OPT 218: Stereo, Sensory Fusion, EOMs
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
1st degree = simultaneous perception of 2 separate images
2nd degree = flat fusion of 1 image
3rd degree = stereopsis, 3D
What are Worth's 3 Degrees of Fusion?
emerges at 3-4 mos and developed by 6 months
By what age do almost all infants appreciate random dot stereogram targets (global)?
random dot stereograms with no monocular cues = need bifoveation to pass, so suppressing or constant strab will fail
What is global stereopsis?
Randot targets/shapes
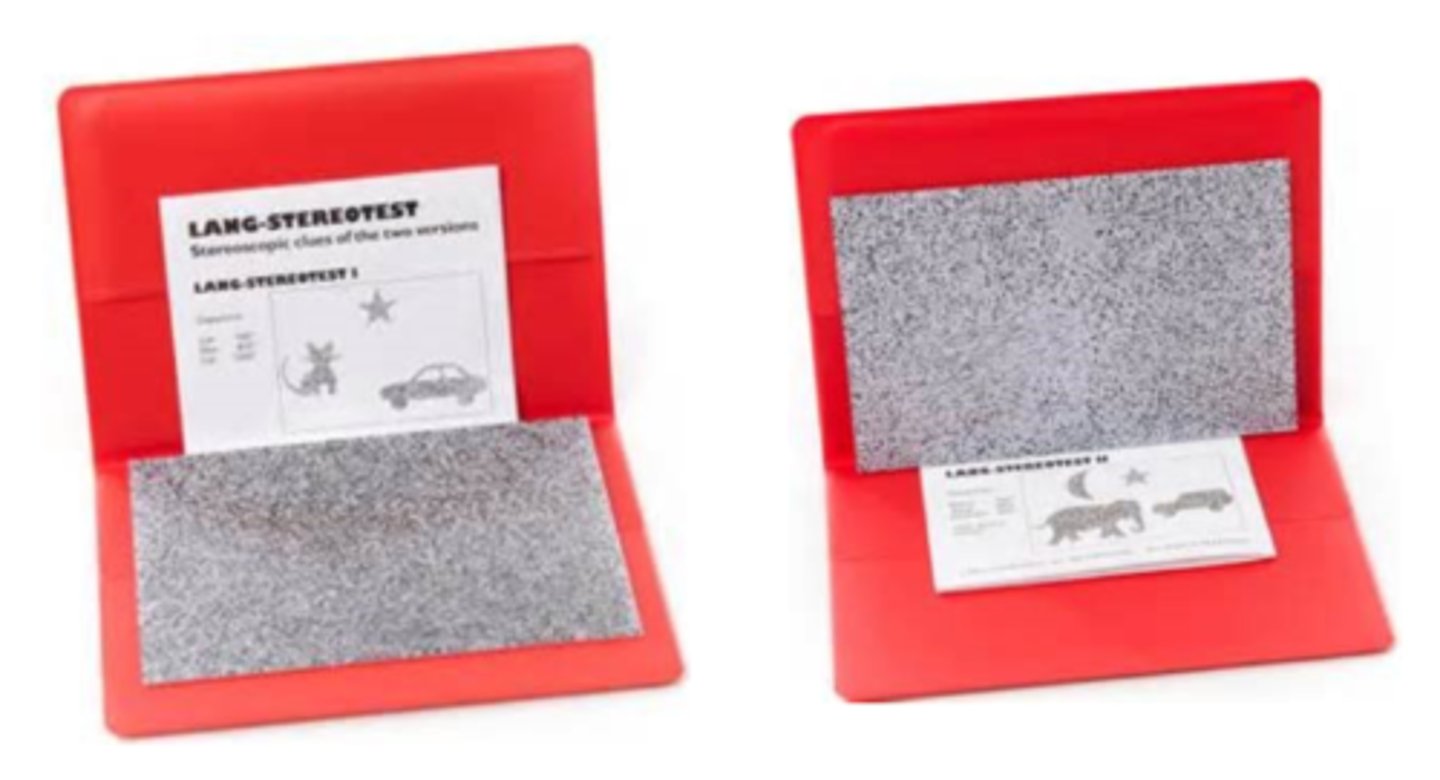
Lang
PASS
What are 3 examples of global stereopsis tests?
similar targets laterally displaced = monocular cues exist = do not need bifoveation to pass
What is local stereopsis?
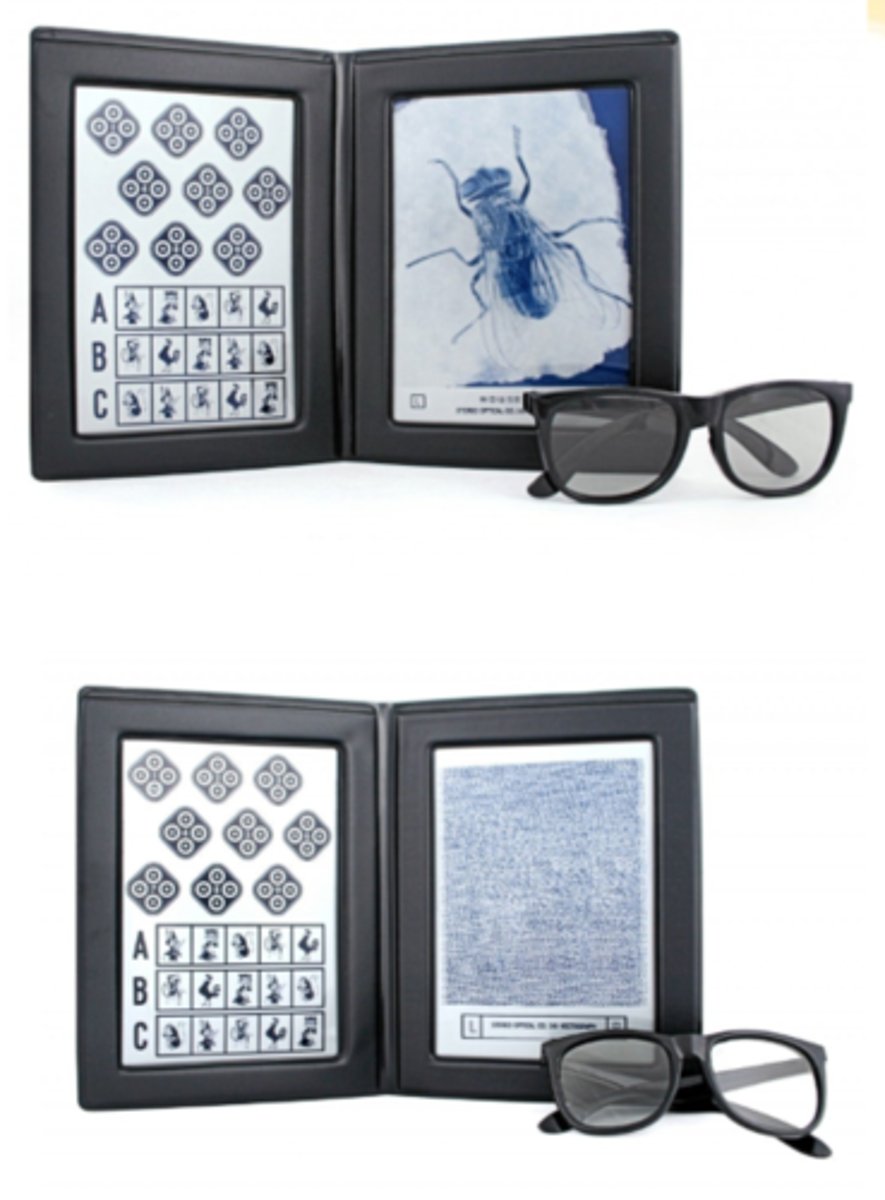
Titmus fly
Wirt circles/animals
R+L
FBAT
What are 4 examples of local stereopsis tests?
local test for stereopsis using anaglyph R/G glasses with the book at 20-30cm
What is the Bernell FBAT test for infants?
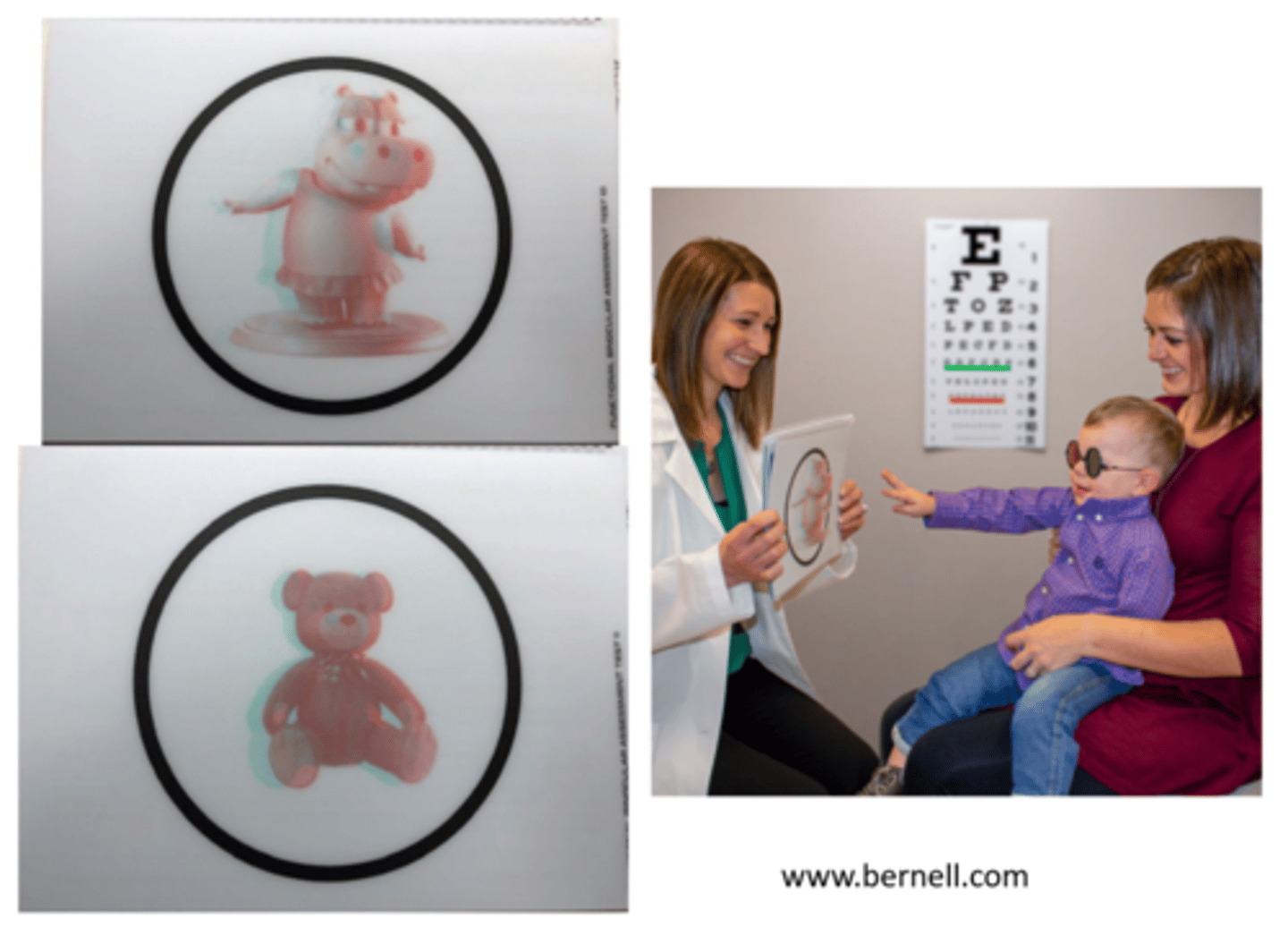
does child reach for target?
do they grab it in air or touch the page?
if they touch the page, probably not bifoveating!
What response do we look for with Bernell FBAT in infants?

