2.5- Biological Membranes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
roles of cell surface membranes
Control exchange of material
Compartmentalisation
sites of chemical reactions
cell signalling→ interface for communication between cells
fluid mosaic model of membranes
fluid:
proteins and phospholipids can move around via diffusion
phospholipids move sideways within their layers
proteins interspersed throughout bilayer and move about with it
some proteins may be in a fixed position
mosaic due to scattered pattern produced by proteins
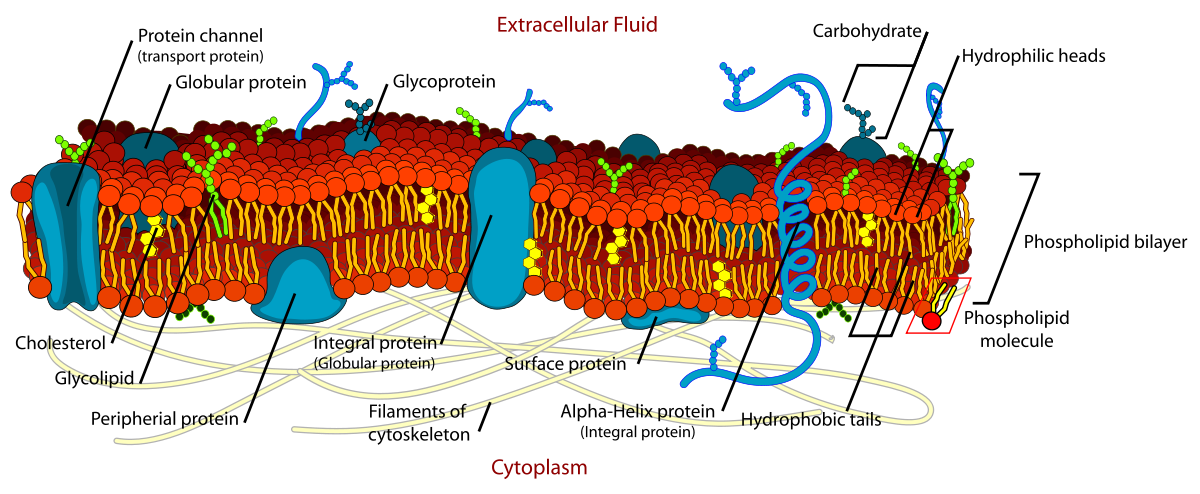
components of the fluid mosaic model of membranes
phospholipids
cholesterol
glycolipids and glycoproteins
transport proteins
phospholipids in the cell membrane
forms phospholipid bilayer
acts as a barrier to most water-soluble substances→ non-polar hydrophilic tail
ensures water soluble molecules cannot leak out of the cell and unwanted water cannot get in
can act as signalling molecules by:
moving within bilayer to activate other molecules
being hydrolysed , releasing small water soluble molecules that bind to specific receptors in cytoplasm
cholesterol in the cell membrane
increases fluidity of cell membrane
stops phospholipid tails packing too closely together
at high temps:
cholesterol bind to hydrophobic tails of phospholipids, causing them to pack more closely together
Increases mechanical strength and stability of membranes
glycolipids and glycoproteins in the cell membrane
contain carbohydrate chains that exist on the surface→ allows them to act as receptor molecules
bind with substances at cell’s surface
some act as cell markers or antigens for cell-to-cell recognition
types of glycolipid/protein receptors
signalling→hormones, neurotransmitters
Endocytosis
Cell adhesion and stabilisation→ carbohydrate forms H-bonds
transport proteins
create hydrophilic channels to allow ions and polar molecules to travel through the membrane.
