reach the bottom because of its large size
does DNA sequencing provide the exact DNA sequence?
NO provides COMPLIMENTARY SEQUENCE
since dideoxy nucleotides are being detected and they pair with the template (they are the opposite base pair of the template)
do dideoxynucleotides have any OH’s at all attached to their 5 carbon sugar?
why is this important?
NO they have Oxygen embedded in the ring, phosphate and complimentary base but no OH like deoxyribonucleotide
since it doesn’t have OH you can not attach anymore nucleotides onto it and it terminates with the base attached to it matching the template strand
what are the starting materials to complete Gel Electrophoresis?
single-stranded DNA
radioactively labeled PRIMER
DNA polymerase
dideoxy nucleotides
what are the 4 dideoxy nucleotides mixed in with the single-stranded DNA, primer, and DNA polymerase in gel electrophoresis?
dATP
dTTP
dGTP
dCTP
what direction does gel electrophoresis run? bottom up or top to bottom?
In what direction do you start to read the COMPLIMENTARY strand that is shown by gel electrophoresis ?
top to bottom (biggest stay near top)
5” to 3” (bottom to top)
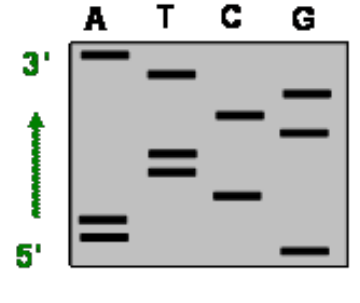
what was the template strand?
C TT G AA CGC AT
reading simply from bottom to top will give you COMPLIMENTARY so must use opposite to get template
For the SANGER METHOD do you mix the single stranded DNA, DNA polymerase, radioactively labeled primer, and all 4 deoxynucleotides ALL TOGETHER?
NO
you make one batch of DNA template strand + primer + Polymerase and you divide it amongst FOUR microtubes
one microtube has ddATP ddCTP ddGTP ddTTP
what and how do you load onto electrophoresis gel
there are 4 columns for each dideoxy nucleotide mixture
each column has either ATCG didoxynucleotide + DNA polymerase + Radioactive primer + DNA template strand
although you can’t visualize the size of the fragments of DNA you can tell the last base pair and the size of each fragment based on how far up it is on or down it is on the gel.
what must you do to a gel electrophoresis to see your results
autoradiography
Sequence of Gel Electrophoresis can be read from _______ on _________ and original template sequence ________
bands
autoradiograph
deduced
AUTOMATED DNA sequences can be done using ____________ _______
dye-labeled segments are applied to a ________ gel and subjected to electrophoresis
fluresent tags
CAPPILARY
Does SANGERs sequencing method deal with PCR?
NO NOT THE SAME THING
Sanger =DNA sequencing
PCR + DNA replication
_______ amplifies a region of DNA between two predetermined siters
Oligonucleotides complimentary to these sites serve as ________ for synthesis of copies of the DNA between the sites
PCR
primers
Each cycle of PCR doubles/quadruples the number fo copies of the amplified DNA
DOUBLES
_______ Polymerase comes from a bacterium that lives in hot springs
why is this SPECIFIC polymerase used in DNA replication during PCR
Taq
since it arises from hot springs it is able to work in hot temperatures
there is no DNA helicase, but DNA is separated by HEAT cranked up to 94 degrees celsius, other DNA polymerases would denature
what are the starting materials of PCR?
double stranded DNA
DNA primers
taq polymerase
SEQ Polymerase Chain Reaction:
double-stranded DNA is denatured at _____ degrees
Primers anneal to each strand of DNA at what temperature?
Taq polymerase synthesizes the DNA strand at what temperature?
94 degrees
5 degrees below melting temperature (t m)
72
what is the flanking sequence in PCR and where is it found?
the sequence that the Primer will bind to
there are two on each strand 4 total
they are complimentary to DNA primer
one primer binds to the flanking sequence at one end of one DNA strand while another primer binds to the flanking sequence on the other end
do the primers have to be the same for both DNA strands? why or why not?
NO BECAUSE the start of the dna is not always going to be the same as the end AND they are complimentary to one another so they wouldn’t se the same
CATAGA
GCATCT
for example CAT not the same as TCT
does the amount of dna primer you add to the PCR initially matter? what about the size of the primer?
YES if you want MULTIPLE cycles then you should use EXCESS primer that will last for multiple cycles
you cannot add primer once PCR has begun to run
if you have a short primer than you will amplify a shorter sequence NEVER WANT TO LENGTHEN
paternity testing and determining family relationships
forensics DNA analysis
Amplicfication of rare DNA
human genetic testing
cloning
RT-PCR and qPCR (reverse transcriptase)
diagnostic tests for disease causing pathogens
human remains identification
all of the following are made possible through
PCR