Continuous variables for multiple categorical variables with two or more groups
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
CONTINUOUS VARIABLES FOR MULTIPLE CATEGORICAL VARIABLES WITH TWO OR MORE GROUPS
What does a factorial ANOVA test? (aov(), then summary())
Full name: analysis of variance
A factorial ANOVA tests the effects of two or more categorical independent variables on a continuous dependent variable. It evaluates:
Main effects of each factor
Interaction effects between factors
What are the null and alternative hypotheses for a factorial ANOVA? (two-way ANOVA??)
Multiple sets of null and alternative hypotheses:
Main effect of predictor A:
H₀: all group means of A are equal
the population means are the same for all groups of predictor A
H₁: at least one group mean differs
the population means are not the same for all groups predictor A
Main effect of predictor B:
H₀: all group means of B are equal
the population means are the same for all groups of predictor B
H₁: at least one group mean differs
the population means are not the same for all groups predictor B
Interaction between predictor A and predictor B: (A*B????)
H₀: the effect of A is the same at all levels of B
the population means for predictor A are the same for all groups of predictor B
H₁: the effect of A differs depending on the level of B
the population means for predictor A are not the same for all groups predictor B
**Make sure you know what main effects and interaction effects look like in a graph (see Section 16.2 of the book)
What do you do after a significant main or interaction effect in ANOVA?
Use post-hoc tests to determine which groups are significantly different from each other:
Pairwise comparisons (TukeyHSD() or posthocPairwiseT())
Planned comparisons for contrasts of a prior interest:
*Adjust p-values for multiple comparisons using a Bonferroni correction: 𝑝′ = 𝑝*𝑚
𝑚 = the total number of comparisons
What is the test statistic and how are degrees of freedom calculated in factorial ANOVA?
Test statistic: F
higher values correspond to a lower probability of H0 being true for a model term
Degrees of freedom:
Factor A: R−1
R is the number of groups for predictor A
Factor B: C−1
where C is the number of groups for predictor B
Interaction A and B: (R−1)(C−1)
Residuals: N − (R*C)
N is the total number of observations
*exact rejection regions depend on degrees of freedom
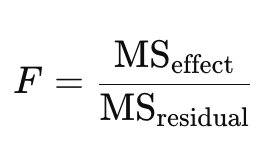
What is the relationship between sums of squares (SS), means of squares (MS), and the F-statistic in ANOVA?
Sums of Squares (SS) measure the total variability:
SSbetween: variability between group means
SSwithin (residual): variability within groups
Mean Squares (MS) are averages of sums of squares: MS = SS / df
F-statistic is the ratio of these mean squares: F = MSbetween / MSwithin
A higher F-value suggests that between-group differences are large relative to within-group variation, which may indicate a significant effect.
What is partial eta squared, and how is it interpreted? (etaSquared()) - Effect size
Partial η² measures the proportion of variance explained by one factor or interaction while controlling for others (0-1): Apply to both main effects and interaction effects.
0.01 = small
0.06 = medium
0.14 = large
*larger values correspond to more unequal means
Partial η² measures the effect size of individual model terms (main effects or interactions), controlling for other terms in the model
What are the assumptions of factorial ANOVA?
Residuals are normally distributed
Check with: Shapiro-Wilk test (shapiro.test()), histogram, QQ plot
Homogeneity of variance: The variance is the same in both groups
Check with: leveneTest()
Residuals are independent