D650 Radio Interp Final Exam
1/527
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
528 Terms
Dental anomalies are — — of form, function, or position of the teeth, bones, and tissues of the jaw and mouth.
craniofacial abnormalities
Dental anomalies are craniofacial abnormalities of —, —-, or — of the teeth, bones, and tissues of the jaw and mouth.
form, function, or position
Dental anomalies are craniofacial abnormalities of form, function, or position of the —, —, and — of the jaw and mouth.
teeth, bones, and tissues
What are the three causes of dental anomalies?
congenital, developmental, aquired
Congenital dental anomalies are typically — —?
genetically inherited
Developmental dental anomalies occur during the — of a tooth or teeth.
formation
Acquired dental anomalies result from what?
Changes to teeth after normal formation
What type of dental anomaly are short roots classified as?
congenital, developmental or aquired
Teeth that form abnormally short roots represent what types of dental anomaly?
congenital or developmental
The shortening of normal tooth roots by external resorption represents what type of dental anomaly?
acquired
Number of teeth such as supernumerary or missing teeth are considered what type of anomaly?
developmental and congenital
Size of teeth such as macrodontia or microdontia are considered what type of anomaly?
developmental and congenital
Eruption of teeth such as transposition are considered what type of anomaly?
developmental and congenital
Morphology of teeth are considered what type of anomaly?
developmental and congenital
Missing teeth as a developmental or congenital abnormality can be seen as —, — or — in patients.
hypodontia, oligodontia, or anodontia
What is hypodontia?
One or few teeth
What is oligodontia?
Numerous teeth
What is andodontia?
All teeth
Fusion, concrescence and gemination are examples of what type of developmental and congenital abnormality?
morphology of teeth
Taurodontism and dilaceration are examples of what type of developmental and congenital abnormality?
morphology of teeth
Dens invaginatus, dens in dente, and dens evaginatus are examples of what type of developmental and congenital abnormality?
morphology of teeth
Dentin dysplasia, regional odontodysplasia, enamel pearls, and talon cusps are examples of what developmental and congenital abnormality?
morphology of teeth
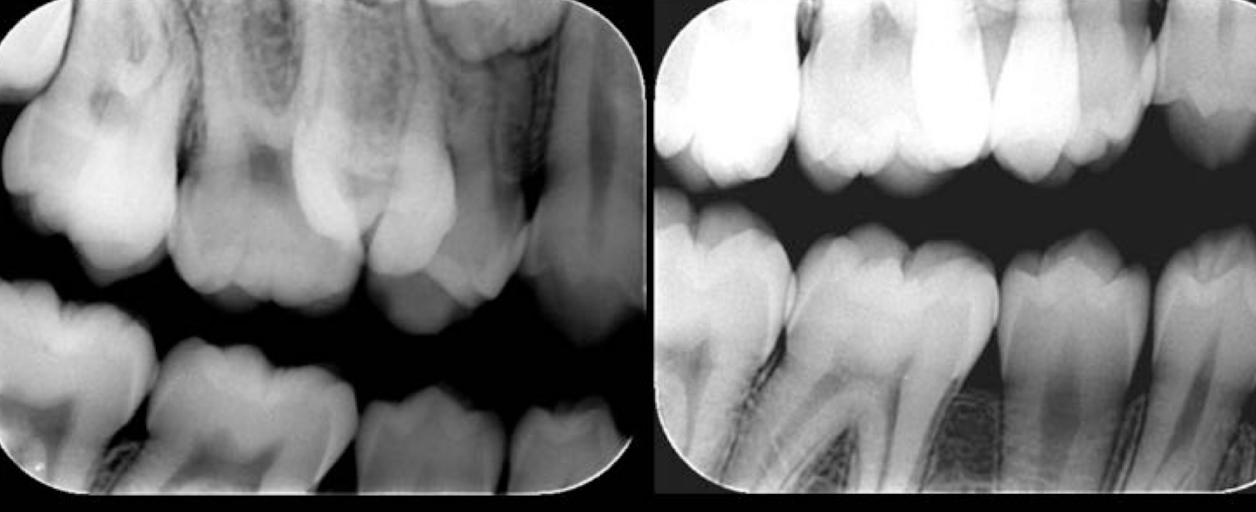
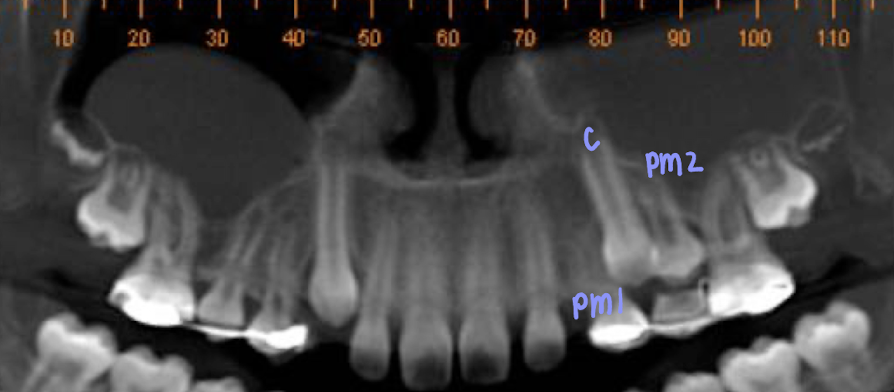
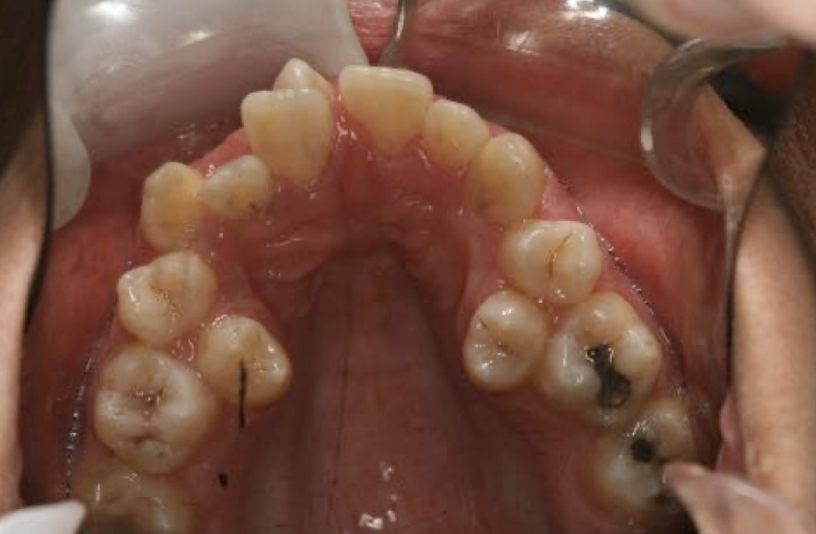
Based on this xray, what developmental and congenital abnormality is observed?
a. number of teeth
b. size of teeth
c. eruption of teeth
d. morphology of teeth
a. number of teeth
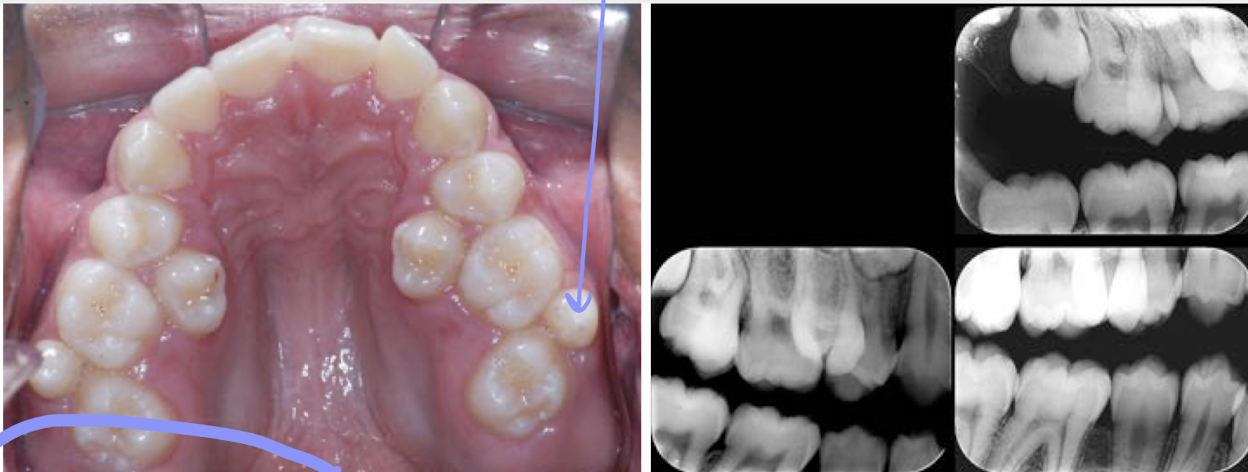
Supernumerary teeth occur in what percentage of the population?
