Biotechnology Principles: Growth, Culture Media, and Metric System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Macronutrients
Elements required in fairly large amounts for cellular functions.
Micronutrients
Metals needed in very small amounts for cellular functions.
Growth factors
Organic compounds required in very small amounts for the growth of organisms.
Autotrophs
Prokaryotes that can build all of their cellular structures from carbon dioxide.
Nitrogen
An essential element important in proteins, nucleic acids, and several other cell constituents.
Iron
A key component in cellular respiration, cytochromes, and iron-sulfur proteins involved in electron transport.
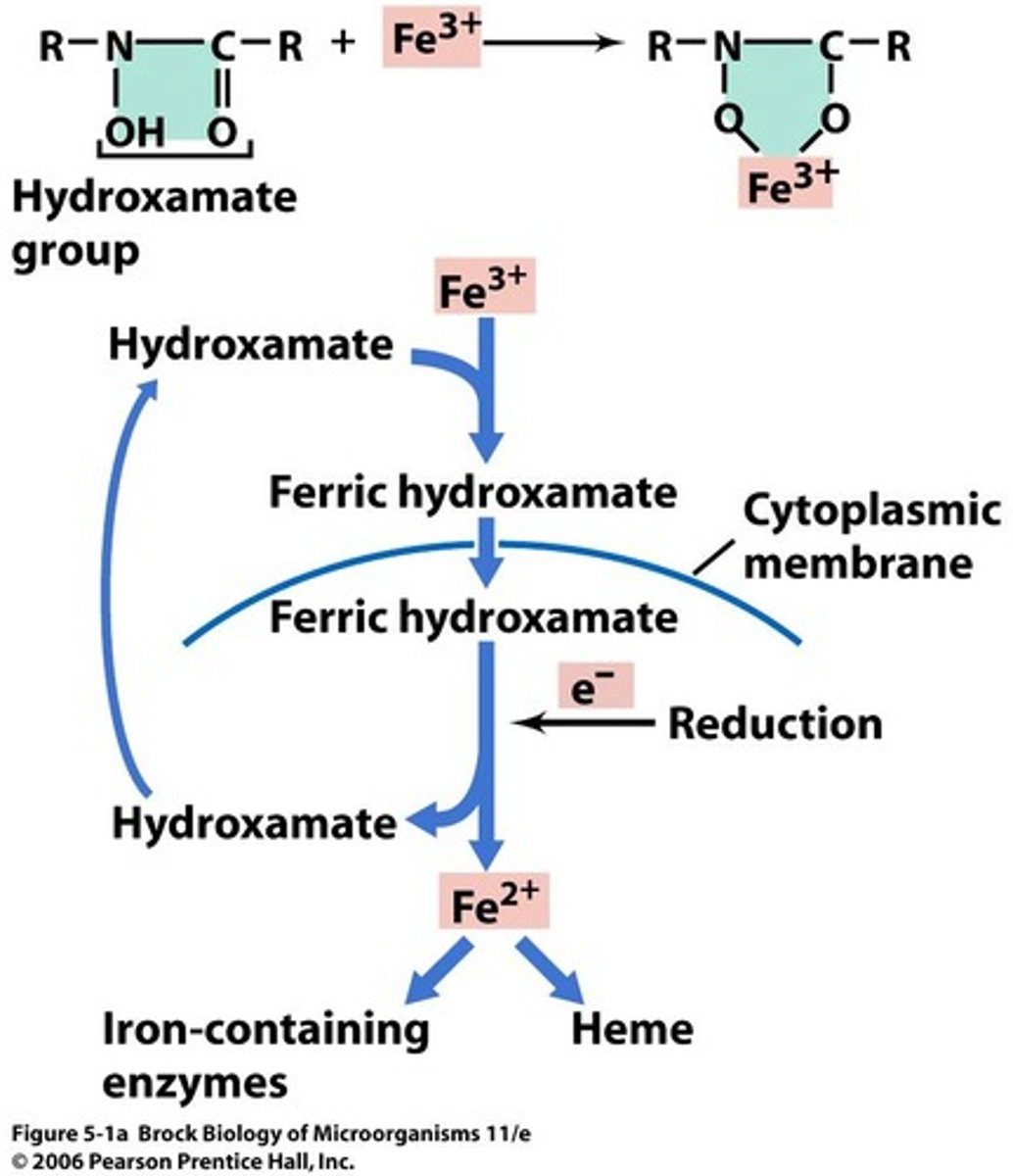
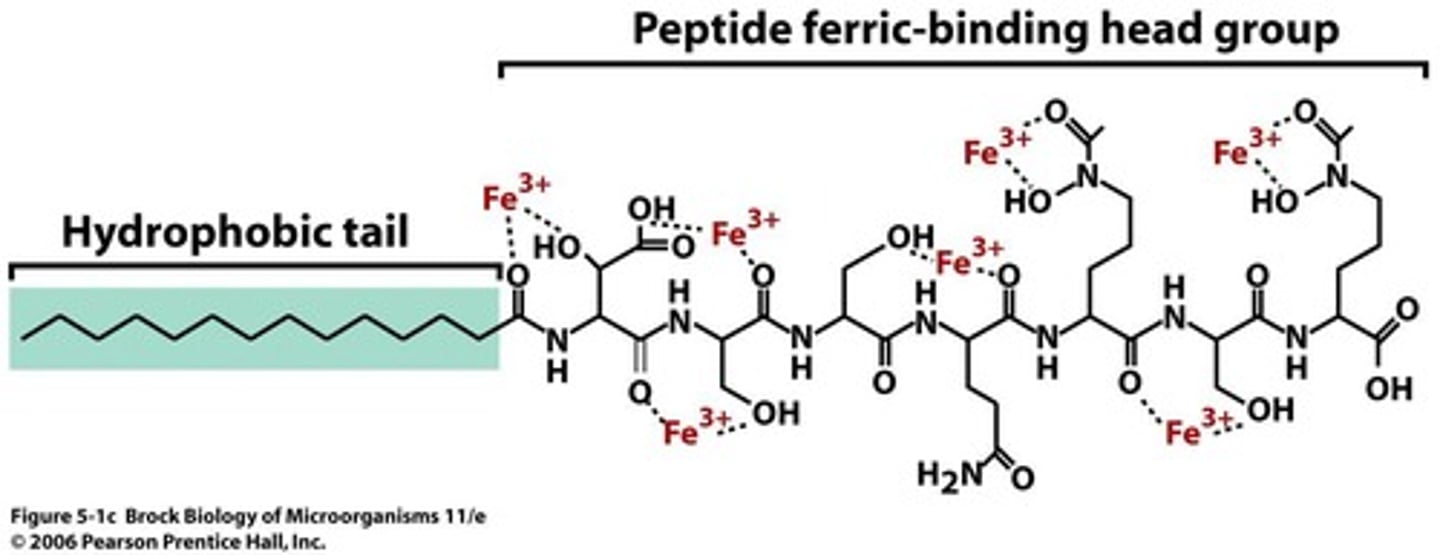
Siderophores
Agents produced by cells to bind iron from insoluble minerals and transport it into the cell.
Hydroxamate
A type of siderophore that binds iron (Fe2+).
Ferric Enterobactin
A type of siderophore that binds iron (Fe2+).
Peptic siderophore
Example includes Aquachelin, which binds iron.
Culture media
Nutritional solutions that supply the needs of microorganisms.
Chemically defined medium
Culture media with known chemical compositions.
Undefined medium
Culture media with complex, unknown compositions.
Selective media
Media used for the isolation of particular species of microorganisms.
Differential media
Media used for comparative studies of microorganisms.
Enriched media
Media that provide additional nutrients to support the growth of specific microorganisms.
Aseptic technique
Practices used to prevent contamination by other microorganisms during culture.
Semisolid culture media
Culture media prepared by adding a gelling agent to liquid media.
Solid Culture Media
Such solid culture media immobilize cells, allowing them to grow and form visible, isolated masses called colonies.
Liquid Medium
A type of culture media that is in liquid form.
Solid Medium
A type of culture media that is in solid form.
Free Energy (Gf0)
The energy in a chemical reaction that is available to do useful/important work.
Change in Free Energy (∆G0')
The change in free energy during a reaction.
Energy Change (ΔG)
The changes in energy during chemical reactions expressed in kilojoules.
Exergonic Reactions
Chemical reactions that occur with the release of free energy, also known as catabolism.
Endergonic Reactions
Chemical reactions that occur with the consumption of free energy, also known as anabolism.
Activation Energy
The energy required to bring all molecules in a chemical reaction into the reactive state.
