Suture Materials and Patterns SA
1/157
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
What is suture’s important role in wound repair?
provides hemostasis
supports healing tissue by apposing and supporting tissue layers
Tissues have different requirements for suture support, depending on what?
type of tissue
anticipated duration of healing
What tissue type needs support for only a few days?
muscle, subcutaneous tissue, skin
What tissue type needs support for weeks?
fascia
What tissue type needs support for months?
tendon
Healing of wounds may be delayed by what?
infection
obesity or malnutrition
neoplasia
drugs
collagen disorders
hypoproteinemia
radiation therapy
What is the function of suture?
to maintain apposition of tissue until wound’s tissue strength returns
What characteristics describe the ideal suture?
easy to handle
reacts minimally in tissue
inhibits bacterial growth
holds securely when knotted
resists shrinking in tissue
absorbs with minimal reaction after the tissue has healed
noncapillary
nonallergenic
noncarcinogenic
nonferromagnetic
True or false: the ideal suture material does not exist.
True
What is the most commonly used standard for suture size?
United States Pharmacopeia (USP)
What is the smallest suture size in USP?
12-0
What is the largest suture size in USP?
7
Is there any advantage to using a suture that is stronger than the tissue to be sutured?
No
The smallest diameter suture that will adequately secure wounded tissue should be used in order to what?
minimize trauma as the suture is passed through the tissue
reduce the amount of foreign material left in the wound
The flexibility of a suture is determined by what?
its torsional stiffness and diameter
What sutures are indicated for ligating vessels or performing continuous suture patterns?
flexible
Braided polyester sutures have what degree of stiffness?
intermediate
Nylon and surgical gut are relatively ___ compared with silk suture.
stiff
What influences the ease with which suture is pulled through tissue (its “drag”) and the amount of trauma it causes?
the surface characteristics of a suture
Sutures with _____ surfaces require greater tension to ensure good apposition of tissues and have less knot security.
smooth
Braided materials have more ____ than monofilament sutures.
drag
Braided materials are often coated to reduce what?
capillarity
What is the process by which fluid and bacteria are carried into the interstices of multifilament fibers?
capilarity
What sutures are considered noncapillary?
monofilament
Capillary suture materials should not be used in what sites?
those that are contaminated or infected
Sutures should be as strong as what?
the normal tissue through which they are being placed
What is measured by the force in pounds that the suture strand can withstand before it breaks when knotted?
knot tensile strength
Should tensile strength of the suture greatly exceed the tensile strength of the tissue?
No
What is defined as the holding capacity of a suture expressed as a percentage of its tensile strength?
relative knot security
What is defined as the strength required to untie or break a defined knot by loading the part of the suture that forms the loop?
knot-holding capacity
What is defined as the strength required to break an untied fiber with a force appliedd in the direction of its length?
tensile strength
Suture materials may be classified according to what?
their structure (monofilament vs multifilament)
their behavior in tissue (absorbable vs non absorbable)
their origin (synthetic vs organic vs metallic)
What type of suture is described by the following:
less tissue drag
do not have interstices
material can be damaged by forceps or needle holders and predispose to breakage
monofilament
Care should be used in handling monofilament suture because nicking or damaging the material with forceps or needle holders may do what?
weaken the suture and predispose it to breakage
Generally, is multifilament or monofilament more fliable and flexible?
multifilament
Multifilament suture may be coated to do what?
reduce tissue drag and enhance handling characteristics
What suture type is described by the following:
nonwicking
more memory
does not handle as well
monofilament
Which suture type is described by the following:
wicking
less memory
good handling
multifilament
Absorbable sutures of organic origin are what in regards to degradation in tissue?
gradually digested by tissue enzymes and phagocytized
Absorbable sutures of synthetic polymer origin are what in regards to degradation in tissue?
prinicpally broken down by hydrolysis
Nonabsorbable sutures are ultimately what in regards to behavior in tissue?
encapsulated or walled off by fibrous tissue
Absorbable suture materials lose most of their tensile strength within?
60 days
What is the most common nonsynthetic absorbable suture material which is made from the submucosa of sheep intestine ot the serosa of bovine intestine and elicits a notable inflammatory reaction?
catgut (surgical gut)
What suture is rapidly removed from infected sites or areas where it is exposed to digestive enzymes and is quickly degraded in catabolic patients?
surgical gut
When wet, knots ties with surgical gut suture may do what?
loosen
Synthetic abosrbable suture are broken down by what?
hydrolysis
What suture type causes minimal tissue reaction and infection or exposure to digestive enzymes does not significantly influence the rate of absorption of most?
synthetic absorbable suture
What types of synthetic absorbable sutures are more rapidly hydrolyzed in alkaline environments, but are relatively stable in contaminated wounds?
polyglactin 910 and polyglycolic acid
What synthetic absorbable sutures are rapidly degraded in infected urine?
polyglycolic acid, polyglactin 910, and poliglecaprone 25
What synthetic absorbable sutures are acceptable for use in sterile bladders and those infected with E coli?
polydioxanone, polyglyconate, and glycomer 631
Any suture that is degraded via hydrolysis may be at risk for accelerated degradation when the bladder is infected with what?
