Lecture Notes on Lab Safety Hazards
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for reviewing chemical and health hazards in the lab.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
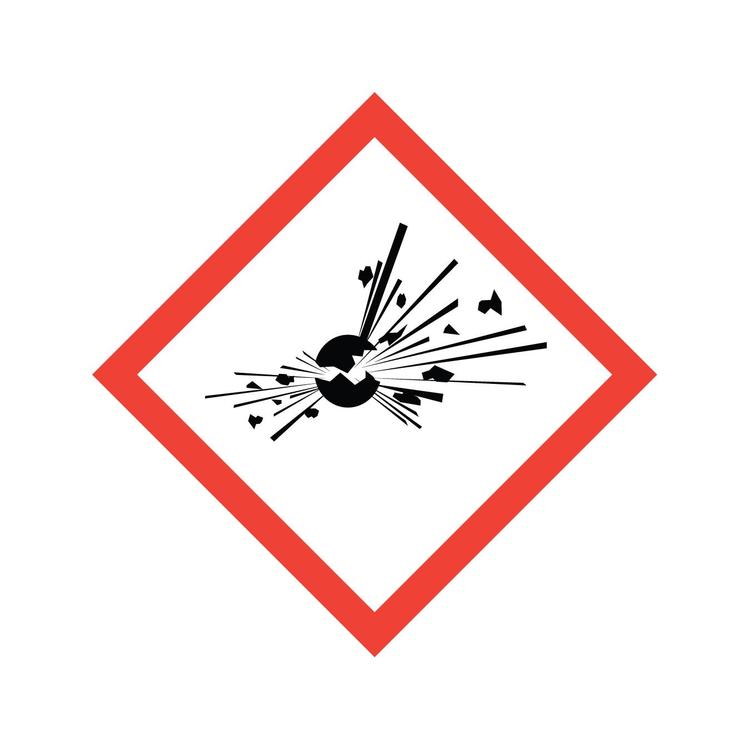

Explosive
Any chemical, compound, mixture, or device, the primary or common purpose is to function by explosion.

Flammables
Flammable materials that can vaporize and form flammable mixtures with air when in open containers, when leaks occur, or when heated, or may become flammable with certain catalysts.

Reactive
Properties and physical conditions of a single chemical or mixture that have the potential to generate heat, energy, and gas by-products that have the potential to do harm.

Pyrophoric
Ignite intensely in air
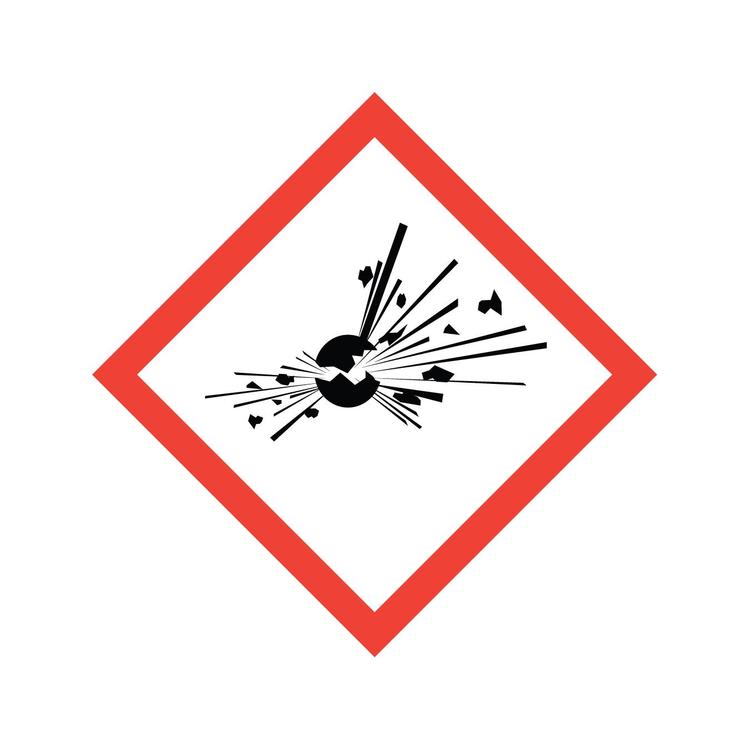

Organic Peroxides
A class of organic compounds that contain the peroxide functional group (-O-O-). Often highly reactive and can be hazardous due to their tendency to decompose, sometimes violently, under heat, friction, or contamination.
Emits Flammable Gas
Substances and mixtures which, in contact with water, emit flammable gases, including those that will emit flammable gases due to moisture in the air.
Corrosives
A highly reactive substance that causes obvious damage to living tissue or to metal, acting directly by chemically destroying the part (oxidation) or directly by causing inflammation.

