Gen Eco Final Exam
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
T or F: Water has a tremendous capacity to hold heat
True
What happens to water as it gets warmer?
It becomes less dense
T or F: Biomes that experience high humidity exhibit less variation in temperatures.
True
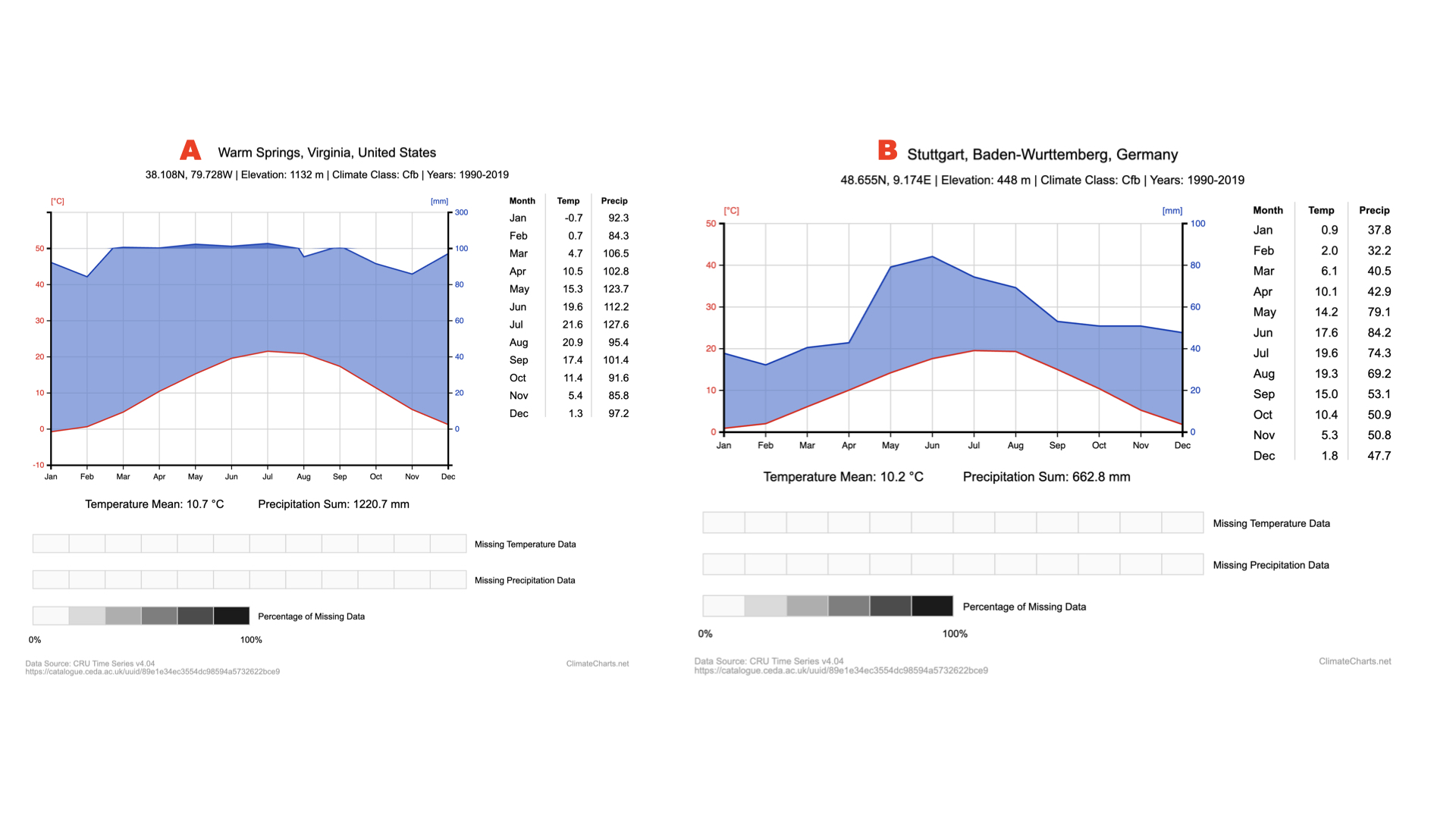
Above you can see climate diagrams for 2 different forests, (A) the George Washington National Forest in VA and (B) the Black Forest in Germany. How do these two forests differ in terms of precipitation ranges?
Forest A exhibits a greater amount of precipitation but less variation than forest B.
What factors determine the nature of a given biome?
Elevation, Precipitation, Latitude, Temperature
All of them
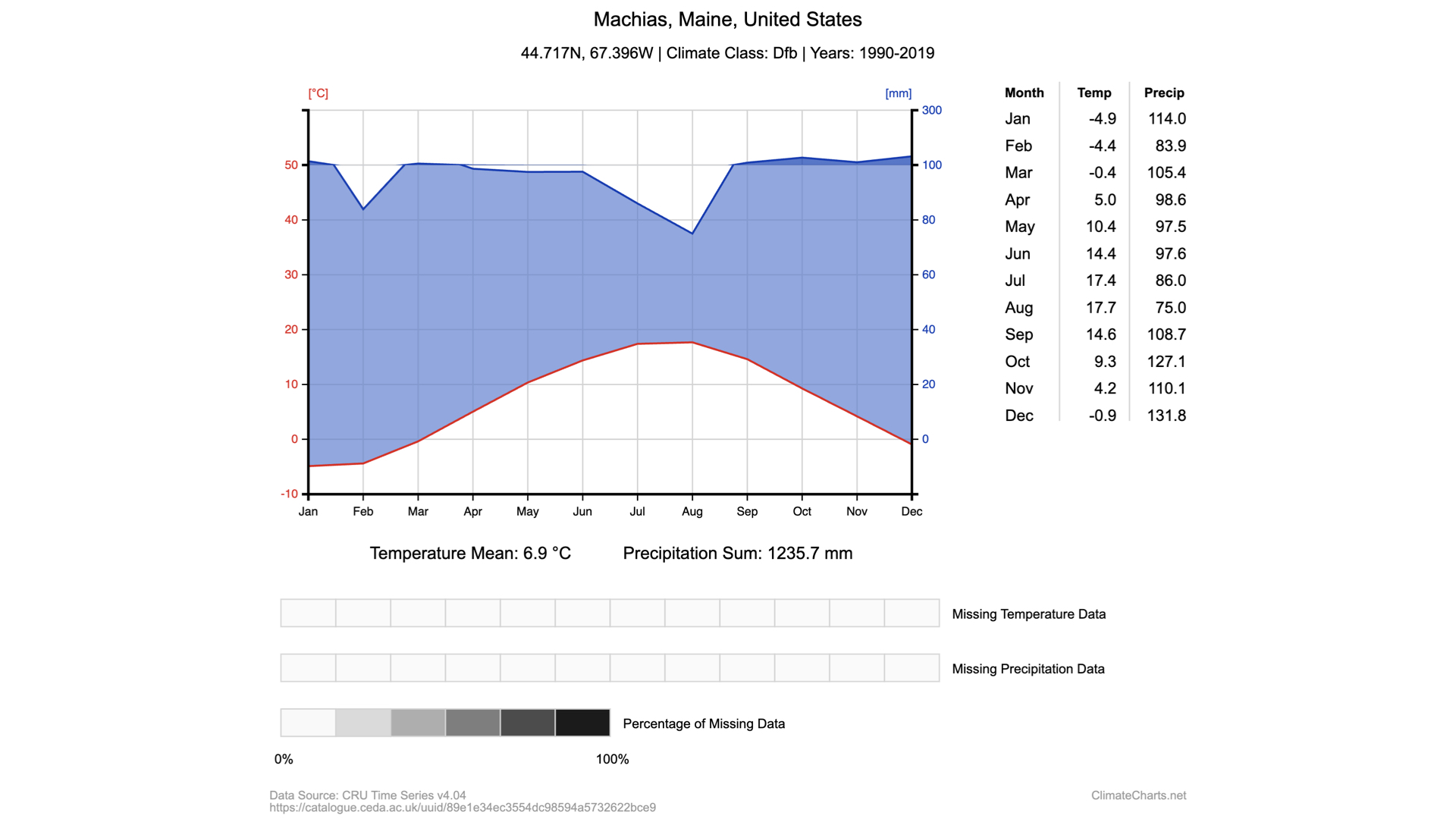
What is being graphed in the diagram above?
Precipitation and temperature
Why do cold water currents sink below warm water currents?
Cold water is more dense than warm water
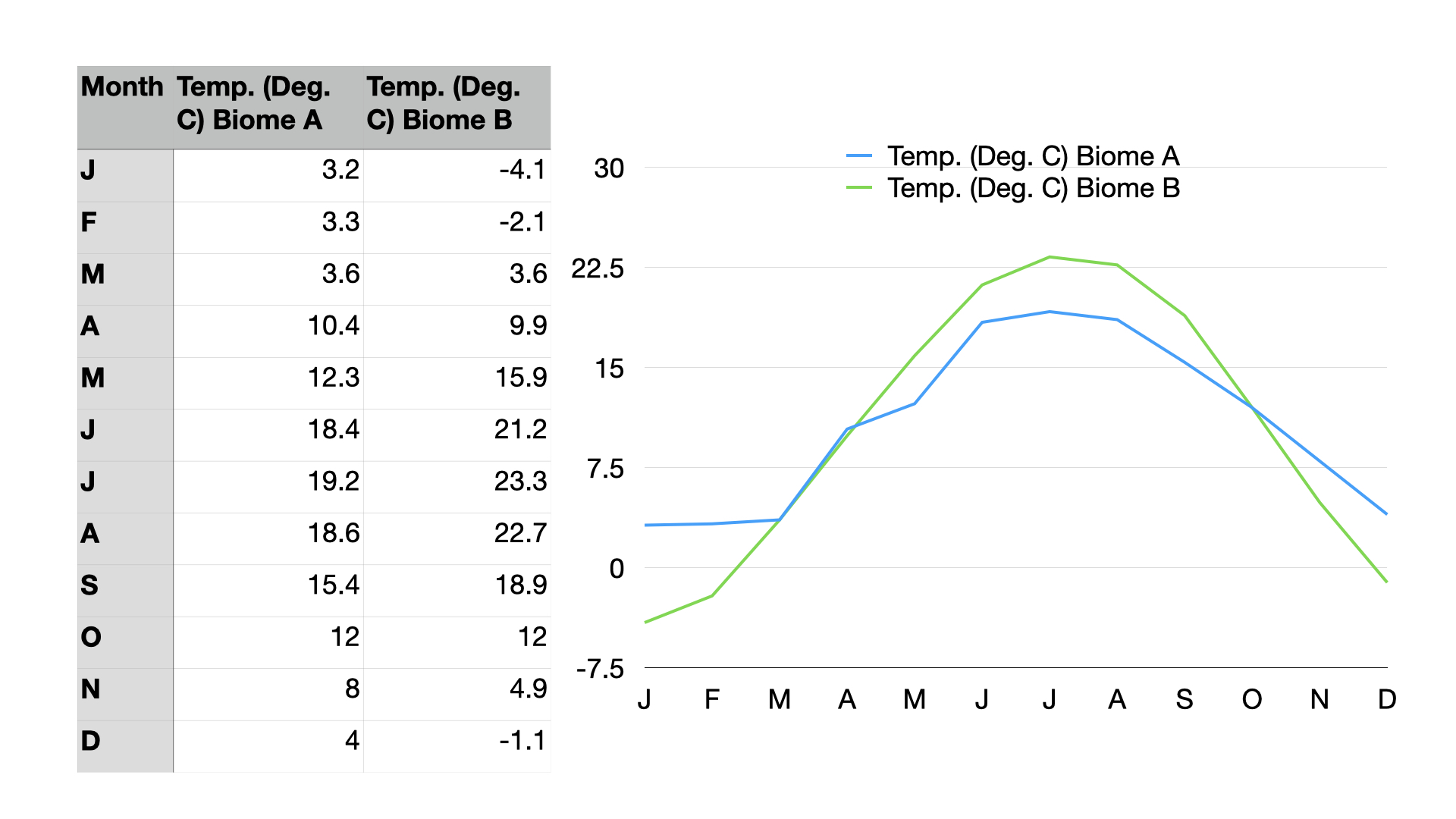
The data shown above shows temperatures for two different hypothetical biomes, A and B. One is a terrestrial biome and the other is an adjacent aquatic biome. Which is the terrestrial biome and which is the aquatic biome?