global test for stereopsis using polarized glasses with the cards at 40cm, using preferential looking to see if the child looks at the blank or smile
What is the stereo smile/PASS test for infants (6-17 mos)?
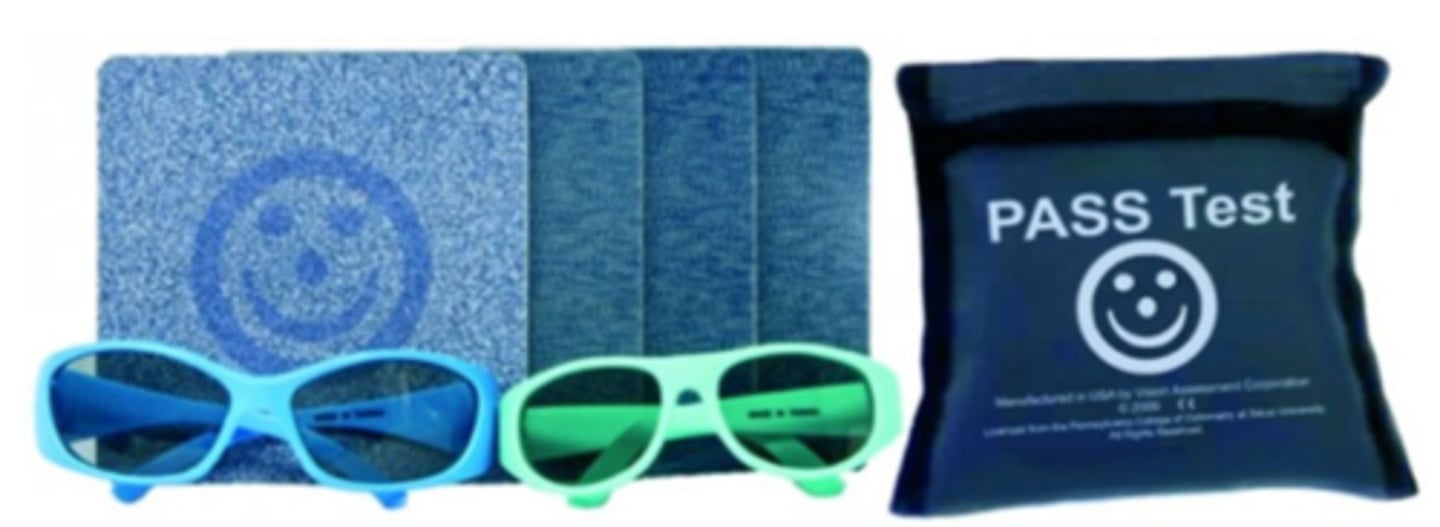

yes, because each card has a different disparity level of 480", 240", 120", 60"
Can we quantify stereopsis with stereo smile/PASS for infants?

global test for stereopsis using polarized glasses with the cards at 1m, using preferential looking to see if the child looks at the blank or stereo E
What is the random dot E/PASS test for toddlers/preschoolers (1-3 yrs)?
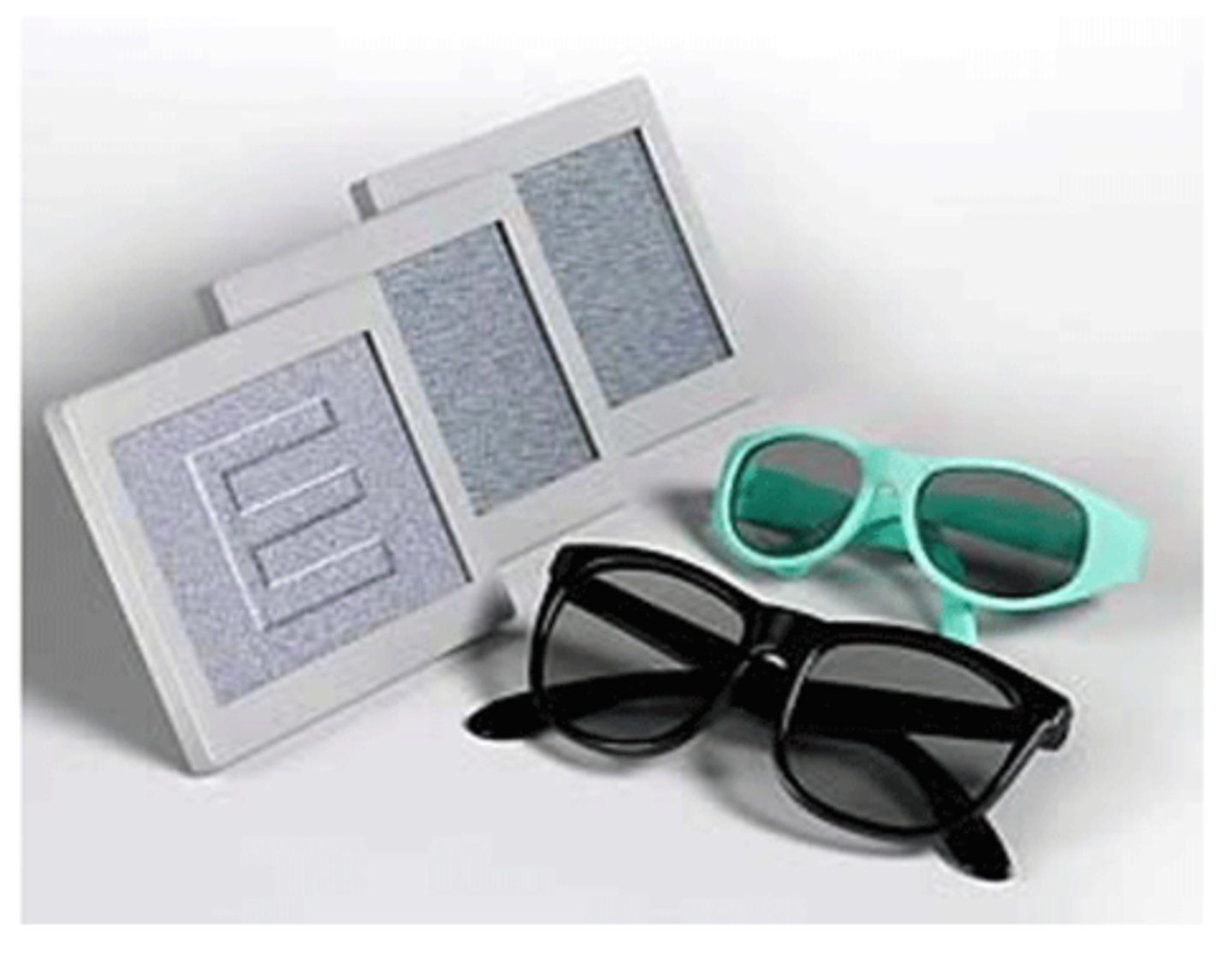

yes, because at 1m this is equal to 252"
Can we quantify stereopsis with random dot E/PASS for toddlers/preschoolers (1-3 yrs)?
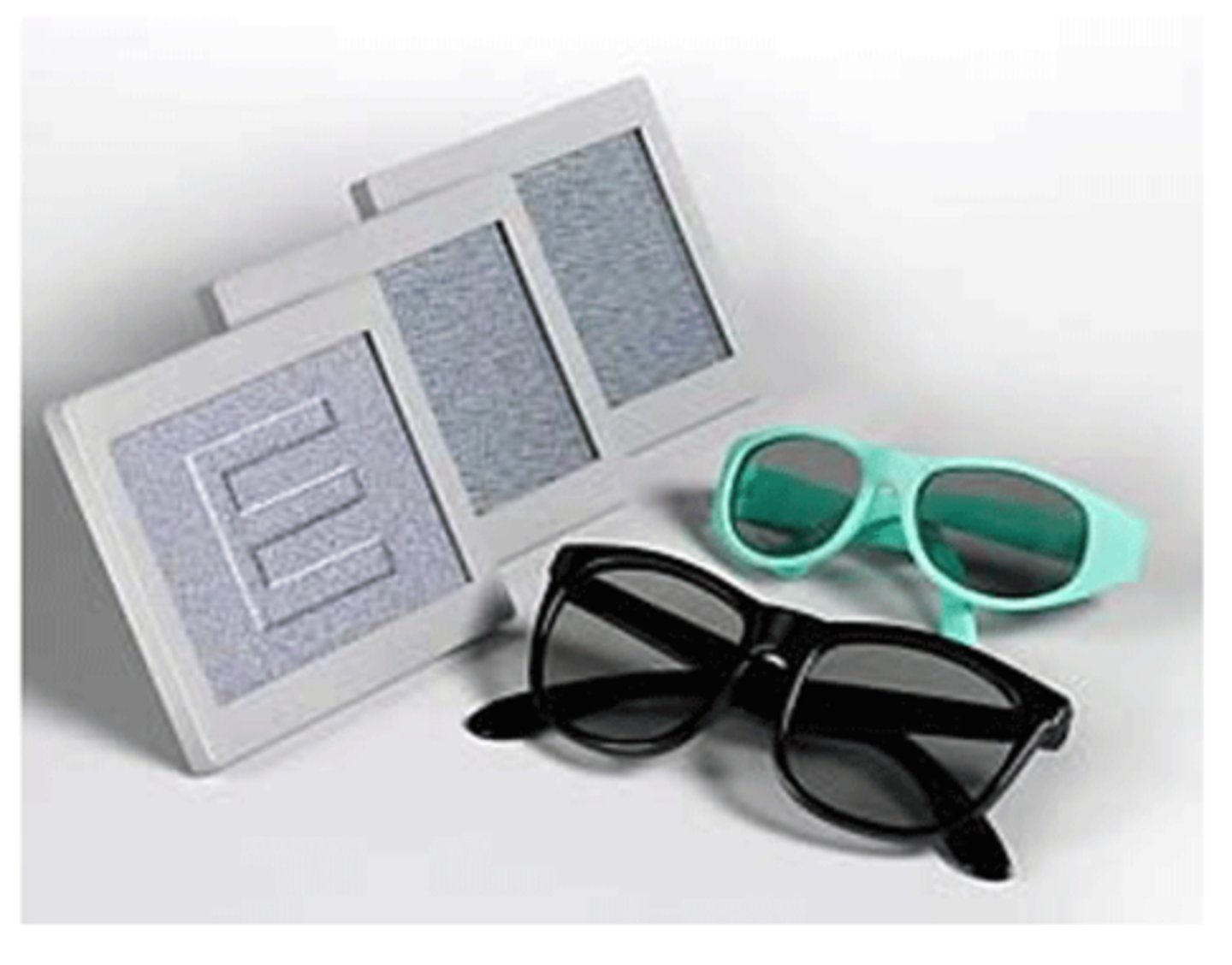

