Geometry - Chapter 10
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Circles and stuff. Theorems.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Tangent Line to a Circle
A line is tangent to a circle, if and only if, the line is perpendicular to the radius of the circle.
External Tangent Congruence
Tangents from a common external point are congruent.
Congruent Circles Theorem
Circles are congruent if, and only if, their radii are equal.
Congruent Central Angles Theorem
In a circle, two minor arcs are congruent if and only if, their central angles are equal.
Similar Circles Theorem
All circles are similar
Congruent Corresponding Chords Theorem
In a congruent circle, or the same circle, two minor arcs are congruent if their corresponding chords are congruent
Equidistant Chords Theorem
In the same/congruent circle(s), chords are congruent if and only if they are equidistant.
Perpendicular Chord Bisector Theorem (+CONVERSE)
If a diameter is perpendicular to a chord, then it bisects the chord and its arc.
If a chord is bisected (and its arcs), then the diameter is perpendicular to the chord.
Measure of an Inscribed Angle Theorem
The measure of an inscribed angle is half of the measure of its intercepted arc.
Inscribed Angles of a Circle Theorem
If two inscribed angles in the same circle intercept the same arc then they are congruent.
Inscribed Right Triangle Theorem (+CONVERSE)
If a right triangle is inscribed, its hypotenuse is the diameter.
If the diameter is the hypotenuse of an inscribed triangle, then the angle opposite is a right angle.
Tangent and Intersected Chord Theorem
If a tangent and a chord intersect at a point on a circle, then the measure of each angle formed is ½ the measure of its intercepted arc.
Inscribed Quadrilateral Theorem
A quadrilateral can be inscribed in a circle if, and only if, its opposing angles are supplementary.
Angles Inside a Circle Theorem
If two chords intersect inside a circle, then the measure of each angle is ½ the sum of the measure of the arcs intercepted by the angle and its vertical angle.
Angles Outside the Circle Theorem
If a tangent and a secant, two tangents, or two secants, intersect outside a circle, then the measure of the angle formed is ½ the difference of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
Circumscribed Angle Theorem
The measure of a circumscribed angle is equal to 180 degrees minus the measure of the central angle that intercepts the same arc.
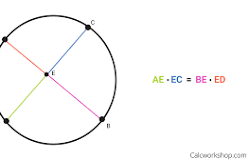
Segments of Chords Theorem
If two chords intersect in the interior of a circle, then the product of the lengths of the segments of one chord is equal to the product of the lengths of the segments of the other chord.
Please go to notes for further review on definitions and formulas.
OK