1-4%
How are supernumerary teeth easily identified?
By counting and recording all the teeth in the jaws
Supernumerary teeth may have a greater incidence in what two groups?
Asians and Indigenous populations
Do supernumerary teeth occur twice as often in males or females?
Males
Where are single supernumerary teeth most commonly located?
In the anterior maxilla
What are single supernumerary teeth that are found in the anterior maxilla referred to as?
mesiodens
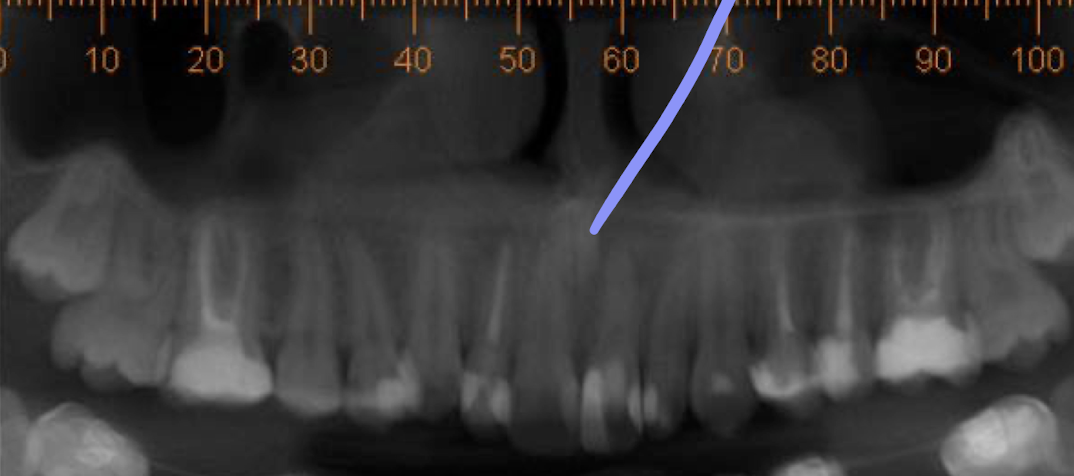
What is the purple line pointing to?
a mesioden
What condition does ‘Stranger Things’ start Gaten Matarazzo have?
Cleidocranial dysplasia