global test for stereopsis using polarized glasses to identify kid friendly shapes
What is the randot preschool test for preschoolers (3-5 yrs)?
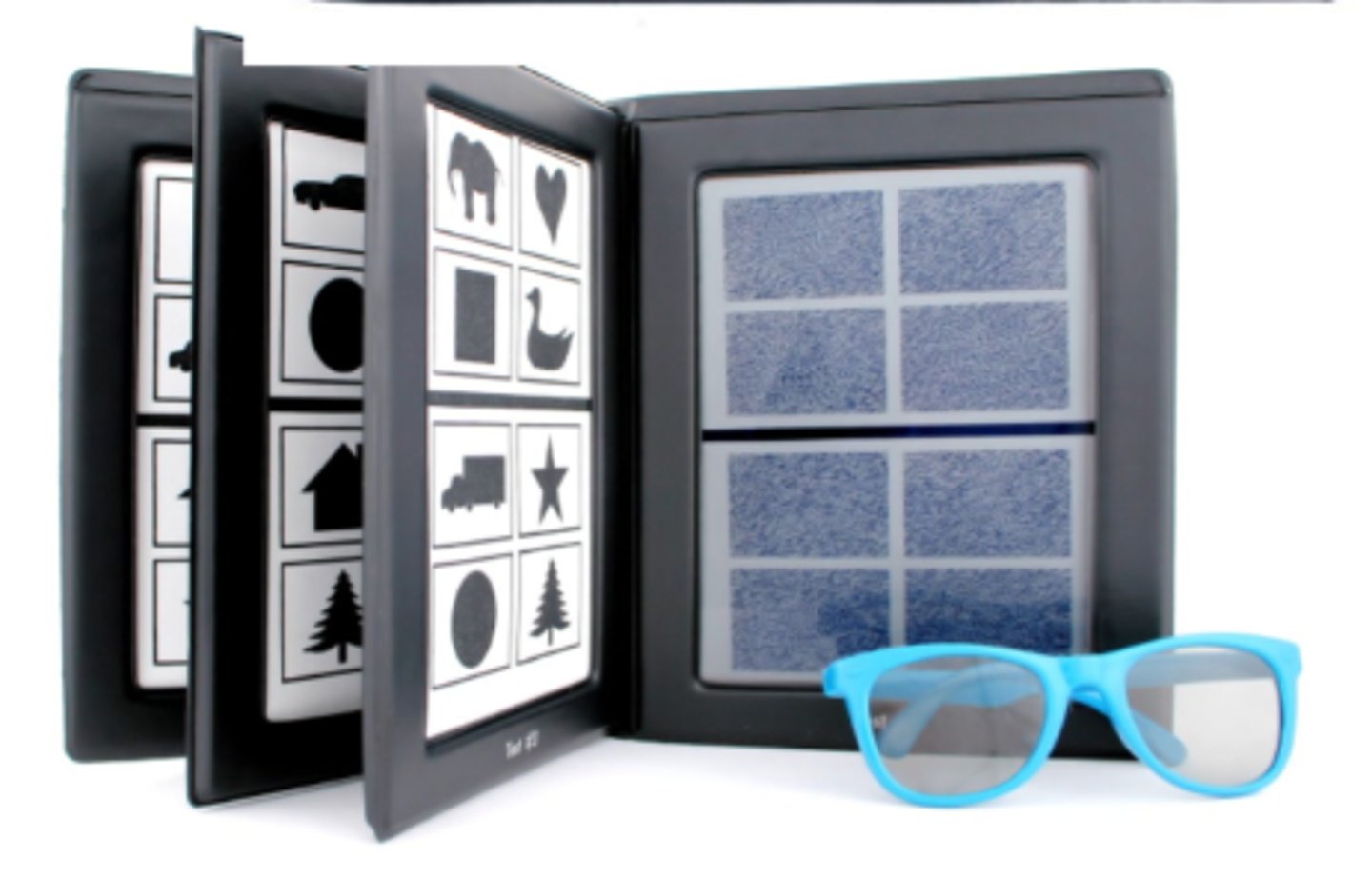

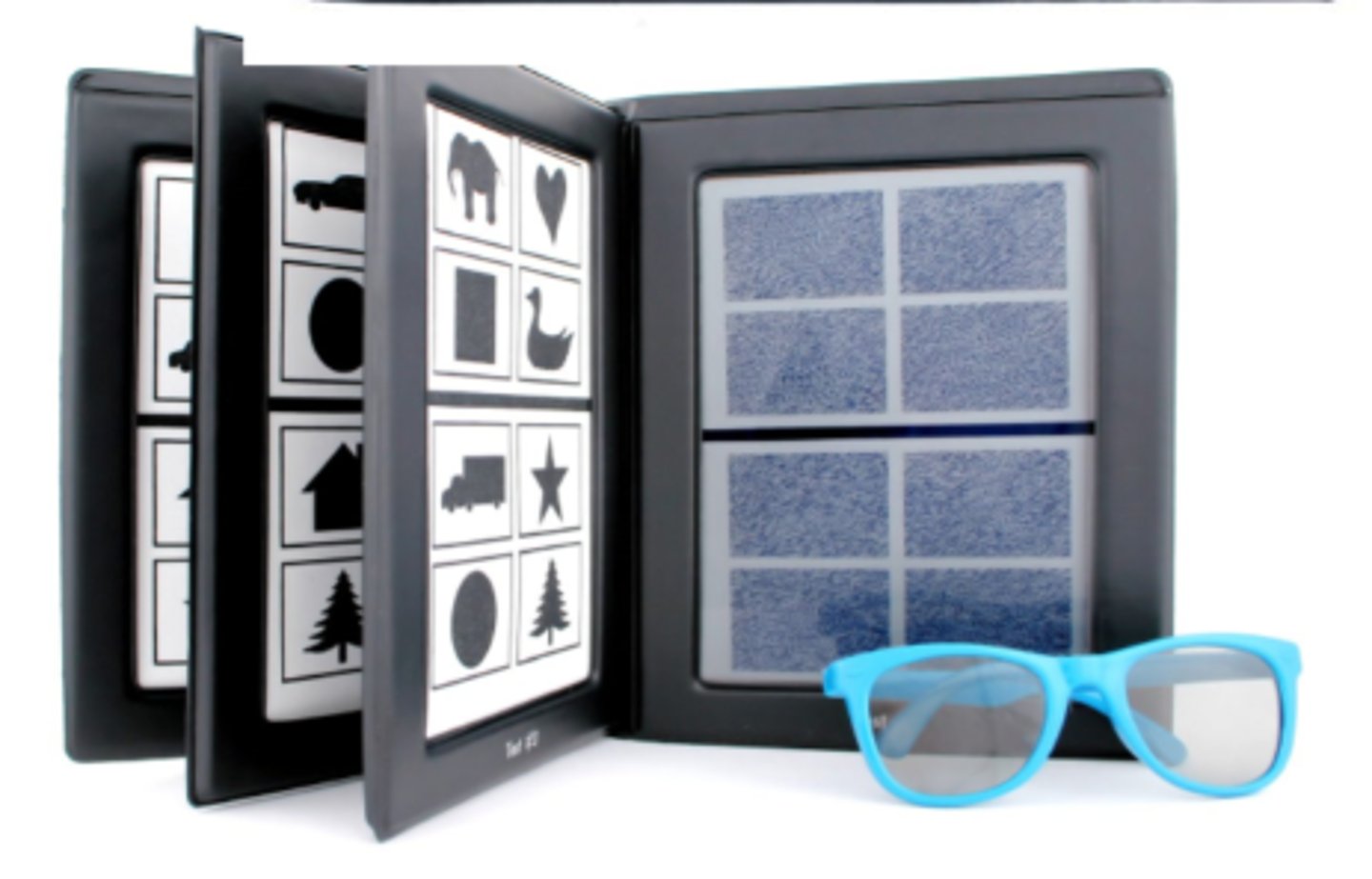
3 books with different levels:
800"-400"
200"-100"
60"-40"
How do we quantify stereopsis with randot preschool test for preschoolers (3-5 yrs)?

global test for stereopsis without polarized glasses held at 40cm for child to point to or name each figure
What is the Lang stereo test for toddlers/preschoolers?
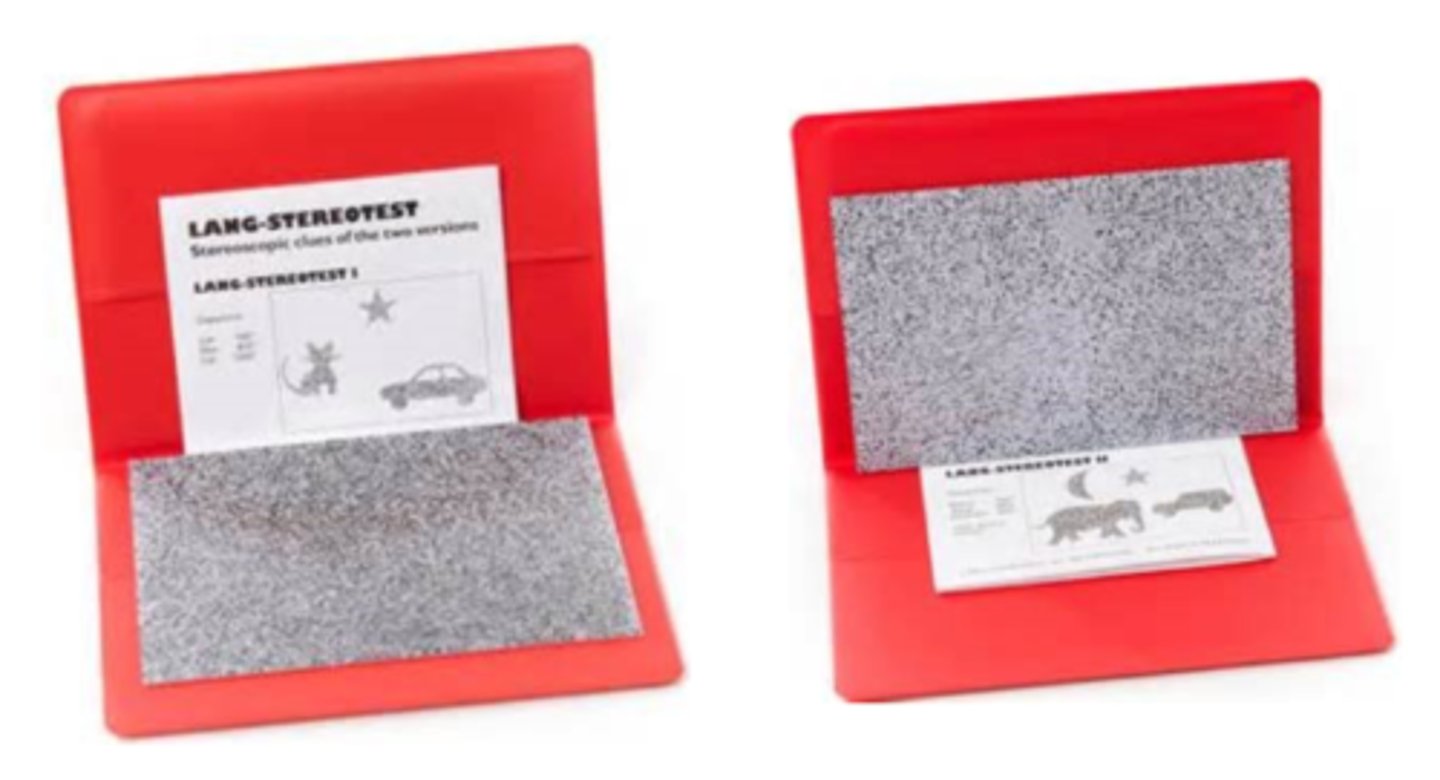

figures represent 3 disparities so whichever figures they name tells us sec of arc
How do we quantify stereopsis with the Lang test for toddlers/preschoolers?

