GI Clinical Medicine of the GI Tract (Dr. Johansen)
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
What is the helpful mnemonic for differential diagnosis of a presentation?
VINDICATE SLEEP
Vascular
Infectious/Inflammatory
Neoplastic
Degenerative
Iatrogenic/idiopathic
Congenital/developmental
Autoimmune/Allery
Traumatic/toxic
Endocrine/metabolic
Social/behavioral
Legal
Environmental
Economic
Psychological
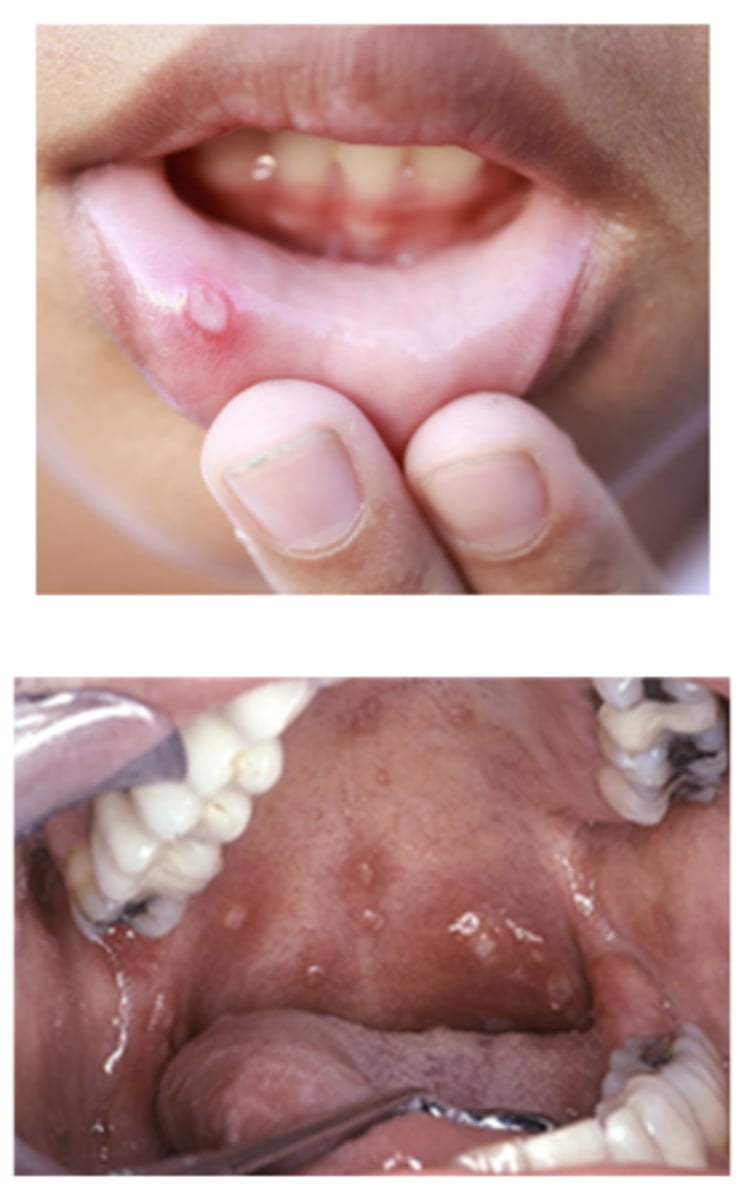
__________ is also called "canker sores", can be solitary or multiple
Aphthous Stomatitis (ulcers)
Predisposing factors for this condition include:
- Stress
- Viral illness
- Hormonal changes
- Food/drug hypersensitivity
- Familial
- Trauma
- Immunodeficiency
Aphthous Stomatitis (ulcers)
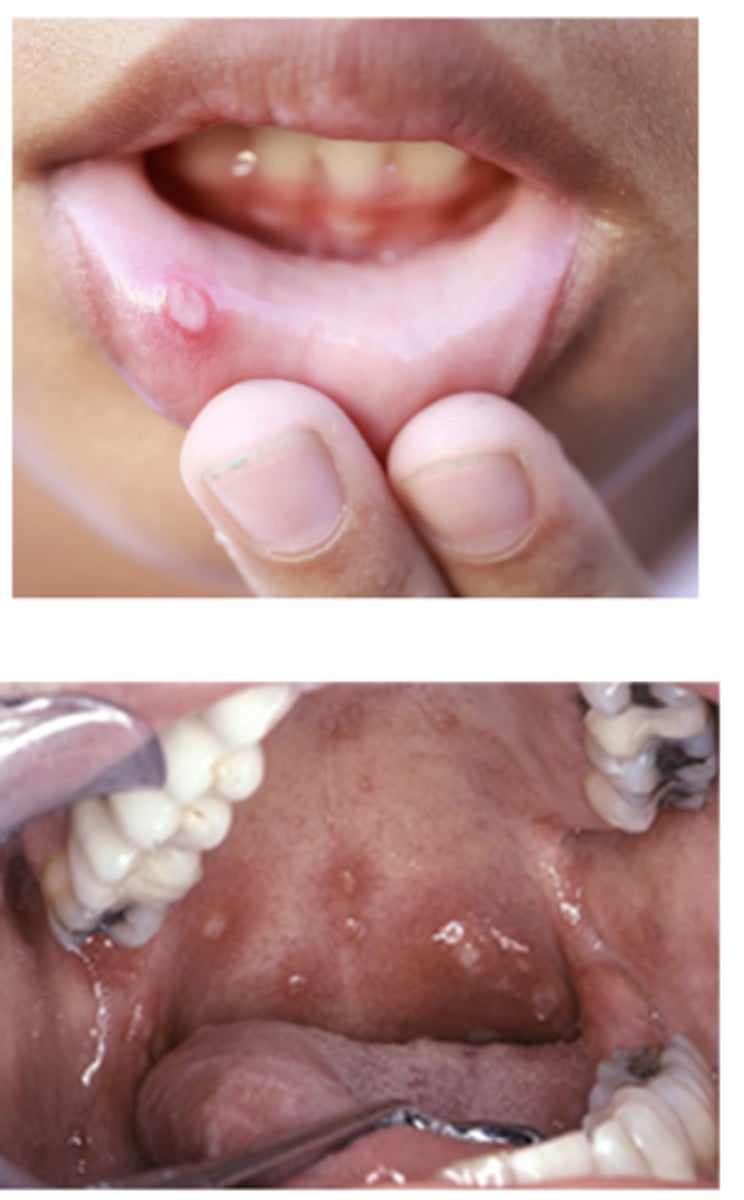
Aphthous Stomatitis (ulcers) can present in what GI conditions?
- Crohn's disease
- Celiac disease
- Iron deficiency anemia
Aphthous Stomatitis (ulcers) presents most commonly in what GI condition?
Crohn's disease
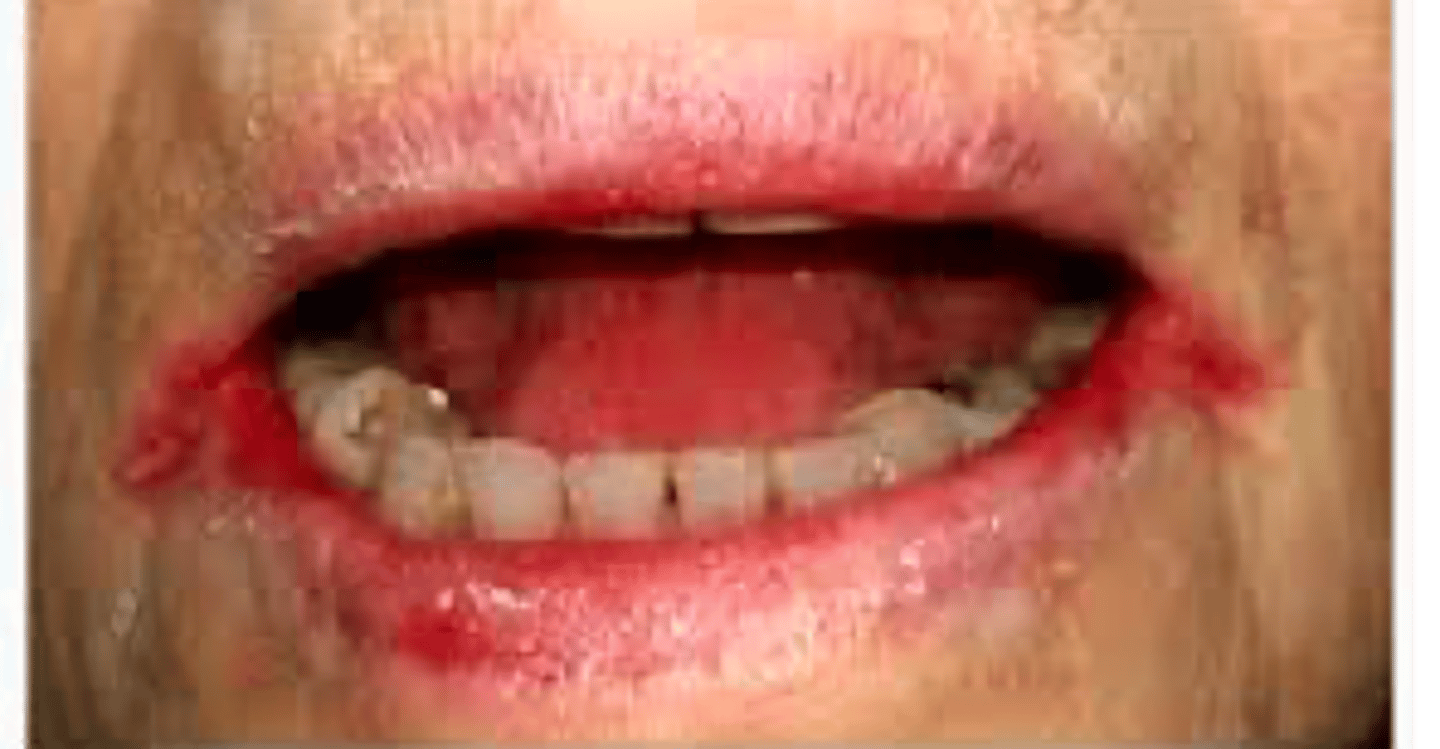
What has the following characteristics?
- Dryness at the corners of the mouth leading skin breakdown, redness, crusting, fissures
- May become infected
Angular Cheilitis
Define the following:
Inflammation of the lips
cheilitis
The following can all cause what?