B is the terrestrial biome and A is the aquatic biome
Where do we expect to see greater variation in temperatures? (Humidity)
In areas with low humidity
T or F: Biomes that experience high humidity exhibit more variation in temperatures.
False
Where do we expect to see greater variation in temperatures? (equator)
Farther from the equator
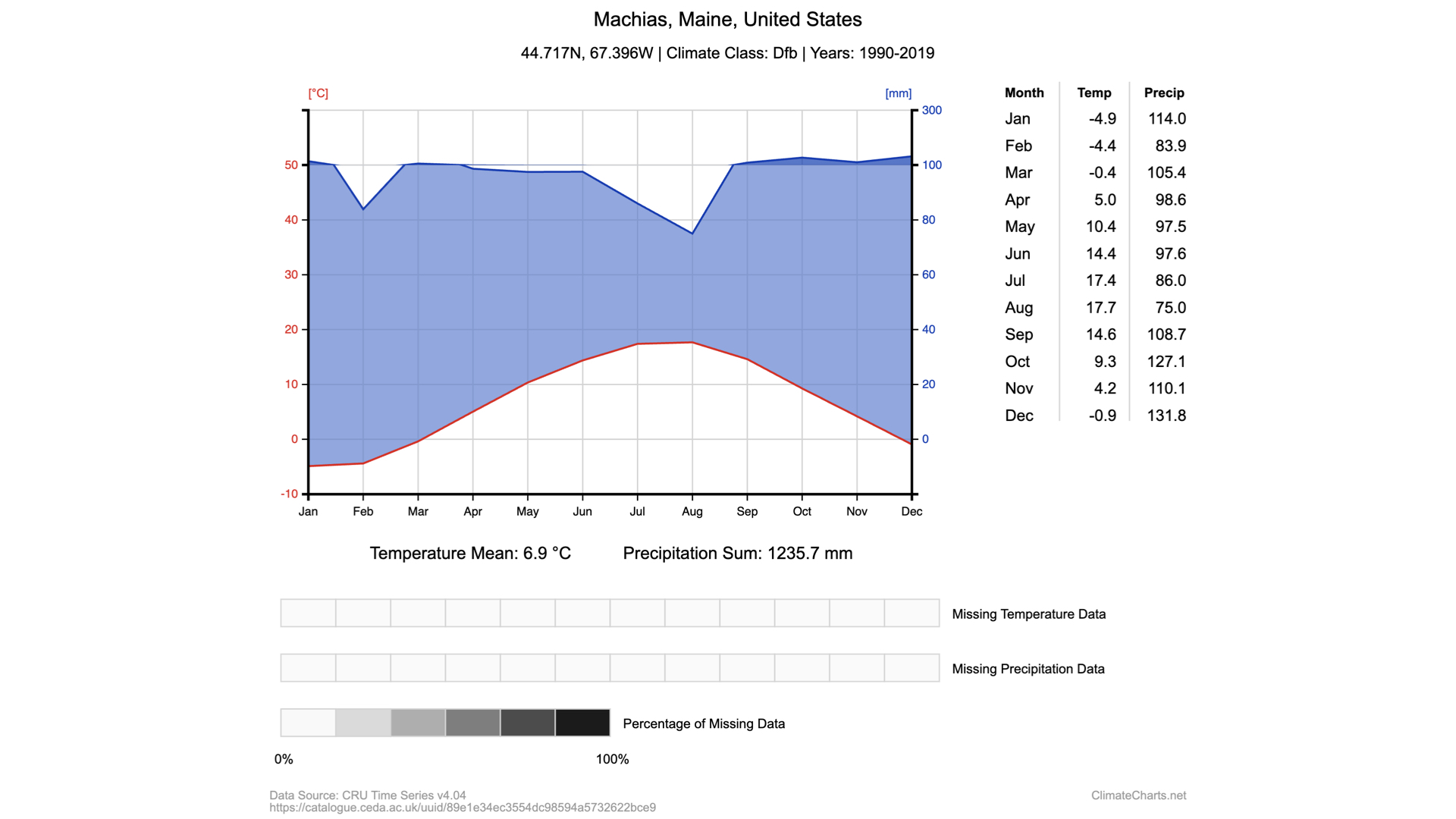
What can you tell about Machias from just the graph shown above? (what and how long)
Precipitation and temperature changes over the course of a calendar year
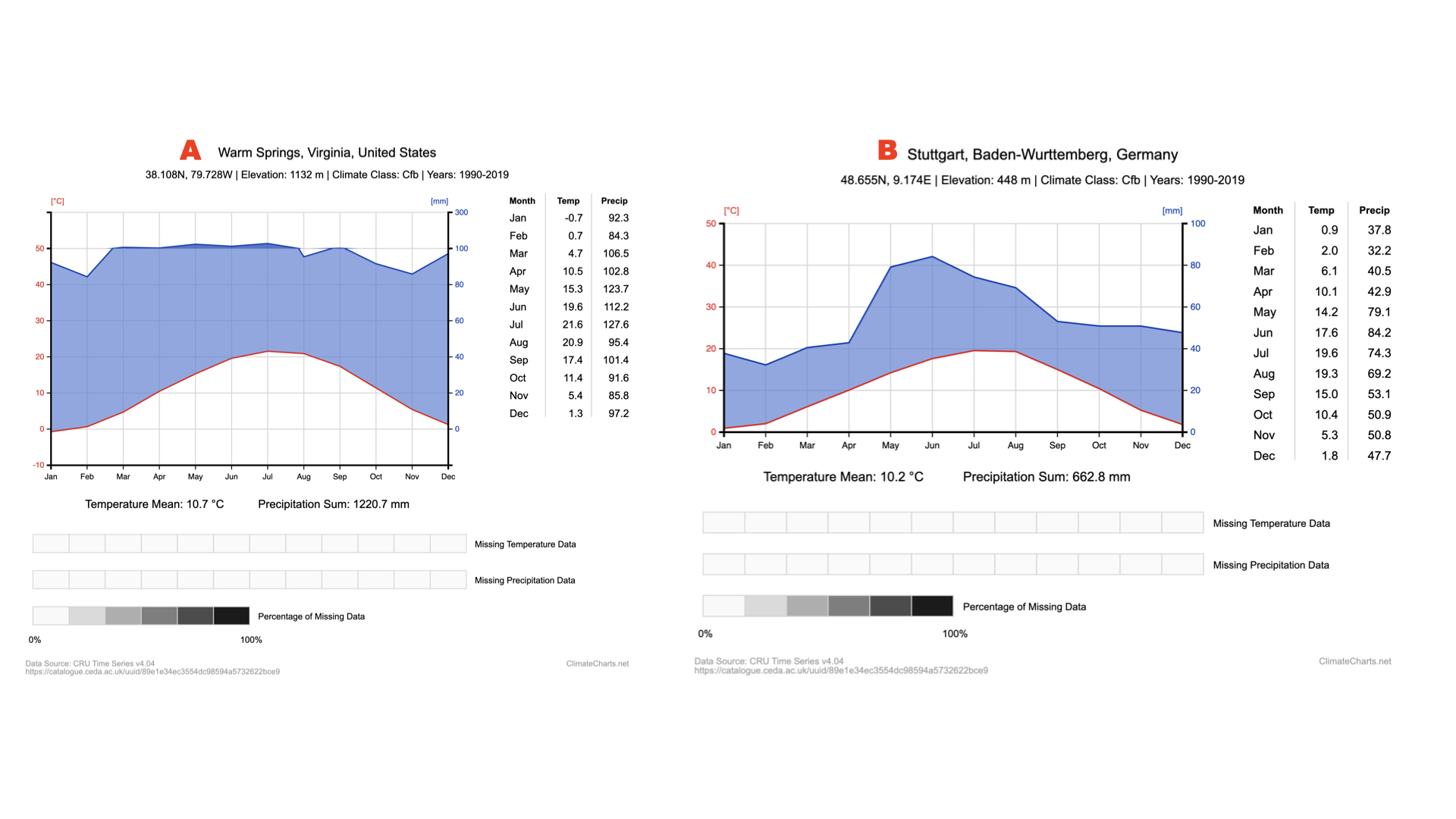
Above you can see climate diagrams for 2 different forests, (A) the George Washington National Forest in VA and (B) the Black Forest in Germany. How do these two forests differ in terms of temperature ranges?
Forest A exhibits greater variation in temperature than forest B
T or F: Water has a poor capacity to hold heat?
False
What happens to water as it gets warmer?
