m1 (for long quiz) (quiz2 not included)
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Antheroma
also known as plaques
blood pressure
the outward pressure of blood against blood vessel walls, is the product of blood flow from the heart and inward resistance of blood vessel walls
baroreceptor reflex
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
2 ways of regulation of blood pressure
baroreceptor reflex
responsible for short-term regulation of blood pressure (moment to moment regulation of blood pressure)
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
all medicine target what pathway
carotid sinus
aortic arch
two main locations of baroreceptor
HYPERTENSION
◼ Persistent diastolic BP greater than 90 mm Hg and systolic BP greater than 140 mm Hg
◼ American Heart Association : > 140/90
◼ WHO : > 160/95
Primary or Essential Hypertension
hypertension caused by genes (no specific identifiable causes)
hypertension due to specific disease/identifiable cause
Secondary Hypertension
hypertension caused by comorbidities
secondary hypertension
pheochromocytoma
dusty color tumor
○ Pheochromocytoma
○ Renal Artery Constriction
○ Cushing’s Syndrome
○ Primary Aldosteronism
○ Thyroid/Parathyroid Disease
secondary hypertension is due to specific disease/identifiable causes:
Joint National Committee
JNC
<120/<80
normal hypertension BP
120-139/80-89
Prehypertension BP
140-159/90-99
Stage 1 Hypertension BP
≥160/≥100
Stage 2 hypertension BP
CHF
CAD
Renal Disease
Ischemic Stroke
Atherosclerosis
Retinal Disease
Aneurysm
Cardiomyopathy
What are the Complications of Hypertension?
pheochromocytoma
causes excessive production of catecholamines
increased Cardiac Output
Systemic Vascular Resistance
two main mechanisms that lead to hypertension
hypertension
stress
pheochromocytoma
causes of increaed cardiac output that leads to hypertension (??)
stress
atherosclerosis
renal artery disease
pheochromocytoma
thyroid dysfunction
cerebral ischemia
causes of increaed vascular resistance that leads to hypertension (??)
diuretic
drugs to decrease blood volume
beta blockers
drugs to decrease cardiac output
vasodilators
drugs to decrease vascular resistance
1. DIURETICS
2. SYMPATHOPLEGICS
3. DIRECT VASODILATORS
4. AGENTS THAT BLOCK PRODUCTION OR ACTION OF ANGIOTENSIN (ANGIOTENSIN ANTAGONISTS)
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS
DIURETIC AGENTS
AGENTS TO LOWER BLOOD PRESSURE BY DEPLETING THE BODY OF SODIUM AND REDUCING BLOOD VOLUME
CAIs - PCT
Loop Diuretics - TAL
Thiazides - DCT
K sparing - CD
Osmotic diuretics
drugs that modify salt excretion
ADH antagonist
ADH antagonist
Osmotic diuretics
drugs that modify water excretion
thiazide-like diuretic
Indapamide
furosemide
most famous diuretic
spironolactone
eplerenone
K sparing diuretics - aldosterone antagonist
Triamterene
Amiloride
K sparing diuretics - ENac inhibitors
Carbonic anhydrase Inhibitor
weakest diuretic
decrease
Inhibition of Carbonic Anhydrase: __ bicarbonate concentration in the blood
Block the Na+/K+/2Cl- symporter (cotransporter) in thick ascending loop of Henle
MOA of loop diuretics
Amiloride and Triamterene
inhibit the Na+ influx through ion channel (ENaC)
Spironolactone, Eplerenone
antagonize the effect of aldosterone (mineralocorticoid)
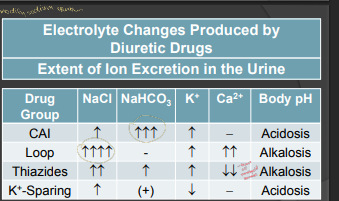
-
syndrome of antidiuretic hormone
SIADH
MINOXIDIL
Orally active vasodilator
Minoxidil (Rogaine)
Used topically as a stimulant to hair growth for correction of baldness
Edema due to sodium and water retention
Reflex tachycardia
Flushing
Headache
Hirsutism/Hypertrichosis
Adverse Effects of Minoxidil
MINOXIDIL and HYDRALAZINE
Dilates arterioles but not veins
severe hypertension
hydralazine is effective in __ hypertension
nitrates
hydralazine when combined with __, it is effective in heart failure
systemic Lupus Erythrematosus
SLE
Lupus-like syndrome
Cardiovascular effects (Hypotension, Reflex tachycardia, Palpitation, Angina)
CNS effects (Headache, Nausea, Anorexia)
Adverse Effects of Hydralazine
SODIUM NITROPRUSSIDE
Parenterally administered vasodilator
SODIUM NITROPRUSSIDE
Dilates both arterial and venous vessels
SODIUM NITROPRUSSIDE
Used in treating hypertensive emergencies as well as severe heart failure
Hypotension
Metabolic acidosis
Arrhythmias
Methemoglobinemia may also develop during infusion
Accumulation of Cyanide
Adverse Effects of SODIUM NITROPRUSSIDE