• Irritation: chemical, dry mouth, poor fitting dentures, edentulism
• Iron deficiency, riboflavin deficiency, poor nutrition
• Infection
• Allergies
• Decreased immune function
Angular Cheilitis
saliva plays a large role in the occurrence of this condition due to conditions such as edentulism and is even considered as a cause of contact dermatitis:
Angular Cheilitis
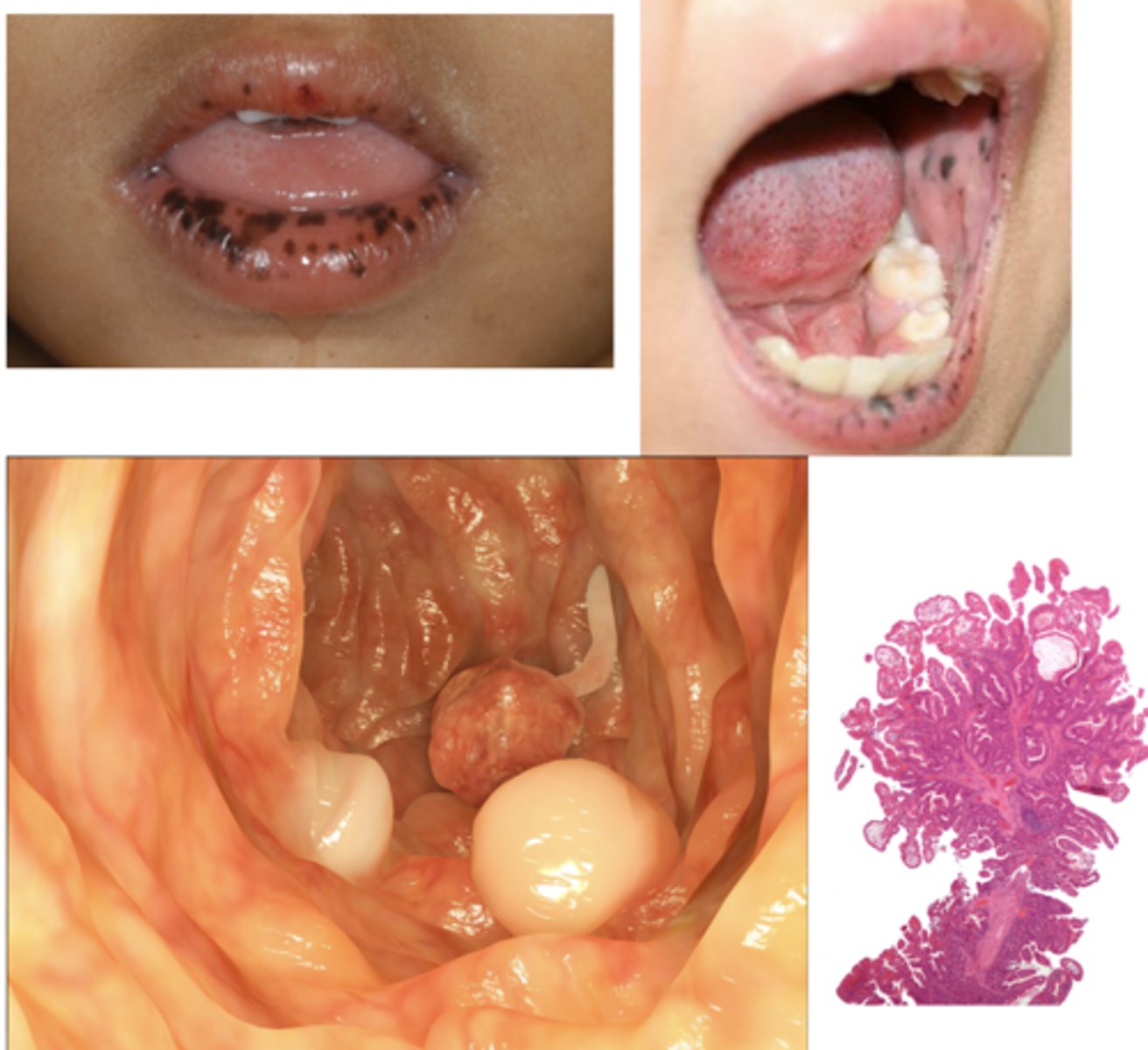
What has the following characteristics?
- Presentation: Pigmented macules (1-5mm flat dark lesions) on lips and buccal mucosa (83-95%)
- Can fade after puberty
- Can also have lesions on fingers, soles and around eyes
- Autosomal dominant
- Presents in 1st-3rd decade
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome (mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation)
this condition is associated with multiple polyps of GI tract, leading to an increase risk for multiple cancers, ESPECIALLY GI cancer (stomach, small intestine, colon, pancreas):
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
What are the 5 complications of polyps?
- Intestinal obstruction
- Abdominal pain
- GI bleeding
- Malignant transformation
- Rectal prolapse
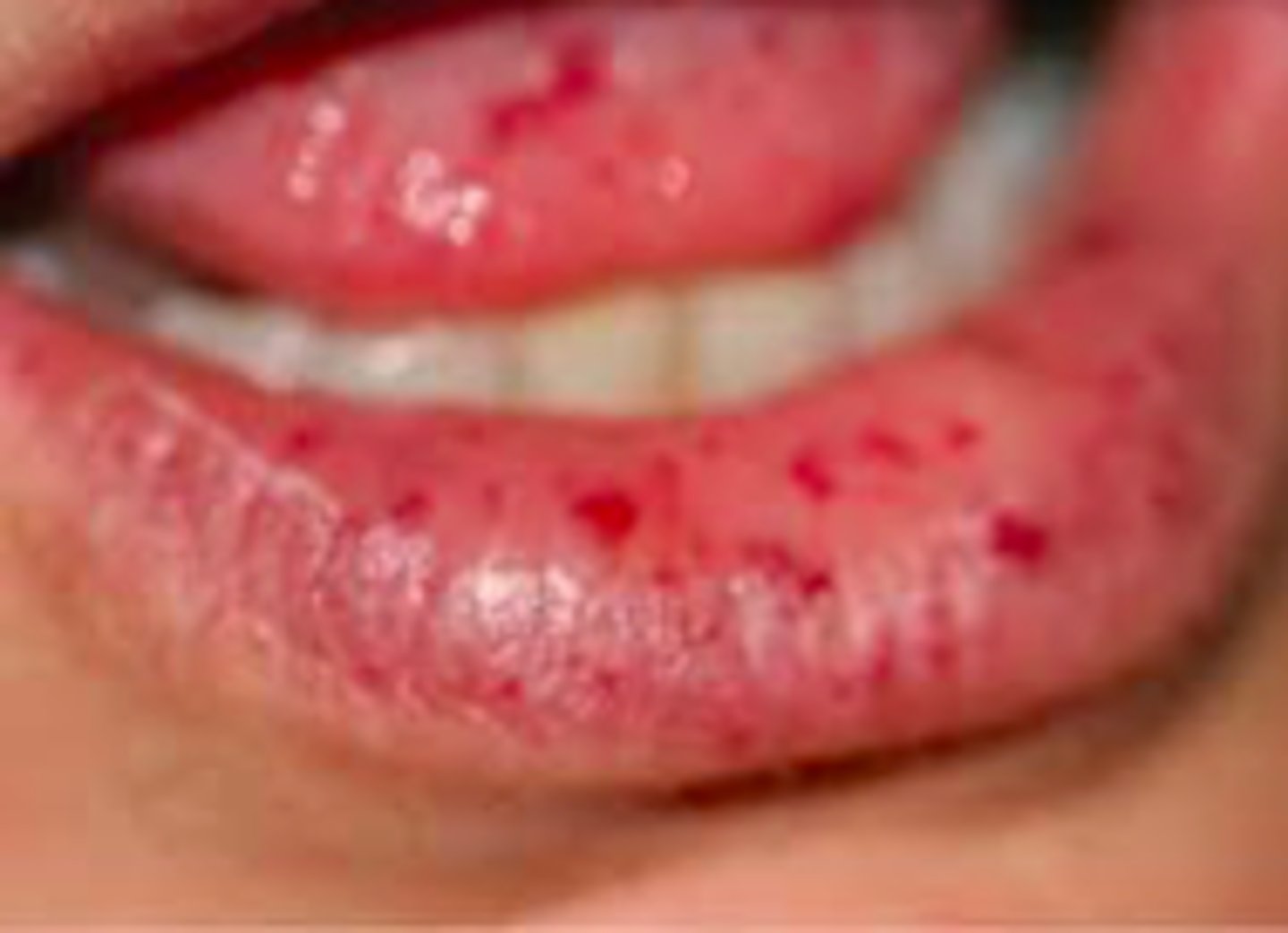
What has the following characteristics?
- Presentation: Vascular malformations of skin and internal organs (GI tract, lungs, brain)
- Autosomal dominant
- Presents in 2nd or 3rd decade
- Small, dilated blood vessel near surface of skin/mucous membranes. Common on lips, tongue, face, chest, fingers, GI tract
- Arteriovenous shunts/malformations (AVMs)
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome)
Complication of this condition include:
- Epistaxis (nosebleeds) - 97% (very common!)
- GI bleeding – 33%
- Iron deficiency
- Stroke
- Pulmonary hemorrhage/embolis
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome)
What has the following characteristics?
- Presentation: Creamy white/yellow “curd-like” plaques on tongue, oral mucosa
- Often asymptomatic
- Symptoms: “cotton mouth”, loss of taste, odynophagia
- Oral mucocutaneous candida infection, oral “thrush”
- Diagnosis: clinical or by yeast
- Can accompany esophageal candidiasis
Oral candidiasis
Patients with oral candidiasis should raise cause for concern of ____________
Immune suppression (diabetes, HIV/AIDS, Cancer, Medications, Chemotherapy, Steroids, Antibiotics, Smoking, etc.)