Two types:
channel proteins
carrier proteins
specific to a particular ion or molecule
factors effecting cell membrane permeability
temperature
solvent concentration
affect of temperature on cell membrane permeability below 0C
phospholipids have less kinetic energy= membrane is less fluid=very rigid
proteins become denatured= more permeable
ice crystals form in the membrane=membrane can fracture=increased permeability
affect of temperature on cell membrane permeability between 0C and 45C
membranes are fluid→ phospholipids move easily
semi permeable→ as temp increases, kinetic energy of phospholipids increases=more movement=more gaps in membrane so increased permeability
affect of temperature on membrane permeability above 45C
bilayer breaks down→ increased Ek=phospholipids move far away from one another
membrane becomes freely permeable→proteins denature- increased membrane permeability
membrane may burst→ heat causes water inside the cells to expand- puts pressure on membrane causing
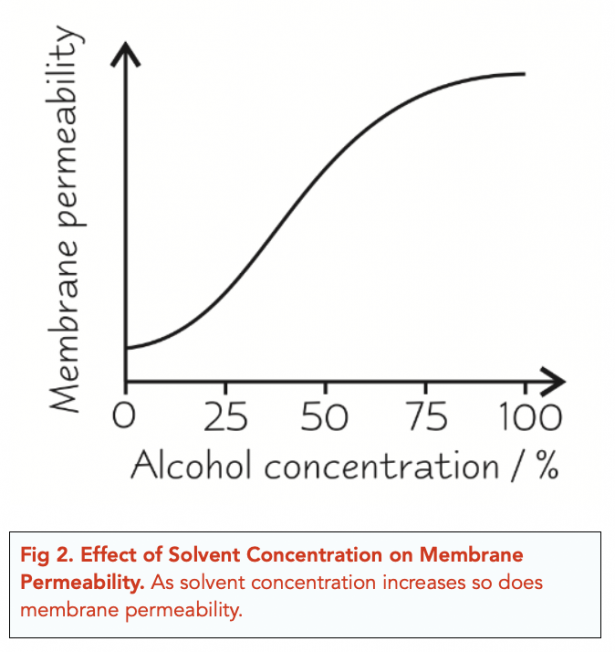
effect of solvents on cell membranes
increase permeability→ lipids dissolve in alcohol so cell membrane will break down in solvents= cell membrane more fluid and permeable as it breaks down
what substances can and can’t cross phospholipid bilayer
CAN:
lipid soluble/ non-polar
small
e.g. steroids, oxygen, carbon dioxide
CAN’T:
water soluble/ non polar
large molecules
e.g. glucose, amino acids
how are proteins embedded in the membrane
intrinsic:
span full plasma membrane→ act to transport water soluble/ charged molecules across the membrane
extrinsic:
located on the surface/ partially embedded- never fully extend across entire cell surface membrane
what is diffusion
the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
passive process→ energy that particles have comes from their natural inbuilt motion rather than from an external source
factors affecting rate of diffusion
temp→ higher temp=higher Ek=higher rate of diffusion
diffusion distance→ longer distance= lower rate
surface area→ larger surface area= more area over which diffusion can take place
size of diffusing molecules→ smaller ions= higher rate of diffusion
concentration gradient→ steeper gradient= higher rate of diffusion
Fick’s Law

facilitated diffusion and the role of channel and carrier proteins
only occurs at specific points on plasma membrane where there are specific protein molecules
channel proteins
form water filled channels across membrane and allow water soluble molecules to cross e.g. ions
channels are specific→ will only allow certain molecules to cross- will remain closed if molecule is not there
carrier proteins
carriers that span the membrane
when the specific molecule e.g. glucose, is present, it binds to the carrier protein→ carrier changes shape so molecule can cross
water potential
represented using psi (𝛙)
measured in kPa
created by the pressure of water particles
under standard conditions pure water has a WP of 0kPa
if solute is added, WP is less than 0→ more solute= more negative
what is osmosis
the movement of water molecules from an area of high water potential to a low water potential through a partially permeable membrane
hypotonic solution
more water
less solute
hypertonic solution
less water
more solute
more negative WP
isotonic solution
same solute concentration and water concentration compared to body fluids
animal cells in hypertonic solution
water leaves cell through partially permeable membrane by osmosis
cell will shrink and shrivel up→ crenation
