Requirements Engineering I
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
What is a requirement?
A need perceived by a stakeholder.
A capability or property that a system shall have.
A documented representation of a need, capability or property.
What is a stakeholder?
A Stakeholder is a person or organization who influences a system’s requirements or who is impacted by that system.
Where do we need and use requirements?

What are Cyber-physical systems?
Cyber-physical systems contain both software and physical components.
What are Socio-technical systems?
Socio-technical systems span software, hardware, people and organizational aspects.
What is a system?
A principle for ordering and structuring.
A coherent, delimitable set of elements that – by coordinated action – achieve some purpose.
A system may comprise other systems.
How can the purpose achieved by a system be delivered?

What are the forms of requirements?

What is the traditional definition of Requirements Engineering (RE)?
The application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the specification and management of requirements; that is the application of engineering to requirements.
What is the customer-oriented definition of RE?
Understanding and documenting the customers’ desires and needs.
What is the risk-oriented definition of RE?
Specifying and managing requirements to minimize the risk of delivering a system that does not meet the stakeholders’ desires and needs.
What is the contemporary definition of RE?
The systematic and disciplined approach to the specification and management of requirements with the goal of understanding the stakeholders’ desires and needs and minimizing the risk of delivering a system that does not meet these desires and needs.
What are the four major tasks of RE?
Eliciting the requirements
Analyzing and documenting the requirements
Validating the requirements
Managing and evolving the requirements
Who are requirements engineers?
People act as requirements engineers if they:
elicit, document, validate and manage requirements,
have in-depth knowledge of Requirements Engineering, enabling them to define RE processes, select appropriate RE practices and apply them properly,
are able to bridge the gap between the problem and potential solutions
What are the costs and benefits of RE?