this condition is seen when GI diseases are treated with steroids, and in advanced GI cancer or chemotherapy for GI cancers:
Oral candidiasis
T/F: Hyperdontia (supernumerary teeth) can be associated with underlying conditions
true
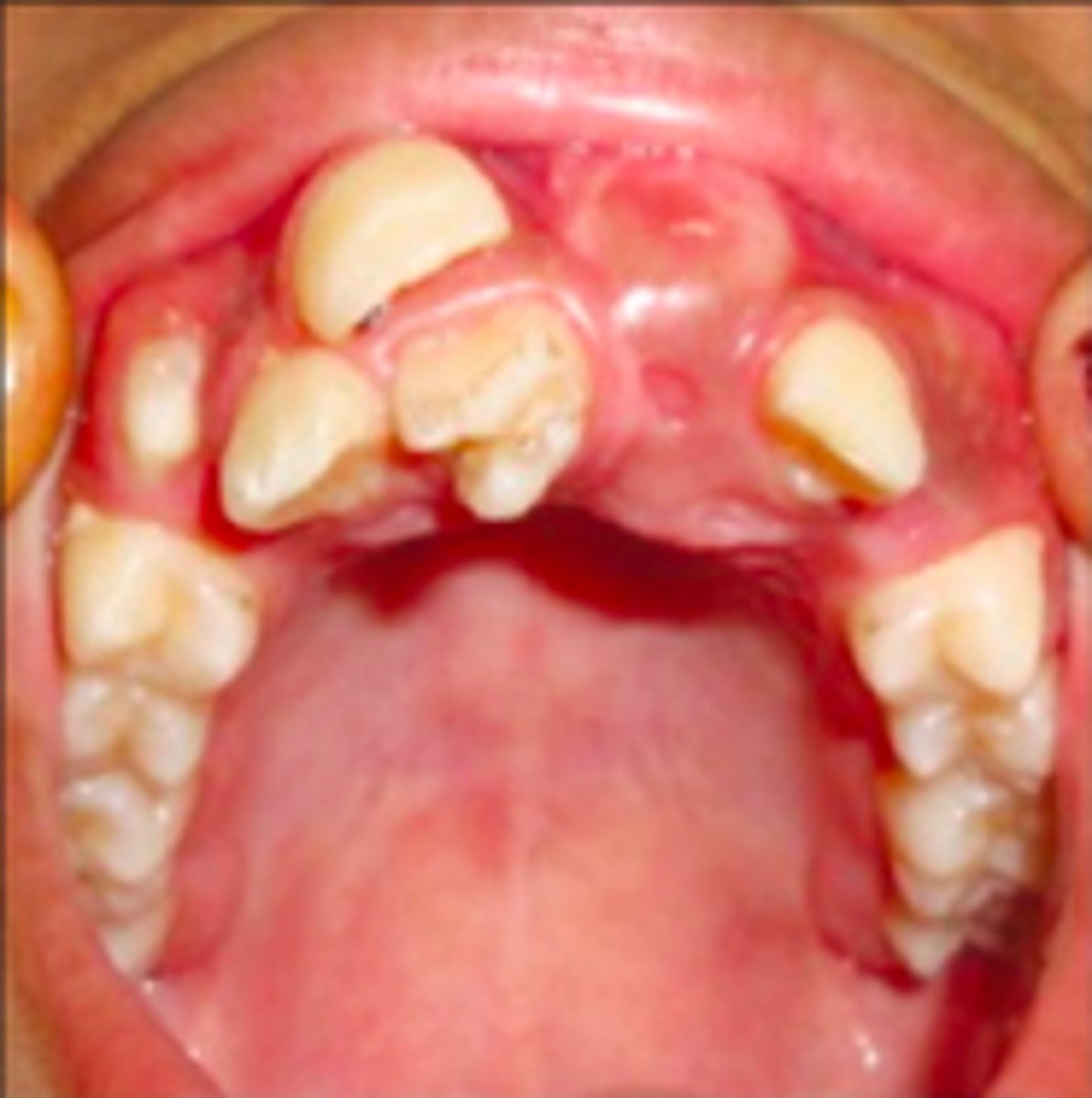
Hyperdontia can be a sign and associated with what GI condition?
Gardner syndrome
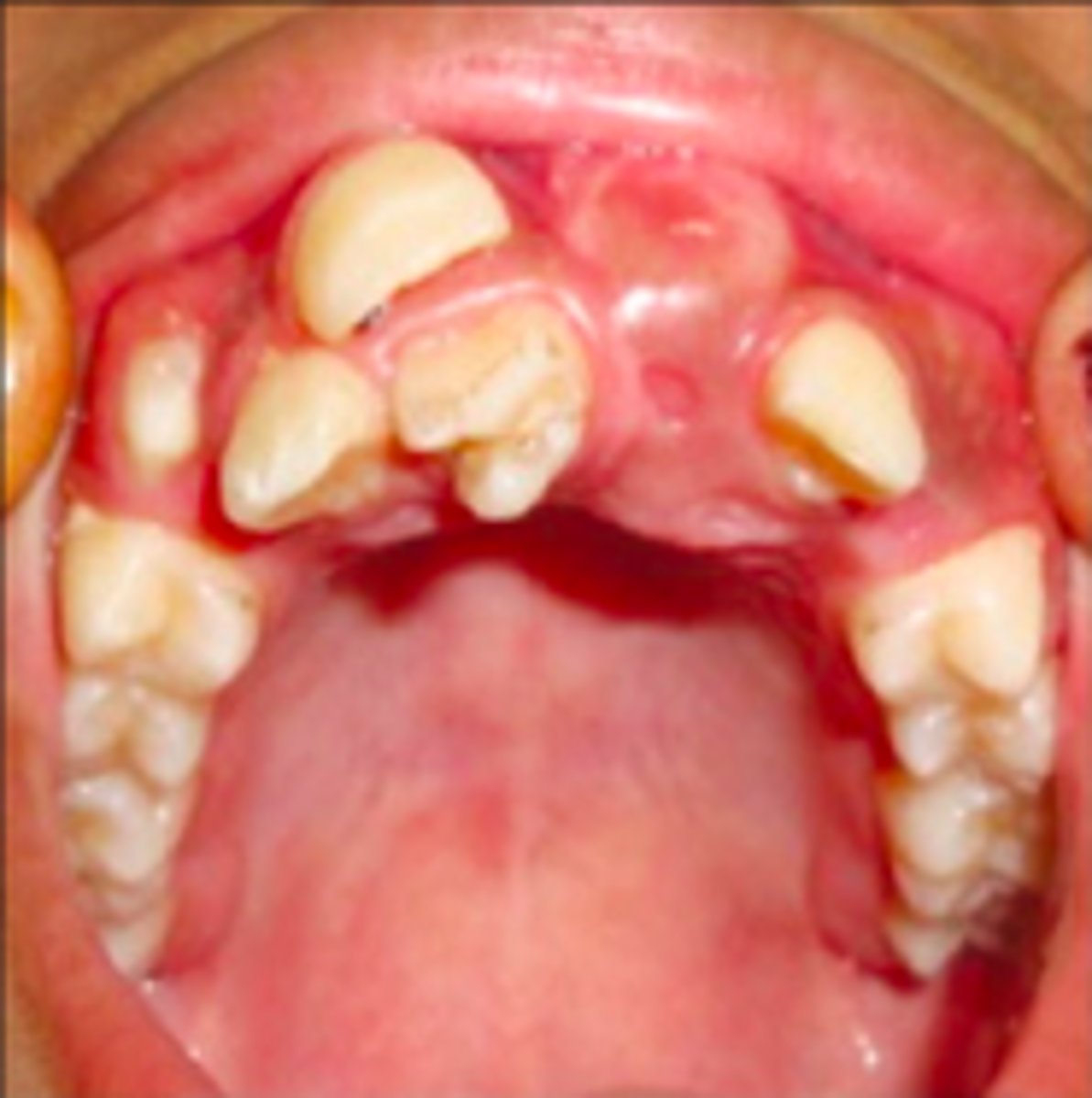
What has the following characteristics?
• Autosomal dominant
• Supernumerary teeth
• Osteomas
• Odontomas
• Many colon polyps with 100% chance of malignant change
• Variant of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
• Colon cancer at 20-40 yo without treatment
Gardner syndrome
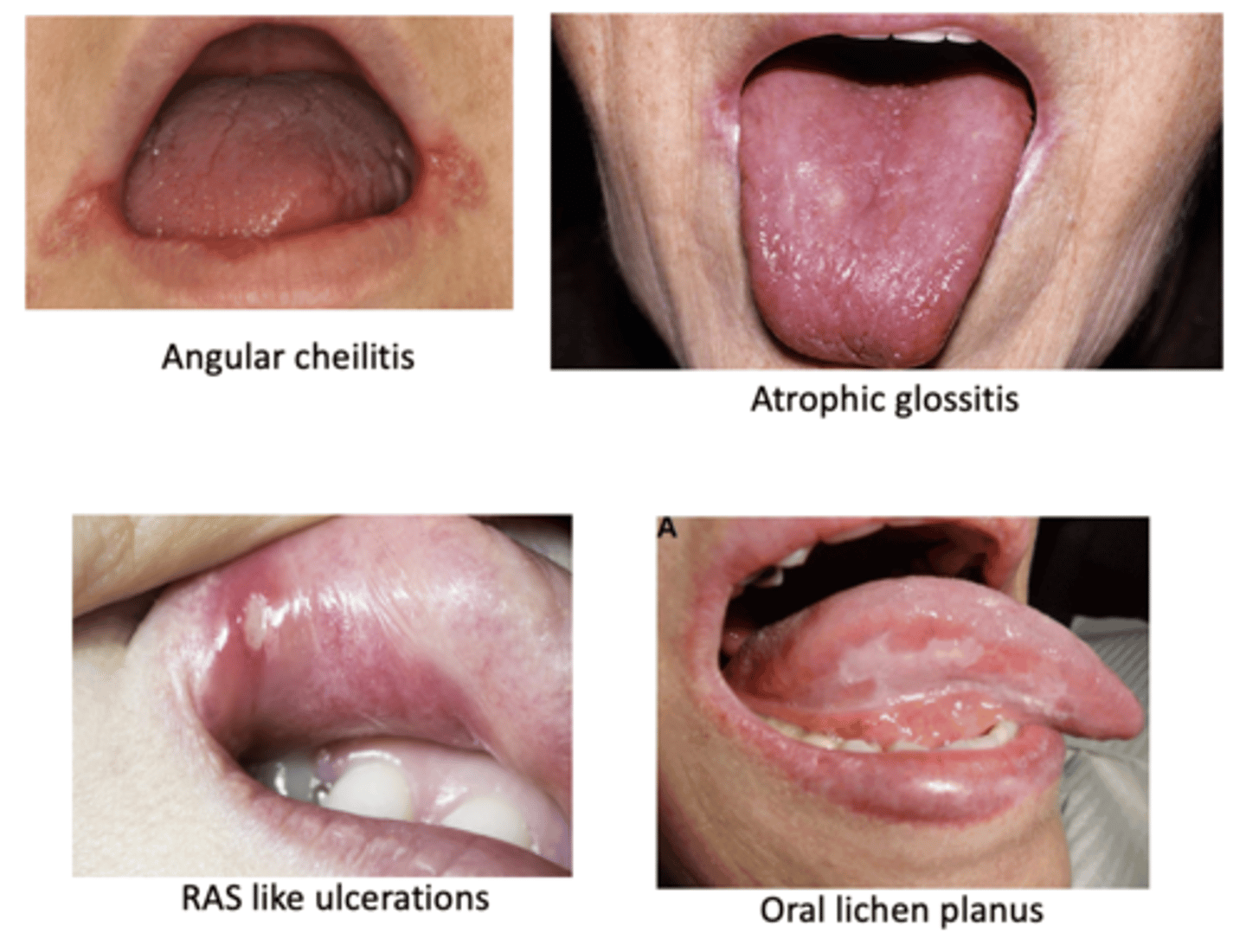
Signs of _____ in the mouth can cause suspicion for these conditions
• Angular cheilitis
• Atrophic glossitis
• RAS like ulcerations
• Oral lichen planus
• Xerostomia
• Numbness
• Burning sensation
• Dysgeusia (altered taste perception)
• Other symptoms/signs: Short of breath, fatigue, pallor
Anemia
Many GI disorders are associated with anemia due to...