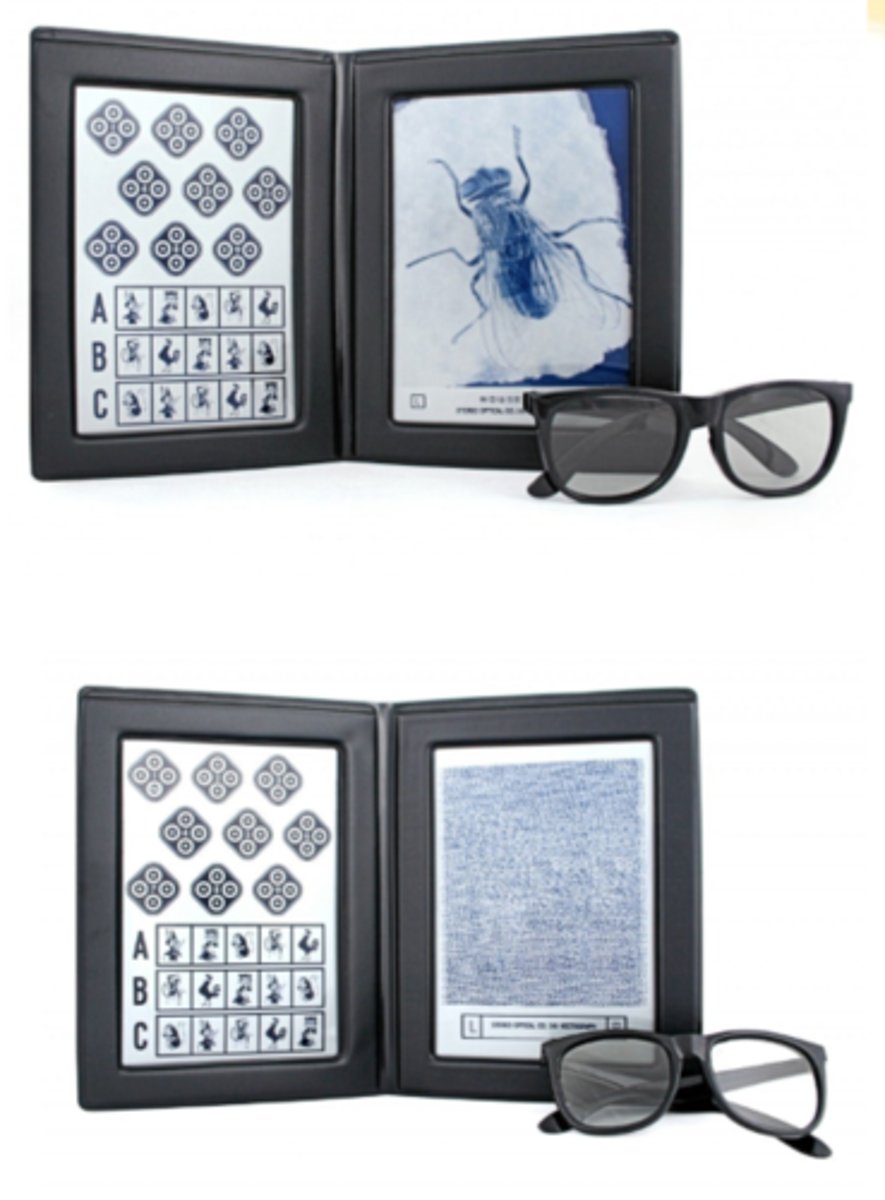
using polarized glasses to analyze...
global = match or identify shapes (forms) from 500" to 250"
local = identify Wirt circles/animals on random dot background
What is the Randot stereo test for school-aged?

fly = local = 3000"
butterfly = global = 1200-2500"
What is the difference between the titmus fly vs stereo butterfly tests for school-aged?

both have local stereopsis Wirt circles/animals on a non-randot background
What is the commonality between the titmus fly vs stereo butterfly tests for school-aged?

global test for stereopsis using anaglyph R/G glasses to look at the 3 screening plates, 1 suppression plate, and 2 quantitative test plates
What is the TNO stereo test for preschool/school-aged?

overestimates stereo compared to polarized tests
What is a disadvantage of the TNO stereo test for preschool/school-aged?

distance Randot = 8 tests done at 10 feet, giving us a range of 400" - 60"
How do we test stereo at distance?

Lang
Which is the only stereo test used without glasses?
Randot
Which stereo test is considered the highest level of stereo and thus, the most preferred?
determine binocularity / 2nd degree fusion (sensory fusion) even if there is no stereopsis, esp if distance strab, decreased VA in one eye w/o Rx, complaints of DV
What is the purpose of the flashlight tests in school aged?
testing sensory fusion while wearing R/G glasses (R on OD)
How do we perform the 4 dot procedure?
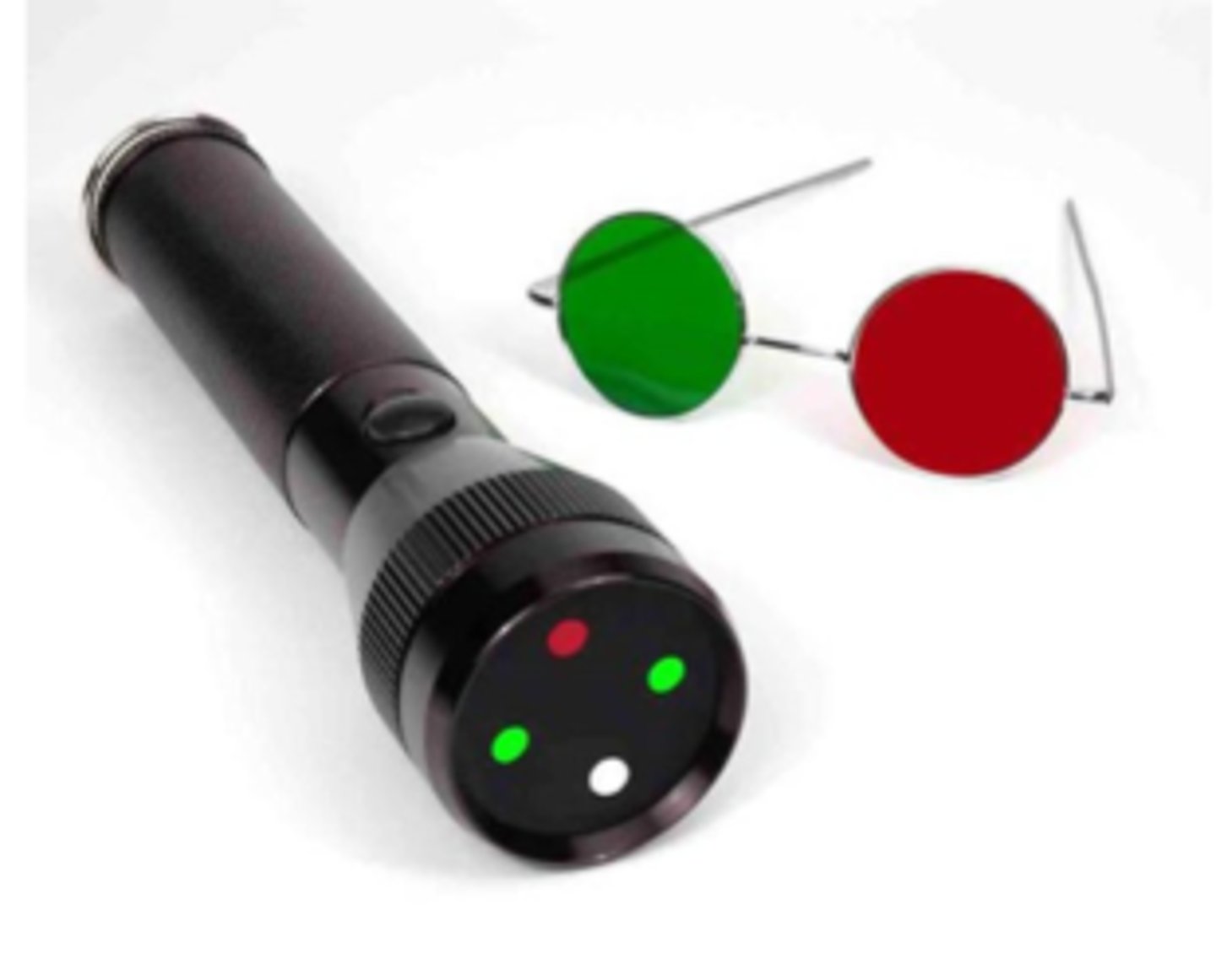