What are the nine principles of RE?
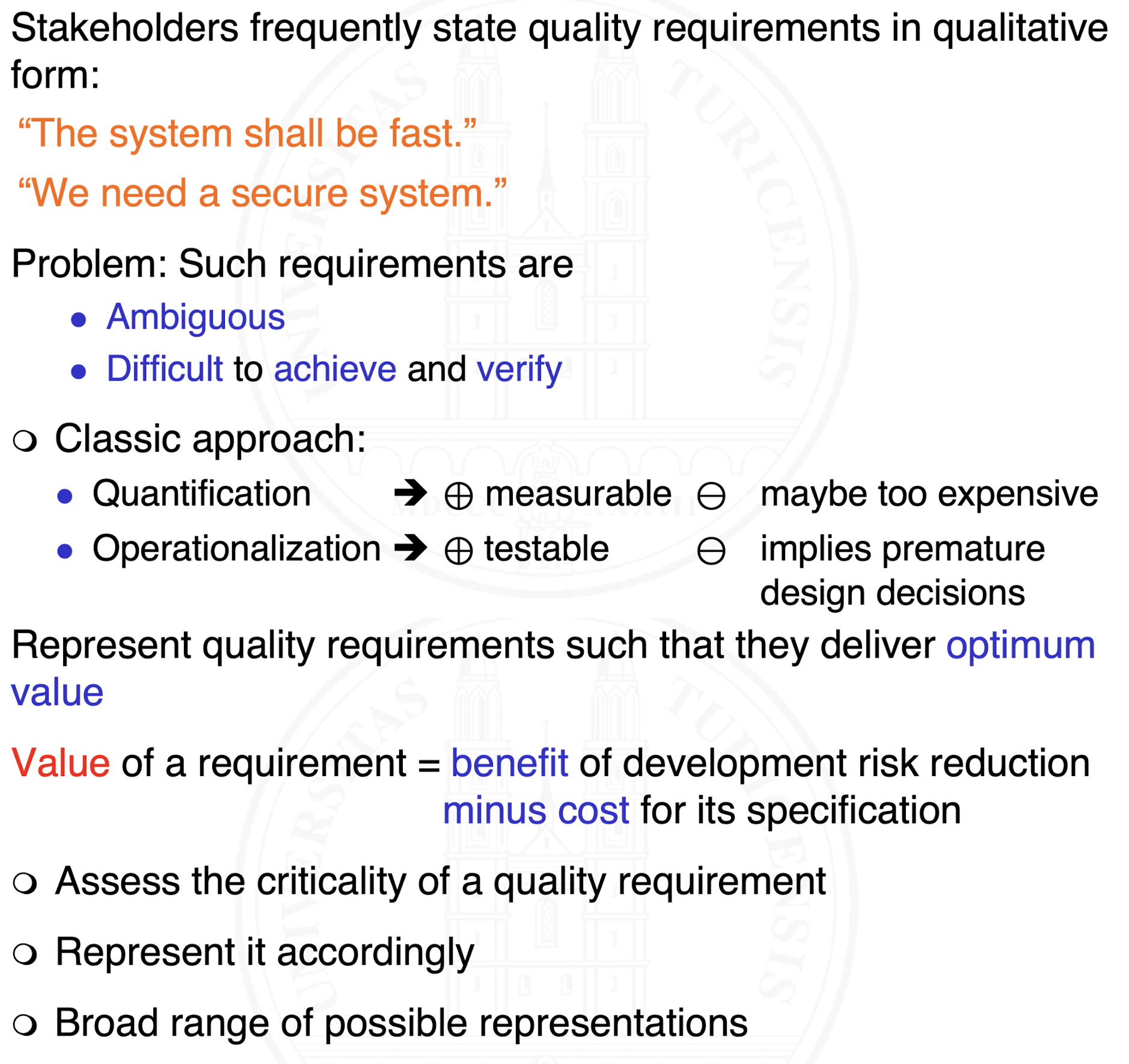
What is the value of a requirement?
The benefit of reducing development risk (i.e. the risk of not meeting the stakeholders’ desires and needs)
minus the cost of specifying the requirement
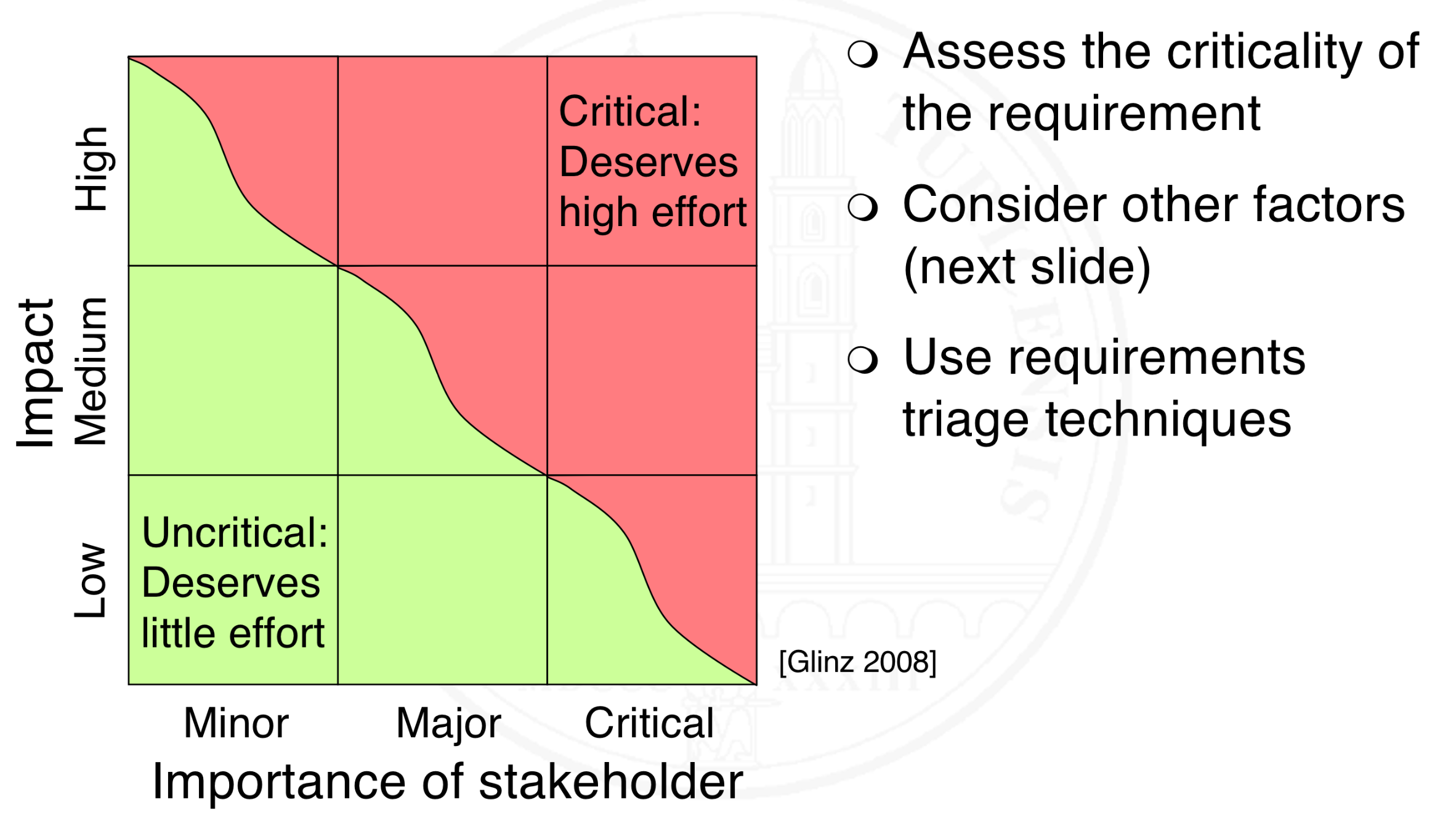
How is the risk of a requirement assessed?
Specification effort
Distinctiveness
Shared understanding
Reference systems
Length of feedback-cycle
Kind of customer-supplier relationship
Certification required
The effort invested into requirements engineering shall be inversely proportional to the risk that one is willing to take.
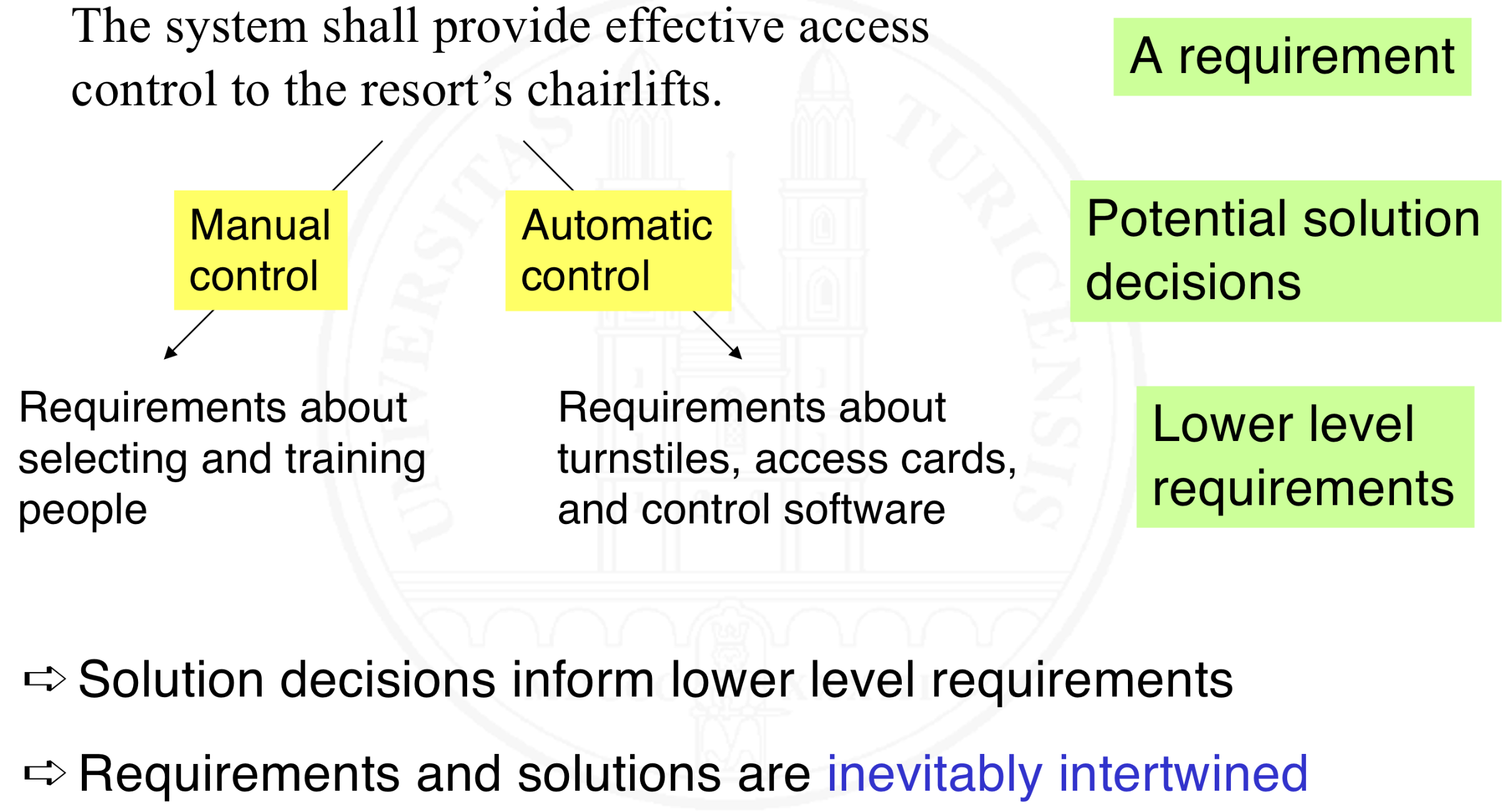
How are specification and implementation intertwined?
Hierarchical intertwinement: high-level design decisions inform lower-level requirements
Technical feasibility: non-feasible requirements are useless
Validation: what you see is what you require
How can requirements be classified?
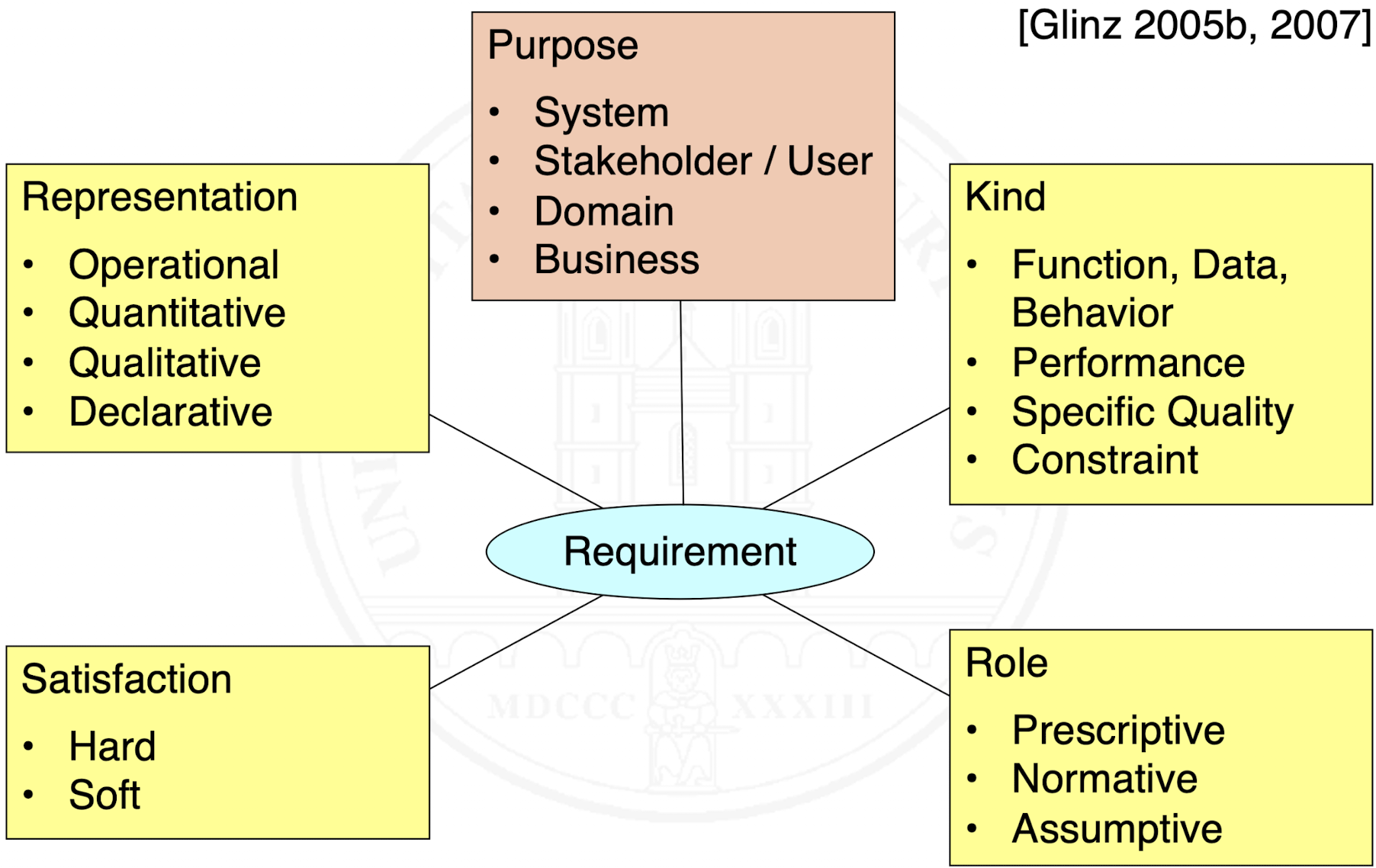
How can requirements be classified by kind?
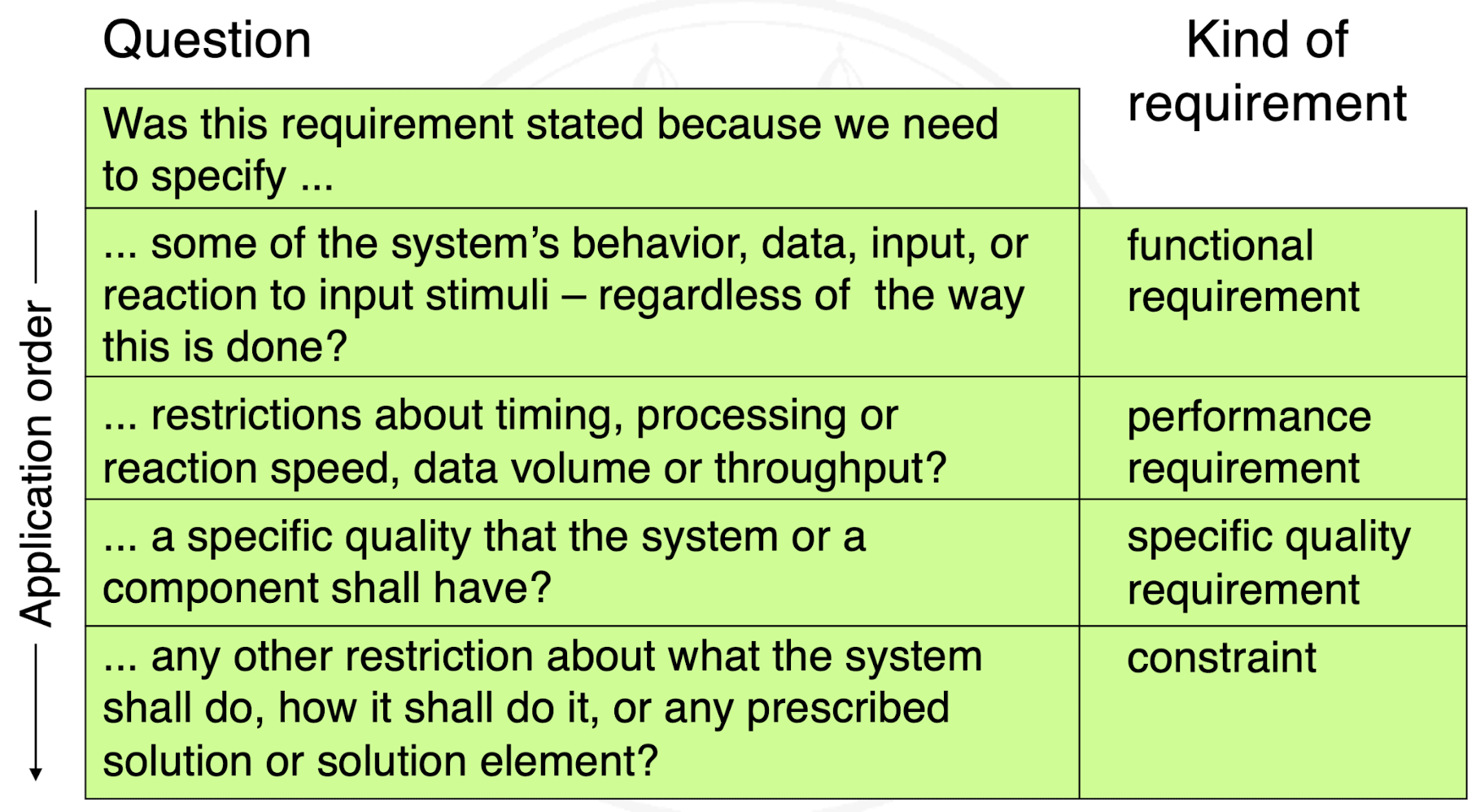
DEFINITION. Functional requirement – A requirement concerning a result or behavior that shall be provided by a function of a system.
DEFINITION. Quality requirement – A requirements that pertains to a quality concern that is not covered by functional requirements
Can be sub-classified into:
performance requirement
specific quality requirement
DEFINITION. Constraint – A requirement that limits the solution space beyond what is necessary for meeting the given functional requirements and quality requirements.
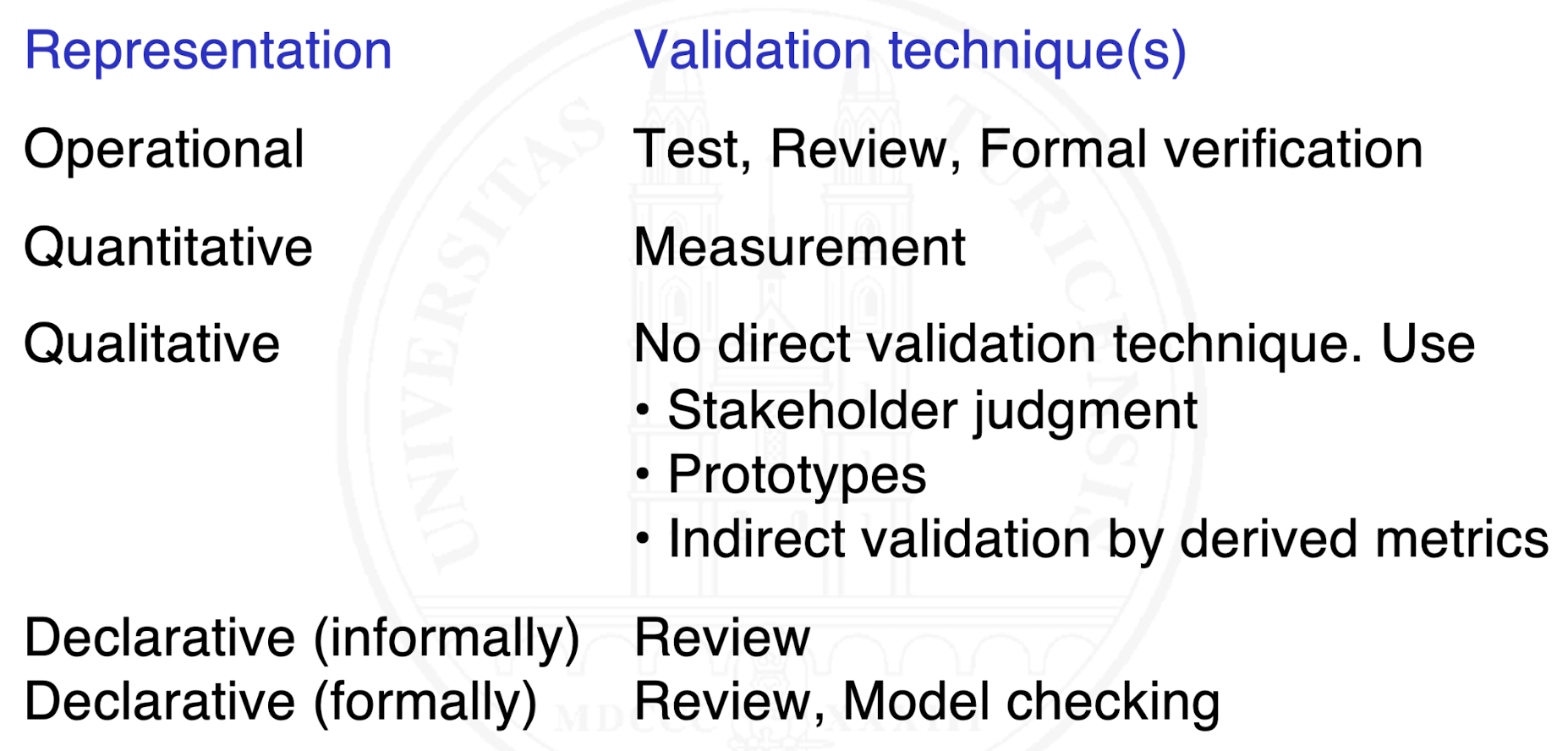
How can requirements be classified by representation?
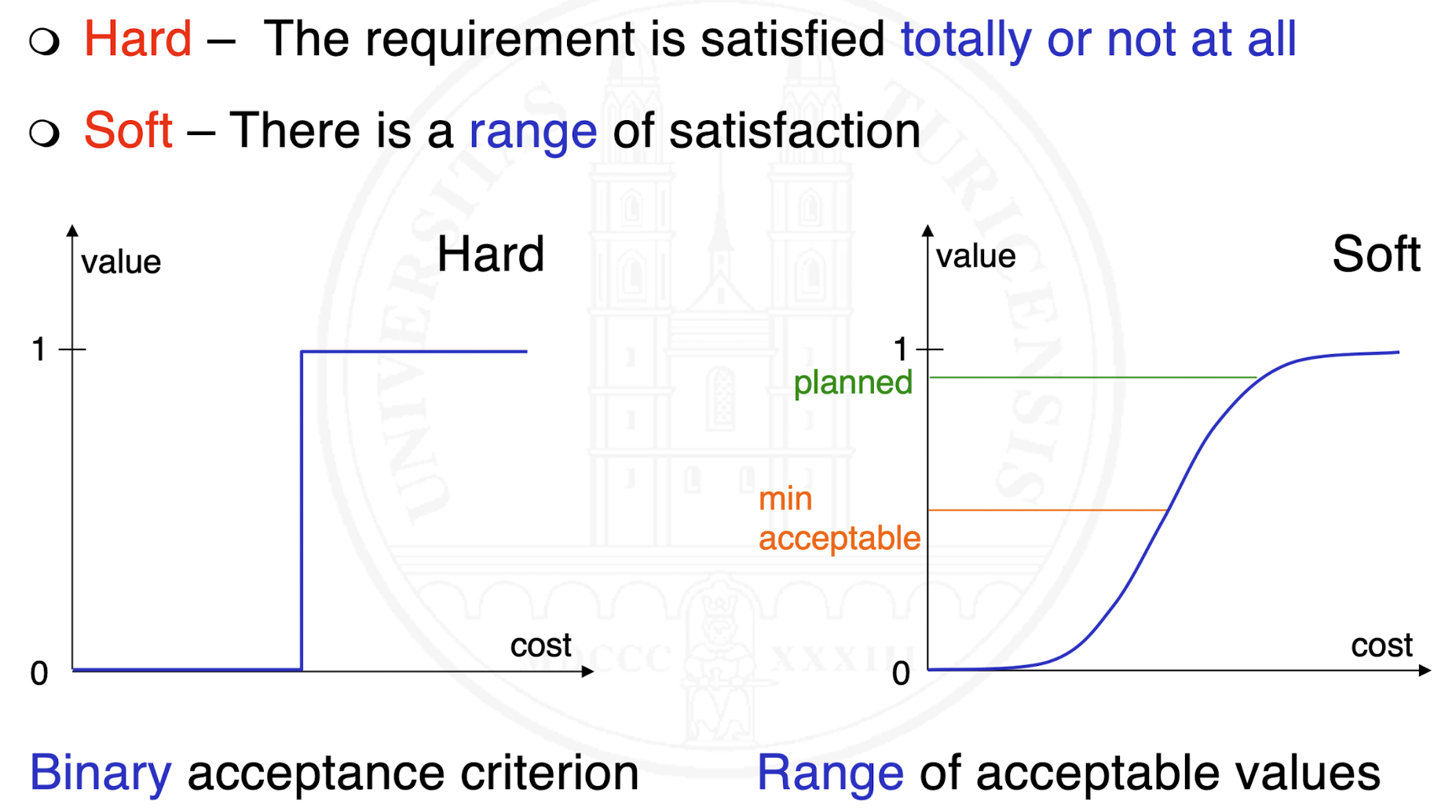
How can requirements be classified by satisfaction?
How can requirements be classified by role?