- Malabsorption
- Blood loss
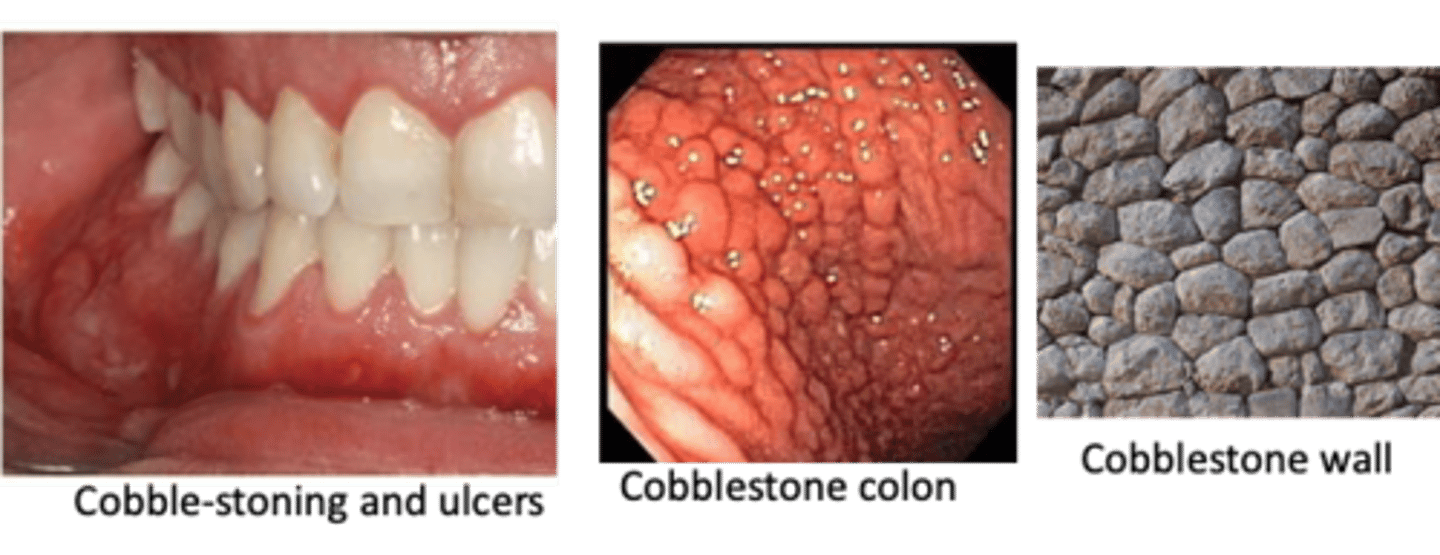
____________ is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) characterized by bouts of abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, nutritional deficiencies due to lesions involving anywhere in the GI tract, including oral cavity
Crohn’s Disease
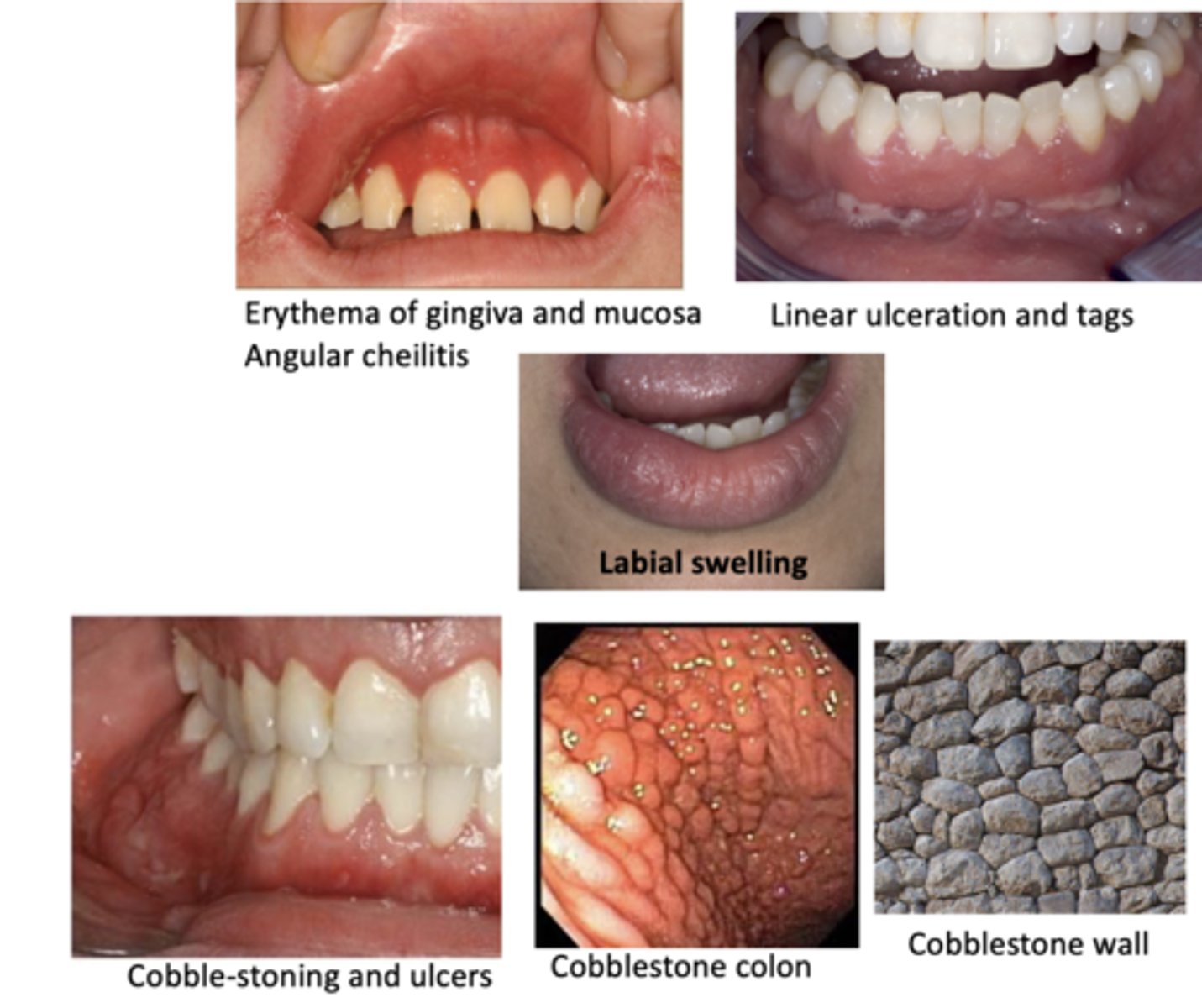
Oral manifestations of this disease include:
• Cobble-stone appearance
• Linear ulceration
• Mucosal tags
• Mucositis and gingivitis
• Labial and facial swelling
• Angular cheilitis
• Aphthous ulcers
Crohn's Disease
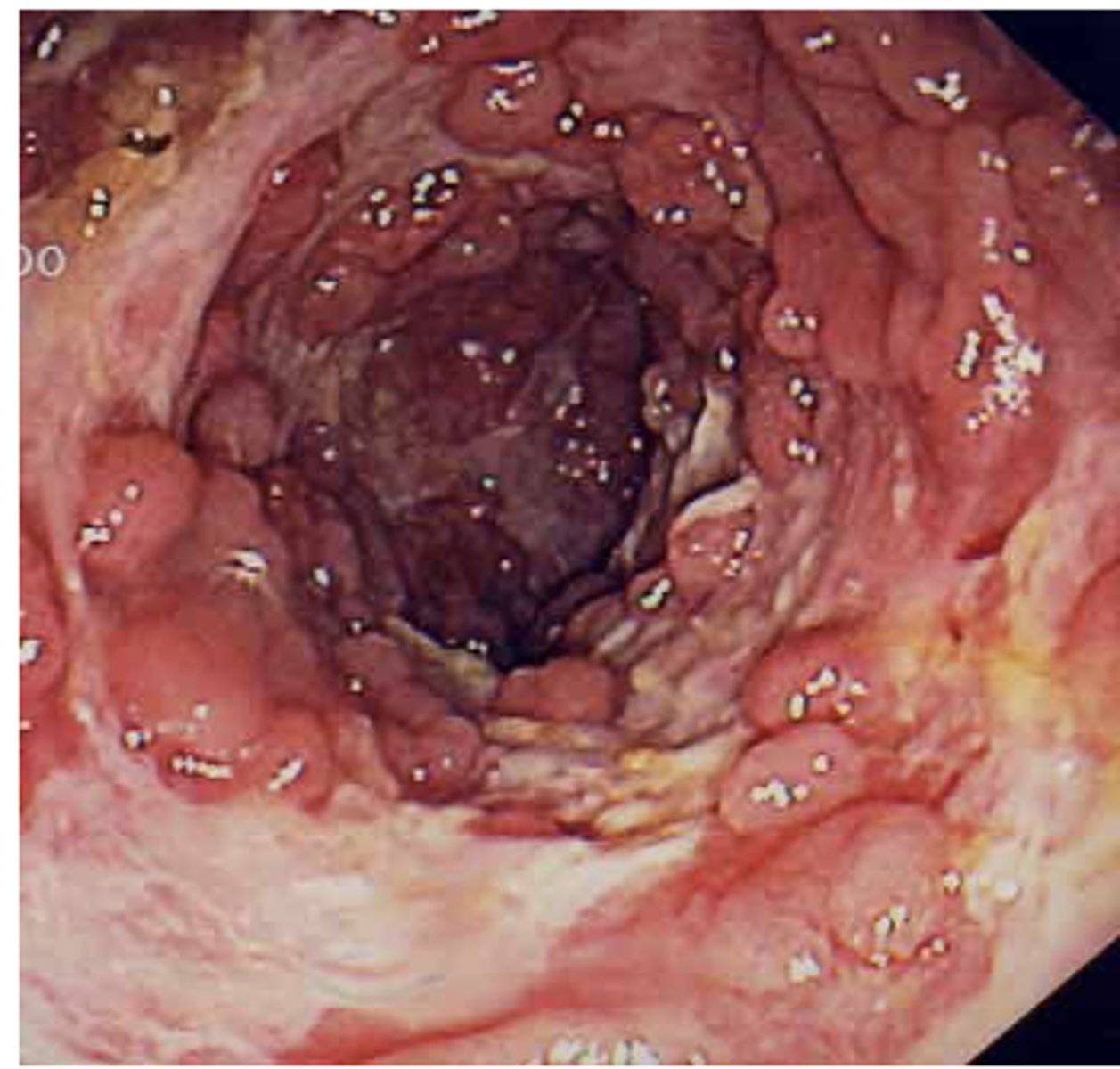
ID this pathology:
- Signs and symptoms: chronic abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, extra-intestinal manifestations
- Onset: 15-25, can be later
- Pathology: Transmural inflammation of bowel wall, can affect anywhere in GI, commonly spares rectum