It becomes less dense
T or F: Biomes that experience high humidity exhibit more variation in temperatures.
False
Which of the following statements best describes the variation in temperatures seen in aquatic and terrestrial environments?
Terrestrial environments experience more variation in temperatures than aquatic environments do
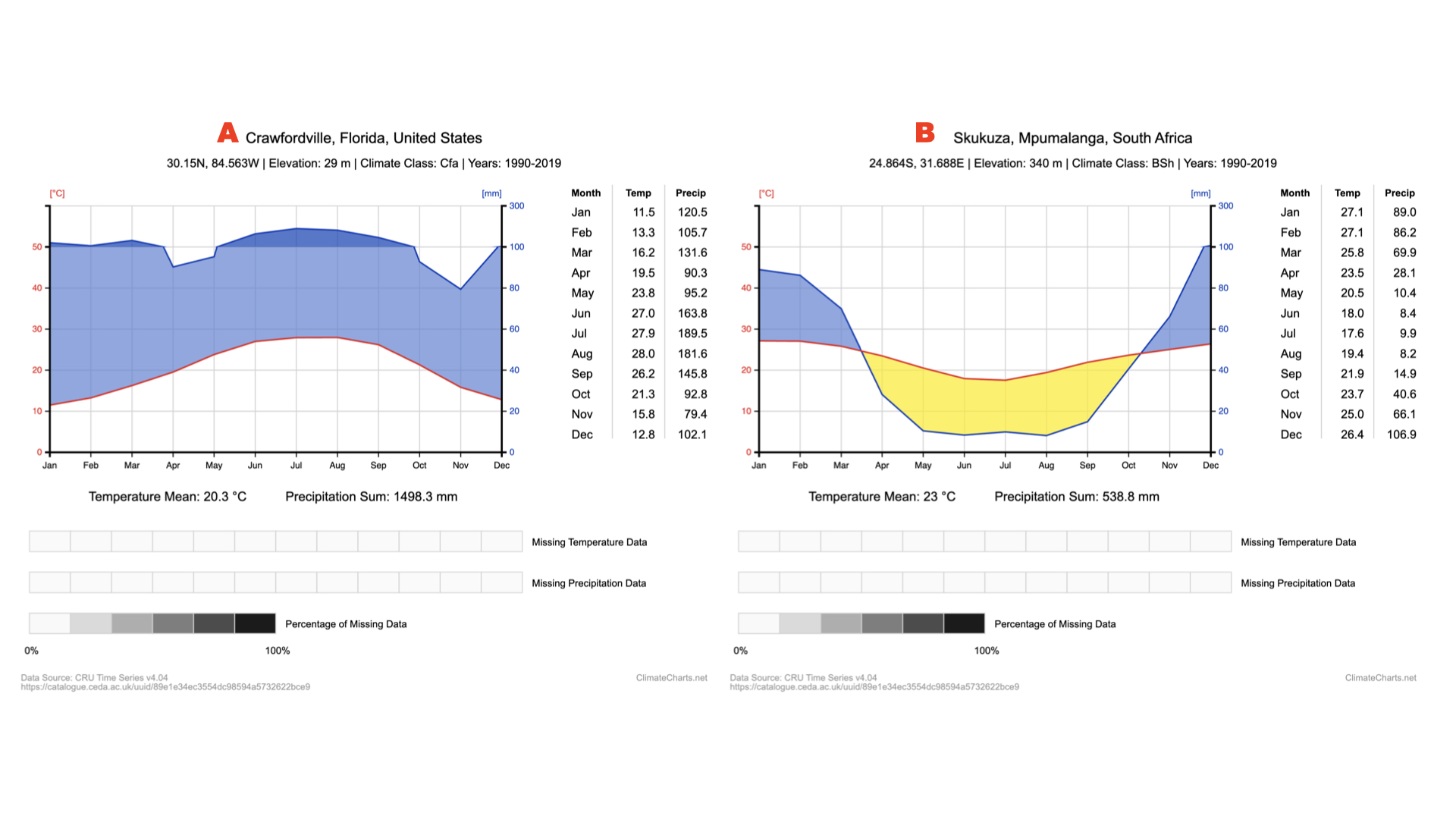
Above you can see climate diagrams for 2 different sub-tropical savannahs, (A) the Appalachicola National Park in FL and (B) the Kruger National park in South Africa. How do these two savannahs differ in terms of temperature ranges?
Savannah A exhibits greater temperature variation than savannah B.
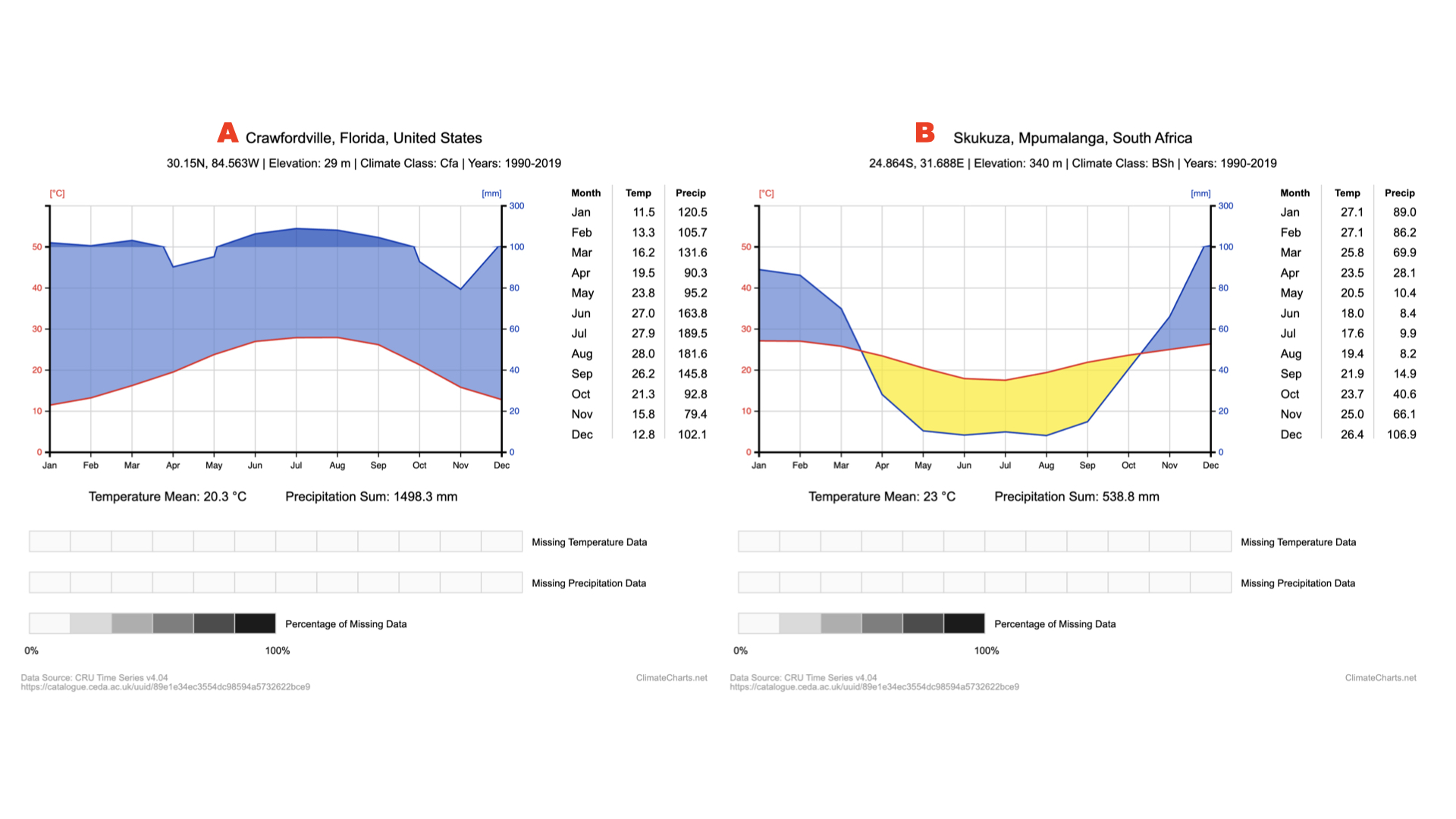
Above you can see climate diagrams for 2 different sub-tropical savannahs, (A) the Appalachicola National Park in FL and (B) the Kruger National park in South Africa. How do these two savannahs differ in terms of precipitation ranges?
Savannah A exhibits a greater amount of precipitation and more variation than savannah B.
T or F: Organisms lose heat to cellular respiration and metabolism.