How can requirements be classified by purpose?
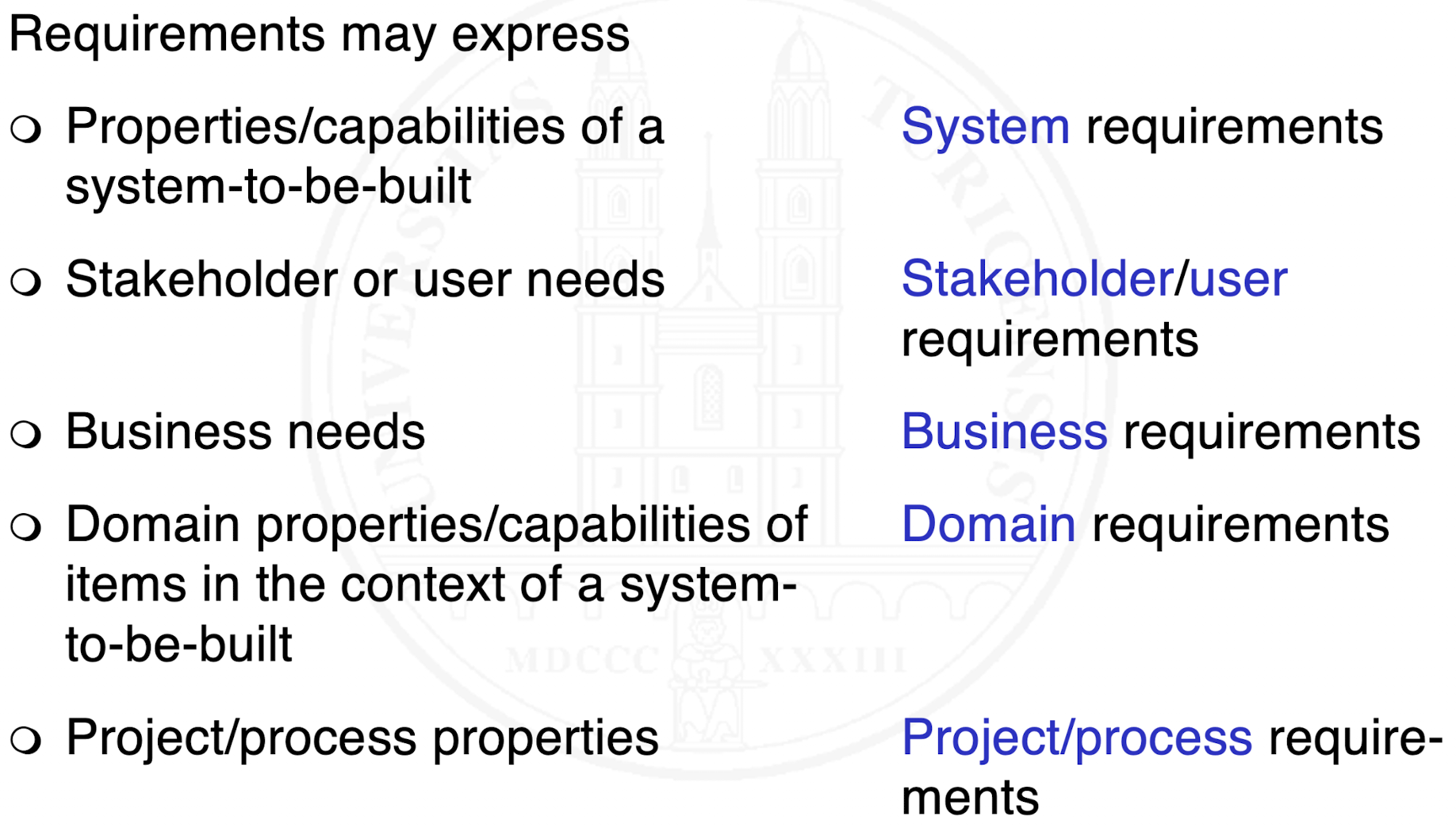
Why do we classify requirements in so many different ways?

How should we classify requirements when in doubt?

Classify the following requirements with respect to their kind, representation, satisfaction, role, and purpose.
a) When the system is in normal mode, the system shall unlock a turnstile for a single turn if the turnstile’s sensor unit senses a valid access card.
b) The system shall be compliant with GDPR.