Do cleidocranial dysplasia patients have a clavicle bone?
no
Hypodontia is in the permanent dentition except what teeth?
third molars
What percentage of the population has hypodontia?
3-10%
What groups of people most frequently have hypodontia?
Asian and Indigenous populations
What is the order of most common missing teeth?
Third molars
Mandibular second premolars
Maxillary lateral and mandibular central incisors
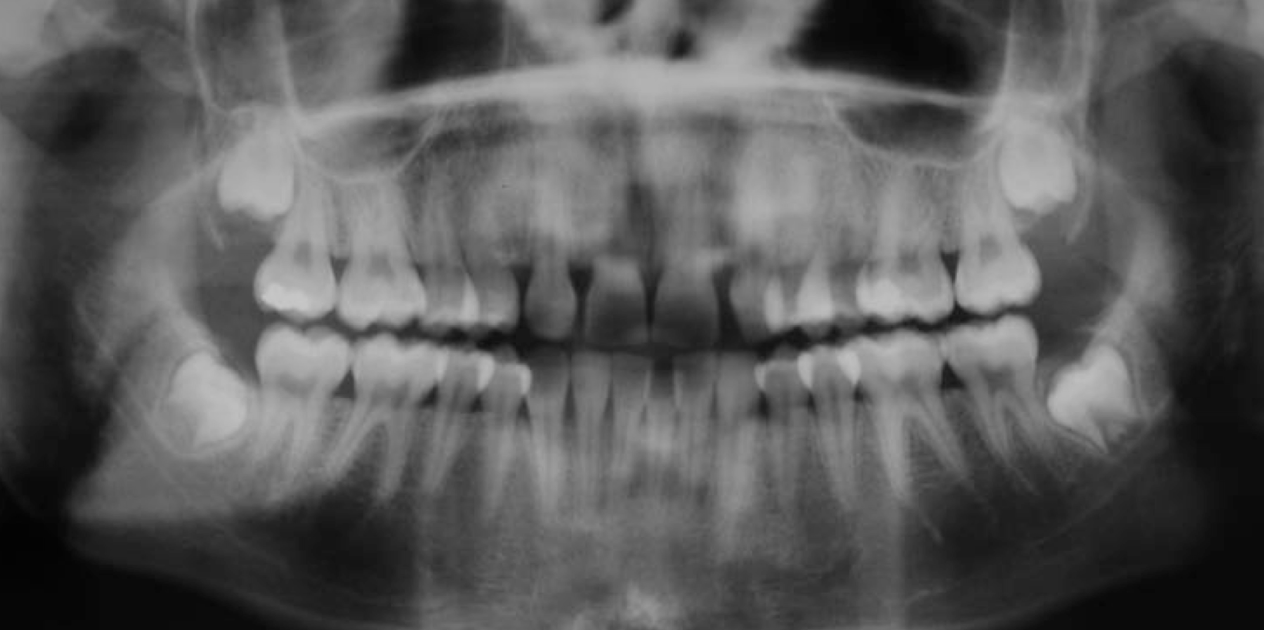
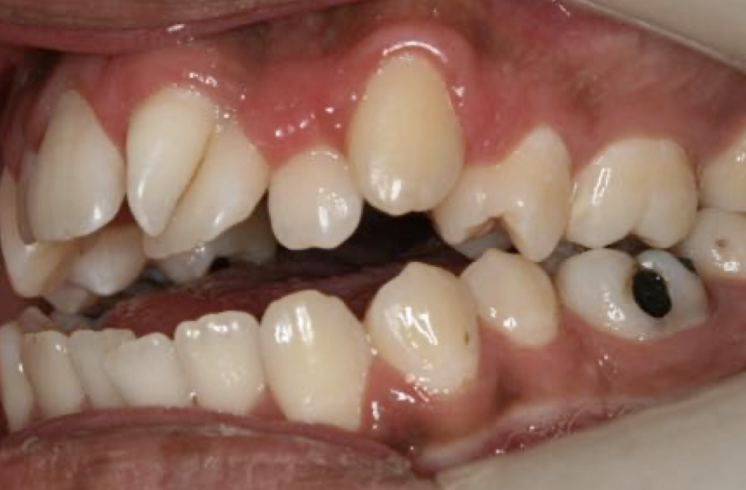
Is this x-ray, what teeth are missing?
Maxillary lateral incisors
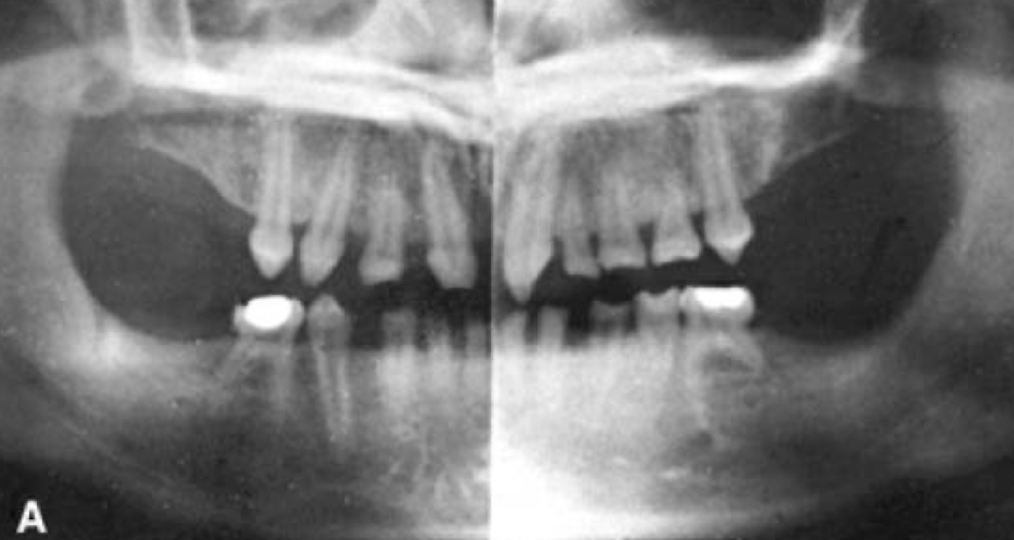
What condition does this patient have that results in missing teeth?