animal cells in hypotonic solution
water enters cell through partially permeable membrane by osmosis
cell will continue to gain water until membrane is stretched too far and cell bursts→ cytolysis
animal cells in isotonic solution
movement of water molecules into and out of the cell occurs at the same rate→ no net movement
plant cells in hypertonic solution
water leaves plant cell through partially permeable membrane by osmosis
water leaves vacuole of plant cell→ volume of plant cell decreases
protoplast shrinks and no longer exerts pressure on cell wall→ plasmolysis
plant cells in hypotonic solution
water enters plant cell through partially permeable membrane by osmosis
water enters vacuole of plant cell→ volume increases
expanding protoplast pushes against cell wall and pressure builds up inside cell
when plant cell is fully inflated with water→ turgid
active transport
movement of molecules and ions through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to region of higher concentration using energy from respiration
what does active transport require
energy→ provided by hydrolysis of ATP
carrier proteins→ require energy to change shape allowing it to transfer the molecules/ ions across the cell membrane
where is active transport important
reabsorption of useful molecules and ions into the blood after filtration into kidney tubules
absorption of some products of digestion from digestive tract
loading of sugar from photosynthesising cells of leaves into phloem tissue for transport around plant
loading of inorganic ions from the soil into root hairs
endocytosis and exocytosis
endocytosis→ bulk transport into cells:
segment of plasma membrane surrounds and encloses particle and brings it into the cell, enclosed in a vesicle
exocytosis→ bulk transport out of cells
vesicle containing substances is moved towards and then fuses with plasma membrane
types of endocytosis
phagocytosis:
bulk intake of solid material by cell
carried out by phagocytes
vacuoles formed are phagocytic vacuoles
pinocytosis:
bulk intake of liquids
if the vacuole that is formed is extremely small then the process is called micropinocytosis
exocytosis
substances packages into secretory vesicles formed from Golgi body
vesicles travel to cell surface membrane→ fuse with membrane and release contents outside the cell
antiport vs symport
antiport→ carries two different types of ions in different directions
symport→ transporting ions in one direction
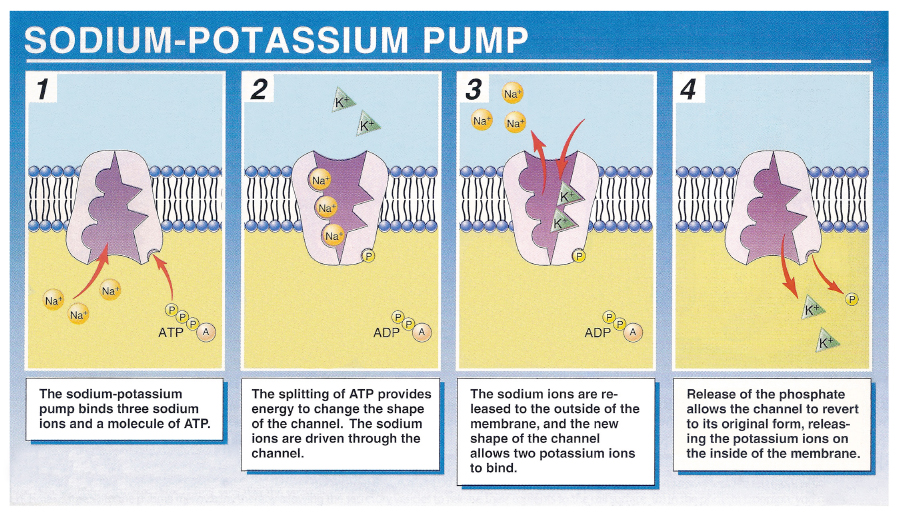
the sodium potassium pump
carrier proteins have sites that combine reversibly with only certain solute molecules or ions
also have regions that binds to ATP, allowing for its hydrolysis to release energy→ helps protein change shape and carries ion from one side of membrane to other
the sodium potassium pump has a repeating cycle of conformational (shape) changes to transport 3 sodium ions out of and 2 potassium ions into the cell
co transport of glucose (indirect active transport)
sodium ions are actively transported out of the epithelial cell, via sodium potassium pump, into the blood→ creates a lower concentration of Na+ in epithelial cell than in the lumen
Na+ diffuse into epithelial cells down conc. gradient via facilitated diffusion→ as sodium ions diffuse, they carry either glucose or amino acid molecules with them→ co-transport
glucose/AA molecule pass into blood via facilitated diffusion through separate carrier protein→ moving against their concentration gradient