What forms of shared understanding exist?
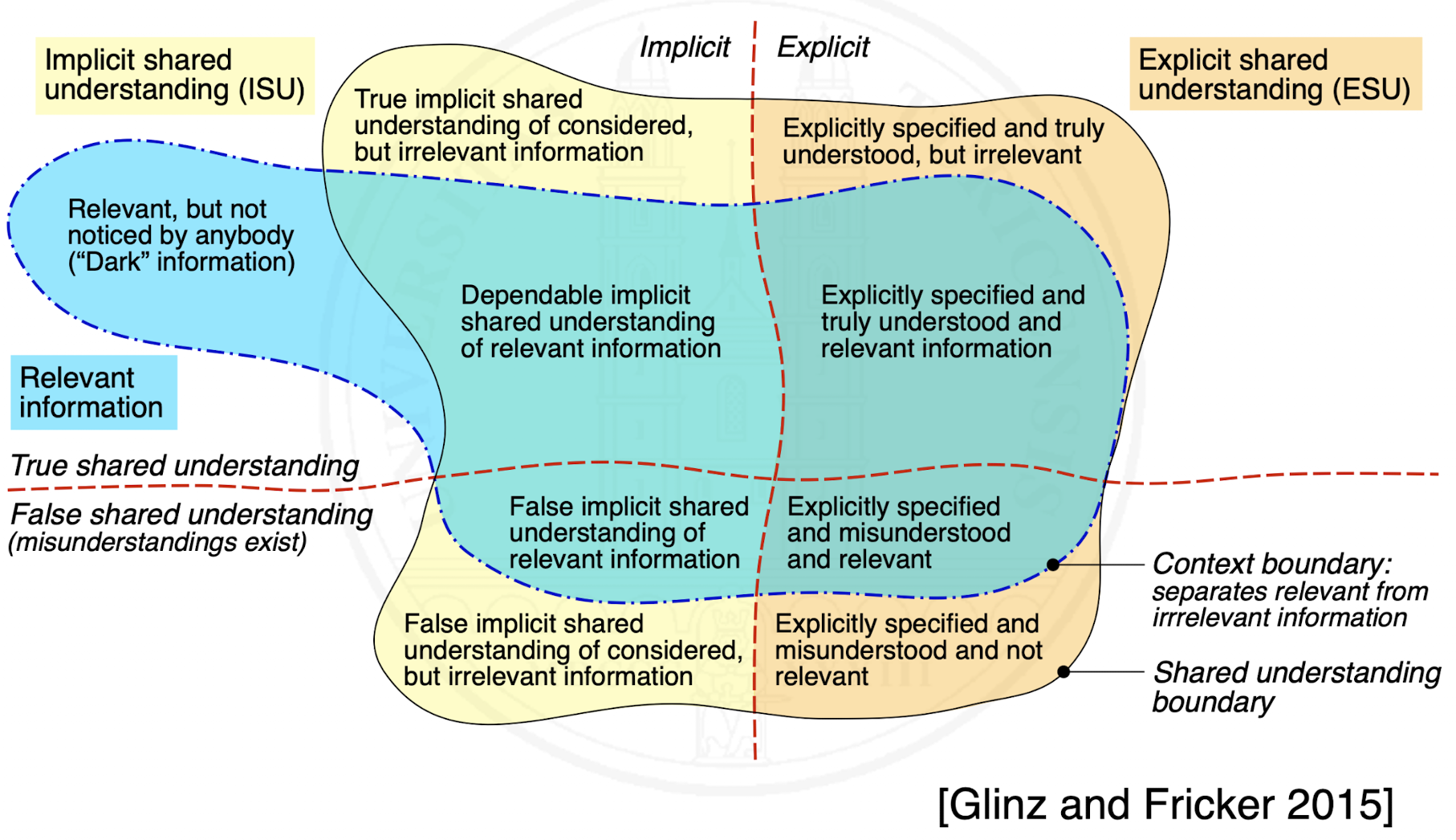
What does value mean in the context of specifications?
Value means
The benefit of an explicit specification
Bringing down the probability for developing a system that doesn’t satisfy its stakeholders’ expectations and needs to an acceptable level
minus
The cost of writing, reading and maintaining this specification
What are enablers and obstacles in shared understanding?
+ Domain knowledge
+ Previous joint work or collaboration
+ Existence of reference systems
+ Shared culture and values
+ Mutual trust
+/– Contractual situation
+/– Normal vs. radical design
– Geographic distance
– Outsourcing
– Regulatory constraints
– Large and/or diverse teams
– Fluctuation
What does context mean in the context of specifications?
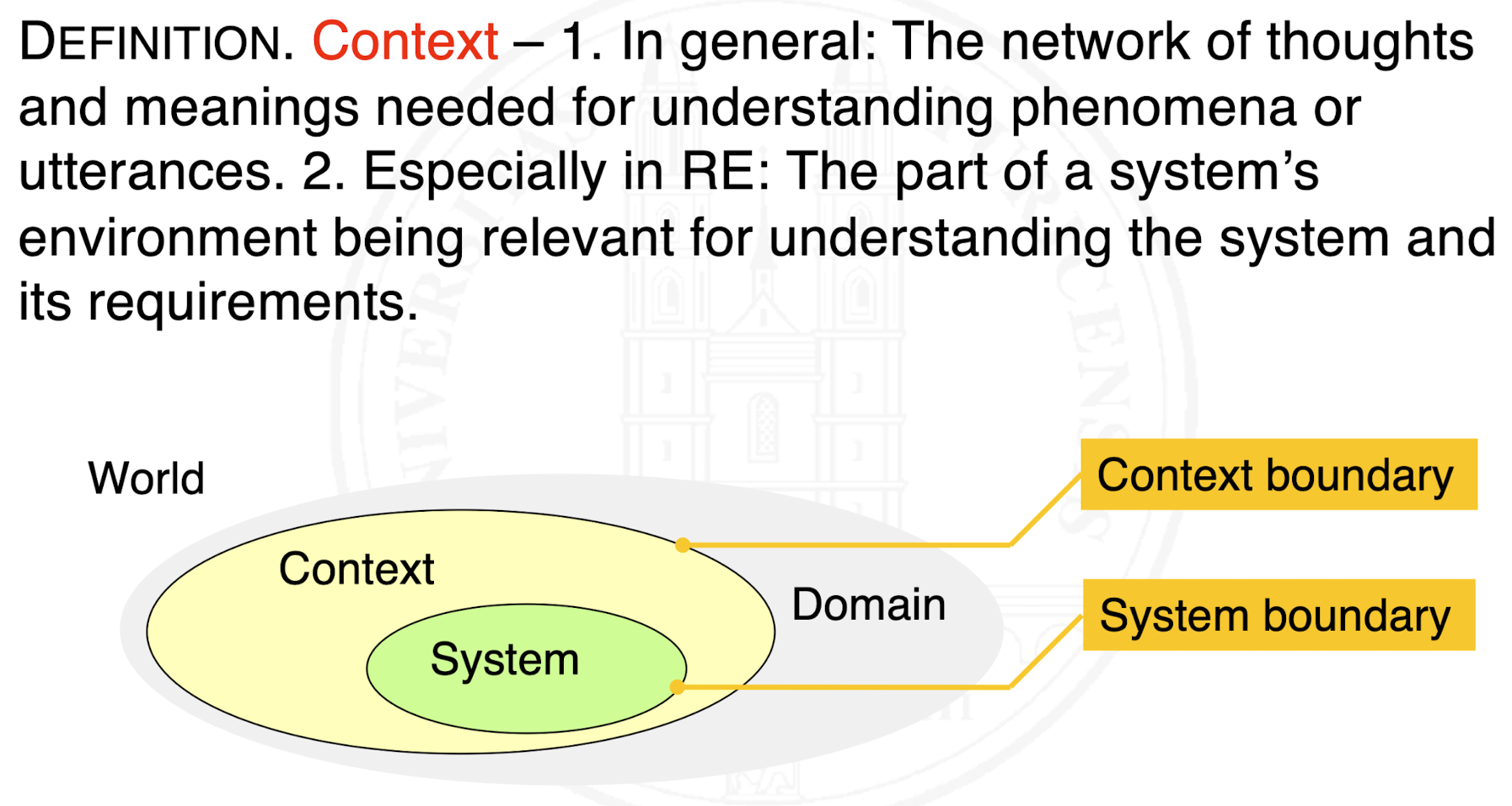
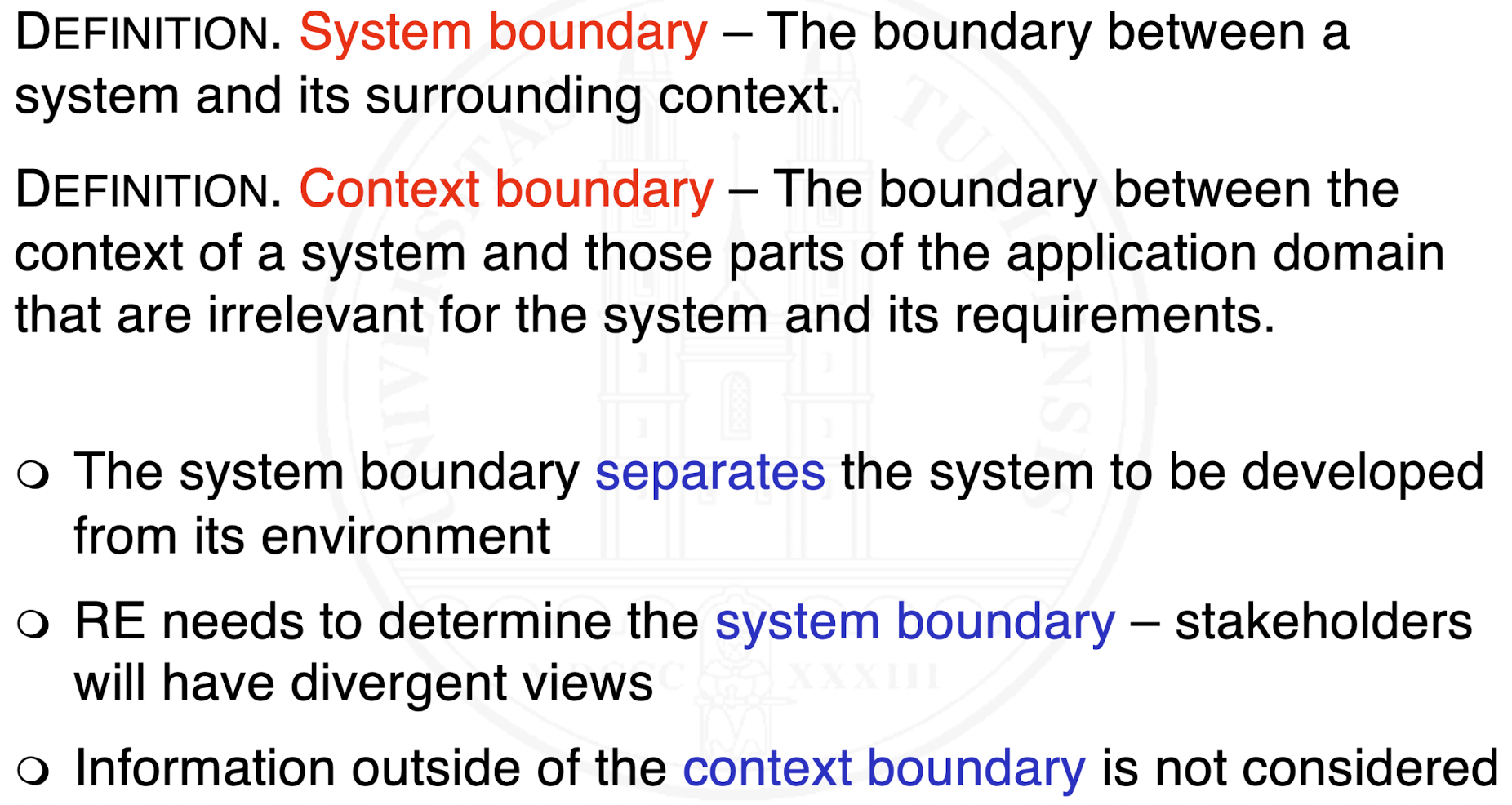
What is the system boundary and the context boundary?
What are context models?
Modeling a system in its context
Determine the level of specification
Usually no system internals (➜ system as black box)
Model actors which interact directly with the system
Model interaction between the system und its actors
Model interaction among actors
Represent result graphically
What is the scope of a system development?
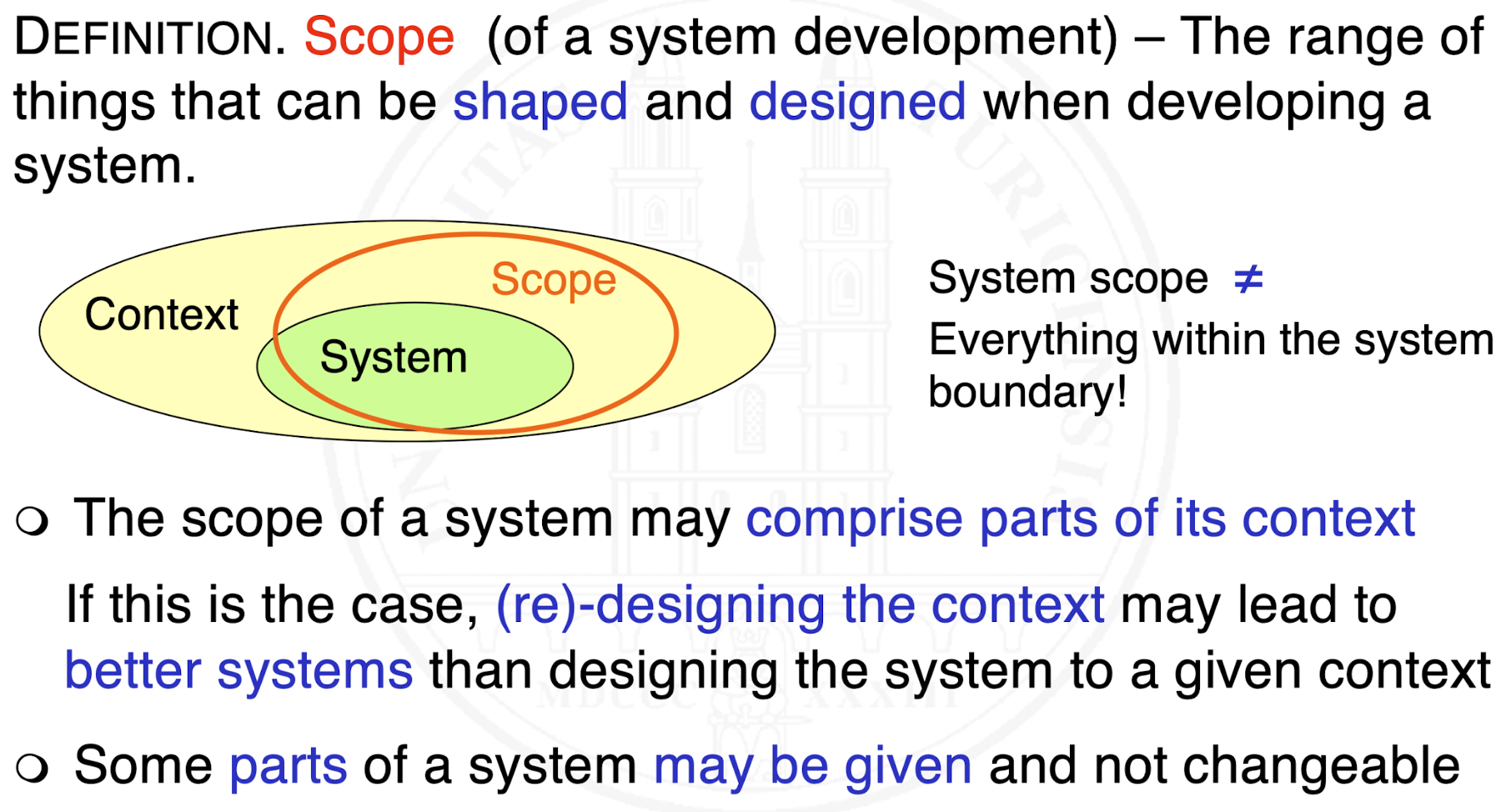
How do we distinguish between requirements and design decisions?
Distinguish operationally:
If a statement is owned by stakeholders (i.e., changing it requires stakeholder approval), it’s a requirement
If a statement is owned by the supplier (i.e. the supplier may change it freely), it’s part of the technical solution
What competencies are contributed by RE and product design?