Ectodermal dysplasia
A positive correlation exits between — — (mesiodistal or buccolingal dimensions) and — —.
tooth size, body height
Do males or females have larger primary and permanent teeth?
males
Beyond normal variations, individuals may have usually large or small teeth.
Large teeth = ?
Small teeth = ?
Macrodontia
Microdontia
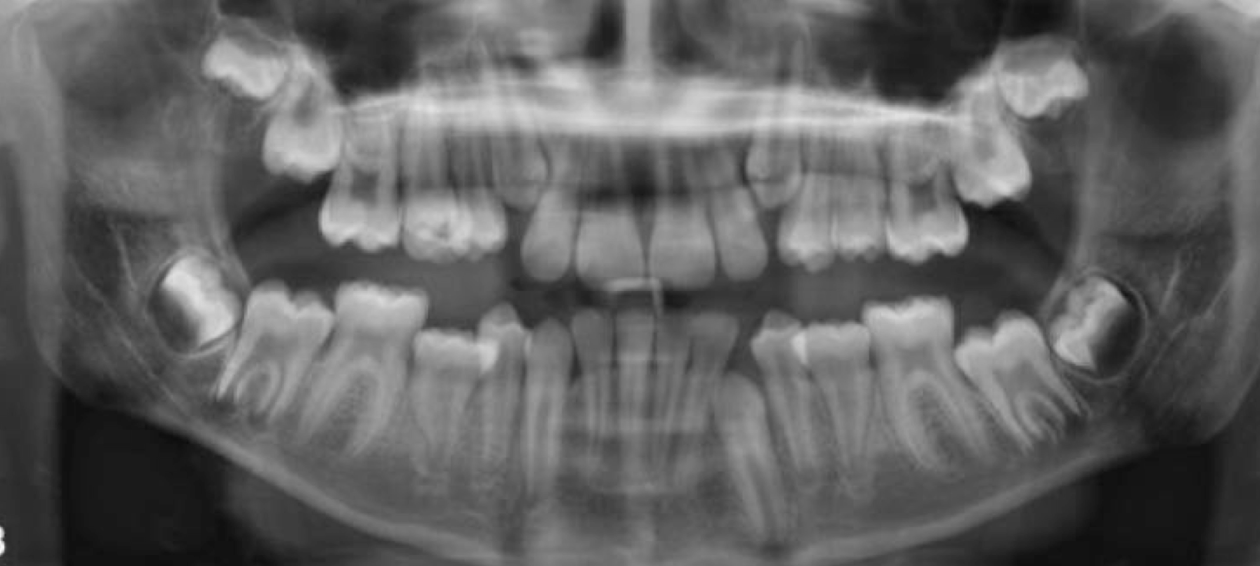
Based on this x-ray, what dental anomaly does this patient have?
Macrodontia
In macrodontia, the teeth are larger than normal; however, macrodontia rarely affects what?
the entire dentition
What teeth are typically involved in macrodontia?
A single tooth
Individual contralateral teeth OR
A group of teeth
Does macrodontia occur sporadically or systematically?
Often sporadically
What is the cause of macrodontia?
Unknown
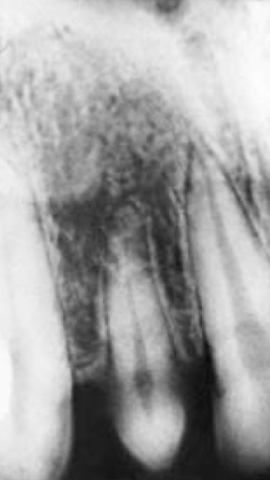
What is the condition of this tooth?
Microdontia
In microdontia, the teeth are — than normal.
smaller
As with macrodontia, microdontia may involved all the teeth or be limited to a — — or — — —.
Single tooth
Group of teeth
Which teeth are most often affected in microdontia?
Lateral incisors and third molars
Is generalized microdontia rare or common?
extremely rare
What is transposition?
A condition in which two typically adjacent teeth have exchanged positions in the dental arch.