False
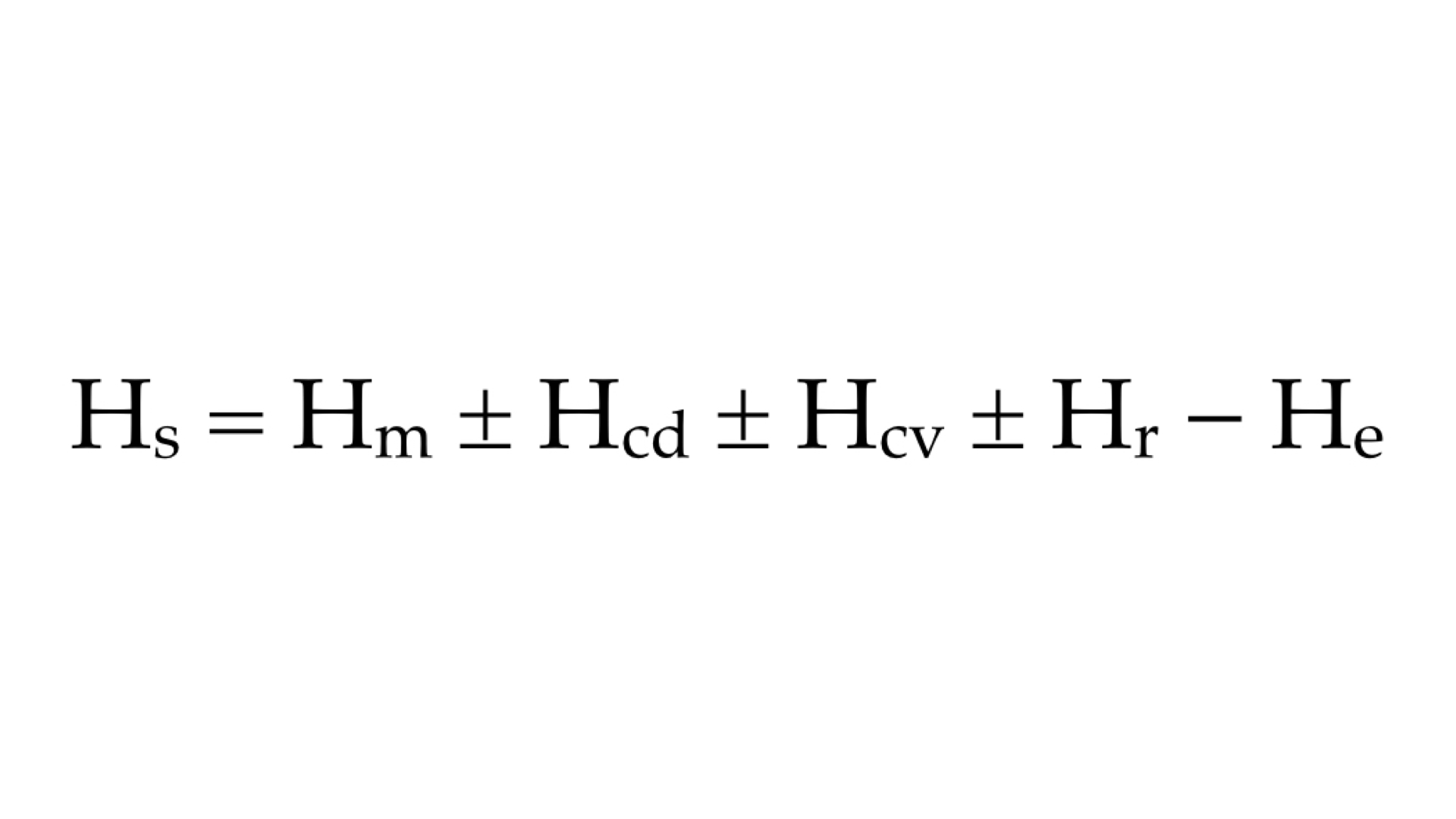
Which element of the equation for stored heat shown above is an example of how you can lose body heat by sitting on a cold surface?
Hcd
T or F: Ectotherms do not regulate their internal temperatures but allow them to vary with the temperature of their environment.
False
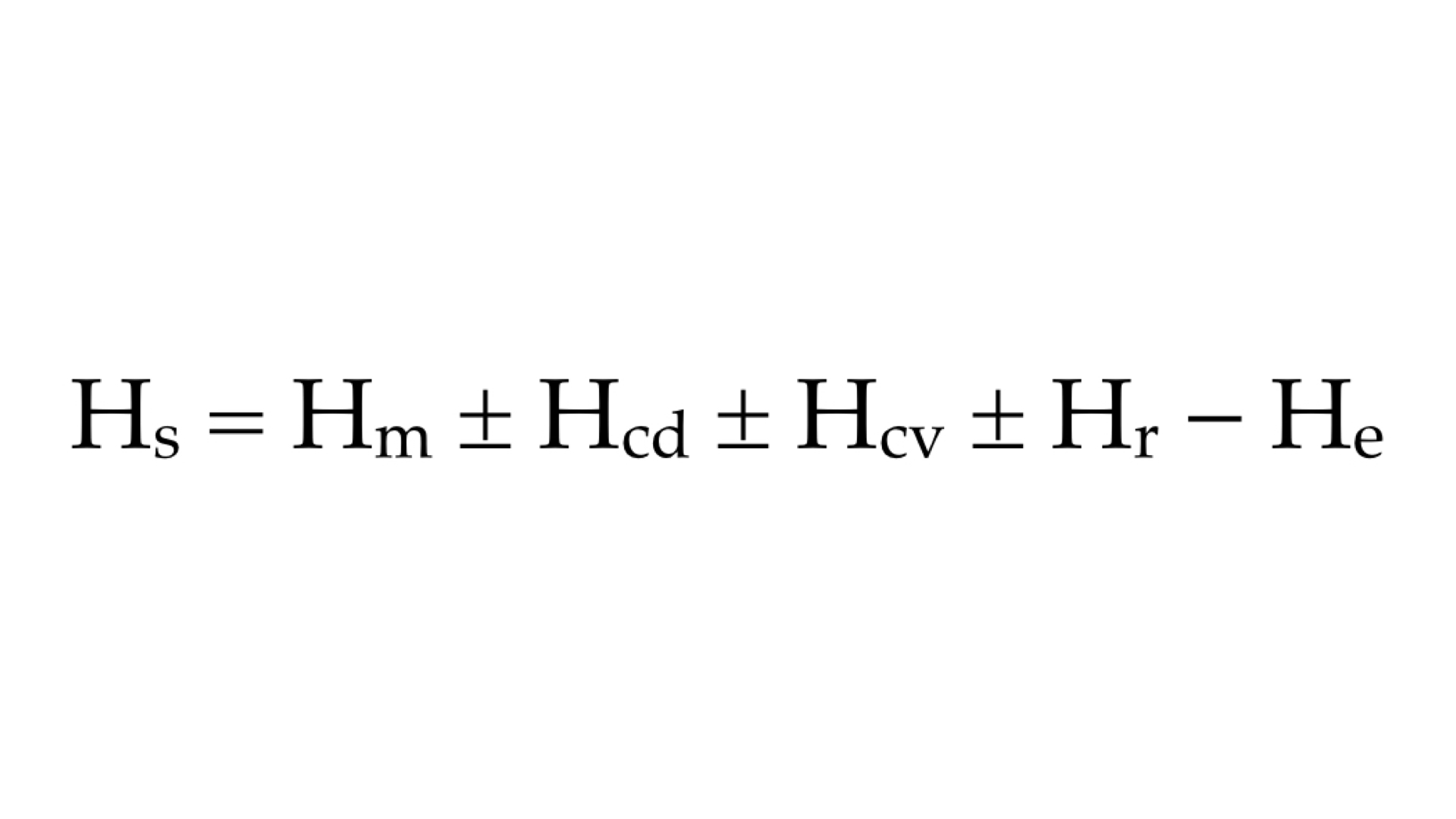
Which element of the equation for stored heat shown above is an example of how you can lose body heat by stepping into a walk-in freezer?
Hcv
Which of the following groups of organisms maintain their internal temperature largely by external means?
ectotherm
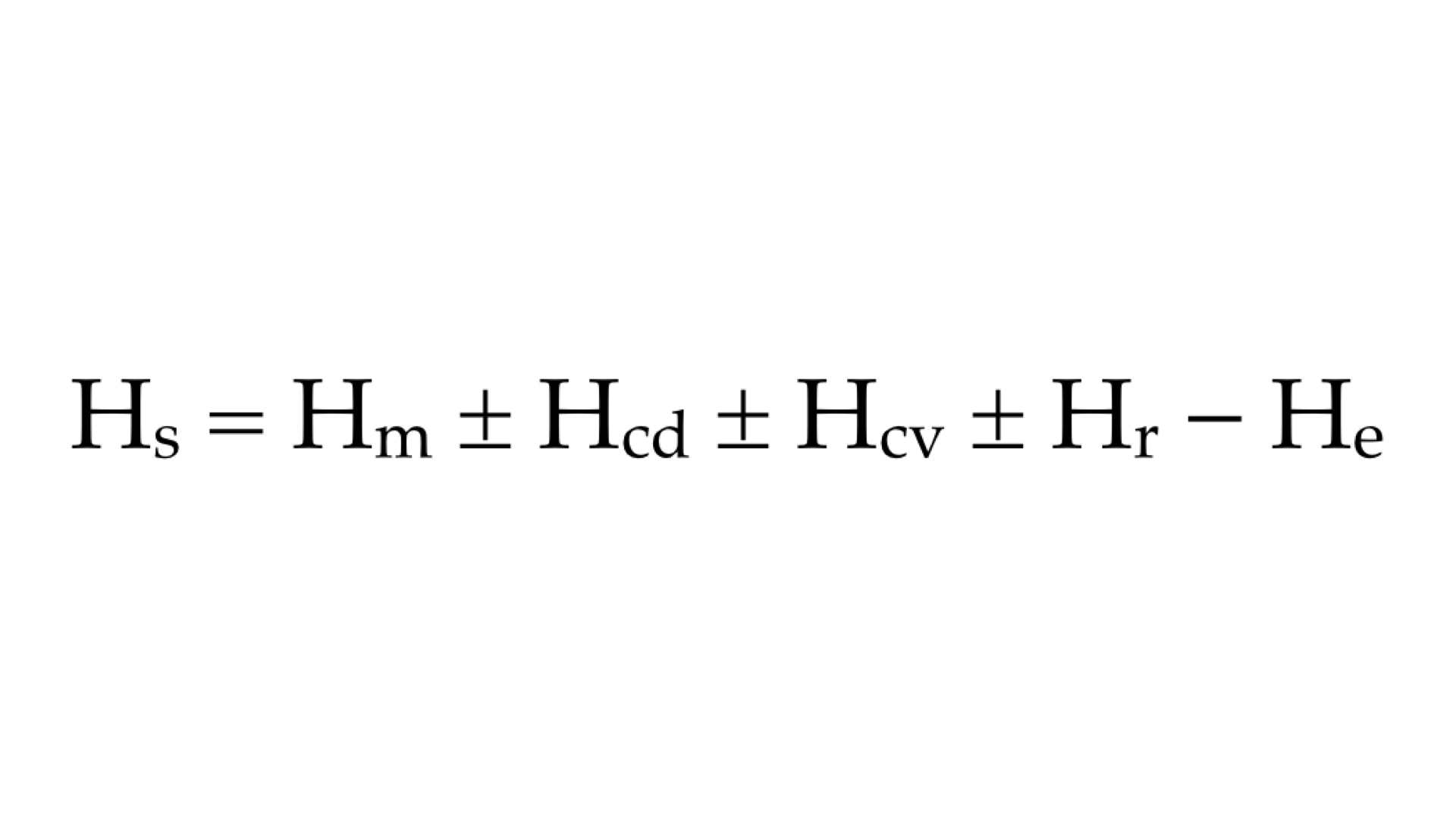
Which element of the equation for stored heat shown above is an example of how you can lose body heat through sweating?
He
Which of the following groups of organisms maintain their internal temperature largely by internal means?
endotherm
T or F: Isosmotic organisms have internal salt concentrations lower than that seen in their environment.
False
If a fish were moved into an environment that had a higher salt concentration than the fish itself, which term best describes the fish in this situation?