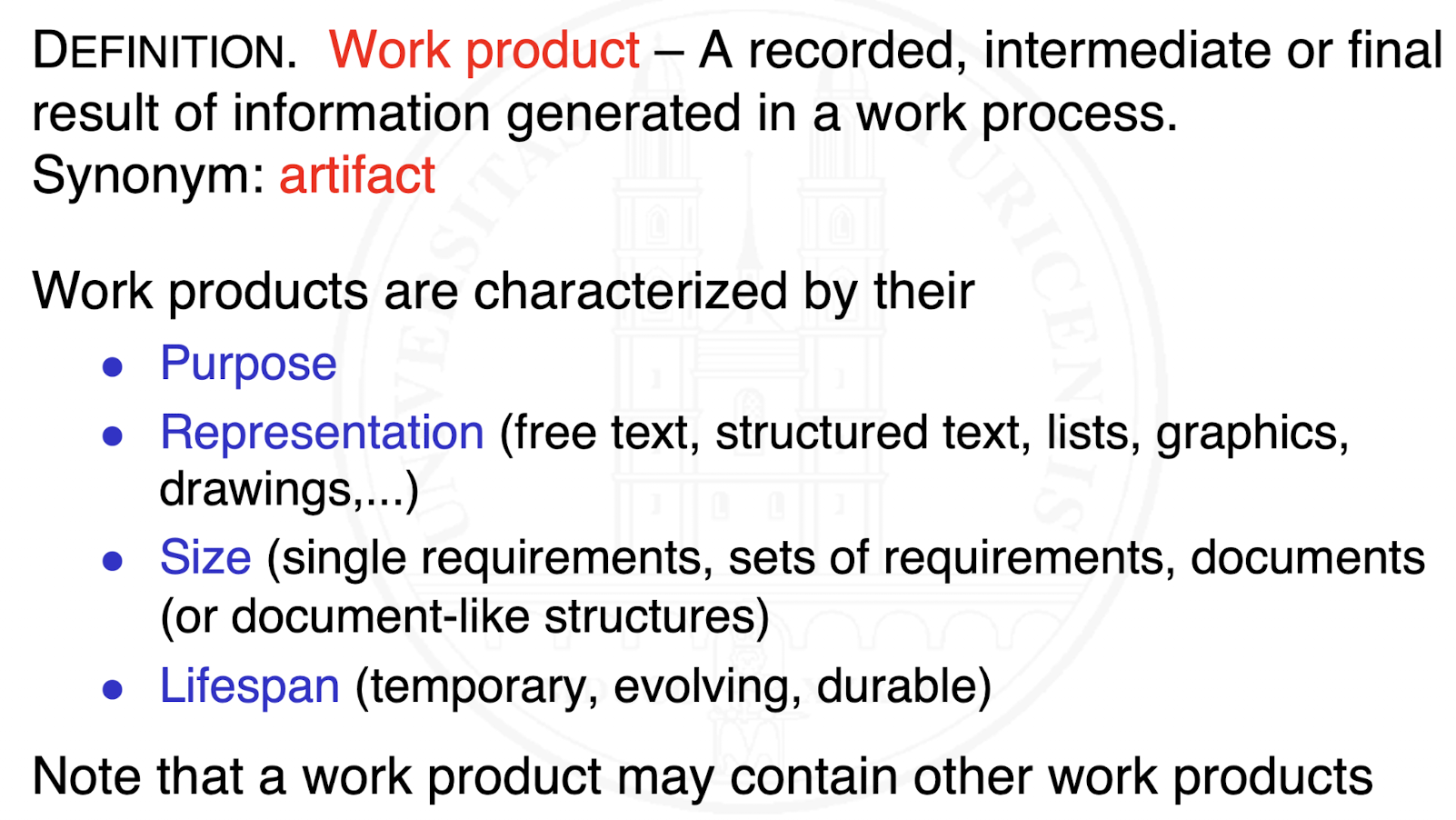
What are work products and their characteristics?
What are single requirements?

What are sets of requirements?
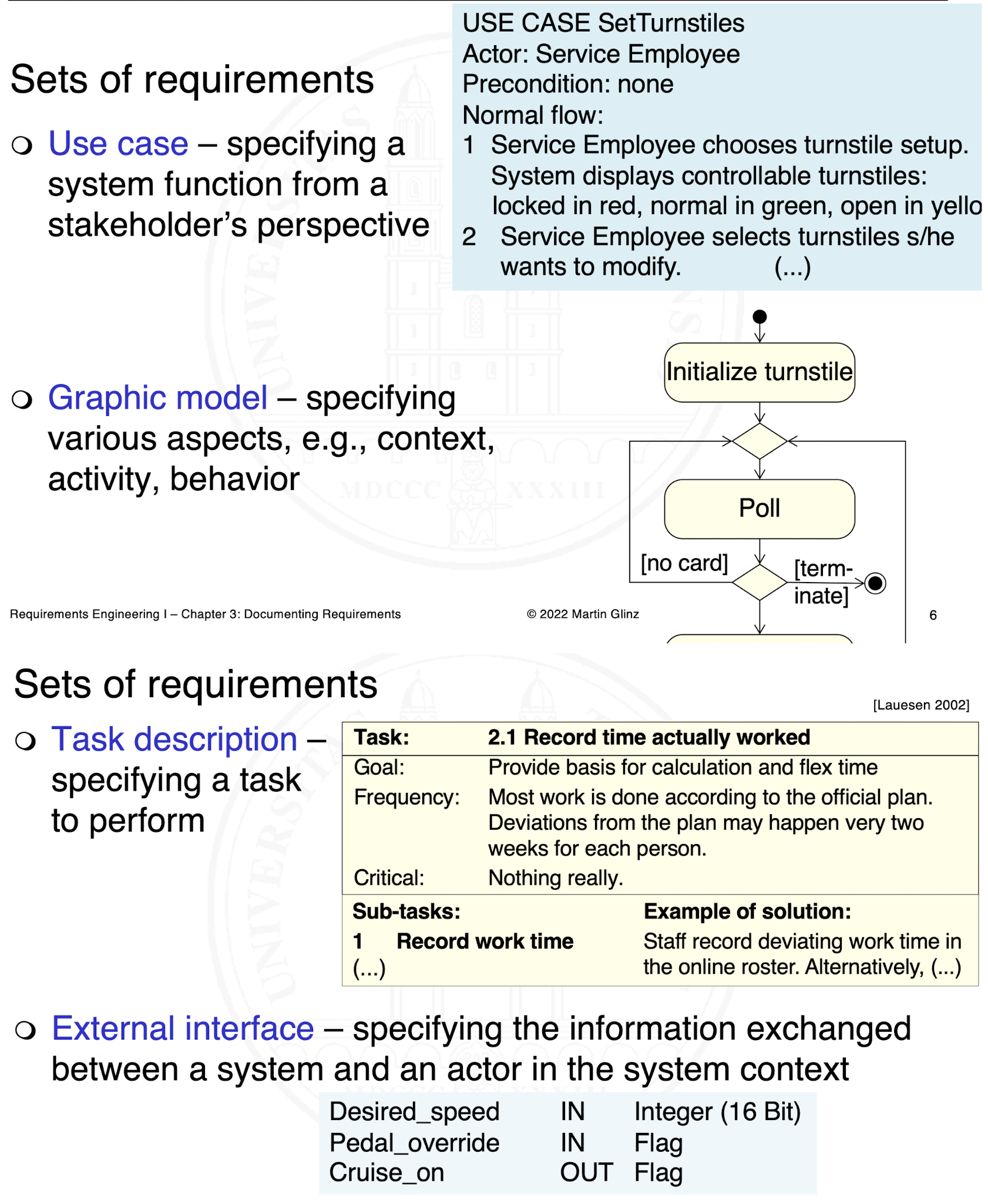
What are the four document types?