Oxidizers
A substance that may not be combustible (flammable) itself but may, generally by yielding oxygen, cause or contribute to the combustion of other material.

Gases Under Pressure
Gases that can be toxic, flammable, oxidizing, corrosive, inert, or a combination of hazards and may be under a great deal of pressure.
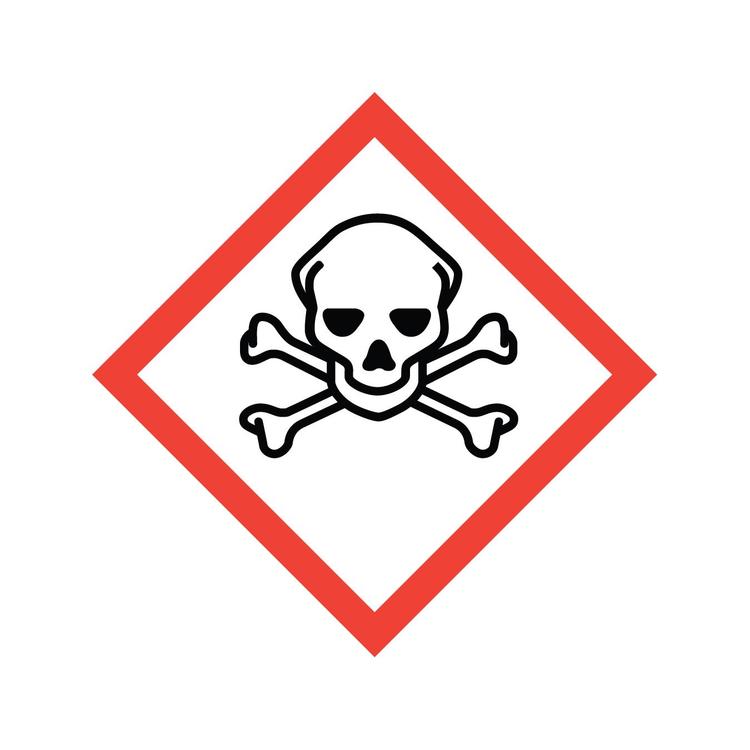

Acute Toxicity
Describes the adverse effects resulting from a single exposure to a substance.
Corrosion / Damage
Changes to the skin tissue or damage to the eye that are not reversible.
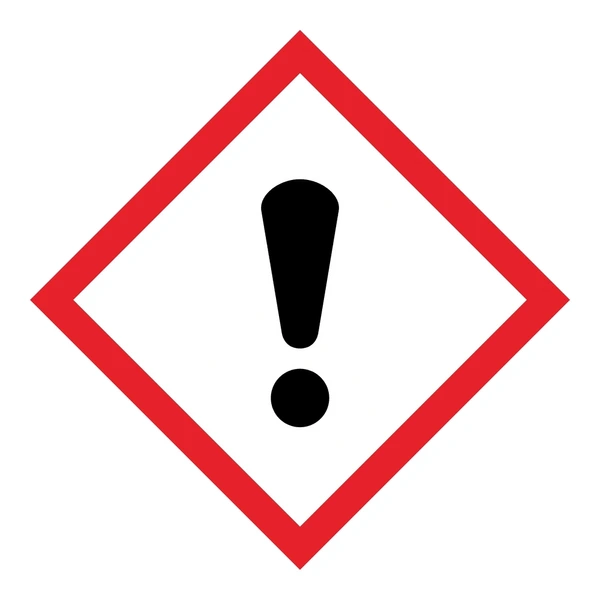