- Complication: Intestinal obstruction, fistulas
crohns disease
_____________ is an inflammatory bowel disease characterized by bouts of bloody diarrhea, often bloody mucosal ulceration of the colon
Ulcerative Colitis
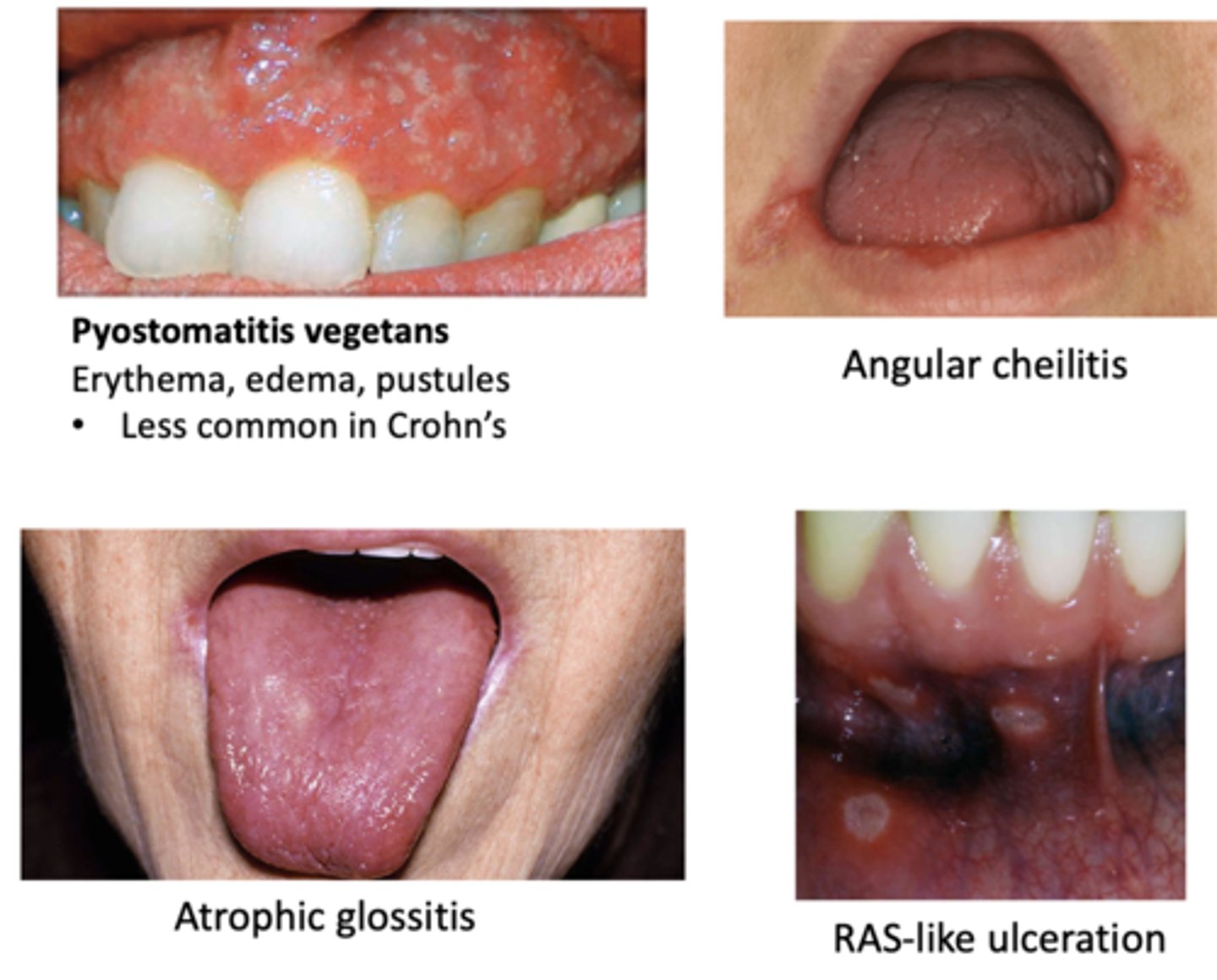
Oral manifestations of this GI disease include:
- Pyostomatitis vegetans (Erythema, edema, pustules)
- RAS-like ulceration
- Angular cheilitis
- Atrophic glossitis
Ulcerative Colitis
What is a risk factor for colon cancer and anemia is common?
Ulcerative Colitis
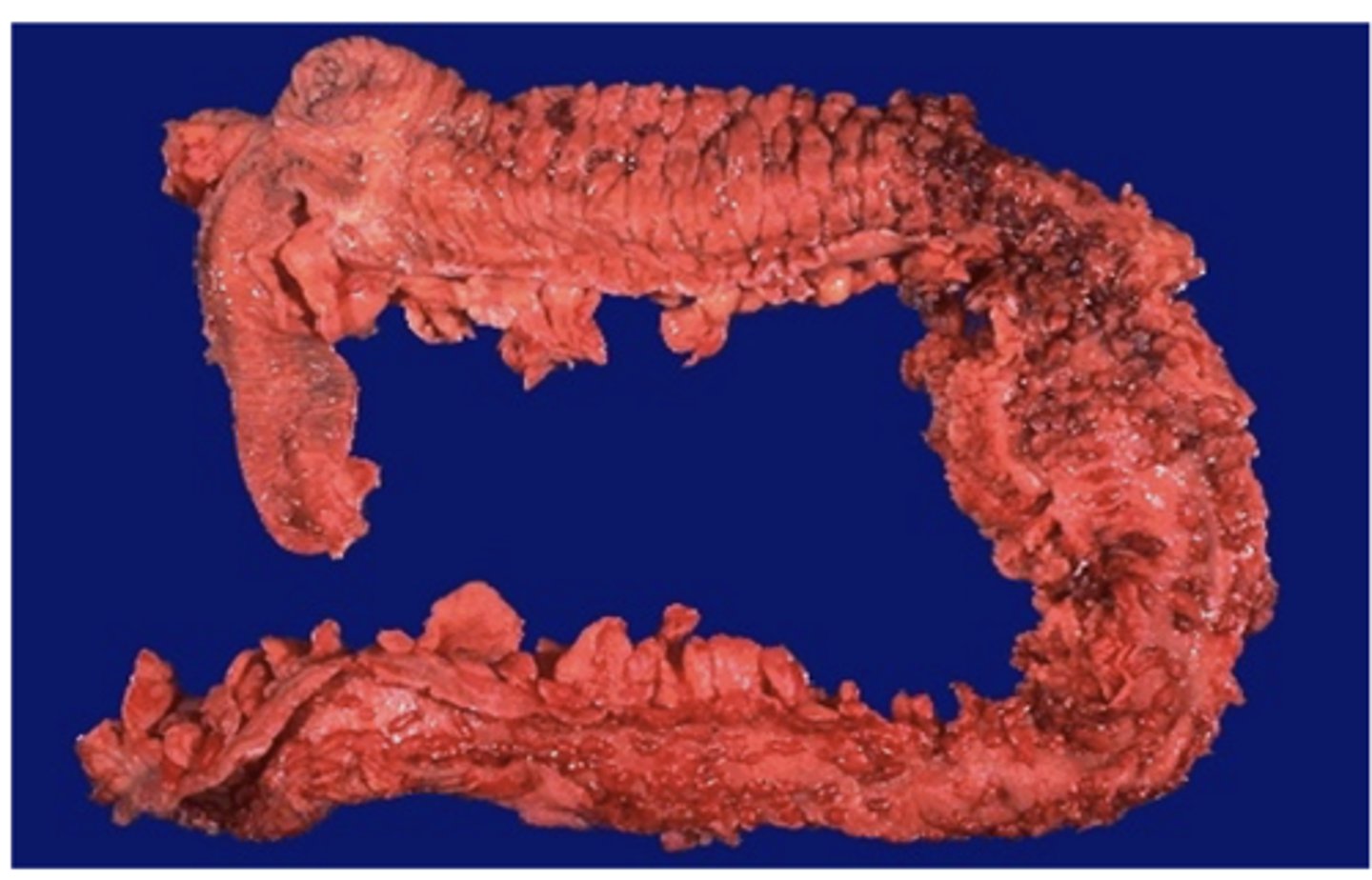
Signs and symptoms of this GI disease include:
• Fever
• Abdominal pain
• Bloody diarrhea, can be nocturnal
• Extra-intestinal manifestations (skin, joints)
• Signs of anemia
• Onset usually 15-25, can be later (same as CD)
Ulcerative Colitis
Increased risk of colon cancer, increases with duration of this GI disease:
Ulcerative Colitis
What is the treatment for ulcerative colitits?