What is a glossary?
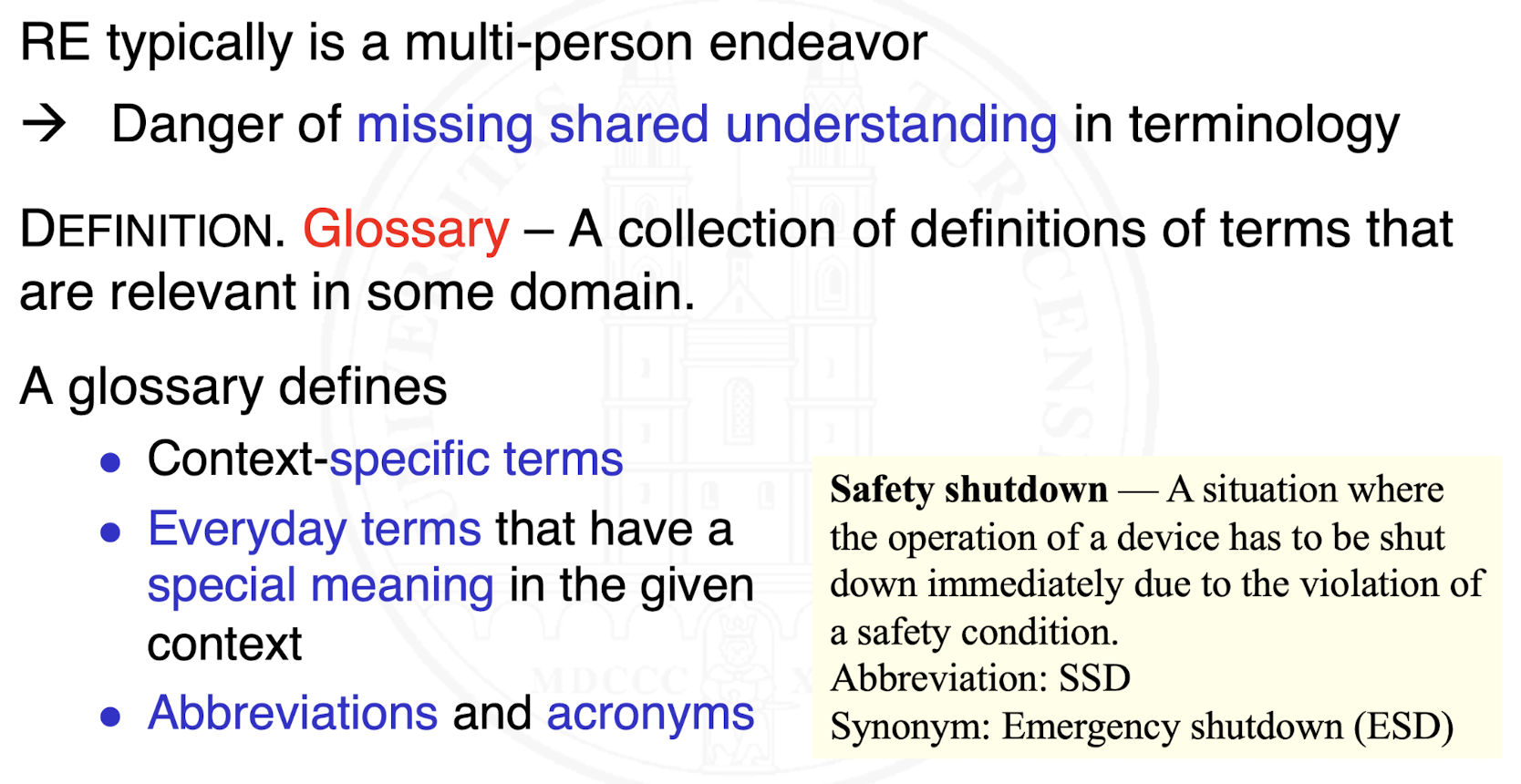
What are rules for creating and maintaining a glossary?

What are prototypes?

What forms of prototypes exist?
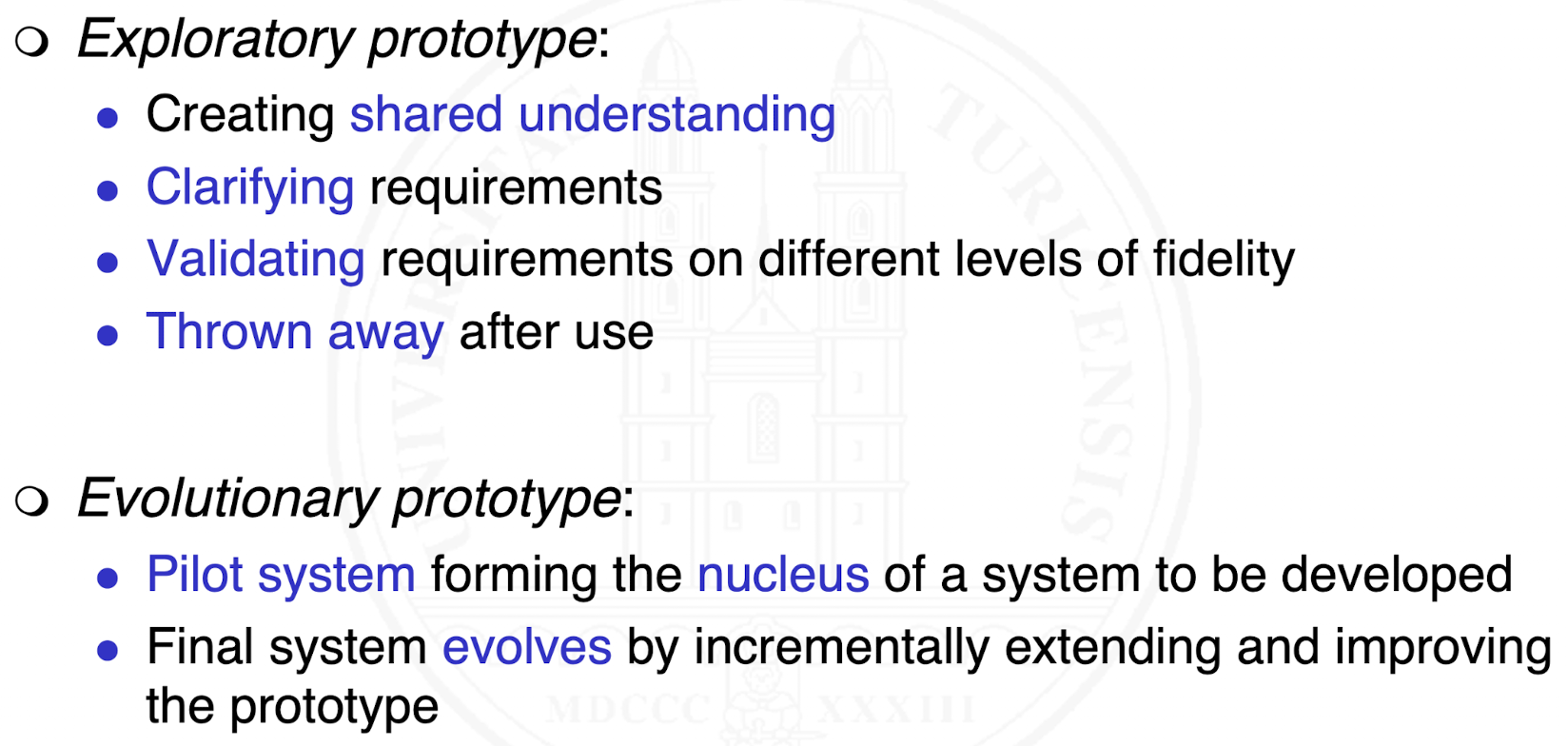
What are examples of exploratory prototypes?

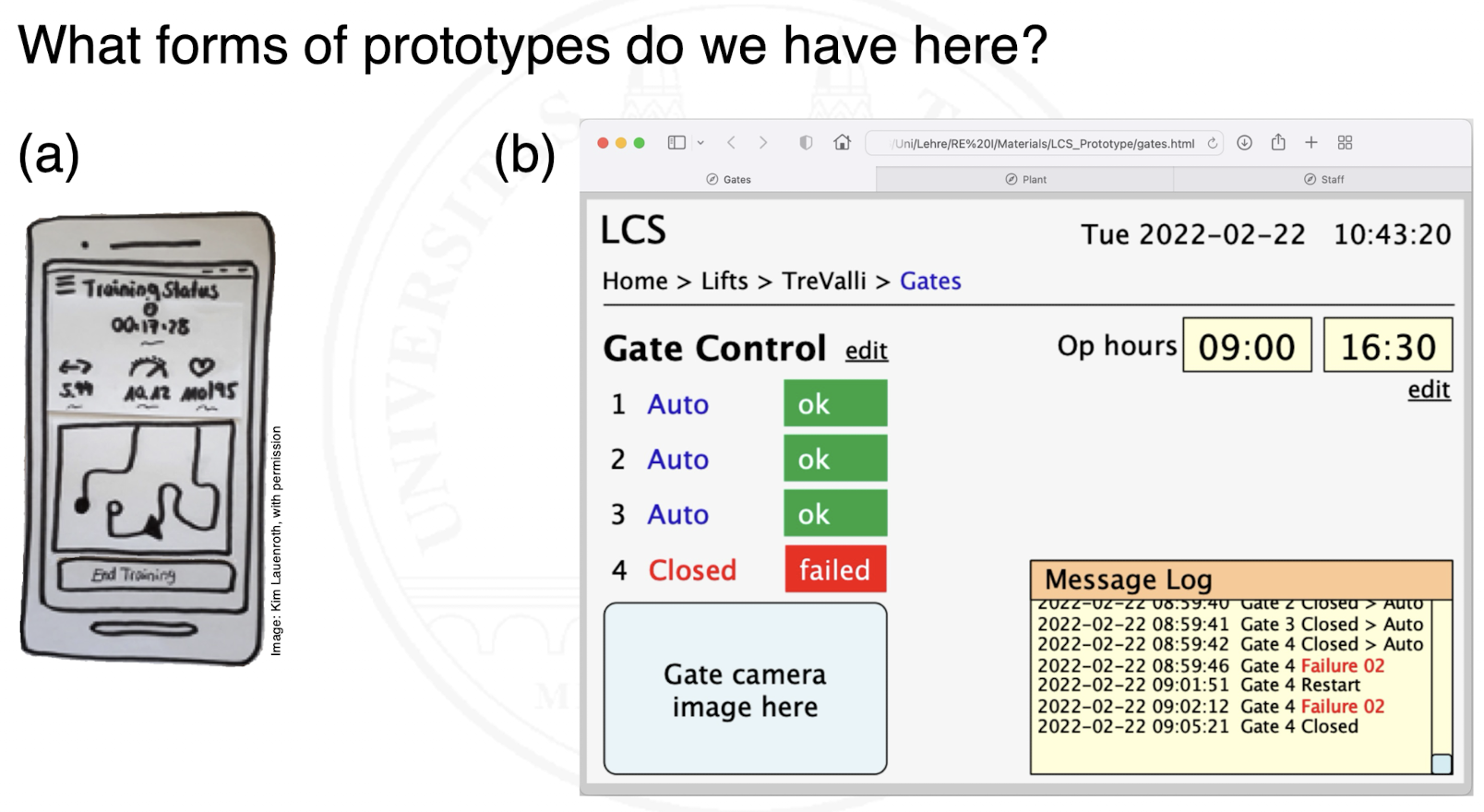
a) Wireframe
b) Mock-up (depending on whether there is some functionality, this could also be a native prototype)
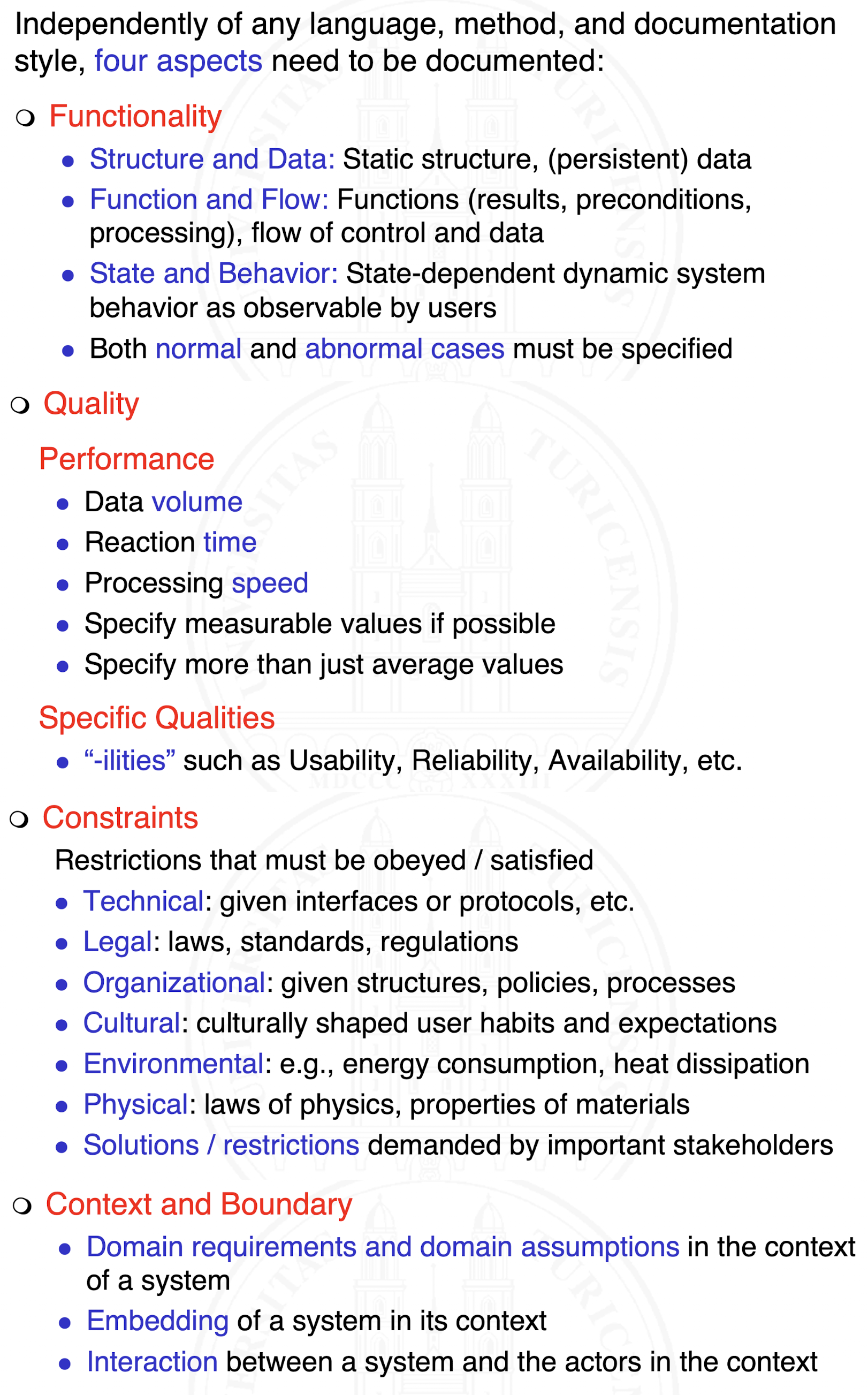
What aspects need to be documented?
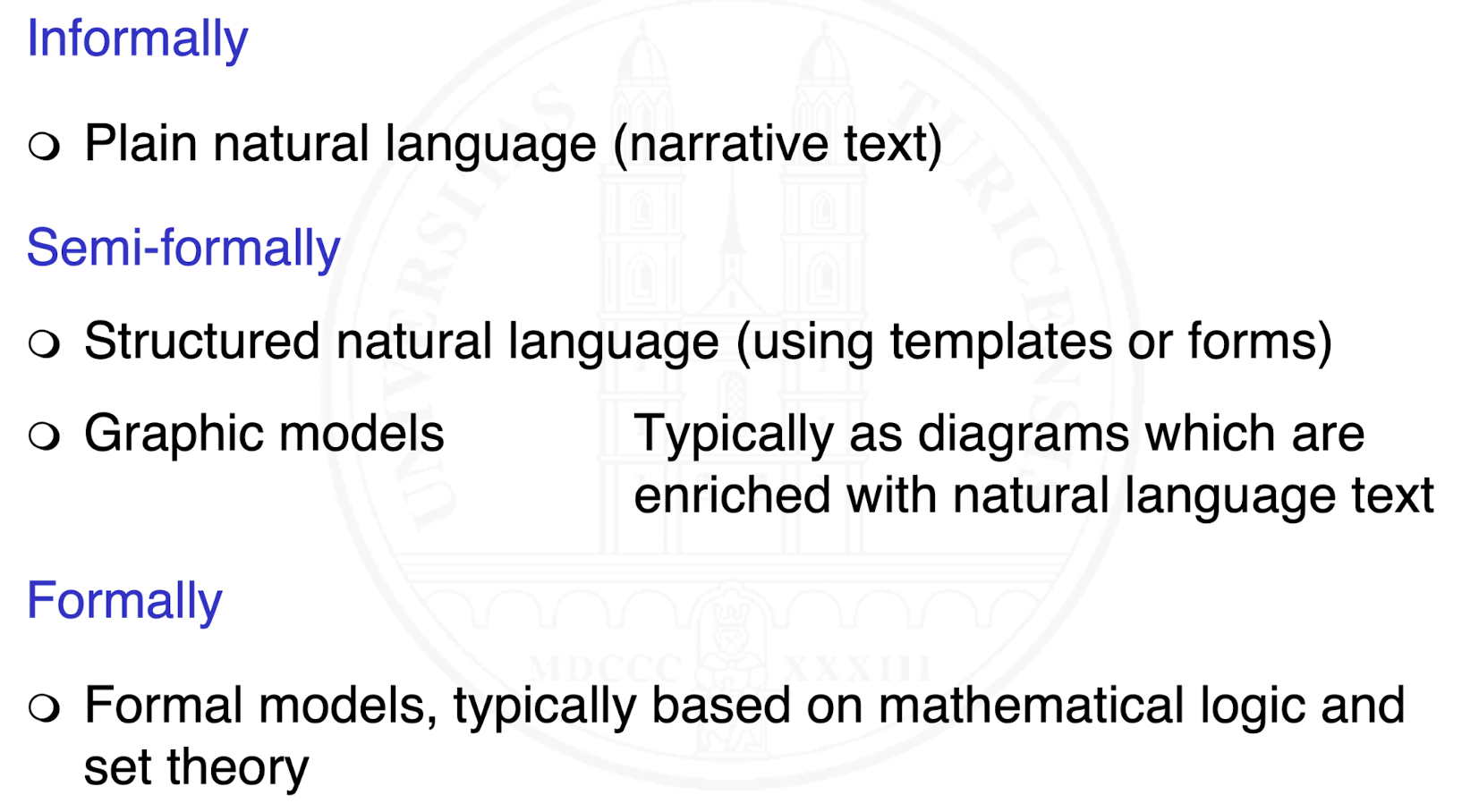
What are ways to document?
What are general rules for requirements documentation?
Specify requirements as small, identifiable units whenever possible
Record metadata such as source, author, date, status
Use structure templates
Adapt the degree of detail to the risk associated with a requirement
Specify normal and exceptional cases
Don’t forget quality requirements and constraints
How do we measure the quality of individual requirements?