Hyposmotic
T or F: The process of cellular respiration requires the consumption of water.
False
If a fish were moved into an environment that had a lower salt concentration than the fish itself, what would happen to the fish?
It would acquire water from its environment
T or F: Hyperosmotic organisms have internal salt concentrations higher than that seen in their environment.
True
T or F: For most organisms, their internal temperature matches that of their environment in magnitude and variation
False
If a fish were moved into an environment that had a higher salt concentration than the fish itself, what would happen to the fish?
It would lose water to its environment
T or F: Organisms generate heat as a byproduct of cellular respiration and metabolism.
True
T or F: The process of cellular respiration involves the production of water.
True
T or F: Aquatic organisms with a higher internal salt concentration than that of their environment will tend to lose water from their tissues to their environment.
False
T or F: Most organisms maintain a relatively stable internal temperature which differs from that of their environment.
True
T or F: Hypoosmotic organisms have internal salt concentrations higher than that seen in their environment.
False
Homeostasis definition
The ability of organisms to regulate their internal environment
T or F: Whether a given trait confers an increase in fitness depends on whether the organism possessing it produces more viable offspring than others in their population.
True
Put the following terms in order from most inclusive (1) to least inclusive (4)- Community Organism Population Ecosystem
Community (2) Organism (4) Ecosystem (1) Population (3)
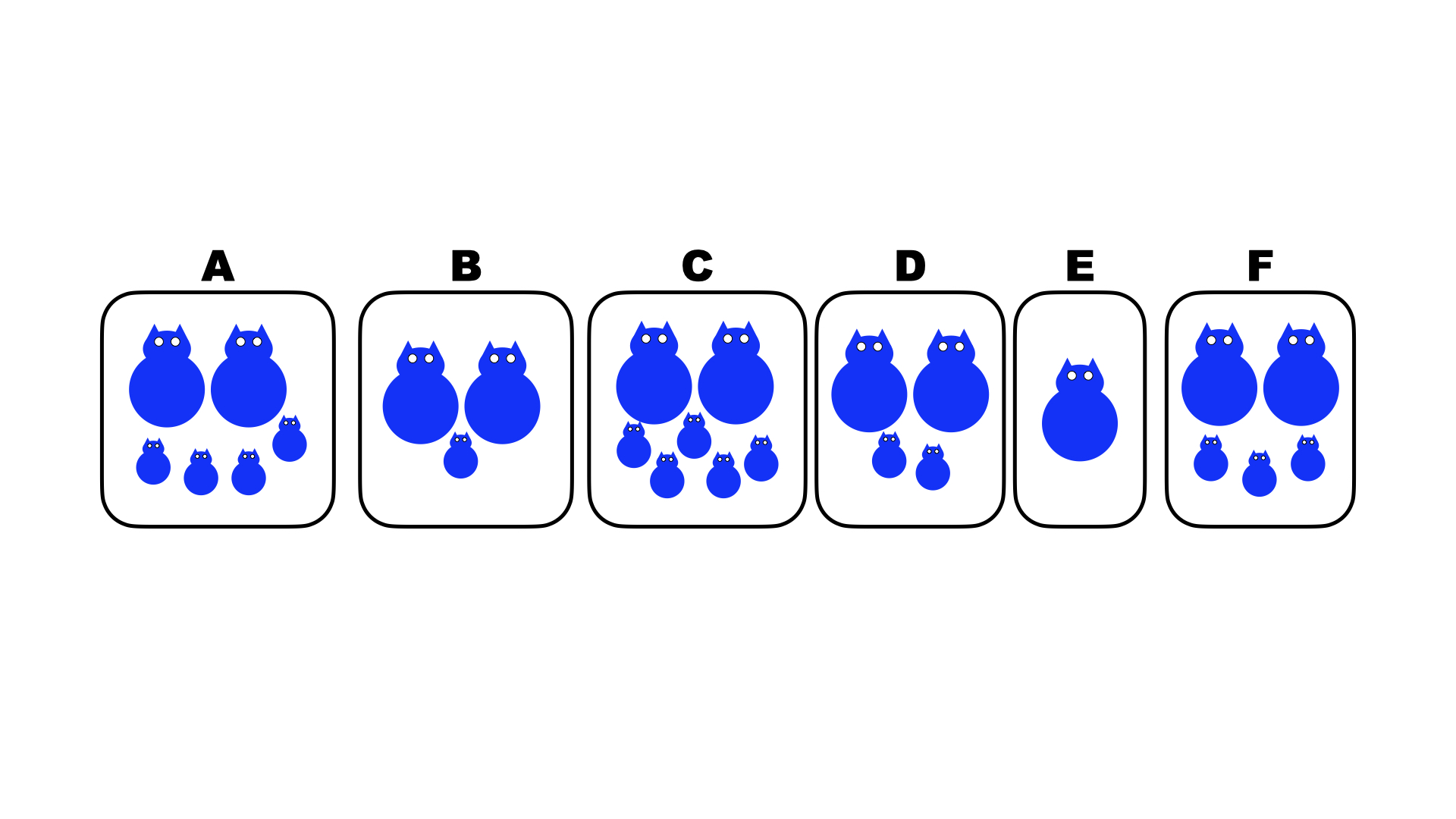
Which of the above pairs of organisms has the lowest non-zero value for fitness?
B
One recent estimate of the number of species on Earth, made by the IUCN, says that there are approximately how many species of organisms on Earth today?
2,000,000
What did Charles Lyell's geological theory of uniformitarianism provide Charles Darwin with as he was formulating his theory of evolution by natural selection?
It showed that Earth is much older than previously thought, which would allow time for evolution to have produced the biodiversity we see on Earth.
Evolution cannot occur in individuals because...
...evolution is described by a change in the frequency of traits in a given population.
At which level of the ecological hierarchy can the frequency of traits be measured?
population
Which of the following statements best describes the difference between natural selection and artificial selection?
Artificial selection occurs much more quickly than natural selection because it is directed by humans
At which level of the ecological hierarchy does evolution occur?
population
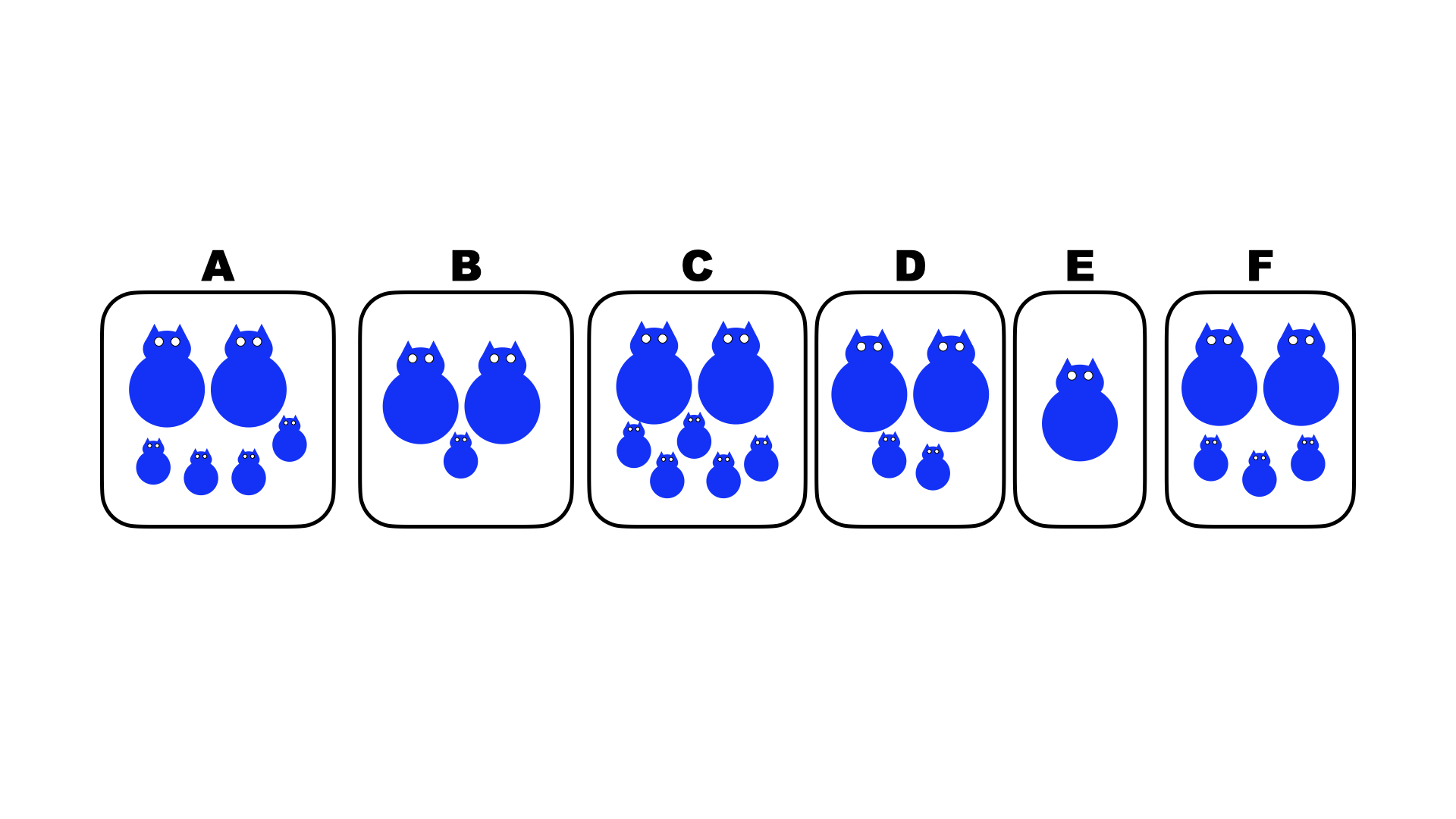
Which of the above pairs of organisms has the lowest fitness?