- Total colectomy
- Medications (including steroids)
Define the following:
An immune-mediated disease to gluten malabsorption
Celiac Disease
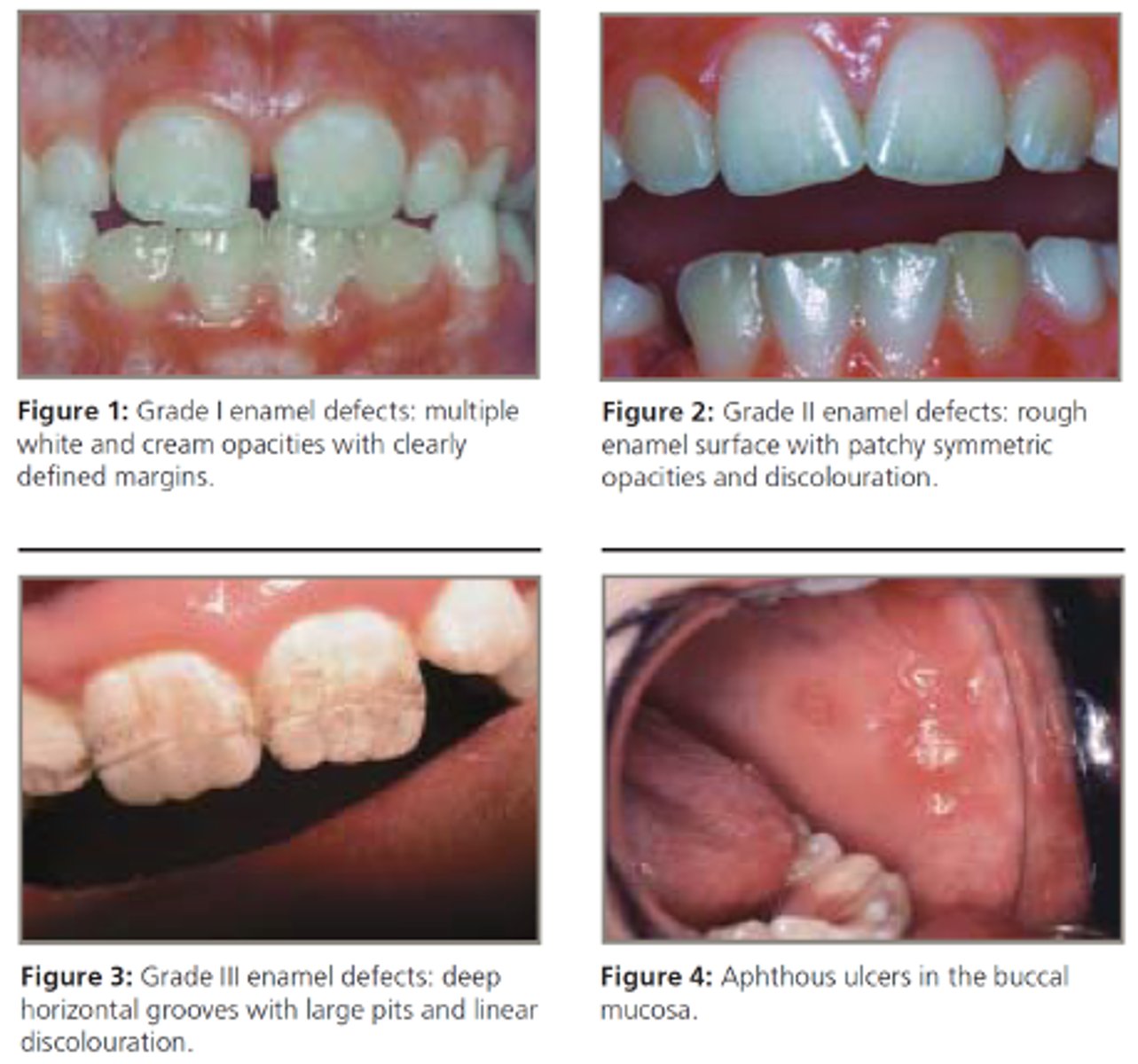
Oral manifestations of this GI disease include:
• Enamel defects including hypoplasia, discoloration and banding
• Aphthous ulcers
Celiac Disease
Symptoms of this GI disease can include:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating weight loss
- Chronic diarrhea
- Steatorrhea (fatty stools)
- Extra-intestinal manifestations
Celiac Disease
Pathology of this GI disease:
Blunting of intestinal villi and inflammation, common in duodenum
Celiac Disease
Diagnosis of this GI disease reveals antibodies to several antigens including tissue transglutaminase:
Celiac Disease
Complications of this GI disease include malabsorption which can lead to malnutrition, and multiple deficiencies (Ca2+, Vit D, Vit K, B12)
Celiac Disease
What is the treatment for celiac disease?
- Gluten-free diet
- Nutritional supplementation for any deficiencies
- Medication and monitoring
Define the following:
Gastric reflux severe enough to cause symptoms and/or tissue injury
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
oral manifestations of this GI disease include:
- Sour taste in mouth
- Bad breath from regurgitation
- Xerostomia
- Gum irritation/bleeding
- Tooth erosion
- Dry mouth
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
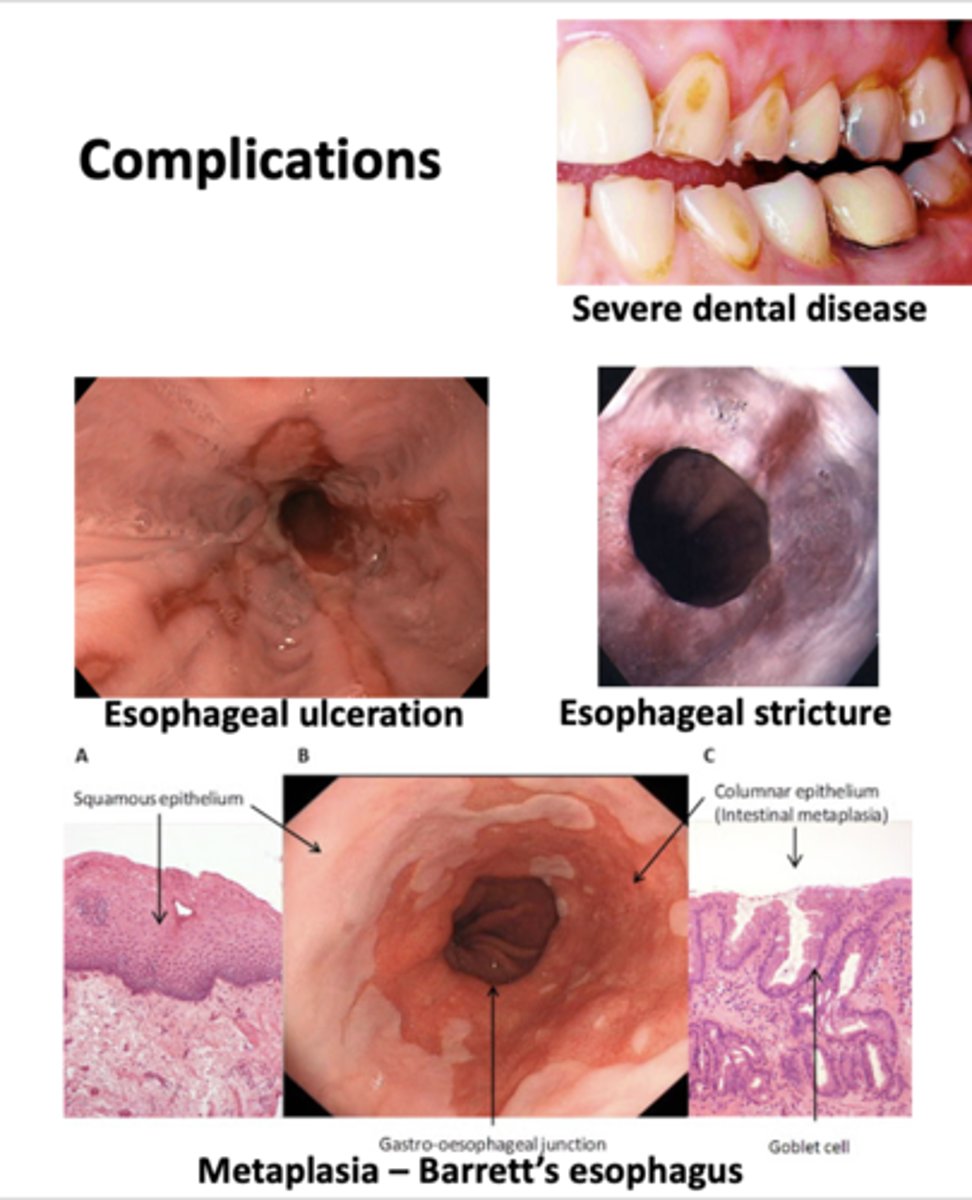
Complications of this GI disease include:
- Severe dental disease
- Esophageal ulceration
- Esophageal stricture
- Barrett's esophagus
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
What are some treatments for GERD?
- Medications (antacids, PPIs, H2 blockers)
- Avoid eating 3h before bedtime
- Eat smaller frequent meals
- Avoid: caffeine, carbonated beverages, alcohol, spicy foods, peppermint, onions, others
- Elevate the head of the bed
- Maintain normal weight
- Smoking cessation
- Wear loose fitting clothing around the waist
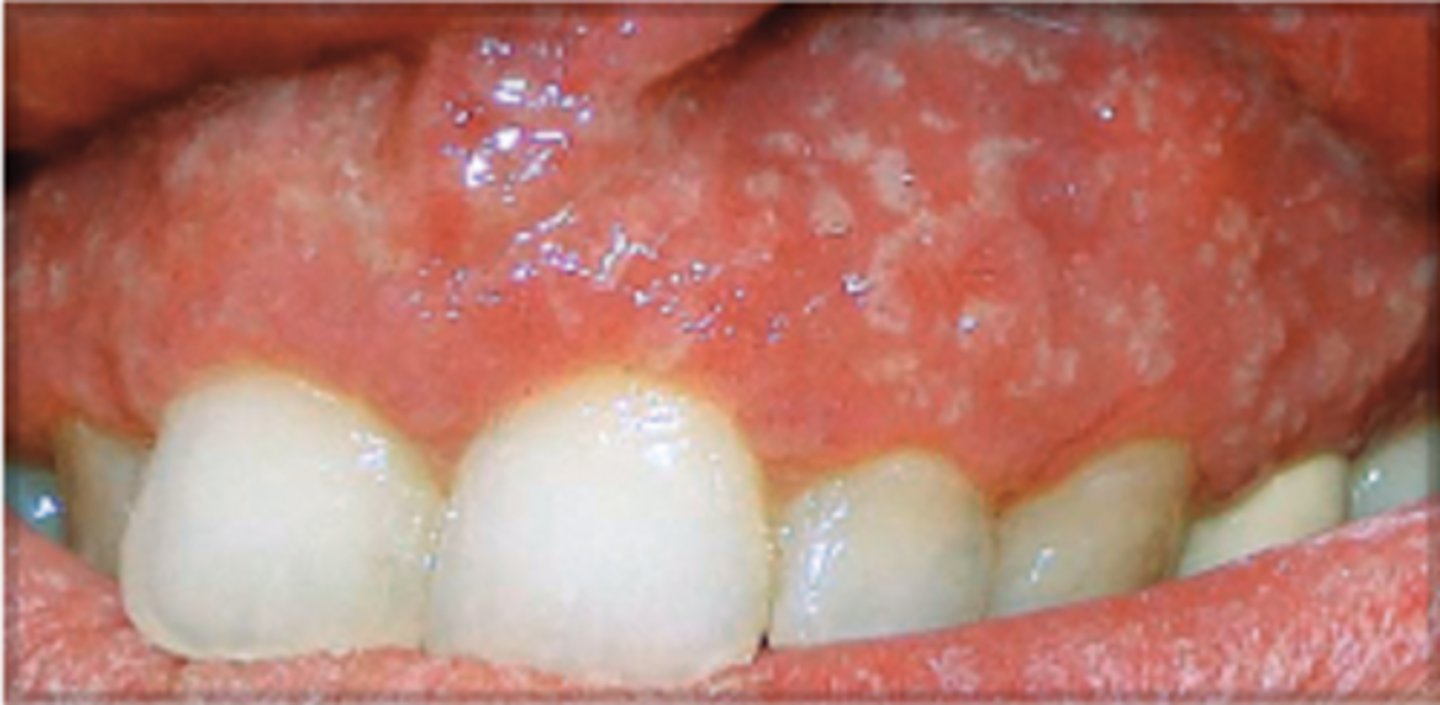
A 20 year-old patient presents with abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea and anemia. Oral exam reveals erythema and pustules on the gingival mucosa as shown in the image. She also has joint pains. A relative had the same disease and had a colectomy which revealed colon cancer. Which of the following conditions does this patient most likely have?