How do we measure the quality of requirements work products?

What are personas?

What is requirements elicitation?
DEFINITION. Requirements elicitation – The process of seeking, capturing and consolidating requirements from available sources, potentially including the re-construction or creation of requirements.
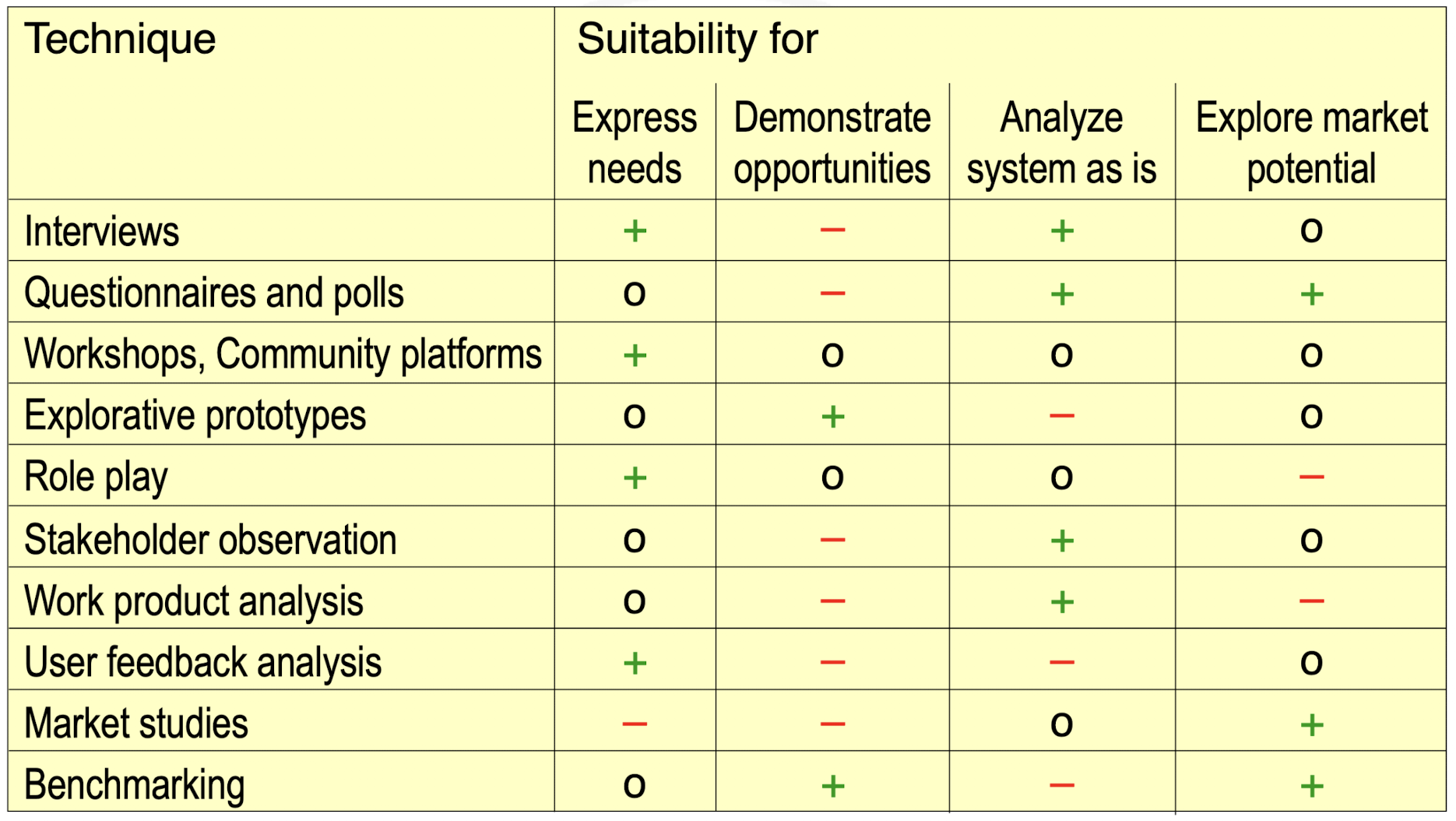
What are elicitation techniques?

Which elicitation technique is suitable for what?
How do we elicit functional requirements?

How do we elicit quality requirements?
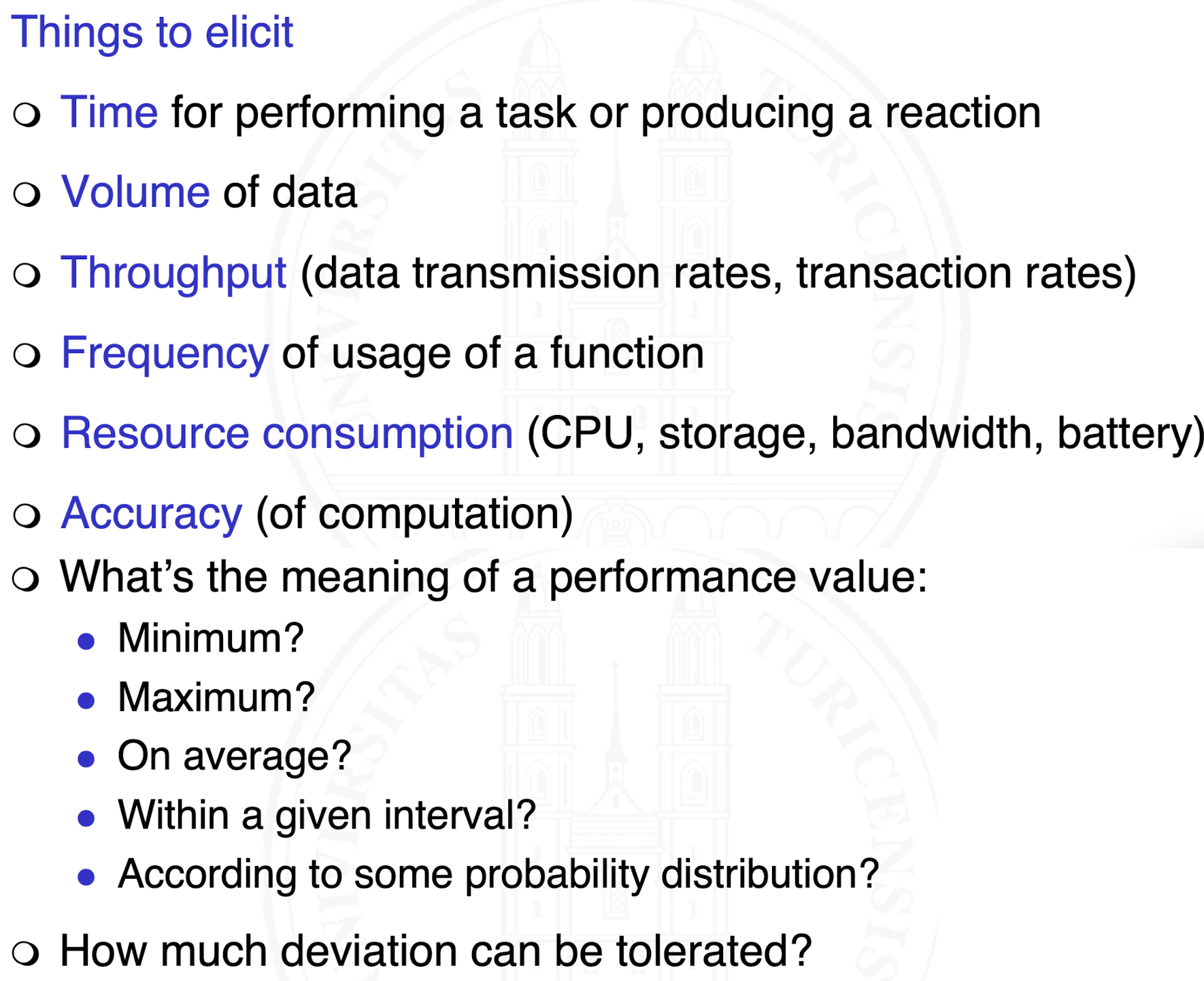
How do we elicit performance requirements?
How do we elicit constraints?