B
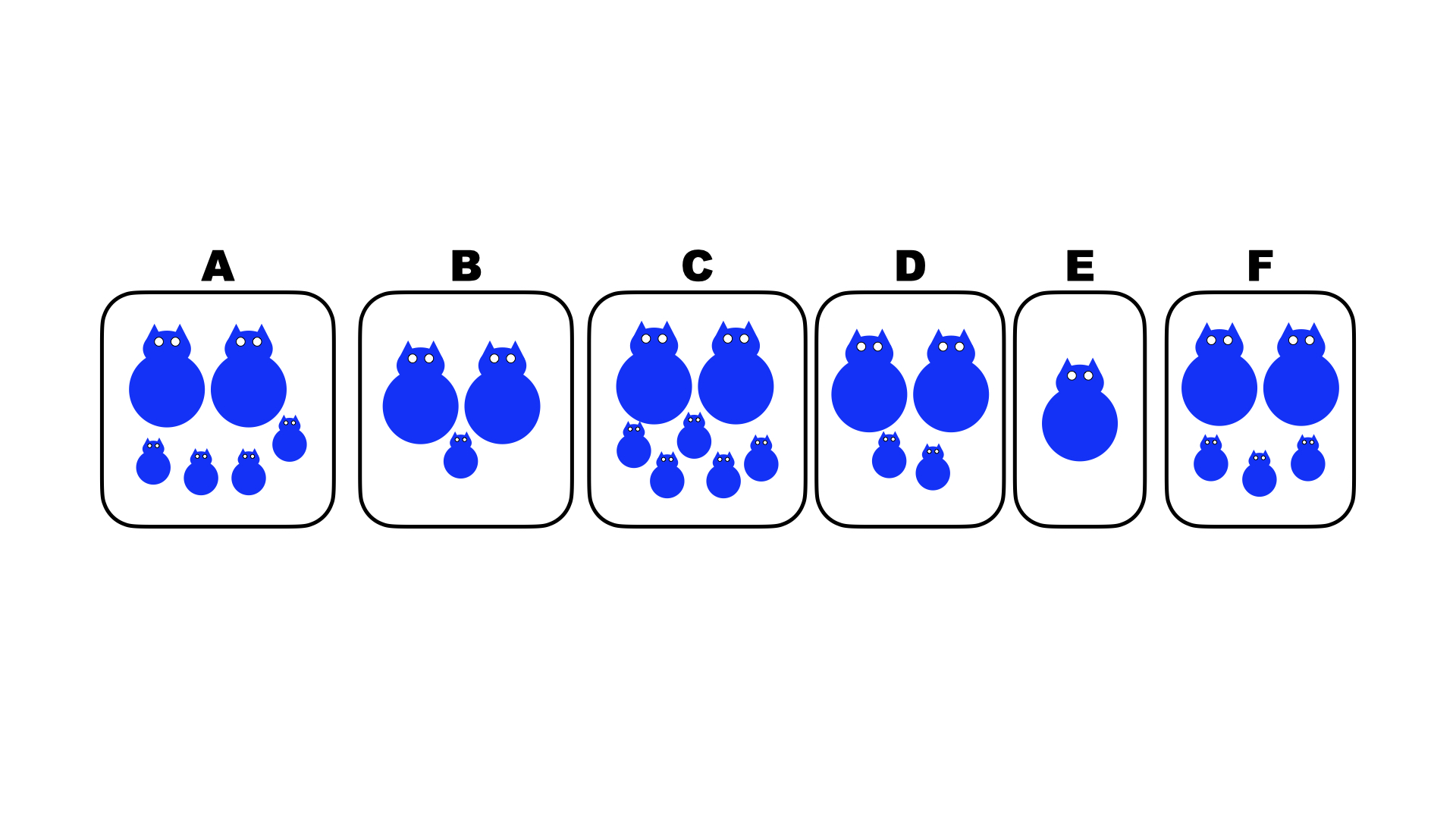
Which of the above pairs of organisms has the highest fitness?
C
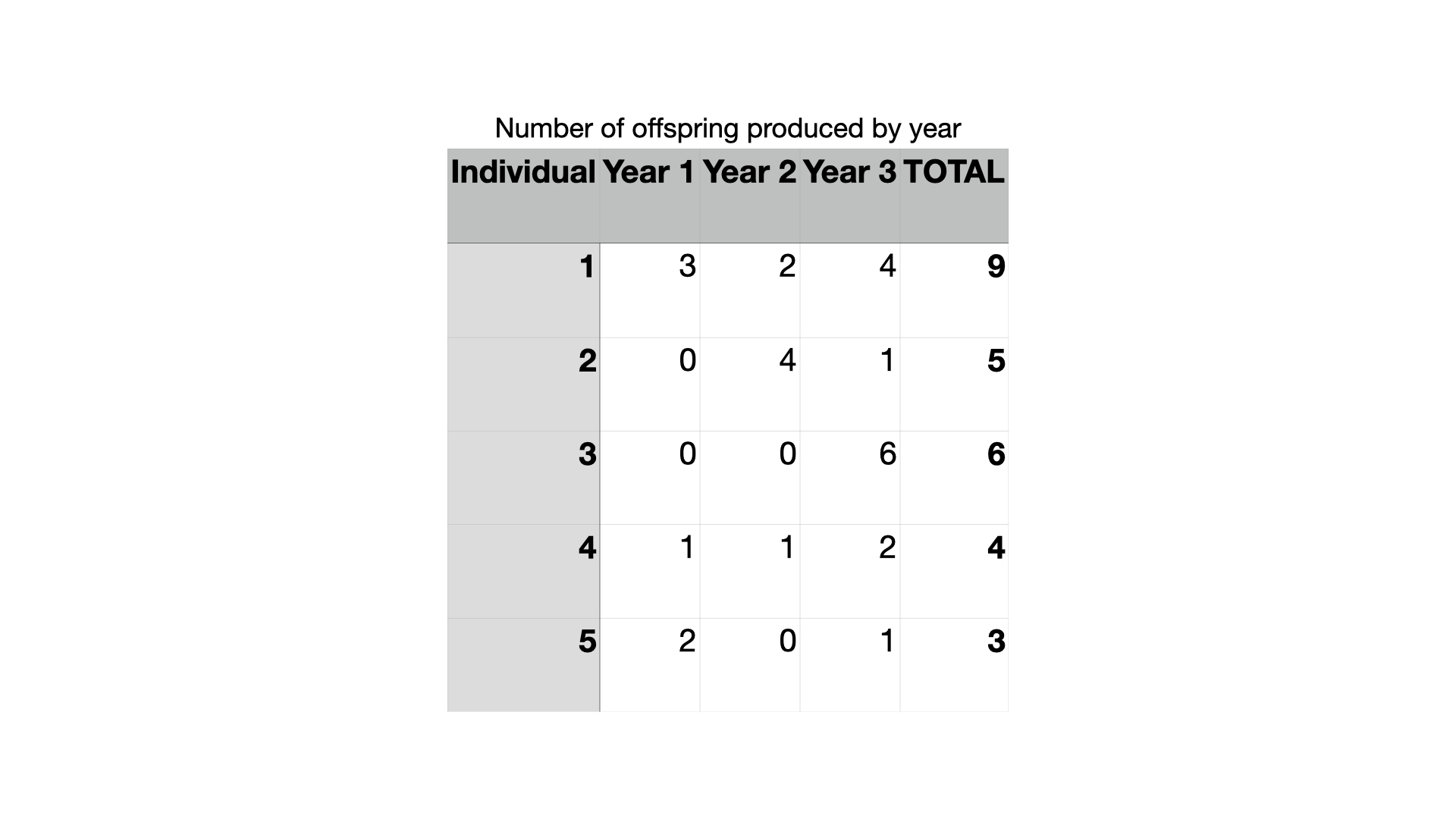
Which of the hypothetical organisms from the table above has the lowest cumulative fitness?
organism 5
At which level of the ecological hierarchy does natural selection operate?
organism
T or F: Darwin was able to describe the means by which organisms inherit traits
False
T or F: Evolution can happen within the span of one organism's life time
False
How do we define evolution in ecological terms?
A change in allele frequencies within a population of organisms
Which of the following hypothetical organisms has the highest fitness?
One who is in the average size class for their species with a greater than average number of offspring
How do we define fitness in ecological terms?
The number of viable offspring produced by an individual
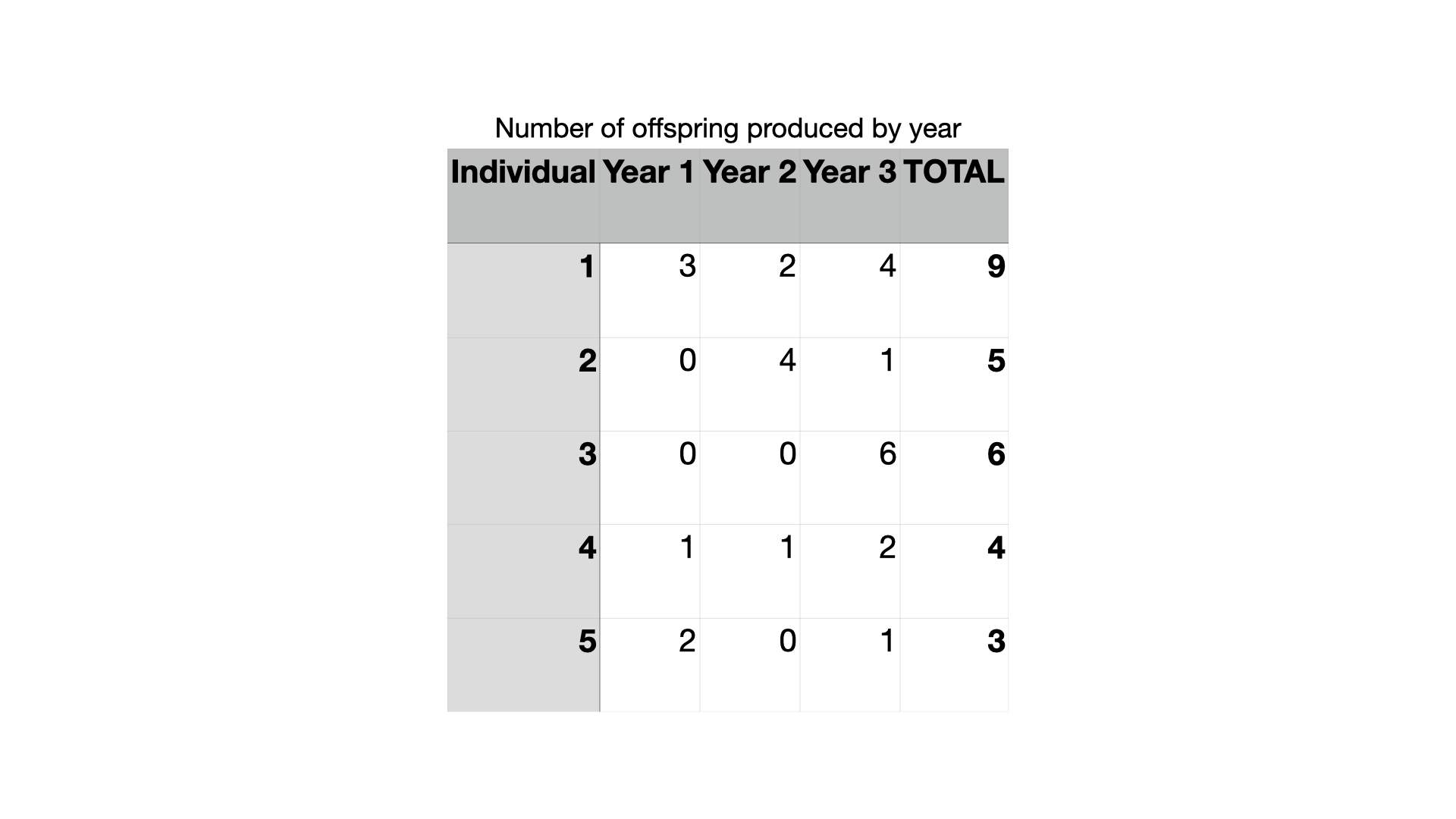
Which of the hypothetical organisms from the table above has the highest fitness for a single year?