A. Crohn's disease
B. Ulcerative colitis
C. Celiac disease
D. Gardner's syndrome
E. Mucocutaneous telangiectasia
B. Ulcerative colitis
Define the following:
Difficult swallowing
Dysphagia
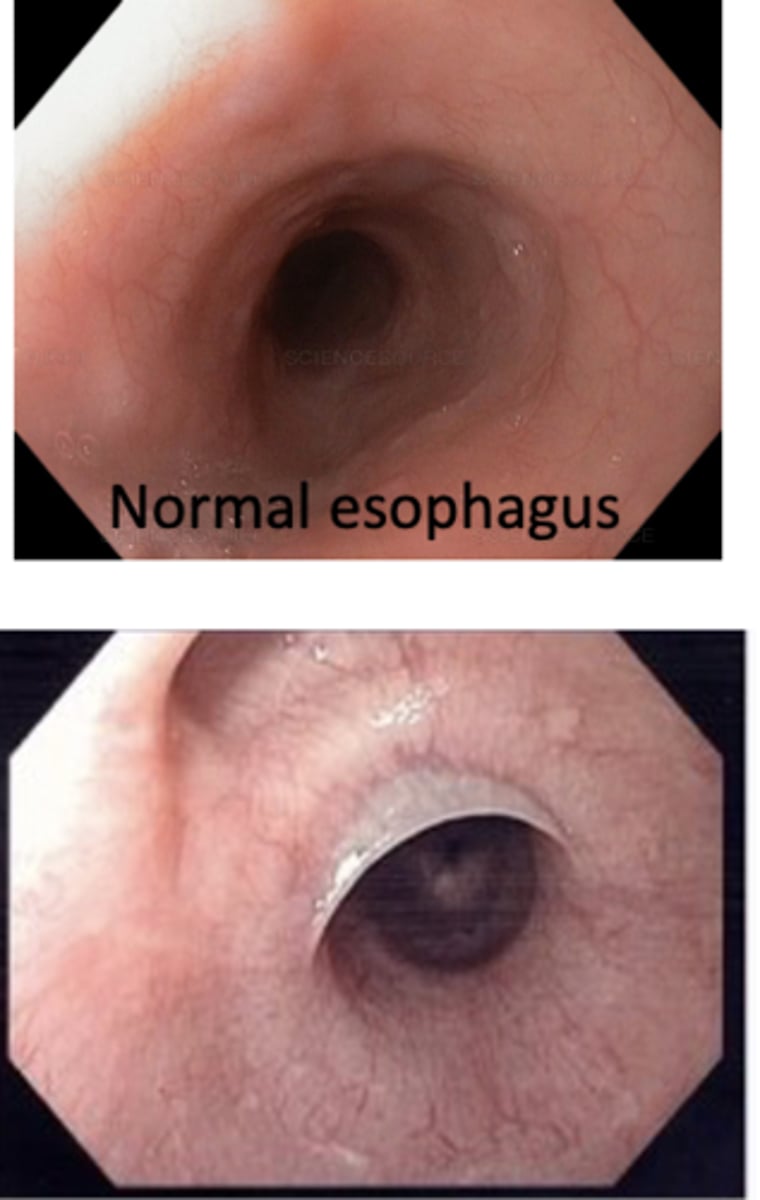
Patient presents with proximal membrane formation and they have an untreated iron-deficiency anemia known as plummer-Vinson syndrome (anemia, hand abnormalities, risk for cancer). What is the diagnosis?
Esophageal web
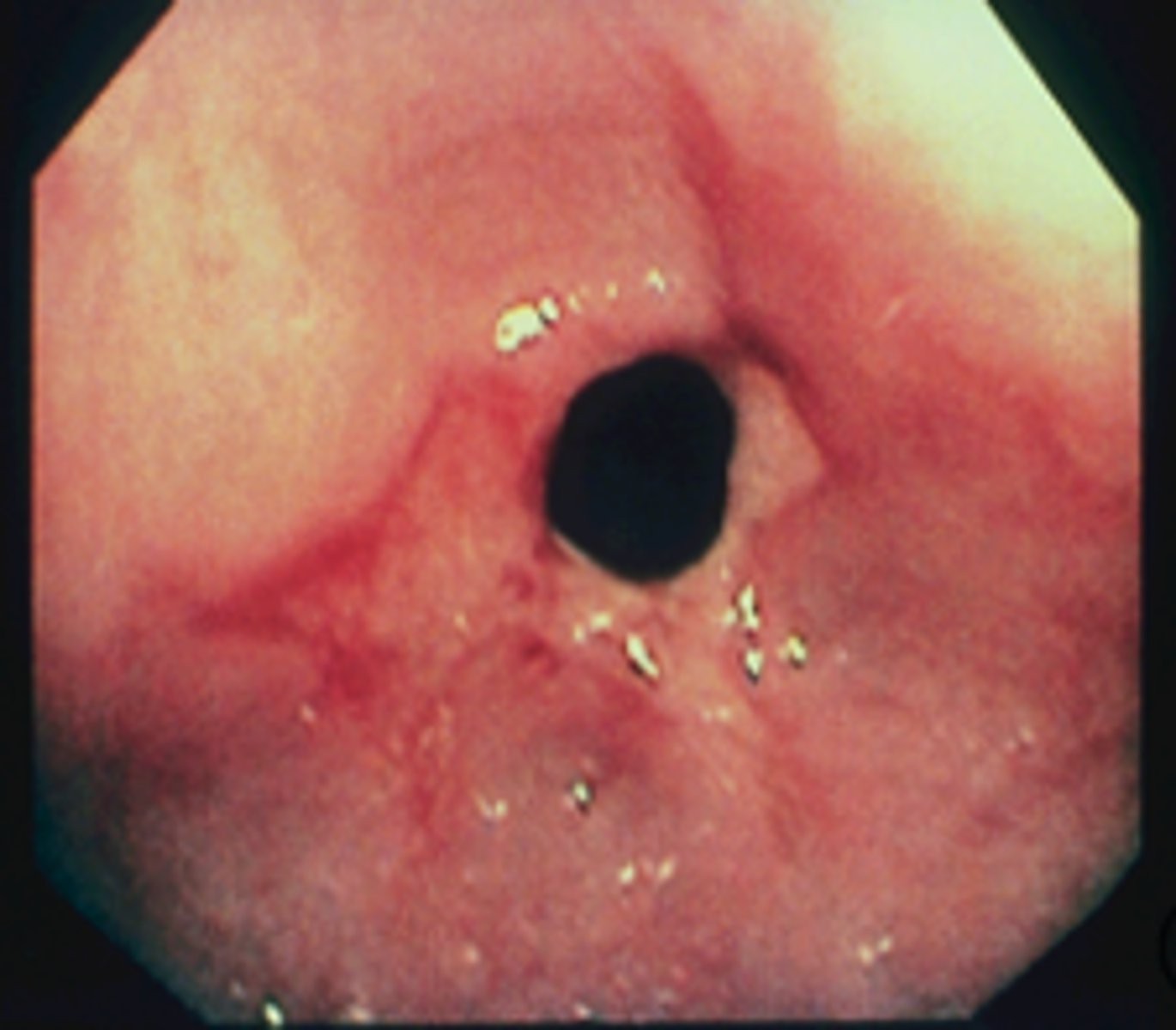
patient presents with dysphagia to solid foods. An endoscopy is performed and a narrowing of the esophogeal wall is noticed as well as signs of GERD. What is the diagnosis?
esophageal stricture
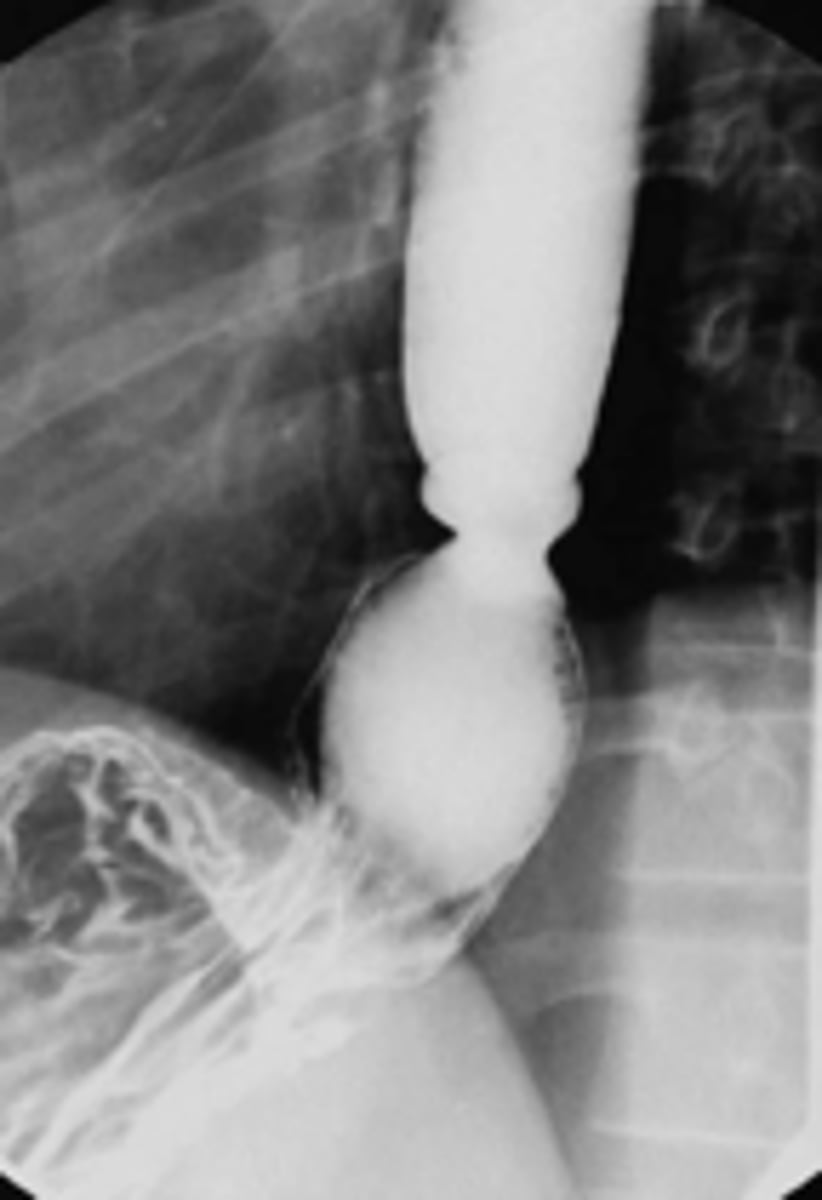
patient presents with dysphagia of large solid foods (steakhouse syndrome). An endoscopy is performed and a narrowing of the distal esophagus is observed. What is the diagnosis?