Catalyst
A substance that is required to activate the reactants in a chemical reaction.
Enzymes
Catalytic proteins that speed up the rate of biochemical reactions by raising the activation energy.
Specificity of Enzymes
The high specificity of enzymes in the reactions they catalyze, found in the three-dimensional structure of the polypeptide(s) in the protein.
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
Reactions that involve the transfer of electrons from electron donor to electron acceptor.
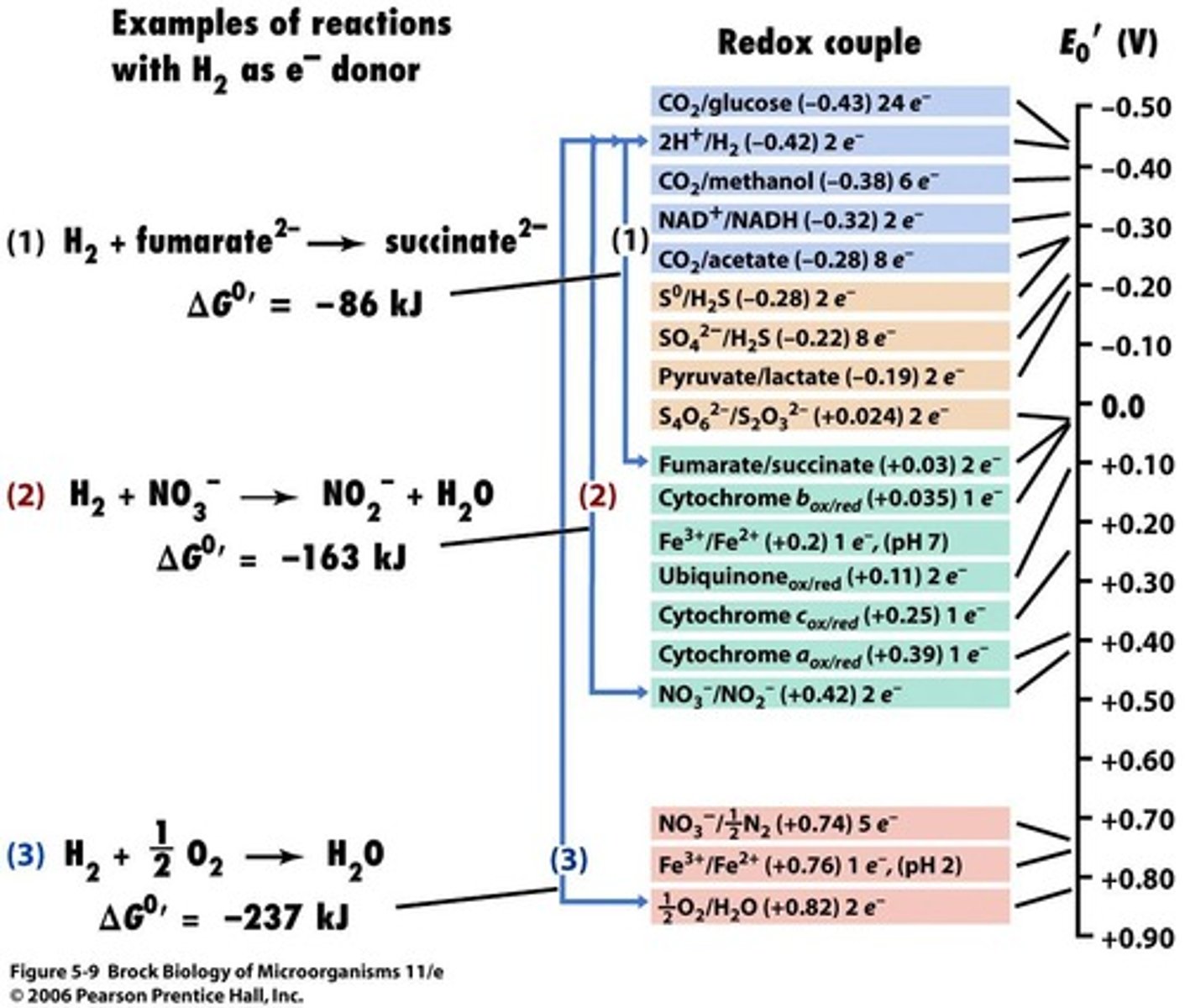
Reduction Potential (E0')
The quantitative expression of the tendency of a compound to accept or release electrons.