to test the depth of suppression bc in dim lighting, we have eliminated all other cues so less likely for pt to suppress (if shallow suppression)
BUT if pt still suppresses in dim then we know it is a more deep/embedded response
Why do we run the 4 dot test for sensory fusion in bright and dim illumination?
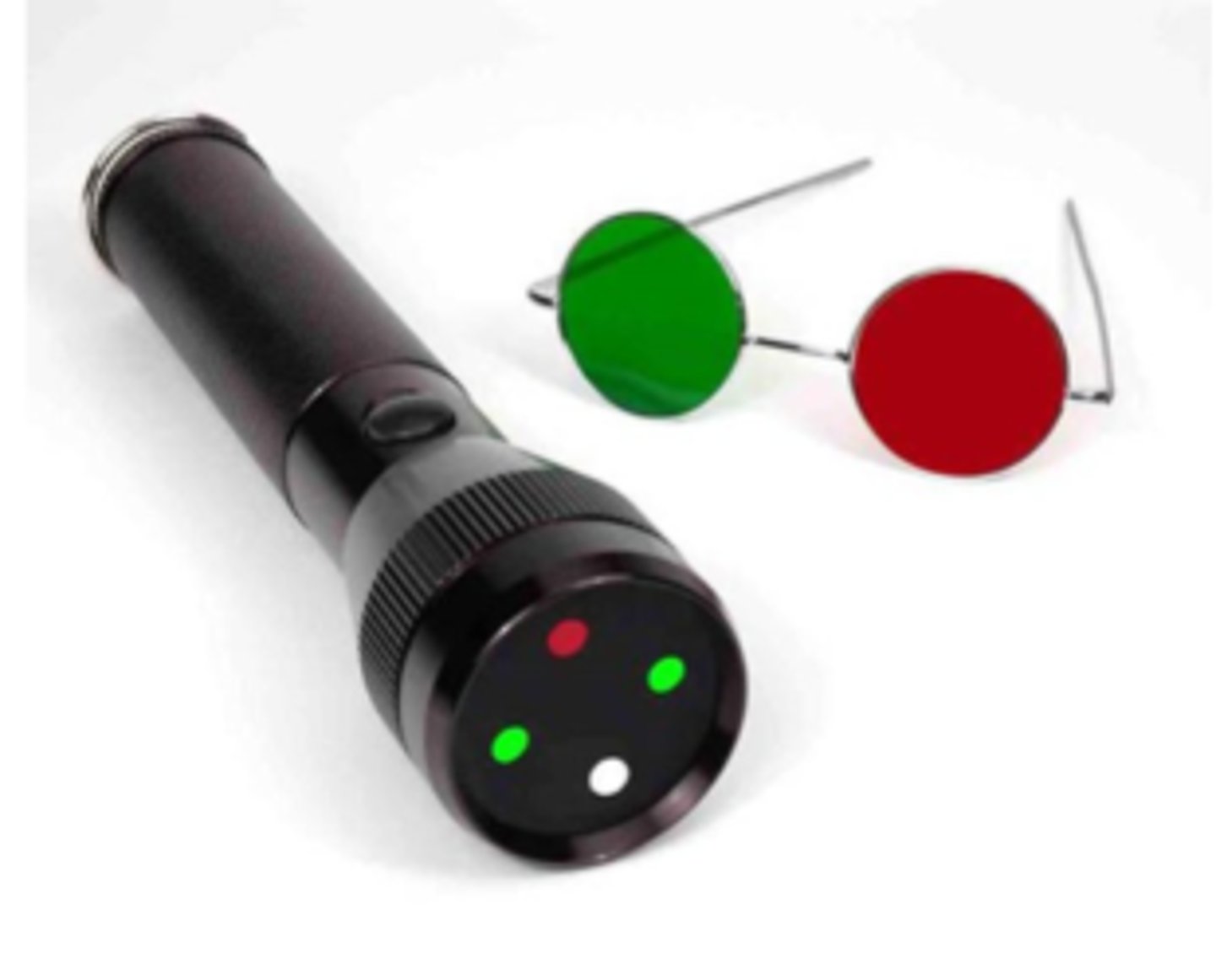

OS suppression
What does it mean during 4 dot if the pt says they see 2 red dots?

OD suppression
What does it mean during 4 dot if the pt says they see 3 green dots?

fusion
What does it mean during 4 dot if the pt says they see 4 dots and no turn?

anomalous correspondence = adaptation to strab
What does it mean during 4 dot if the pt says they see 4 dots w/ eye turn?
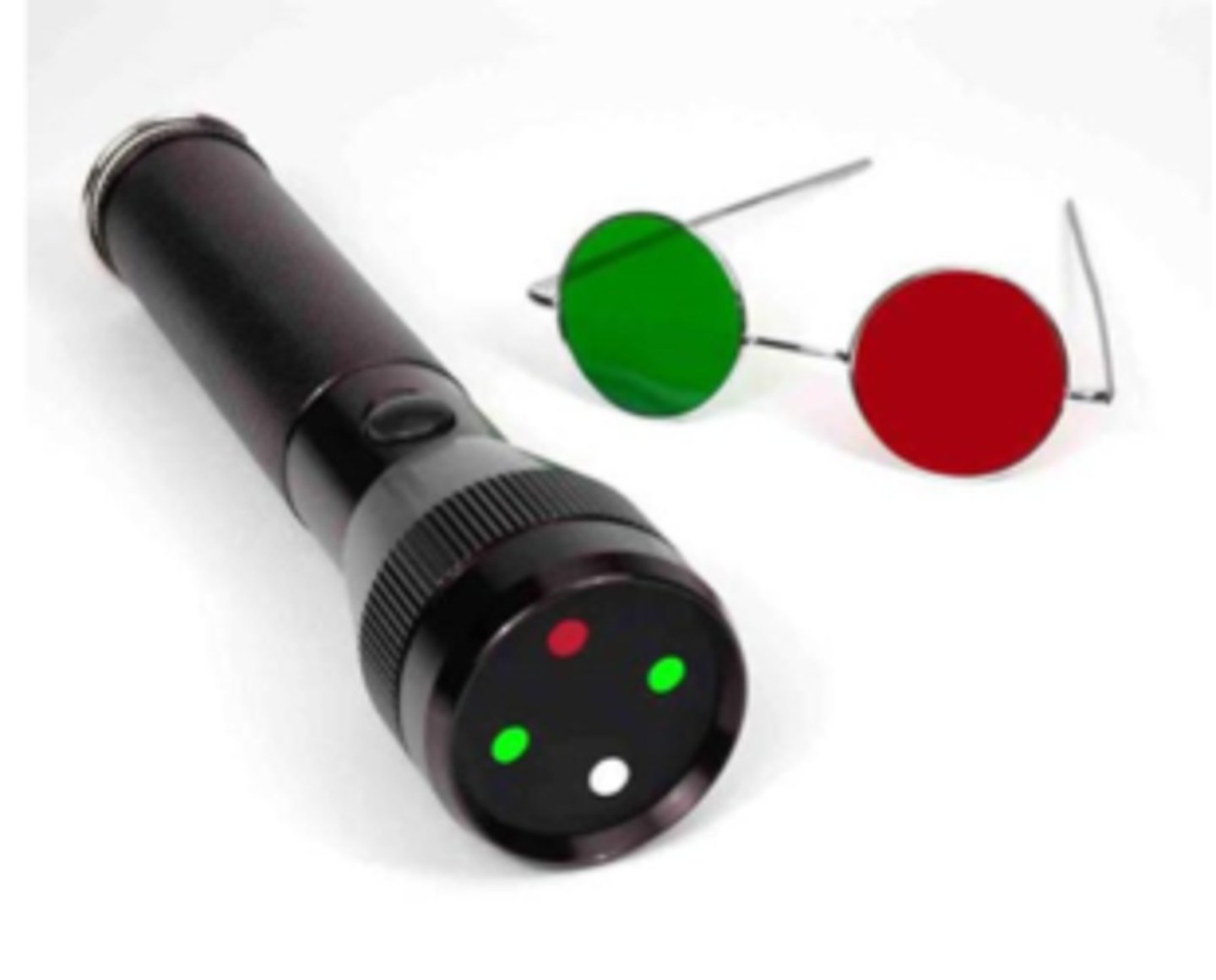

uncrossed = eso
What does it mean during 4 dot if the pt says they see double (5 dots), with red on the right?

crossed = exo
What does it mean during 4 dot if the pt says they see double (5 dots), with red on the left?

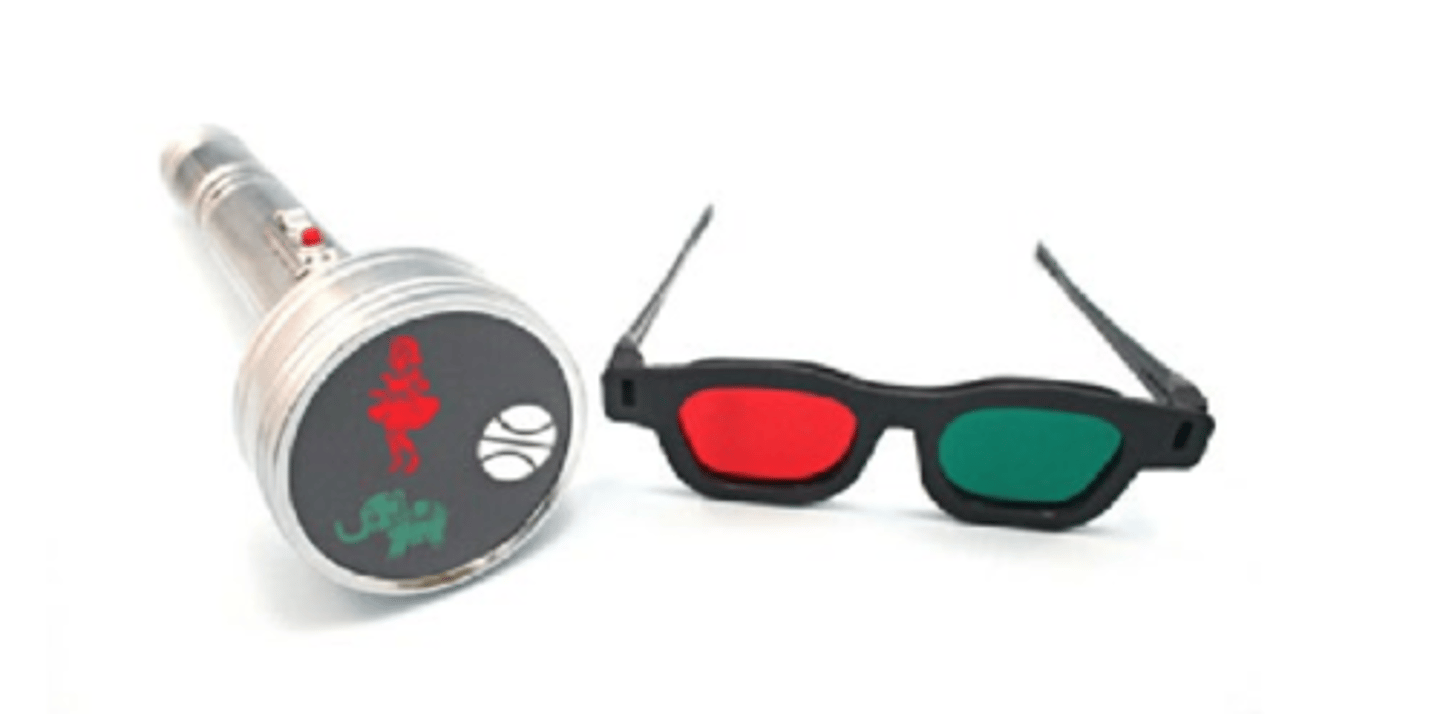
basically exact same as 4 dot but figures instead of dots (usually younger kids)
What is the 3 figure flashlight test for sensory fusion?