Which teeth are the most frequently transposed teeth?
permanent canine and first premolar
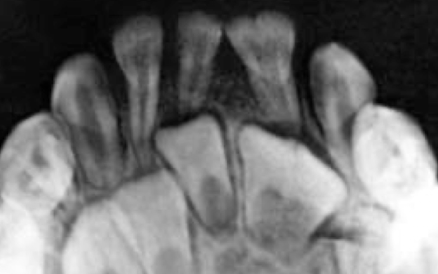
What dental anomaly does this patient have?
Transposition
Fusion of the teeth results from what of developing teeth?
union of adjacent tooth germs
What do some authors believe is the reason for fusion?
When two tooth germs develop so close together that, as they grow, they contact and fuse before calcification is complete.
Fusion results in an increased or reduced number of teeth in the arch?
reduced
Is fusion more common in the deciduous or permanent dentition?
deciduous
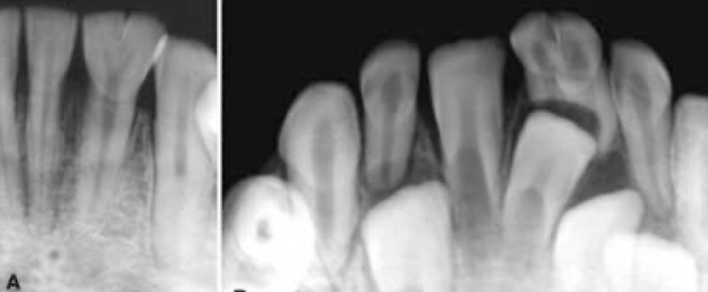
What dental anomaly does this patient have?
Fusion
Gemination is a rare anomaly that arises when a single tooth bud attempts to what?
divide
Gemination is also called
twinning
What is usually the result of gemination?
Invagination of the crown with partial clefting
What is the result of gemination in rare cases?
Complete division through the crown and rooth, producing identical stuctures
What does complete twinning result in?
A normal tooth plus a supernumerary tooth in the arch
What is the cause of gemination?
Unknown, but evidence suggests that it may have a genetic basis
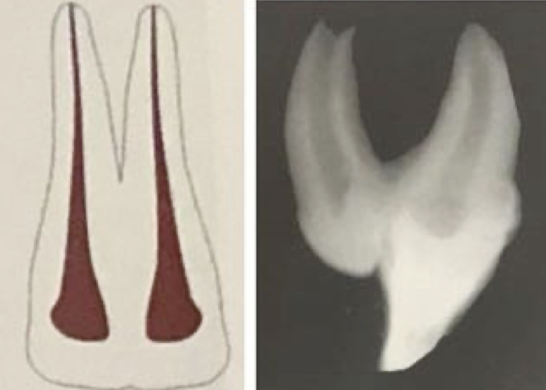
What dental anomaly is seen in this patient?
Gemination
Is this fusion or gemination?
Fusion
Is this fusion or gemination?
Gemination
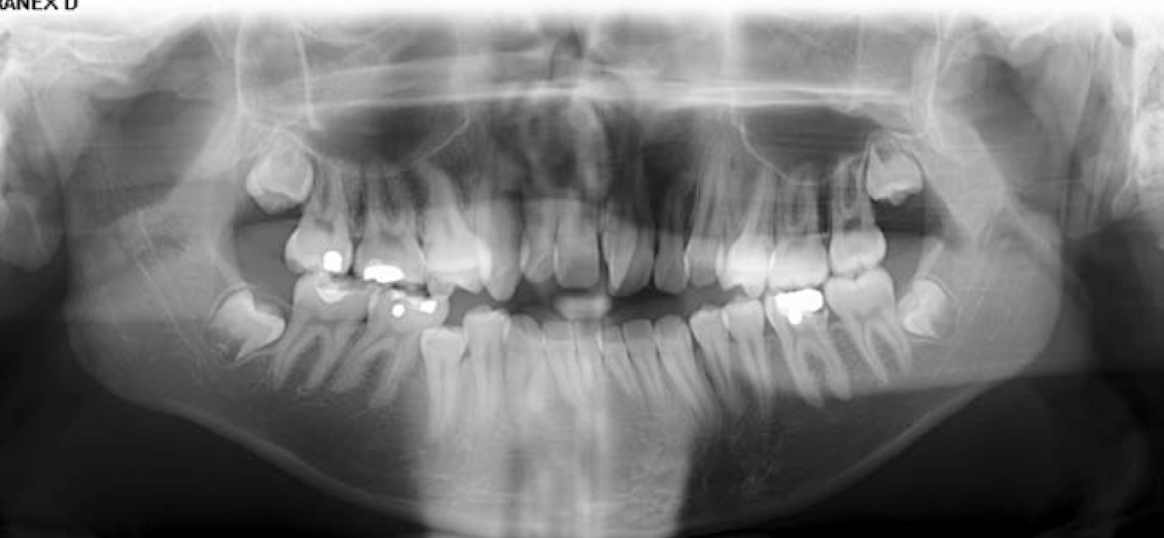
What dental anomaly is seen in this x-ray?