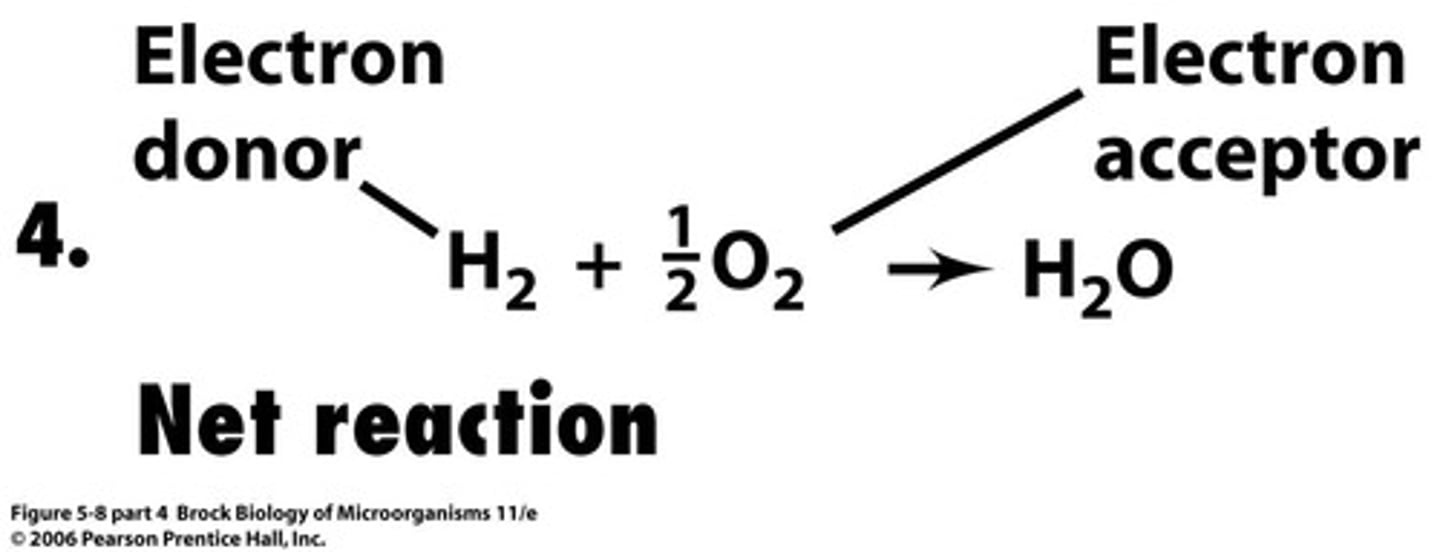
Electron Donor
The substance oxidized in a redox reaction.
Electron Acceptor
The substance reduced in a redox reaction.
Redox Reaction
A chemical reaction in which the substance oxidized is the electron donor and the substance reduced is the electron acceptor.
Reduction Potential
A measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons and thereby be reduced, represented in a vertical tower from most negative E0's to most positive E0's.
Electron Carriers
Molecules that transfer electrons from donor to acceptor in biological systems, which can be membrane-bound or freely diffusible.
Coenzymes
Organic molecules, such as NAD+/NADH, that assist in enzyme activity by transferring electrons and are freely diffusible in the cell.
NAD+/NADH
A coenzyme involved in catabolic reactions, acting as an electron carrier.
NADP/NADPH
A coenzyme involved in anabolic reactions, acting as an electron carrier.
Energy-Rich Compounds
Compounds that store energy released in redox reactions, including adenosine triphosphate (ATP), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), and CoA derivatives.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The prime energy carrier in the cell, formed from energy-rich compounds.
Long-term Energy Storage
The process of forming polymers that can be consumed to yield ATP.
Fermentation
A metabolic process that occurs in the absence of exogenous electron acceptor, characterized by substrate-level phosphorylation.
Respiration
A metabolic process that uses molecular oxygen or other substances as terminal electron acceptors, characterized by oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis
A major pathway of fermentation that produces a small amount of energy conserved as ATP and fermentation products, yielding two ATPs for each glucose consumed.
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
A method of producing ATP directly in glycolysis and fermentation without the use of an electron transport chain.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
A method of producing ATP that involves the electron transport chain and the use of molecular oxygen or other terminal electron acceptors.
Prosthetic Groups
Membrane-bound electron carriers that assist in electron transfer reactions.