organism 3
What conditions are required for evolution to occur by natural selection
There is variation in the population
The variation is heritable
The variation leads to differences in reproductive success

Which of the hypothetical organisms from the table above has the highest cumulative fitness?
organism 1
(t or f) When an organisms survival rate is low we expect them to mature earlier and to invest less in reproduction.
true
(t or f) While r-selected organisms tend to have fewer offspring and exhibit parental care, K-selected organisms tend to have many offspring and exhibit little parental care.
false
(t or f) While K selected organisms exhibit low mortality rates, r selected organism exhibit low survival rates.
true
(t or f) While r-selected organisms are expected to exhibit semelparity, K-selected organisms are expected to exhibit iteroparity.
true
Which of the following traits are used in life history classification schemes?
mortality rate
relative offspring size
age of reproductive maturity
fecundity
(t or f) When an organisms mortality rate is low we expect them to mature earlier and to invest less in reproduction.
false
(t or f) When an organisms mortality rate is low we expect them to mature later and to invest more in reproduction.
true
These types of organisms exhibit iteroparity with larger offspring
K-selected organisms
These types of organisms exhibit reproduction at earlier life stages
r-selected organisms
These types of organisms exhibit parental care
K-selected organisms
(t or f) While K-selected organisms tend to have fewer offspring and exhibit parental care, r-selected organisms tend to have many offspring and exhibit little parental care.
true
these types of organisms exhibit higher survival rates
K-selected organisms
These types of organisms exhibit lower mortality rates
K-selected organisms
(t or f) When an organisms survival rate is low we expect them to mature later and to invest more in reproduction.
false
These types of organisms exhibit lower survival rates
r-selected organisms
These types of organisms exhibit semelparity with smaller offspring
r-selected organisms
Which of the following types of ecological niches best describes the following:
A poorly drained soil layer covered with Sphagnum where Chamaecyparis thyoides (Atlantic White Cedar) is dominant.
fundamental niche
(t or f) Two species can not share the same fundamental ecological niche.
false
what describes the difference between a fundamental and a realized ecological niche?
The presence of competitors and predators
(t or f) An ecological niche describes a particular place but not the conditions found in that place.
false
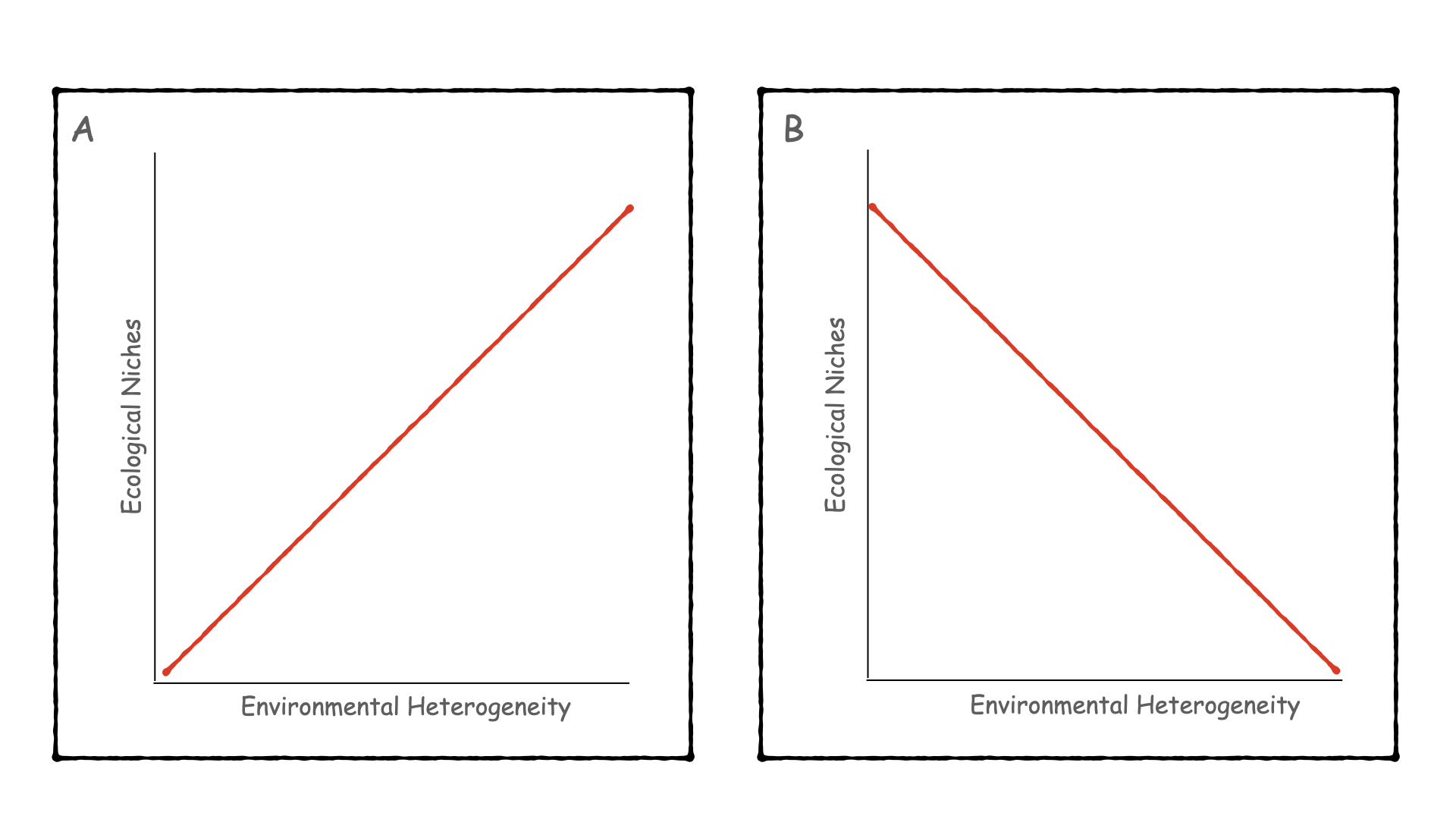
Which of the two panels shown above best describes what we expect to see with regard to the relationship between environmental heterogeneity and ecological niches?
panel a
(t or f) While competition affects individuals, it does not have an affect on the overall biodiversity of a given community.
false
(t or f) According to the competitive exclusion principle, two species can share the exact same ecological niche at the same place and time in a given community.
false
Which of the following types of ecological niches best describes the following:
A xeric habitat at high elevation with high light levels and well drained soil.
fundamental niche
(t or f) An ecological niche describes a set of conditions as much as it does a particular place.
true
Which of the following sets of criteria describe a fundamental ecological niche?
Conditions like temperature, precipitation, and resource availability
(t or f) As competition affects individuals, it also has an affect on the overall biodiversity of a given community.
true
Which of the following sets of criteria describe a realized ecological niche?
A specific geographic location
Which of the following sets of factors describe an organism's fundamental niche?
abiotic factors
Which of the following types of ecological niches best describes the following:
The Cedar Swamp found on the outback trail on the UMM campus.
realized niche
(t or f) Disturbances can sometimes create ecological niches and sometimes destroy them.
true
Which of the following types of ecological niches best describes the following:
Exposed areas at the summit of Cadillac Mountain.
realized niche
In the case of Dodder, a non-photosynthetic plant, that uses modified roots called haustoria to acquire sugars from the phloem of other plants, what kind of symbiosis is described here?
parasitism
Which of the following terms describes an organism that is capable of making its own food?
primary producer
Acacia trees structures called Beltian bodies that are rich in lipids, protein, and sugars and these are harvested by ants that live in these trees. In this case, which part of the food web do the ants belong to?