Increased number of teeth
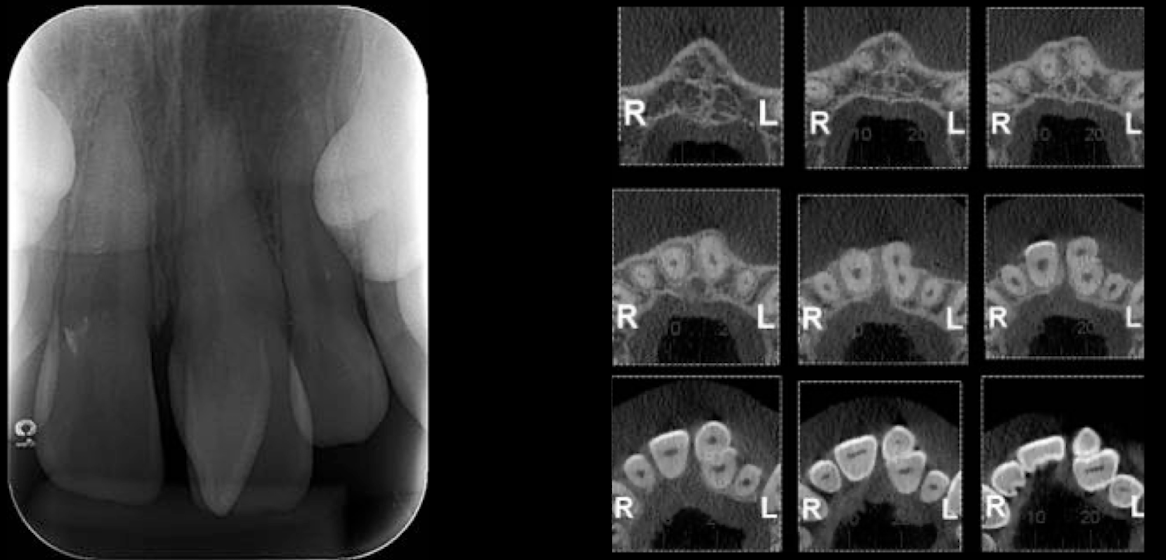
What dental anomaly does this patient have?
Increased number of teeth
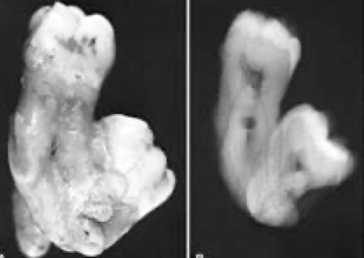
Concrescence occurs when the roots of two or more primary or permanent teeth are fused through —.
cementum
Concrescence occurs when the — of two or more — or — teeth are fused through cementum.
roots, primary, permanent
— occurs when the roots of two or more primary or permanent teeth are fused through cementum.
concrescence
What is the cause of concrescence?
Unknown but some suspect the space restriction during develop, local trauma, excessive occlusal force or local infection after development play an important role
If concrescence occurs during development, it is sometimes referred to as?
true concrescence
If concrescence occurs later in later, it is referred to as?