Primary Electron Donor
The molecule that donates electrons in a redox reaction.
Terminal Electron Acceptor
The molecule that accepts electrons in a redox reaction.
Coenzyme as Intermediary
The role of coenzymes in facilitating interactions between chemically dissimilar molecules during redox reactions.
Fermentation Products
The end products generated from glycolysis during fermentation.
Energy Conservation
The process of storing energy released in redox reactions in the formation of energy-rich compounds.
Polymers in Energy Storage
Long-chain molecules formed for the long-term storage of energy that can be broken down to yield ATP.
Metric System
Developed by the French in the late 1700's. Based on powers of ten, so it is very easy to use. Used by almost every country in the world, with the notable exception of the USA. Especially used by scientists. Abbreviated SI, which is French for System International.
kilo
1000
centi
1/100th
milli
1/1000th
Length
Length is the distance between two points. The SI base unit for length is the meter. We use rulers or meter sticks to find the length of objects.
Mass
Mass is the amount of matter that makes up an object. The SI unit for mass is the gram. A paper clip has a mass of about one gram. The mass of an object will not change unless we add or subtract matter from it.
Measuring Mass
We will use a triple beam balance scale to measure mass. Gravity pulls equally on both sides of a balance scale, so you will get the same mass no matter what planet you are on.
Weight
Weight is a measure of the force of gravity on an object. The SI unit for weight is the Newton (N). The English unit for weight is the pound.
Gravity
Gravity is the force of attraction between any two objects with mass. The force depends on two things: more distance = less gravity = less weight; less distance = more gravity = more weight; more mass = more gravity = more weight; less mass = less gravity = less weight.
Weight and Mass on the Moon
Jill's mass is 30kg regardless of location, but her weight changes based on gravity: 300N on Earth, 50N on Moon, 750N on Jupiter, and 0 Newtons in orbit.
Volume
Volume is the amount of space contained in an object. We can find the volume of box shapes by the formula Volume = length x width x height. In this case the units would be cubic centimeters (cm3).
Base unit for volume
The Liter.
Graduated cylinder
A tool used to measure the volume of liquids.
Meniscus
The curved upper surface of a liquid in a graduated cylinder.
1 cm3 of water
Equals 1 milliliter of water and has a mass of one gram.
Water displacement
A method to find the volume of irregularly shaped objects by measuring the rise in water level.
Volume of a rock
If a rock causes the water level to rise from 7 to 9 ml, the rock must have a volume of 2 ml.
Mass of 50 mL of water
50 grams.
Mass of 1 liter of water
1000 grams or 1 kilogram.
Density
The amount of matter (mass) compared to the amount of space (volume) the object occupies.
Density measurement units
Mass is measured in grams and volume in milliliters (ml) or cubic centimeters (cm3).
Density formula
Density = mass/volume.
Density unit
g/ml or g/cm3.
Density formula wheel
A tool to solve density problems by covering the property you are trying to find.
Finding density using formula wheel
Cover the word density to find density by dividing mass by volume.
Finding mass using formula wheel
Cover the word mass to find mass by multiplying density by volume.
Finding volume using formula wheel
Cover volume to find volume by dividing mass by density.
Understanding density example
If mass = 24g and volume = 8 cm3, then density = 24/8 = 3g/cm3.
Representation in density illustrations
Each 'g' represents 1 gram and each cube represents 1 cm3.
Density interpretation
There are 3 grams in every cm3.
Density of water
1 gram/ml
Mass of water (50 mL)
50 grams
Volume of water (1 kg)
1000 mL
Density of pure water
1 g/ml
Floating and Sinking
Less dense materials will float on top of more dense materials.
Density less than 1 g/mL
Objects will float on top of water.
Density greater than 1 g/mL
Objects will sink in water.
Neutral Buoyancy
Objects with a density equal to the density of water will float in mid water.
Density of Titanic
Must be less than 1 g/mL to float.
Density of Titanic after striking iceberg
Got closer to 1 g/mL as it took on water.
Density of Titanic on ocean floor
Must be greater than 1 g/mL as it is full of water.
Comparing Densities
Where is the most dense object? Where is the least dense object?
Finding mass of a rock
Using a balance scale.
Finding volume of a rock
Using a graduated cylinder and measuring water displacement.
System International (SI) prefixes
Prefixes used regardless of the units.