Bio 2-L17- Principles of Population genetics
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
how does genetic variation arise?
due to mutation and sexual reproduction which results in recombination
what are homologous chromosomes?
chromosomes that are closely related in sequence and match up during meiosis
what is a locus?
fixed position on chromosomes- comparing them we can see alternate versions ALLELES
what are alleles
alternate versions of the DNA sequence that occur at the same locus
types of genetic variation in diploid population
single nucleotide variant-
by insertion or deletion
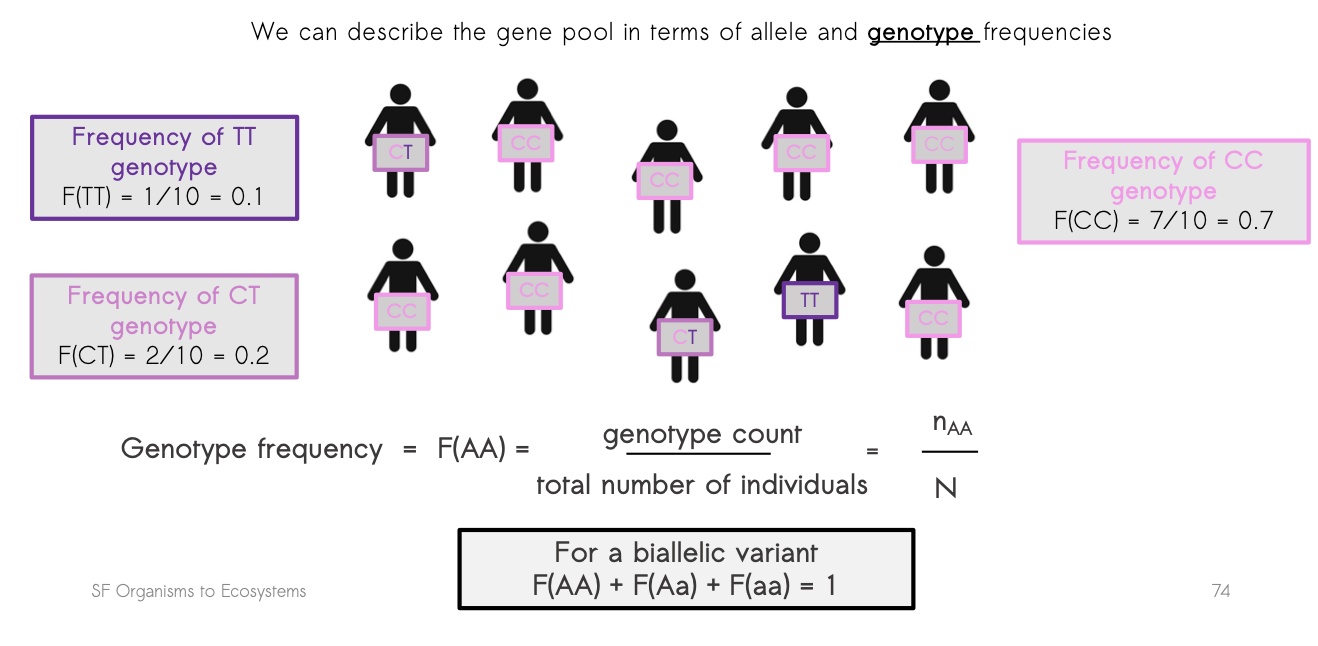
what is genotype?
the genetic material possessed by an indium at a given locus
how is allele frequency calculated
ie for allele A= allele count ie 3/total number of alleles
how is genotype calculated
ways yo could describe gene pools?
allele frequency
genotype frequency
how are allele frequencies calculated given the genotypes?
nA= 2nAA + nAb
nB=2nBB+nAb
frequency is F(A)=F(AA)+F(AB)/2
F(B)=F(BB)+F(AB)/2
what does hardy Weinberg equilibrium show?
It demonstrates that allele and genotype frequencies in a population remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary influences.
what does the hardy Weinberg equilibrium require?
random combinition and random mating
no changes in allele frequencies between generations
no mutation, no selection, no gene flow
large populations
what are some violations on hardy Weinberg?
violations to random mating- this isn’t true
mutations- change allele frequency
genetic drift- small population effects on allele frequencies- founder effect or population bottleneck
gene flow- genetics from one population to another
selection- changes allele frequencies due to differential survival and reproduction of individuals.
what is the hardy Weinberg principle formula?
p² + 2pq + q² = 1
why does non random mating not change allele frequencies?
Non-random mating affects the genotype frequencies but not the overall allele frequencies in the population.
This is because it does not introduce new alleles or remove them; it simply rearranges the existing combinations.