Accumulation of Cyanide
Adverse Effects of SODIUM NITROPRUSSIDE
methylene blue
DOC for methemoglobinemia
Vit. B12
cyanide antidote kit
IV
Cyanide = inhibits complex __ = cellular hypoxia
DIAZOXIDE
Effective and relatively longacting parenterally administered arteriolar dilator
DIAZOXIDE
used to treat hypoglycemia secondary to insulinoma
Hypotension
Reflex tachycardia
Hyperglycemia (inhibit insulin release)
Adverse Effects of Diazoxide
esmelol (htn - tachycardia)
fenoldepam
diazoxide (occasionally)
drugs used for hypertensive emergencies
Dopamine D1 receptor
agonist
MOA of fenoldopam
Reflex tachycardia
Headache and flushing
Increases IOP
toxicities of fenoldopam
PERIPHERAL EDEMA
Reflex tachcardia
vasodilator monotherapy s/e
Lercanidipine
Amlodipine
Lacidipine
vasodilators that can be used as monotherapy
-
nifedine cannot be used as mnotherapy
however, (ADALAT CC) = /
Nifedipine
1st gen dihydropyridine (CCB)
Isradipine
Nicardipine
Felodipine
Nimodipine
2nd gen dihydropyridine (CCB)
Amlodipin
3rd gen dihydropyridine (CCB)
Clevidipine
4th gen dihydropyridine (CCB)
Verapamil (Phenilalkylamine)
Diltiazem (Benzothiazepines)
NON-DIHYDROPYRIDINES CCBs
Verapamil
NON-DIHYDROPYRIDINES
greatest depressant effect on the heart
Diltiazem
NON-DIHYDROPYRIDINES
intermediate action
NON-DIHYDROPYRIDINES
: Cardioselective; Intermediary effects in the heart and blood vessels
Nifedipine
ultra short acting used in emergency management of severe hypertension
Calcium Channel Blockers
Prophylactic therapy in both effort and vasospastic angina
nifedipine
(drug) Abort acute anginal attack
Calcium Channel Blockers in combination with nitrates
Atheroslerotic angina (CCB with what)
verapamil, diltiazem (not approved for this purpose)
drugs for supraventricular tachycardia
Migraine
Preterm labor
Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage – nimodipine
Raynaud’s syndrome
Clinical Uses of Calcium Channel Blocker
Raynaud’s syndrome
spasm of small arteries
ANGIOTENSIN ANTAGONISTS
Reduce peripheral vascular resistance and blood volume
I. Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibitors
II. Angiotensin II-Receptor Blockers
III. Renin Inhibitor - Aliskiren
Angiotensin Antagonists
Captopril
Lisinopril
ACE inhibitors that are not prodrug
○ Saralasin
○ Losartan
○ Valsartan
○ Telmisartan
○ Olmesartan
○ Irbesartan
○ Candesartan
○ Eprosartan
○ Azilsartan
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS (ARBs)
Mild to moderate hypertension
CHF
Diabetes mellitus
In patients with heart failure and chronic kidney disease
Clinical uses of ACE INHIBITORS
ACE INHIBITORS
Can be used safely in ischemic heart disease patients for hypertension
ACE INHIBITORS
Most effective in conditions associated with high renin activity for hypertension
renoprotective
ACEIs exert a __ effect
ACE INHIBITORS
Useful in treating patients with chronic kidney disease for hypertension
Hemophilia
Headache
Fever
Hyperkalemia
Allergy
Orthostatic hypotension
Angioedema
Cough
Less common with ARBs
Renal damage in nondiabetic renal vascular disease
Teratogenic
Adverse effects of Angiotensin Antagonists
Cough
Adverse effect of Angiotensin Antagonists
less common with ARBs
Fetal hypotension, anuria, and renal failure (renal dysgenesis)
Contraindicated during the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy
Adverse effects of Angiotensin Antagonists
angiotensin antagonists to delay diabetic nephropathy
ACEIs
Choice of Antihypertensive Drugs Based on Patient Characteristics
Diabetic patients and those with chronic kidney disease
beta-blockers
calcium antagonists
avoid hydralazine
Choice of Antihypertensive Drugs Based on Patient Characteristics
CAD patients
CHF
Choice of Antihypertensive Drugs Based on Patient Characteristics
ACE inhibitors and/or diuretics
avoid beta-blockers and calcium antagonists
avoid beta-blockers and diuretics
Choice of Antihypertensive Drugs Based on Patient Characteristics
Athletes
calcium antagonists
avoid beta-blockers
Choice of Antihypertensive Drugs Based on Patient Characteristics
Broncho-pulmonary disease patients
avoid beta-blockers and thiazide diuretics
Choice of Antihypertensive Drugs Based on Patient Characteristics
Dyslipidemic patients
calcium antagonist (nifedipine)
Vasodilators or ACE-inhibitors
avoid beta-blockers
Choice of Antihypertensive Drugs Based on Patient Characteristics
Peripheral vascular disease patients