Esophageal "Schatzki" ring
an esophageal web, proximal membrane formation, is a sign of untreated ______
iron deficiency anemia
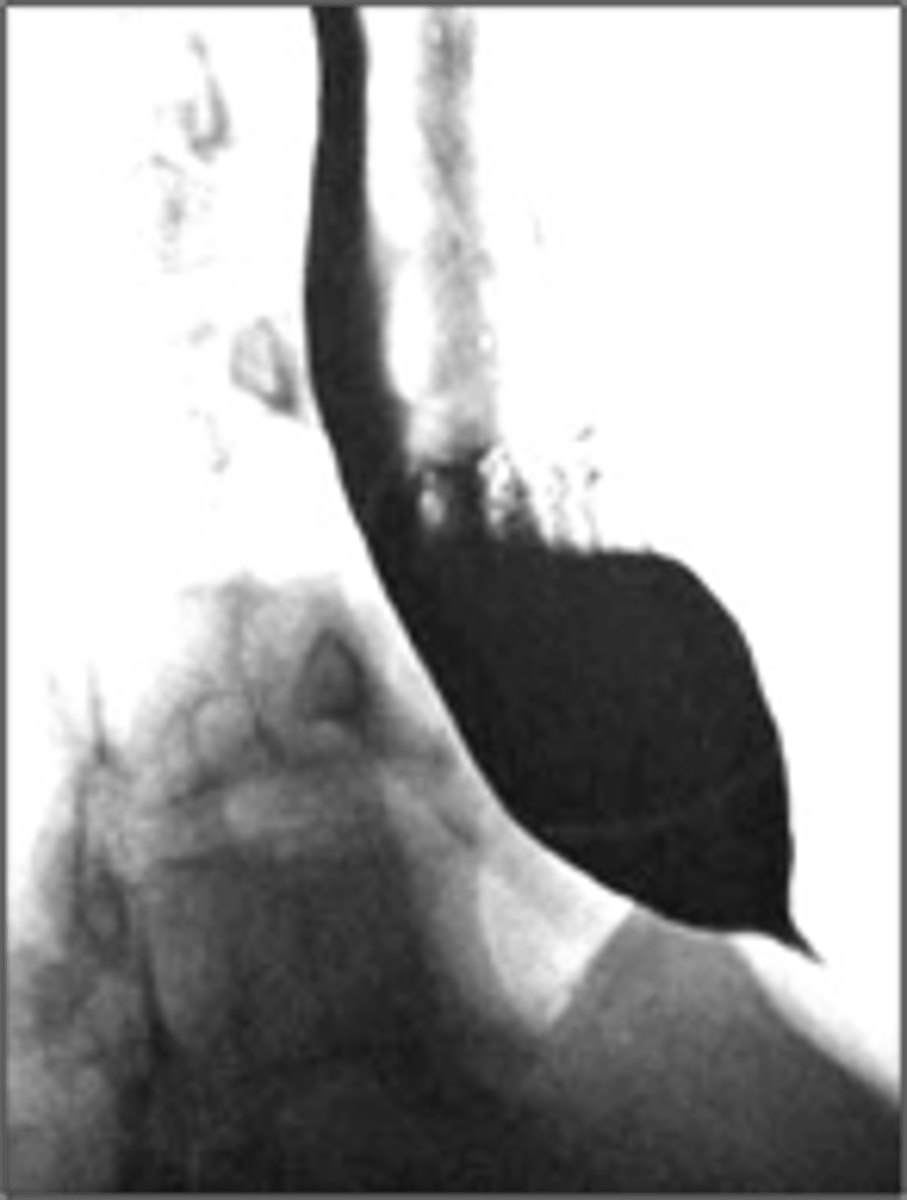
What has the following characteristics?
• Motility disorder
• Dysphagia to solids and liquids
• Absent ganglion cells
• Distal stricture “birds beak” on barium
achalasia
dysphagia to solid foods implies a _______
obstruction
dysphagia to solid AND liquid foods implies a _______
motility disorder
Peptic Ulcers, perforated ulcer and pancreatitis all present pain in what abdominal region?
epigastric region
patient presents with “gnawing” epigastric pain, patient is currently being treated for GERD symptoms with no resolve. H.pylori test comes back positive. What is the diagnosis?
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Injury to the lining of the stomach/duodenum that penetrates through the muscularis mucosa of stomach/duodenum indicates ____________
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
treatment for Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD):
• STOP aspirin/NSAIDs
• Treat for H pylori (multiple options)
• Acid suppression (usually PPI)
• FOLLOW-UP 4-6 weeks to monitor healing and rule out complications or malignant gastric ulcer
Major causes of this GI disorder include:
- H. pylori
- NSAIDs
- Ischemia
- Smoking
- Alcohol
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
What is this complication of peptic ulcer disease?
Acute abdominal pain, hypotension, and air under the diaphragm. Require emergency surgery
Perforation
PUD has a ________ recurrence rate. H. pylori treatment reduces recurrence rate
high
What type of GI bleeding is the following:
- Dark tarry stools (partially digested blood)
- Signs of iron deficiency anemia
Chronic/slow
What type of GI bleeding is the following:
- Bright blood per rectum if significant hemorrhage
- Hypotension if significant hemorrhage
Acute/severe
Define the following:
Inflammation of the pancreas. Insults to the pancreas can lead to activation of enzymes and autodigestion of tissue
Acute Pancreatitis
The following symptoms are associates with what GI disorder?
• Epigastric pain, often dull and steady then becoming severe, radiating to back (50%)
• Nausea and vomiting
• Fever, tachycardia
• Jaundice – less common
Acute Pancreatitis
The following complications are associated with what GI disorder?
- Can be fatal if untreated 15%
- Multiorgan system failure (1st week)
- Sepsis and complications (2nd week)
acute pancreatitis
What is the MOST COMMON cause of acute pancreatitis?
- Alcohol
- Gallstones
What is the diagnosis criteria for acute pancreatitis?
(Need 2 of the 3 for diagnosis:)
- Clinical presentation
- Labs: Elevated lipase (most specific) and amylase (do not indicate severity)
- CT scan
The following symptoms are associates with what GI disorder?
• Maybe asymptomatic until severe tissue lost
• Epigastric abdominal pain, may be intermittent, may radiate to back
• Weight loss
• Diarrhea (steatorrhea)
Chronic Pancreatitis
A patient with a history of heavy alcohol use has epigastric pain radiating to the back, vomiting, fever and jaundice. Which test is most specific for acute pancreatitis?
lipase
What has the following characteristics?
- Chronic inflammation of pancreas leading to irreversible changes
- Can present with normal labs
- Cause is 80% alcohol
- Imaging such as X-ray, CT scan, ERCP can be used
Chronic Pancreatitis
Name 3 complications of Chronic Pancreatitis:
- Malnutrition due to pancreatic insufficiency
- Diabetes (islet cell destruction)
- Pancreatic cancer
There is an association between periodontal disease and the progression of what type of cancer?
Pancreatic cancer
what is an example of a cause of secretory diarrhea?
Vibrio cholerae
you would expect a patient with Vibrio Cholera to have what type of stool?
secretory diarrhea
you would expect a patient with Lactose intolerance to have what type of stool?
osmotic diarrhea
you would expect a patient with Celiac disease to have what type of stool?
malabsorption steatorrhea
you would expect a patient with pancreatic insufficiency to have what type of stool?
maldigestion steatorrhea
you would expect a patient with pseudomembranous colitis to have what type of stool?
inflammatory (exudative) diarrhea
you would expect a patient with irritable bowel syndrome to have what type of stool?
diarrhea secondary to altered bowel motility
Define the following:
Altered mucosal transport or secretory dysfunction – secretion of electrolytes into lumen, water follows
secretory diarrhea
Define the following:
Something in lumen is drawing water into the GI tract i.e. lactose intolerance
osmotic diarrhea
What has the following characteristics?
- Bloating, flatulence, abdominal cramps, nausea, diarrhea
- Occurs 30 mins to 2 hours after ingestion
lactose intolerance
this diarrhea is often characterized by bloating and steatorrhea:
fatty diarrhea
this diarrhea is characterized by elevated WBC count, occult gross blood or pus in stool, i.e. pseudomembranous colitis:
inflammatory/exudative diarrhea
A patient has abdominal pain diarrhea with pus and blood. Stool is positive for C difficile toxin and colonoscopy shows yellow plaques. What medication is a risk factor for this presentation?
Clindamycin
this medication is known to cause gastric ulcers:
NSAIDs
what is the primary mode of prevention for Pseudomembranous colitis?
- Hand washing
- Contact precautions
- Avoid unnecessary antibiotics
- Supportive treatment
- Avoid anti-motility treatment
- IV or PO Flagyl, PO Vancomycin, other
Altered GI flora after use of broad spectrum antibiotics (clindamycin) can cause this GI disorder:
Pseudomembranous colitis
This type of diarrhea is also associated with
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Diverticulitis
- Invasive infectious disease
- Neoplasia (colon cancer/lymphoma)
- Radiation colitis
inflammatory/exudative diarrhea
What has the following characteristics?
- Diarrhea secondary to altered bowel motility
- Symptoms: abdominal pain, disturbed defection, bloating, improves with fasting
- No clear abnormalities
- MOST COMMON GI CONDITION
functional diarrhea
Which type of GI polyp is pre-malignant & neoplastic: hyperplastic or adenomatous polyp?
adenomatous polyp
which type of GI polyp has no malignant potential: hyperplastic or adenomatous polyp?
hyperplastic
What are colon cancer syndromes?
- Peutz-Jeghers
- Familiar Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
- Gardner disease (subset FAP)
- Hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HPNCC – Lynch syndrome)
what age does colon cancer screening start?
45
after the age of 45, patients should get a colon cancer screening every ______ years
10
what is the gold standard for colon cancer screening and prevention, examines entire colon?
colonoscopy
What colon cancer screening method can you do in the comfort of your own home?
Cologaurd
t/f: Cologaurd can be used to prevent cancer
false, can't prevent cancer but helps with early diagnosis!
t/f: Cologaurd can be used to detect early cancer
true
These tests indicate _______:
Hematocrit
• Hemoglobin
• Red cell indices
• Serum iron/ferritin if indicated
• Fecal occult blood test
blood loss and anemia
these test for _______________:
- WBC
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate)
- C-reactive protein
infection/inflammation
A patient on vacation has chronic pancreatitis and they forgot to bring their pancreatic enzyme replacement medication. They have abdominal pain and frequent loose stools which are foul-smelling and float in the toilet.
What category of diarrhea does this patient most likely have?
A. Secretory
B. Exudative
C. Fatty/maldigestive
D. Altered motility/"functional"
E. Inflammatory
C. Fatty/maldigestive