Skin Sensitization
A substance that will induce an allergic response following skin contact.
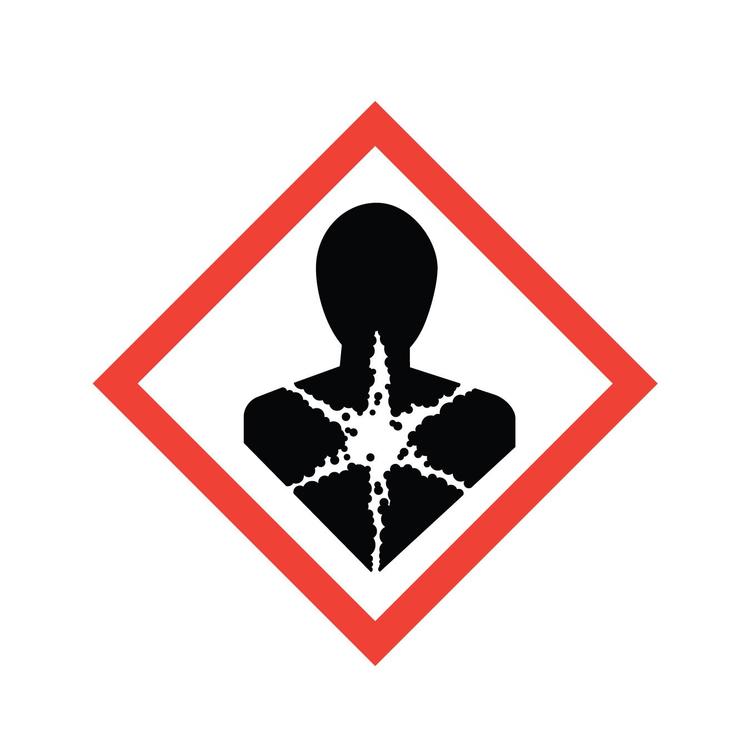

Respiratory Sensitization
A substance that induces hypersensitivity of the airways following inhalation of the substance.
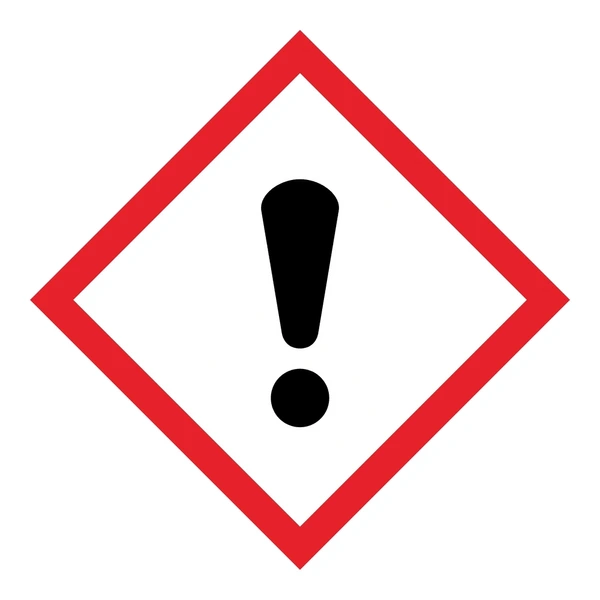

Narcotic Effect
Central nervous system depression including narcotic effects in humans such as drowsiness, narcosis, reduced alertness, loss of reflexes, lack of coordination, vertigo.
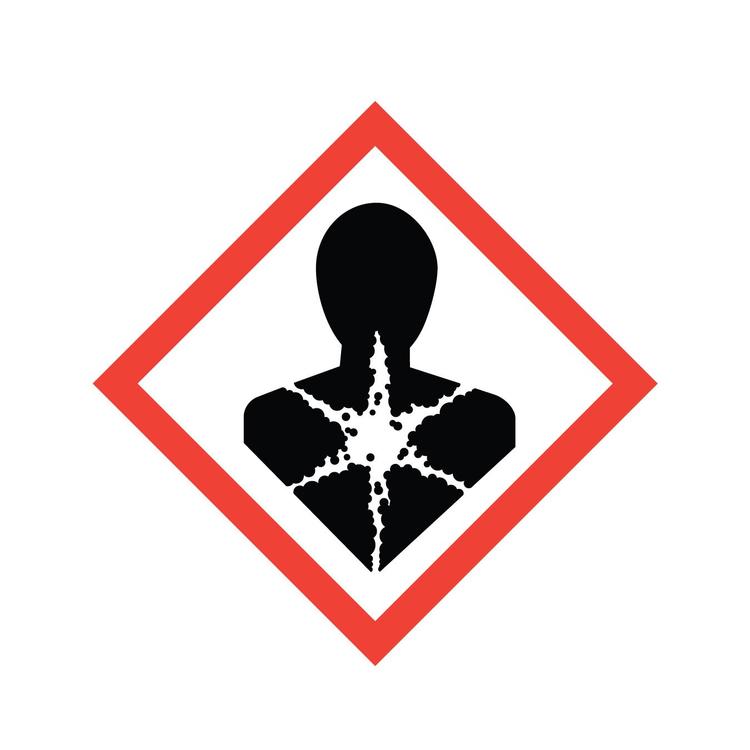