not until school age (5+) unless symptoms warrant bc these eye movements are very involved in reading and sports
At what age do we typically start testing saccades and pursuits? Why?
losing place when reading
brain injury/concussion
athletes
What are some things that may warrant testing saccades?
athletes
attention issues
What are some things that may warrant testing pursuits?
saccades
Are pursuits or saccades more clinically significant?
infants have ability to make pursuits, but not very well or consistently
How well do infants perform pursuits, according to Phillips and Lengyel studies?
infants only a few mos old have initial saccade in wrong direction, succession of saccades, long latency, different sizes
adult-like by 13 months
When do saccades develop to adult-like levels, according to Aslin/Salapatek and Hainline studies?
physiological H with Wolff wand or similar target
OR
NSUCO
What 2 chairside tests do we use for pursuits?
horizontal
vertical
diagonal
circles
Z-axis
stop/start
speed change
List the 7 types of pursuit movement in order based on development.
Wolff wands or similar to test H, V, D overshoots, accuracy, etc.
NSUCO/Maples
What 2 chairside tests do we use for saccades?
pt stands 40cm (or Harmon disrance) from...
saccades = 2 Wolff wands 20cm apart, 10 saccades
pursuits = 20cm circle with 1 wand, 2 CW and 2 CCW
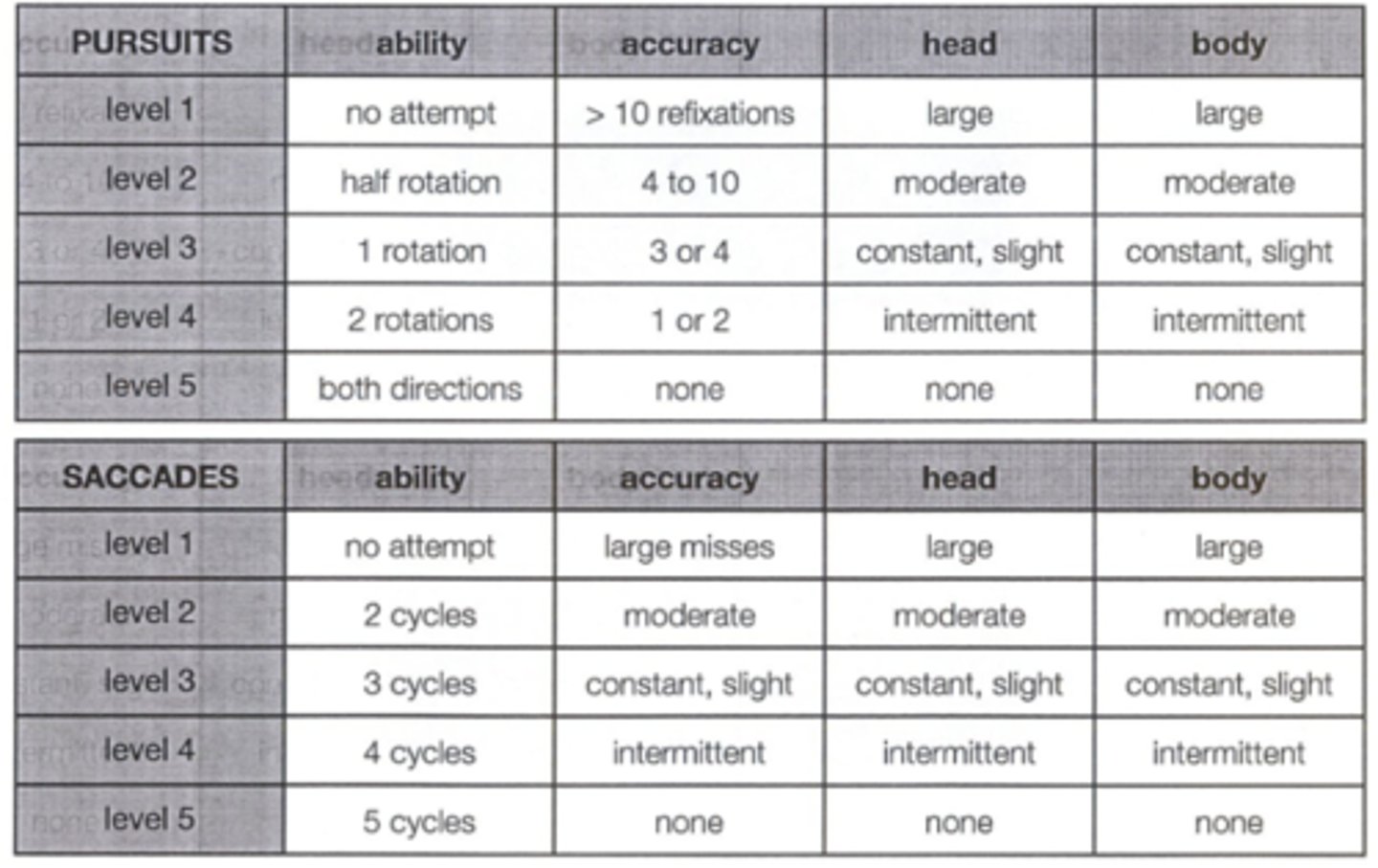
How do we perform the standardized NSUCO test for saccades and pursuits?
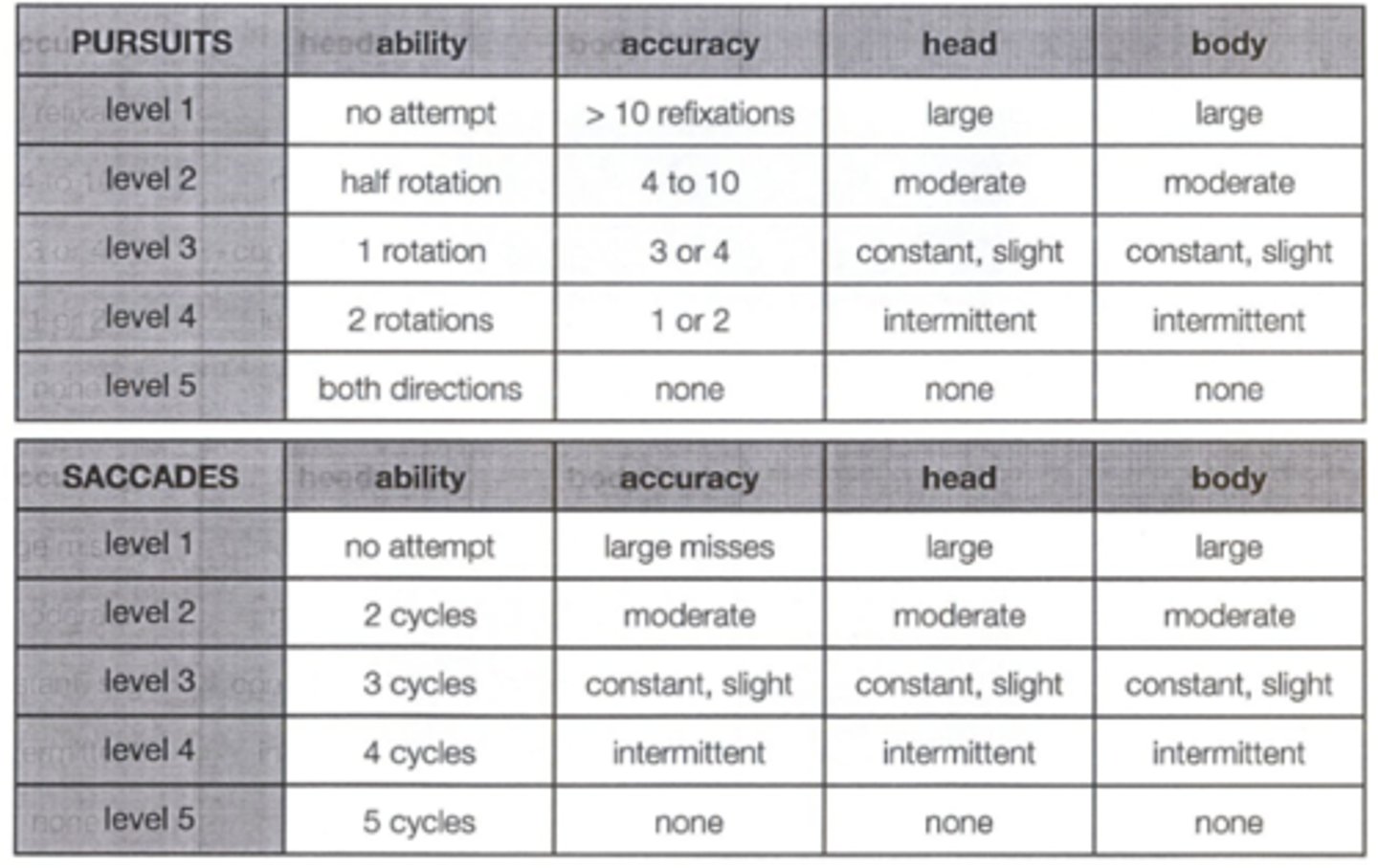
1. ability
2. accuracy - refixations, over/undershoot
3. head movement
4. body movement
all rated levels 1 through 5
Which 4 aspects are we analyzing/scoring during the standardized NSUCO test for saccades and pursuits?
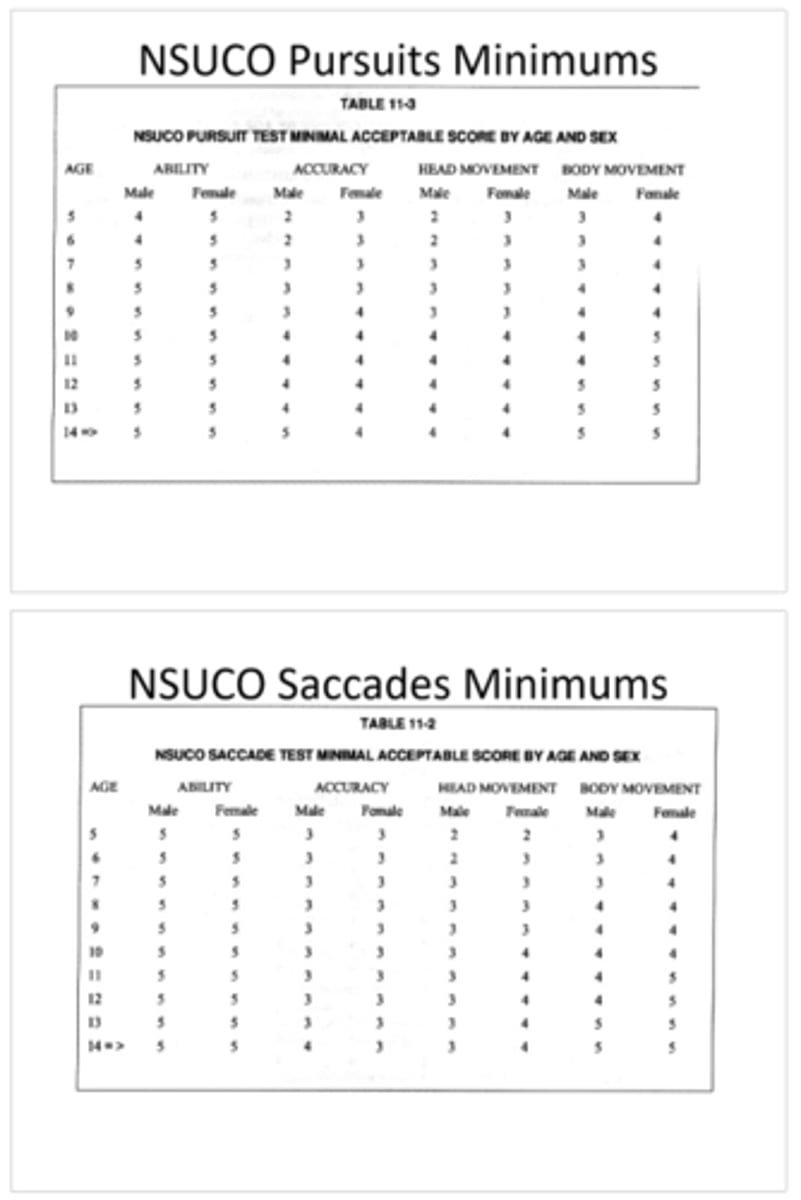
pursuit and saccade minimums for their age and gender
What do we compare a pt's NSUCO score to?
DEM Developmental Eye Movement
K-D King-Devick
What 2 paper tests do we use for saccades?
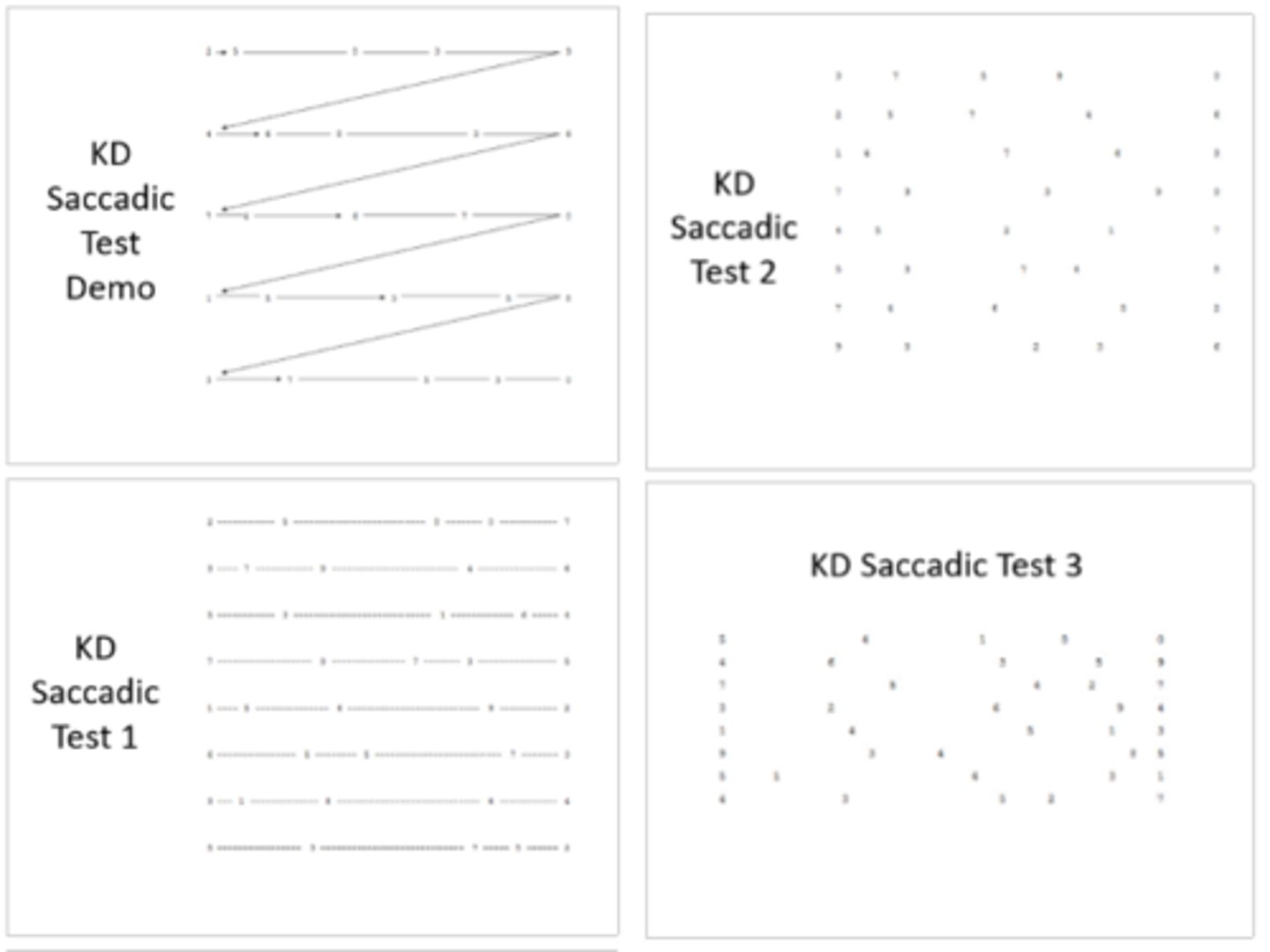
get pt to read off the numbers in each horizontal row as fast as they can, counting time and errors
How do we run the K-D test?
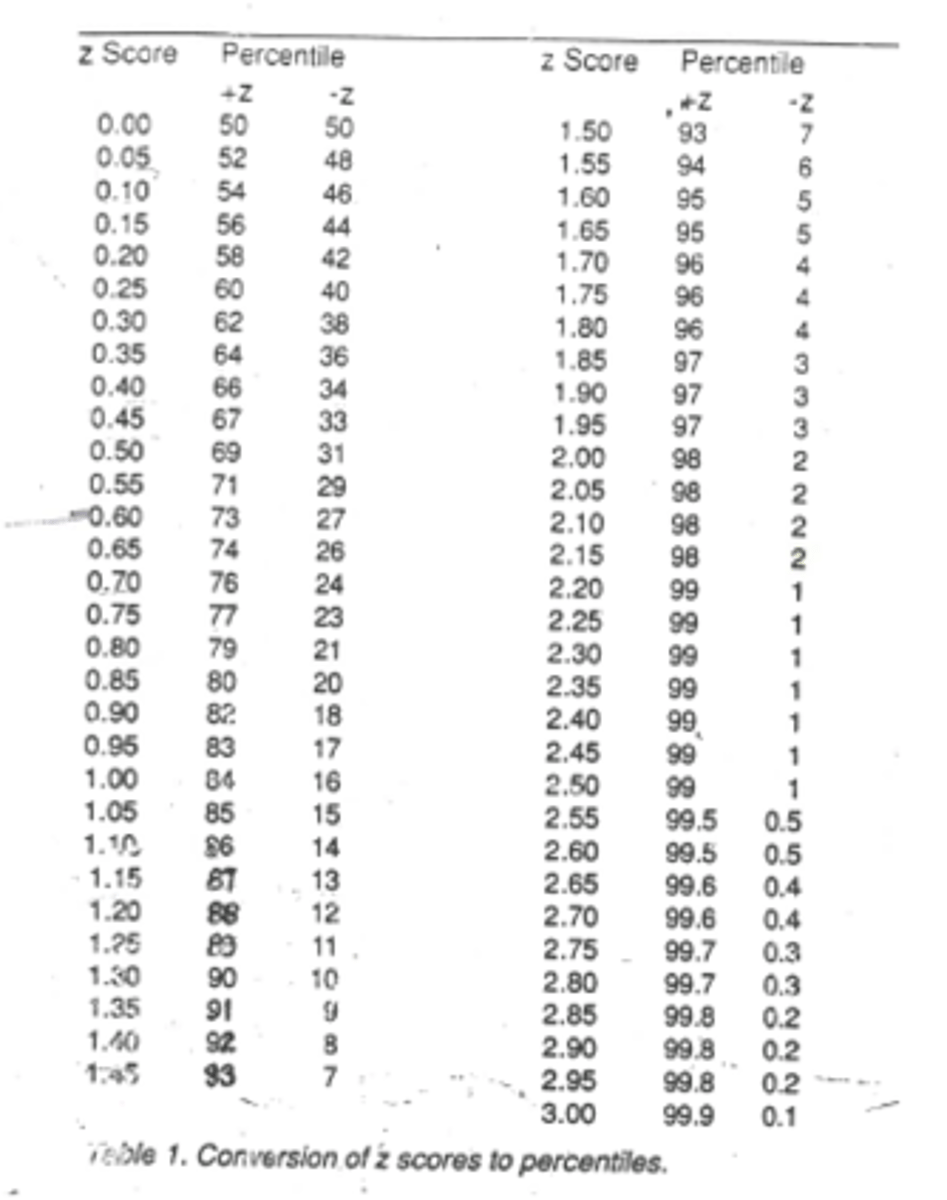
1. find Z score for the pt's time
2. compare Z score to percentile rank table, using the negative z because increased time here is poorer
How do we score the K-D test?
Z = (actual - mean) / SD
How do we calculate Z-score?