acquired concrescence
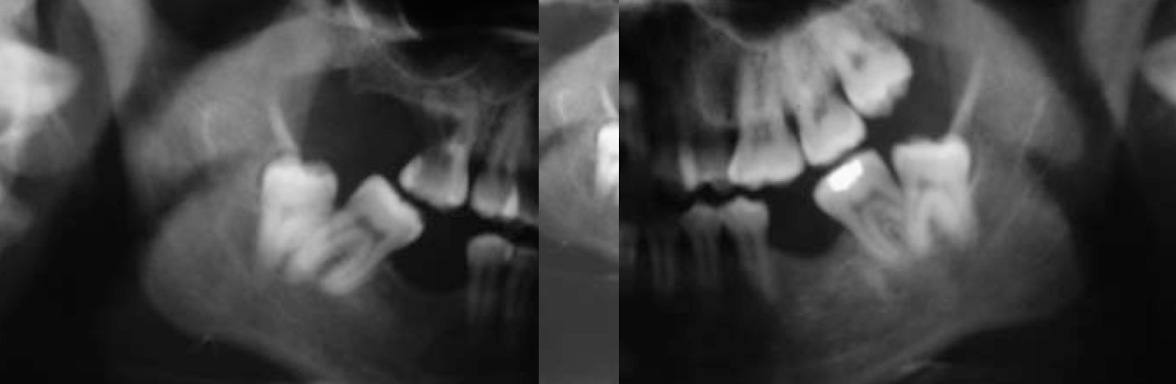
What dental anomaly is seen here?
concrescence
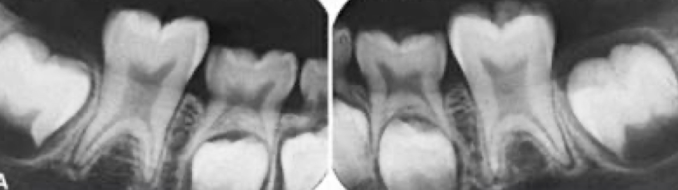
What dental anomaly is seen in these teeth?
concrescence
The bodies of taurodont teeth appear — and the roots are —.
elongated, short
The bodies of — teeth appear elongated and the roots are short.
taurodont
The pulp chamber of taurodont teeth extend from a normal position in the crown through the length of the elongated body, resulting in what?
a more apically positioned pulpal floor
Where does the pulp chamber of taurodont teeth extend from and to?
from a normal position in the crown t the length of the elongated body
Can taurodontism affect any tooth in either the primary or permanent dentitions?
yes
Where is taurodontism usually fully expressed?
in the molars
Where is taurodontism less often expressed?
in the premolars
Can single or multiple teeth show taurodont features?
Both can
What dental anomaly is this?
Taurodontism
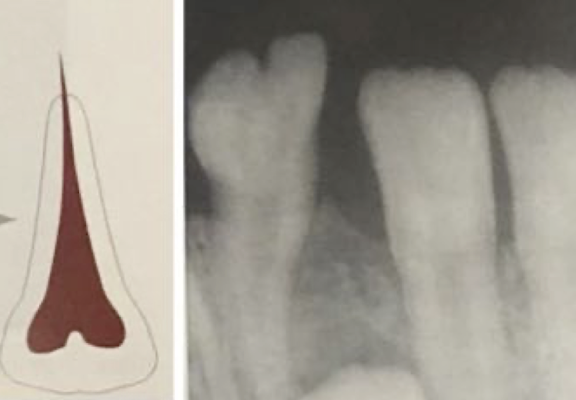
Dilaceration is a disturbance in tooth formation that produces a — — or — in the tooth anywhere in the crown or the root.
sharp bend or curve
Dilaceration is a disturbance in — — that produces a sharp bend or curve in the tooth anywhere in the — or the —.
tooth formation, crown, root
A disturbance in the root formation that produces a sharp bend or curve in the tooth anywhere in the crown or the root
dilaceration
What is the cause of dilaceration
Likely developmental but oldest hypotheses is that it is the result of mechanical trauma to the calcified portion of a partially formed tooth
What dental anomaly is this?
dilaceration
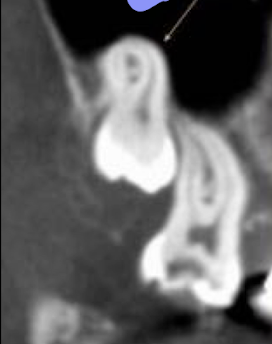
What dental anomaly is this?
dilaceration
Dens invaginatus, dens in dente, and dilated odontome represent varying what?
invagination or infolding of the enamel surface into the interior of a tooth
Name three degrees of invagination or infolding of the enamel surface into the interior of a tooth
dens invaginatus, dens in dente, and dilated odontome
What is the least severe form of enamel invagination?
dens invaginatus
What is the most severe form of enamel invagination?
dilated odontome
Where can invagination occur during tooth development?
crown, root, pulp chamber, and root canal system
Invagination involving the pulp chamber or root canal system can result in what?
a deformity of either the crown or root
Where are invagination anomalies most often seen?
tooth crowns