Carcinogens
A chemical substance or a mixture of chemical substances which induce cancer or increase its incidence.
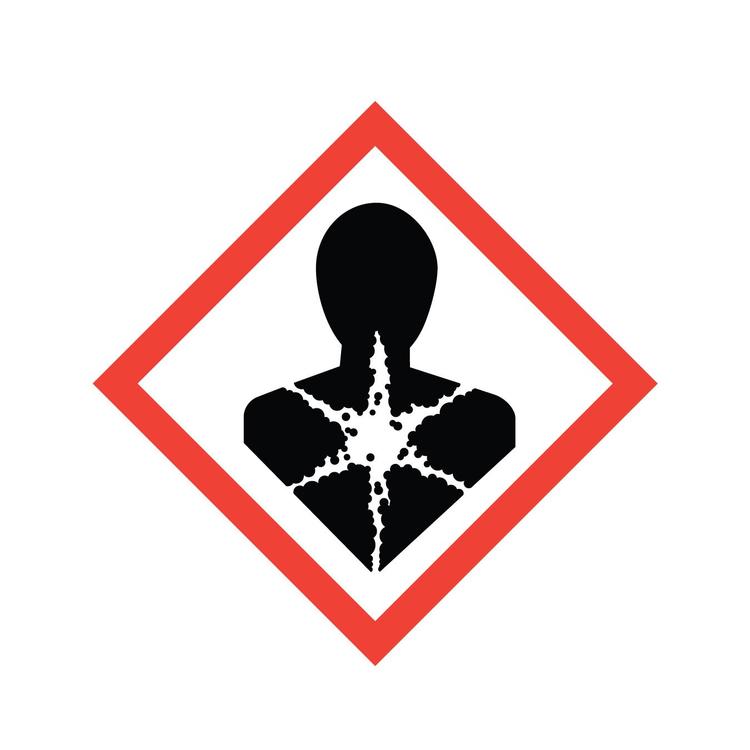

Mutagens
A substance or agent that causes an increase in the rate of change in genes (sections of the bodies DNA cells), leading to defective cells or cancer.
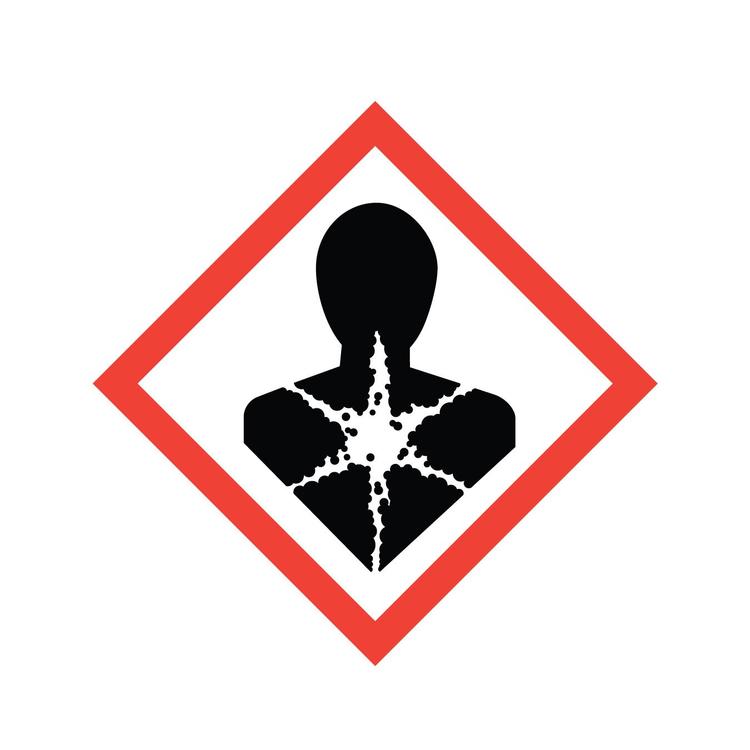