primary consumer
Raptors are birds of prey that tend to consume larger species of fish, which feed on smaller species of fish. In this case, what part of the food web do the raptors belong to
tertiary consumer
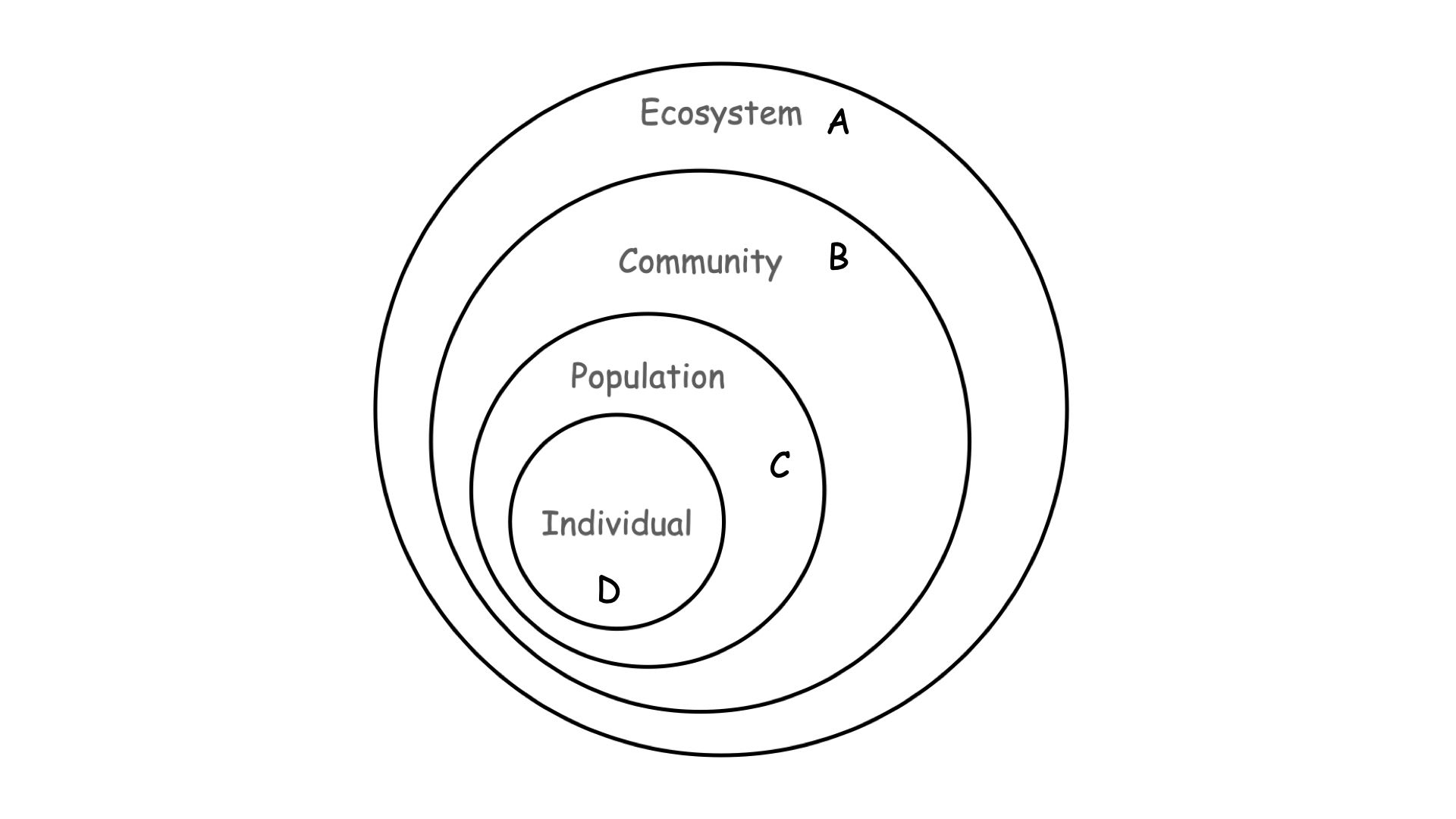
Which of the levels of the ecological hierarchy shown above is defined by measures of fitness?
d
Which of the following term best describes a relationship between two organisms in which one benefits at the other's expense?
parasitism
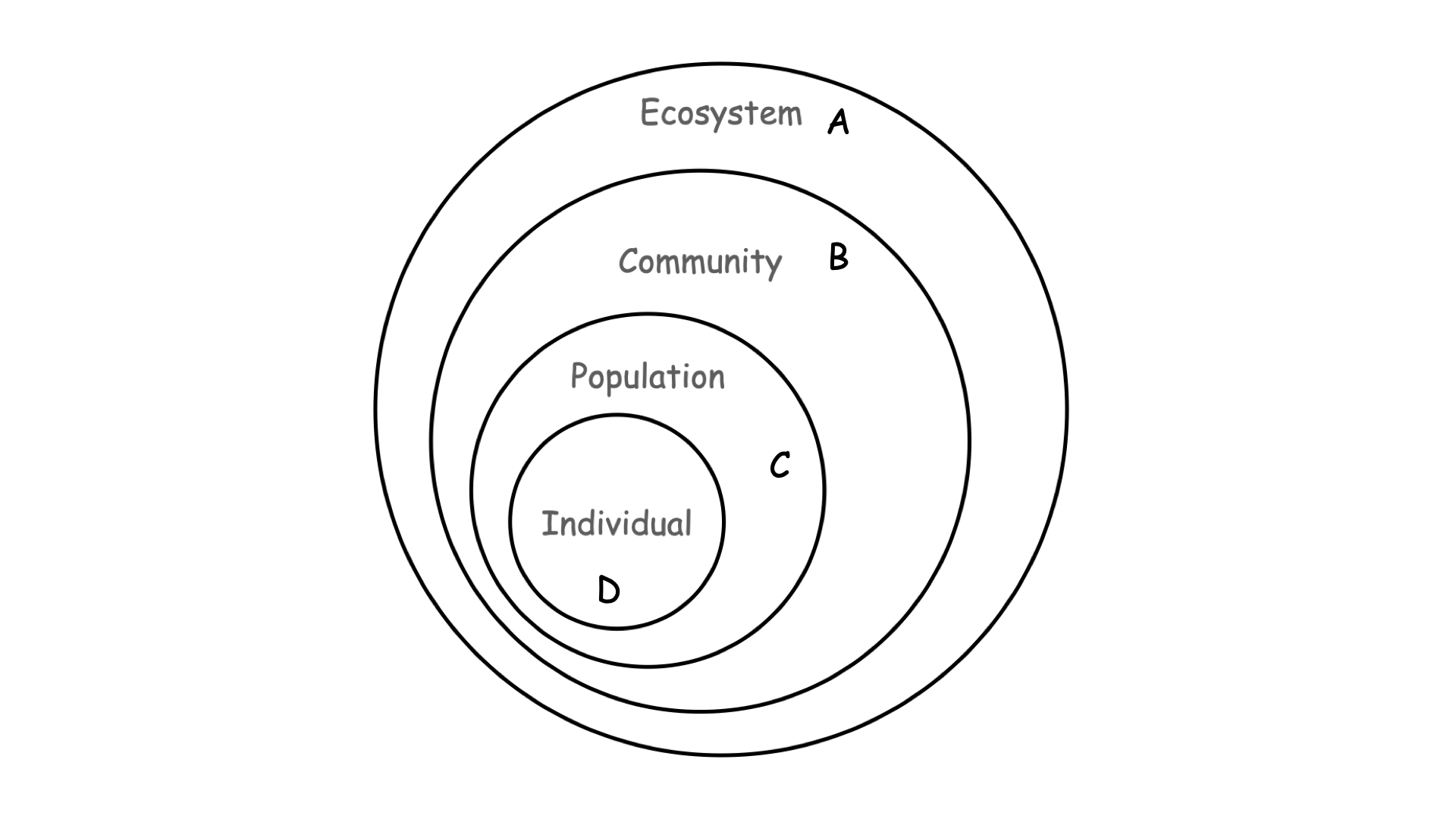
Which of the levels of the ecological hierarchy shown above is defined by intraspecies interactions?
c
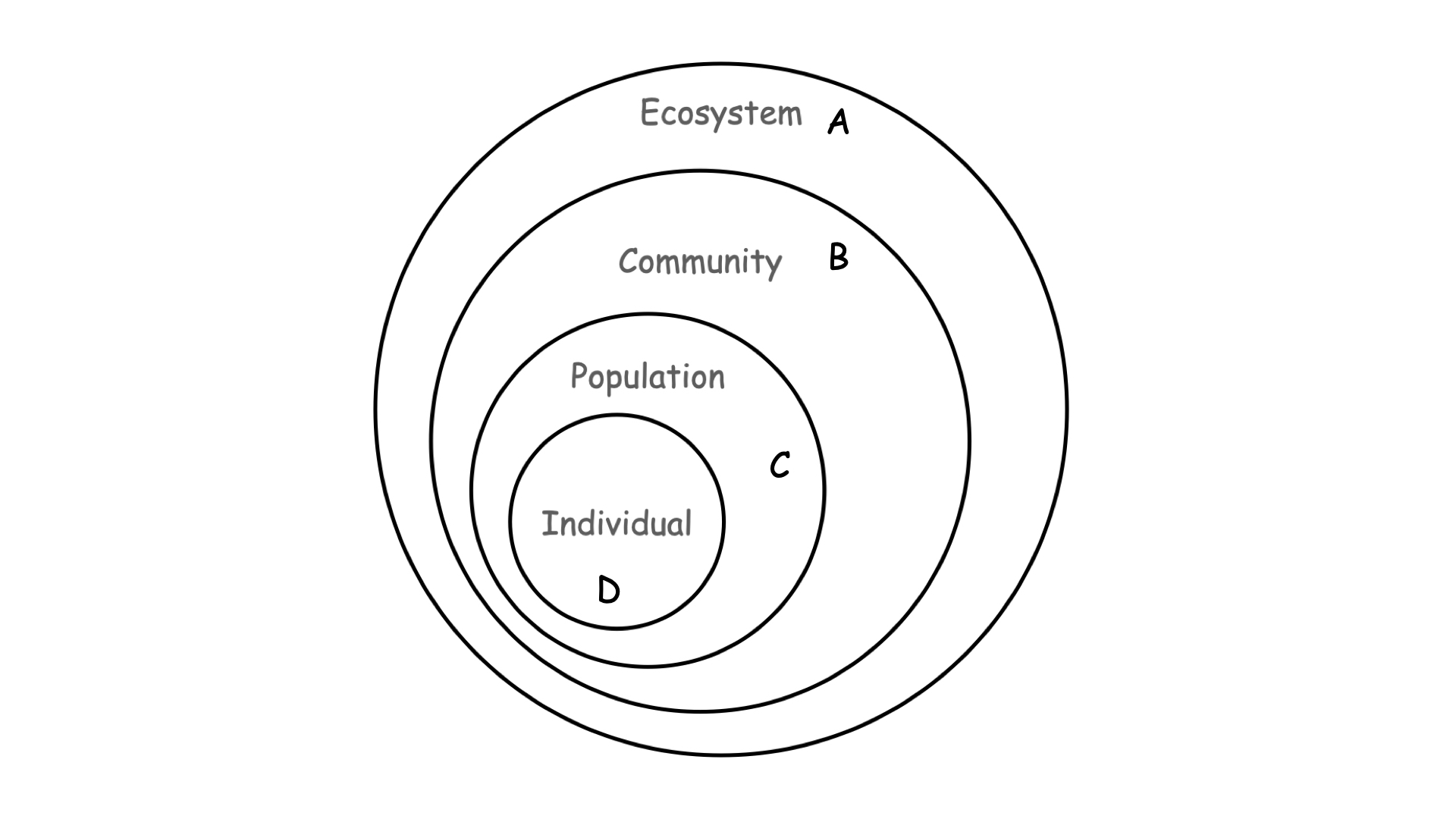
Which of the levels of the ecological hierarchy shown above is defined by interspecies interactions?
b