55.03 - 26.71 / 5.97 = 4.74
negative Z for 4.74 is 0.1%ile
Ex) in what percentile is a 7-year-old who performs K-D test 1 in 55.03sec?
pt has to read as quickly down the columns for A and B, but across the rows for test C = aims to separate saccadic (horizontal) vs language (vertical) problems
How does the DEM test differ from the K-D test?

find the Z score for
1. vertical time (total time A+B)
2. horizontal time (adjusted for errors)
3. errors
4. ratio of H / V adjusted times
and compare these to percentile rank table, using negative Z score for time and positive Z score for ratios
How do we score the DEM?
adjusted time = time x 80 / (80-o+a)
How do we calculate DEM adjusted times?
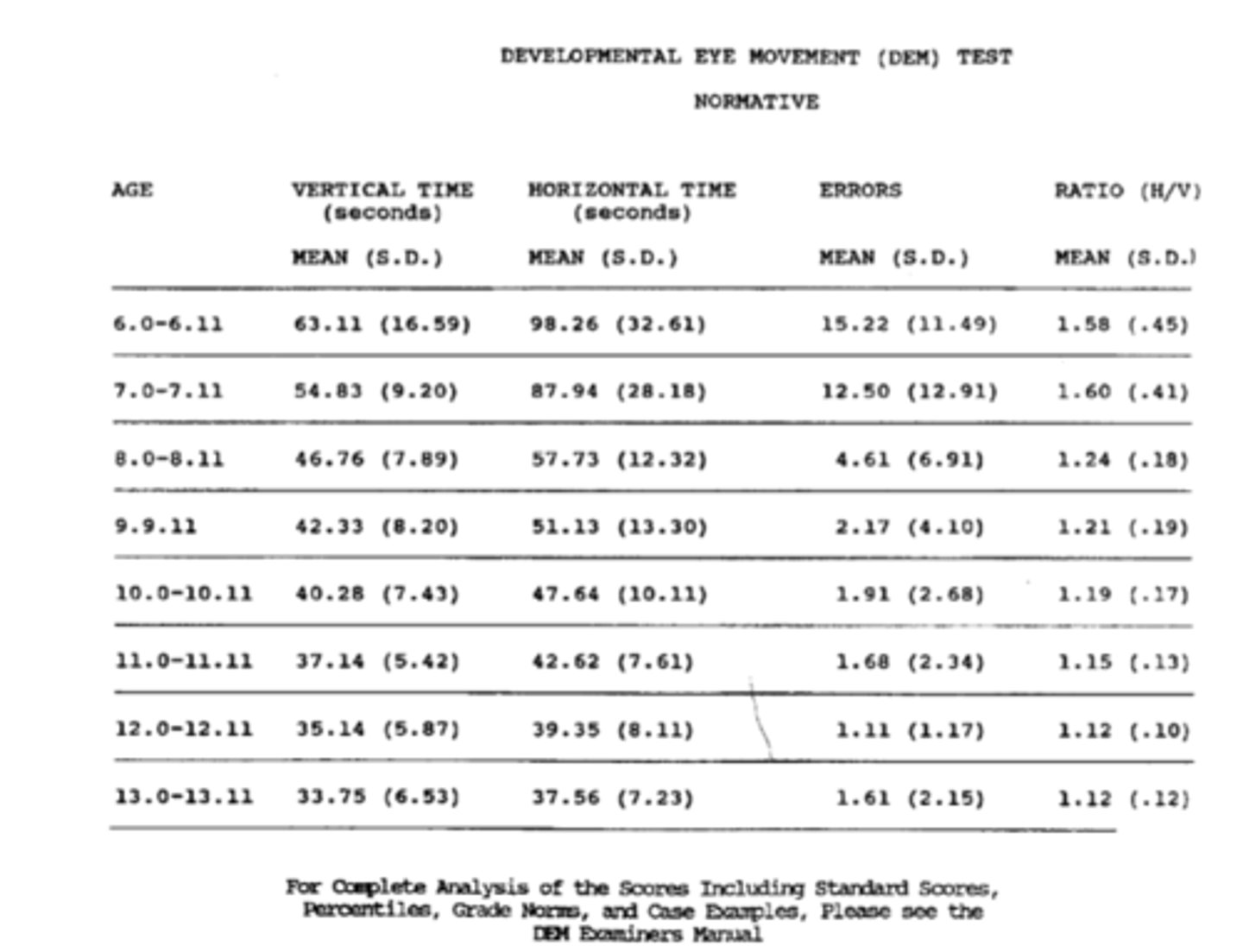
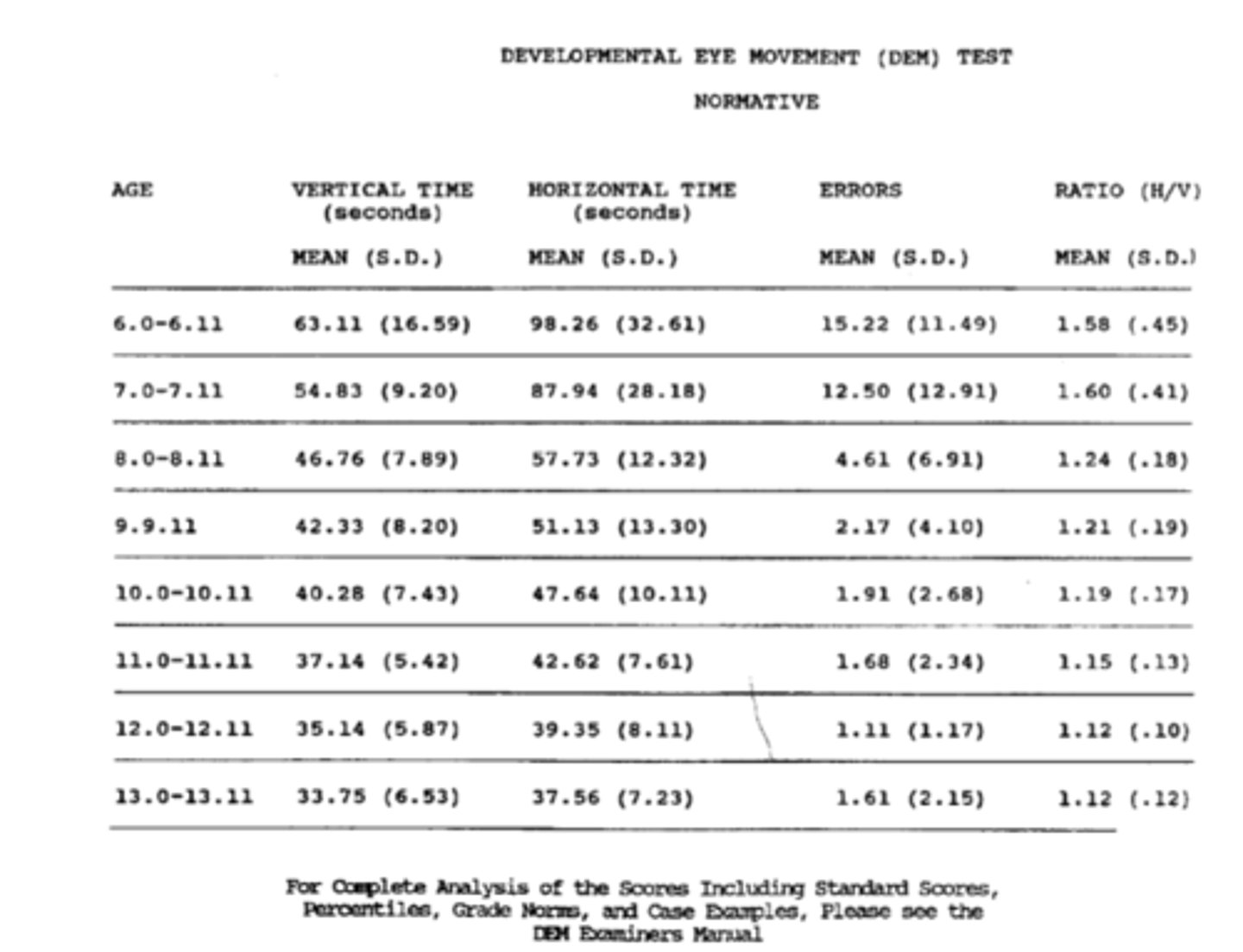
vertical = 2.22 = 1%ile
horizontal adjusted = 1.10 = 14%ile
ratio = -0.049 = 31%ile
Ex) find the percentile of the vertical, horizontal adjusted, and ratio.

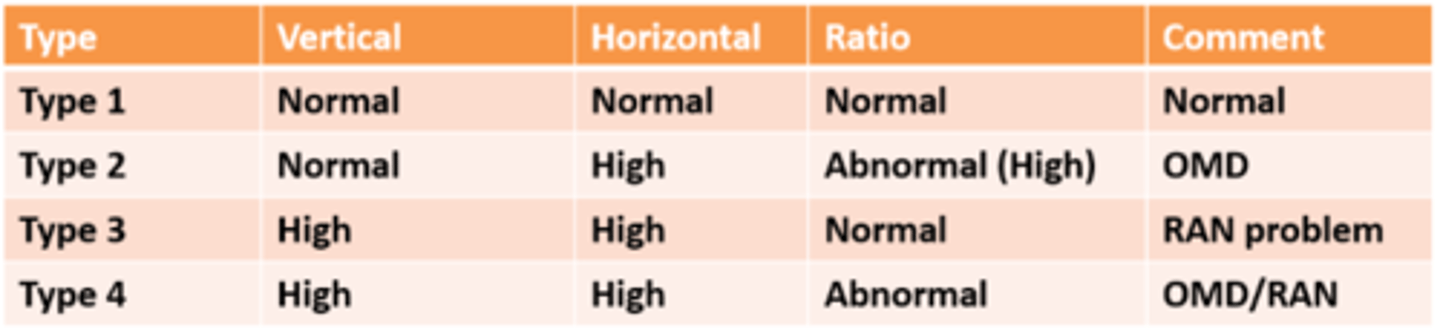
normal vertical
high horizontal
high ratio
= oculomotor dysfunction OMD
How do we know if a child has a saccadic problem (type 2) from their DEM results?
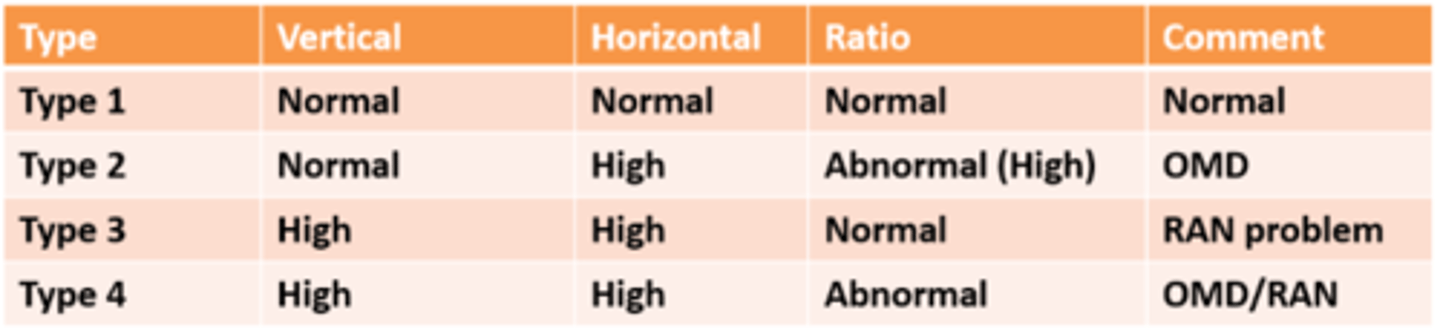
high vertical
high horizontal
normal ratio
= rapid automatic naming RAN problem
How do we know if a child has a language problem (type 3) from their DEM results?
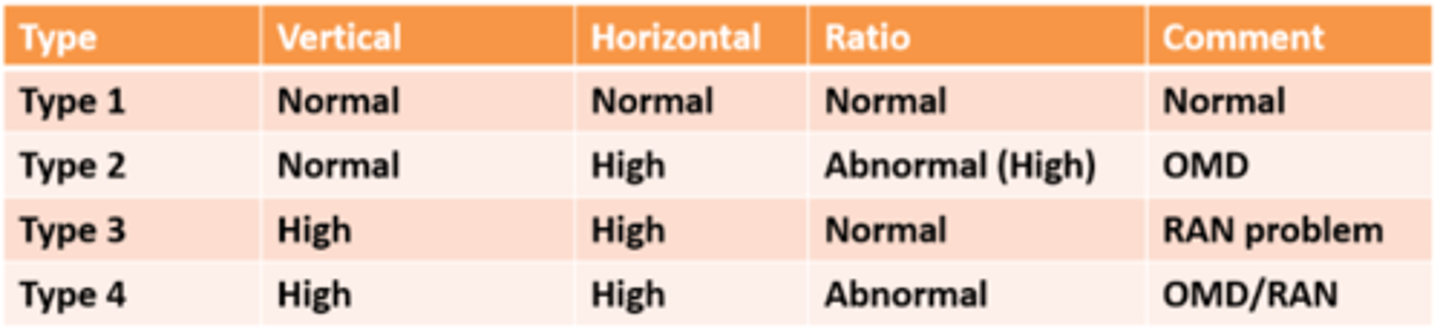
high vertical
high horizontal
abnormal ratio
= both
How do we know if a child has a saccadic and language problem (type 4) from their DEM results?
Readalyzer
Right Eye
What 2 eye tracking tests do we use for saccades?

Readlyzer = pt wears goggles to read so eye movements can be recorded and compared to norms
RightEye = no goggles, pt just looks at various targets so eye movements can be recorded
What is the difference between the Readalyzer and RightEye programs?