Reproductive Toxins
Includes adverse effects on sexual function and fertility in adult males and females, as well as developmental toxicity in offspring.
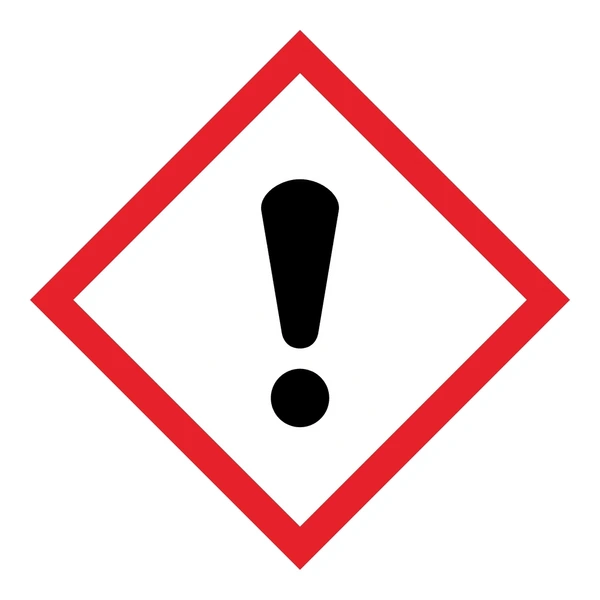

Sensitizer
A chemical that causes a substantial proportion of exposed people or animals to develop an allergic reaction in normal tissue after repeated exposure to the chemical.
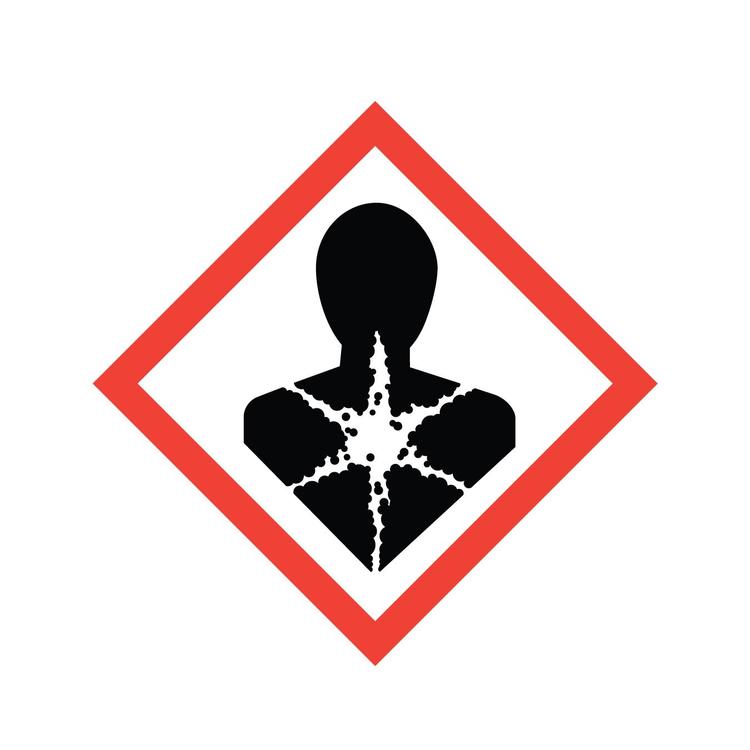

Target Organ Toxicity
Chemicals that can cause adverse effects or disease states manifested in specific organs of the body.
Asphyxiants/ Aspiration Toxicity
Can cause unconsciousness or death by suffocation.