Proteus spp
What is the most common organic nonabsorbable suture?
silk
What type of suture is made by a special type of silkworm?
braided multifilament (organic nonabsorbable)
What type of suture has excellent handling characteristics and is often used in cardiovascular procedures?
organic nonabsorbable suture
What organic nonabsorbable suture does not maintain significant tensile strength after 6 months and is therefore contraindicated for use in vascular grafts?
silk
What type of suture should be avoided in contaminated sites?
organic nonabsorbable suture (silk)
Synthetic nonabsorbable suture is marketed as?
braided multifilament threads or monofilament threads
Synthetic nonabsorbable sutures are typically ____ and induce ______ tissue reaction.
strong, minimal
What should never be implanted in the body because toxic substances are released during their degradation and their use may result in abscess or tumor formation?
cable ties
What is the most commonly used metallic sutures?
stainless steel
Surgical steel is strong and inert with ____ tissue reaction.
minimal
What type of suture has a tendency to cut tissue (or your fingers) and may fragment and migrate?
metallic sutures (stainless steel)
What suture is stable in contaminated wounds and is the standard for judging knot security and for judging tissue reaction to suture materials?
stainless steel
Considerations for suture selection include?
length of time the suture will be required to help stengthen the wound or tissue
risk of infection
effect of the suture material on wound healing
dimension and strength of the suture required
What sutures should be used in skin to prevent wicking or capillary transport of bacteria to deeper tissue?
monofilament sutures
What monofilament nonabsorbable sutures generally have good relative knot security and are relatively non-capillary?
synthetic
Absorbable sutures may be used in skin, but they should ultimately be removed because?
absorption requires contact with body fluids
What sutures are used to obliterate dead space and reduce tension on skin edges?
subcutaneous sutures
What suture material is preferred for subcutaneous sutures?
multi- or monofilament absorbable
Most surgeons routinely close the rectus fascia with what pattern?
simple continuous
When a continuous pattern for abdominal closure is used, what suture should be used?
a strong nonabsorbable or standard absorbable monofilament suture with good knot security
What size suture is preferred for an abdominal closure with continuous suture pattern?
one size larger than would normally be used
When using a continuous pattern for abdominal closure knots should be tied carefully and how many knots (throws) should be placed?
three or four sqaure knot (six or eight throws)
What suture may be may be preferable for a continuous pattern abdominal closure to prevent large amounts of foreign material from remaining permanently in the incision?
standard absorbable suture
What tissue type has poor holding power and is difficult to suture?
muscle
What should you consider when choosing a suture pattern to suture muscle?
sutures placed parallel to the muscle fibers are likely to pull out
What suture material should you use for muscle?
absorbable or nonabsorbable may be used
Suture material used for tendon repair should be ____, ____, and ____.
strong, nonabsorbable, minimally reactive
Suturing tendons with what type of needle is generally less traumatic to those tissues?
taper or taper-cut needle
What size suture should be used for tendons?
the largest suture that will pass without trauma through the tendon
Parenchymal organs (liver, spleen, and kidneys) are generally sutured with what type of suture?
absorbable monofilament
What type of suture (inluding brand name) rapidly dissolves when incubated in sterile urine (6 days) or infected urine (3 days), so it should never be used in a bladder?
polyglycolic acid (Dexon)
What suture is preferred in infected or contaminated wounds?
absorbable suture
True or false: Sutures should be avoided in highly contaminated or infected wounds.
True
Multifilament nonabsorbable sutures should not be used in ____ tissue.
infected
What suture should be avoided in infected or contaminated wounds?
surgical gut
Vessels should be ligated with what suture?
absorbable suture material
Selection of suture needle depends on what?
type of tissue to be sutured
topography of the wound
characteristics of the needle
Most surgical needles are made from what?
stainless steel
What is defined as the amount of angular deformation a needle can withstand before becoming permanently deformed?
surgical yield
What is defined as the needle’s resistance to breaking under a specified amount of bending?
ductility
What is related to the angle of the point and the taper ratio of the needle?
sharpness
The sharpest needles have what?
a long, thin, tapered point with smooth cutting edges
The fraction associated with curved surgical needles indicates what?
how much of a complete circle the needle makes
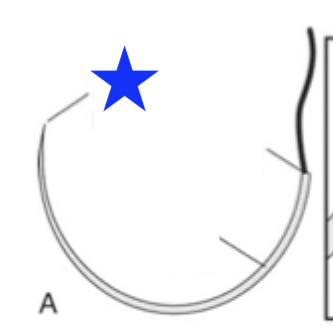
What part of the surgical needle is indicated by the blue star?
needle point
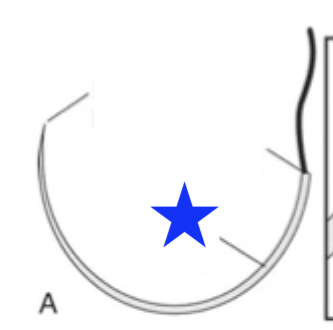
What part of the surgical needle is indicated by the blue star?
needle body
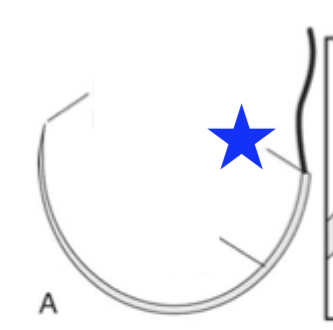
What part of the surgical needle is indicated by the blue star?
swaged end
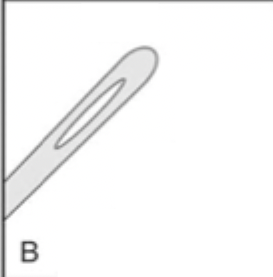
What type of surgical needle is shown?
closed

What type of surgical needle is shown?
french
What are the most commonly used surgical needles in veterinary medicine?
three-eights (3/8) and one-half (1/2) circle needles