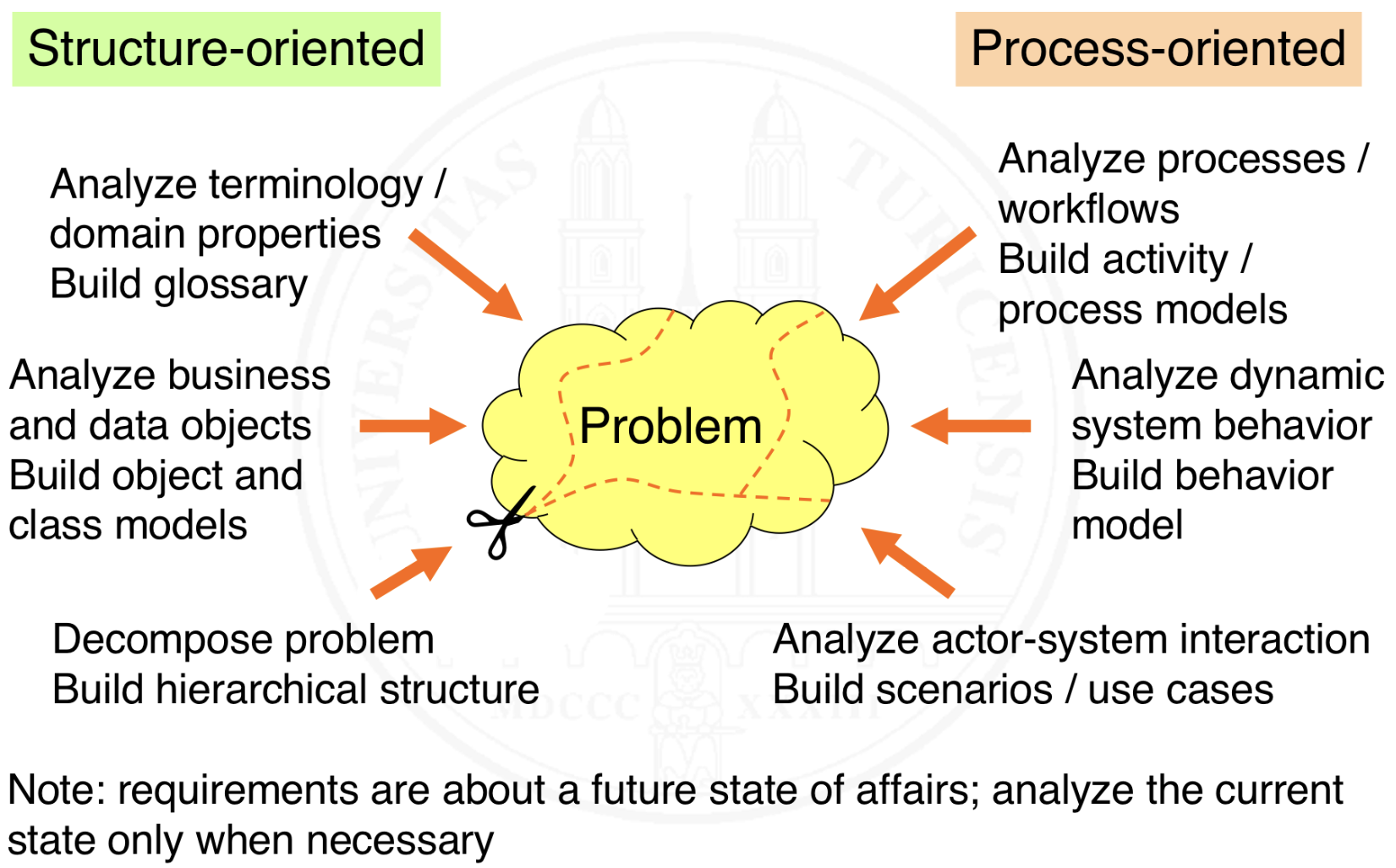
How can we analyze and document elicited information?
Build specification incrementally and continuously
Document requirements in small units
End over means: Result → Function → Input
Consider the unexpected: specify non-normal cases
Quantify critical attributes
Document critical assumptions explicitly
Avoid redundancy
Build a glossary and stick to terminology defined in the glossary
Let a GenAI assist you
What is Kano‘s model?
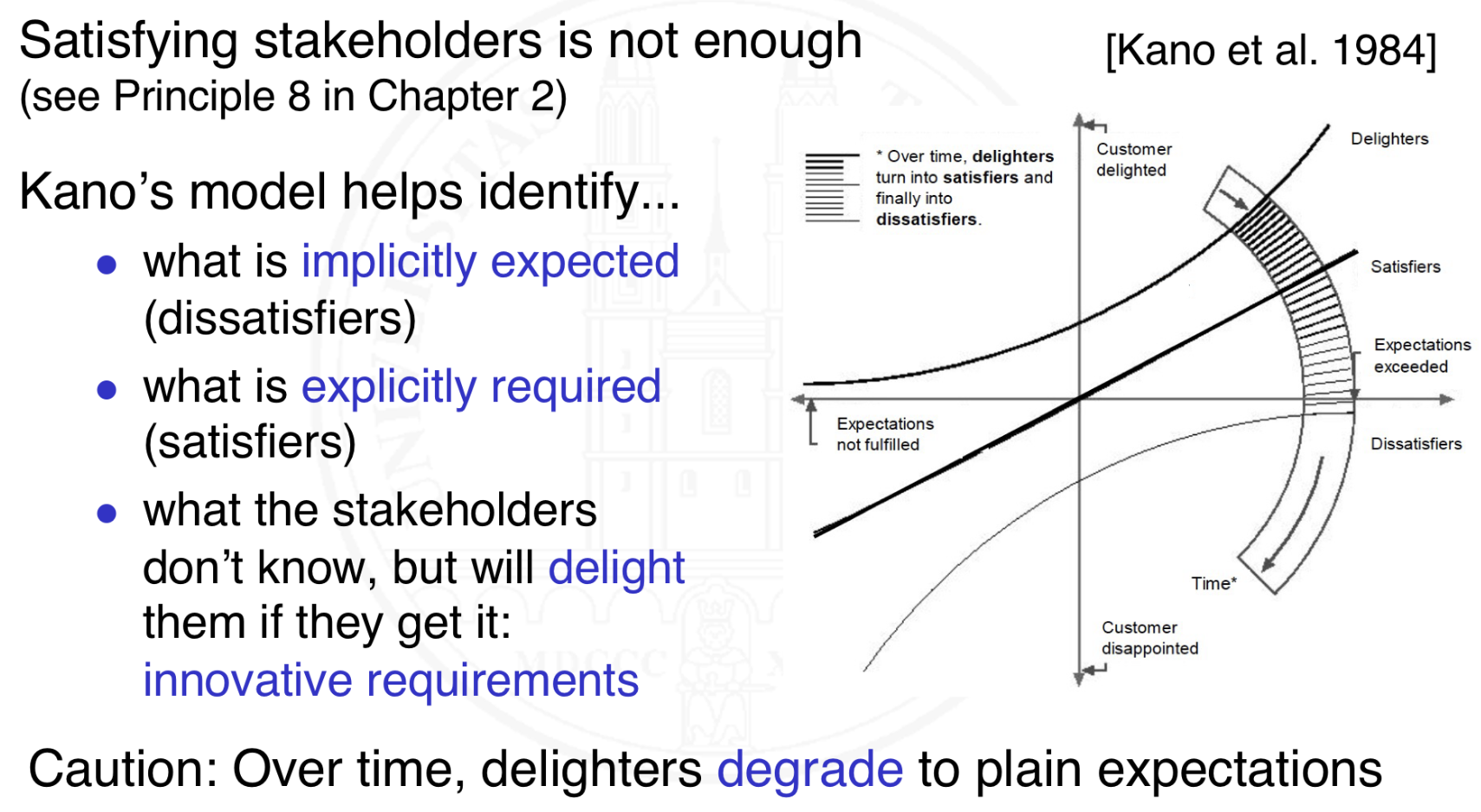
How can we create innovative requirements and where should we innovate?
Where we should innovate:
Functionality – new exciting features
Performance – not just a bit more, but significantly more powerful than previous or competing systems
Usability – making usage an exciting experience

What is conflict analysis and what are potential conflicts?
Identifying the underlying reasons of a conflict helps select appropriate resolution techniques
Typical underlying reasons are
Subject matter conflict (divergent factual needs)
Data conflict (different interpretation of data, inconsistent data)
Interest conflict (divergent interests, e.g., cost vs. function)
Value conflict (divergent values and preferences)
Relationship conflict (emotional problems in personal relationships between stakeholders)
Organizational conflict (between stakeholders on different hierarchy and decision power levels in an organization)
What is conflict resolution?
Various strategies / techniques
Conflicting stakeholders must be involved in resolution
Win-win techniques
Agreement
Compromise
Build variants
Win-lose techniques
Overruling
Voting
Prioritizing stakeholders (important stakeholders override less important ones)
Decision support techniques
PMI (Plus-Minus-Interesting) categorization of potential conflict resolution decisions
Decision matrix (Matrix with a row per interesting criterion and a column per potential resolution alternative. The cells contain relative weights which can be summarized per column and then compared)
What is a process?
DEFINITION. Process – A set of interrelated activities performed in a given order to process information or materials.
An RE process organizes how to carry out RE tasks, using appropriate practices and producing needed work products
What are the three process facets, from which an RE process can be configured?
Time facet: Linear vs. Iterative
Purpose facet: Prescriptive vs. Explorative vs. COTS-Driven
Target facet: Customer-Specific vs. Market-Oriented
Selection criteria indicate how to configure the process in each facet
What is the time facet?
Linear:
Requirements are specified up front in a single phase of the process
Selection criteria:
System development process is plan-driven and mostly linear
Stakeholders can specify their requirements up front
Comprehensive requirements specification required as a contractual basis for outsourcing design and implementation
Regulatory authorities require a requirements specification
Iterative:
Requirements are specified incrementally, starting with general goals and then adding or modifying requirements in every iteration
Selection criteria:
System development process is iterative and agile
Evolving requirements – not known up front
Stakeholders are available such that short feedback loops established for mitigating risk
Duration of project allows for more than 1-2 iterations
Ability to change requirements easily is important
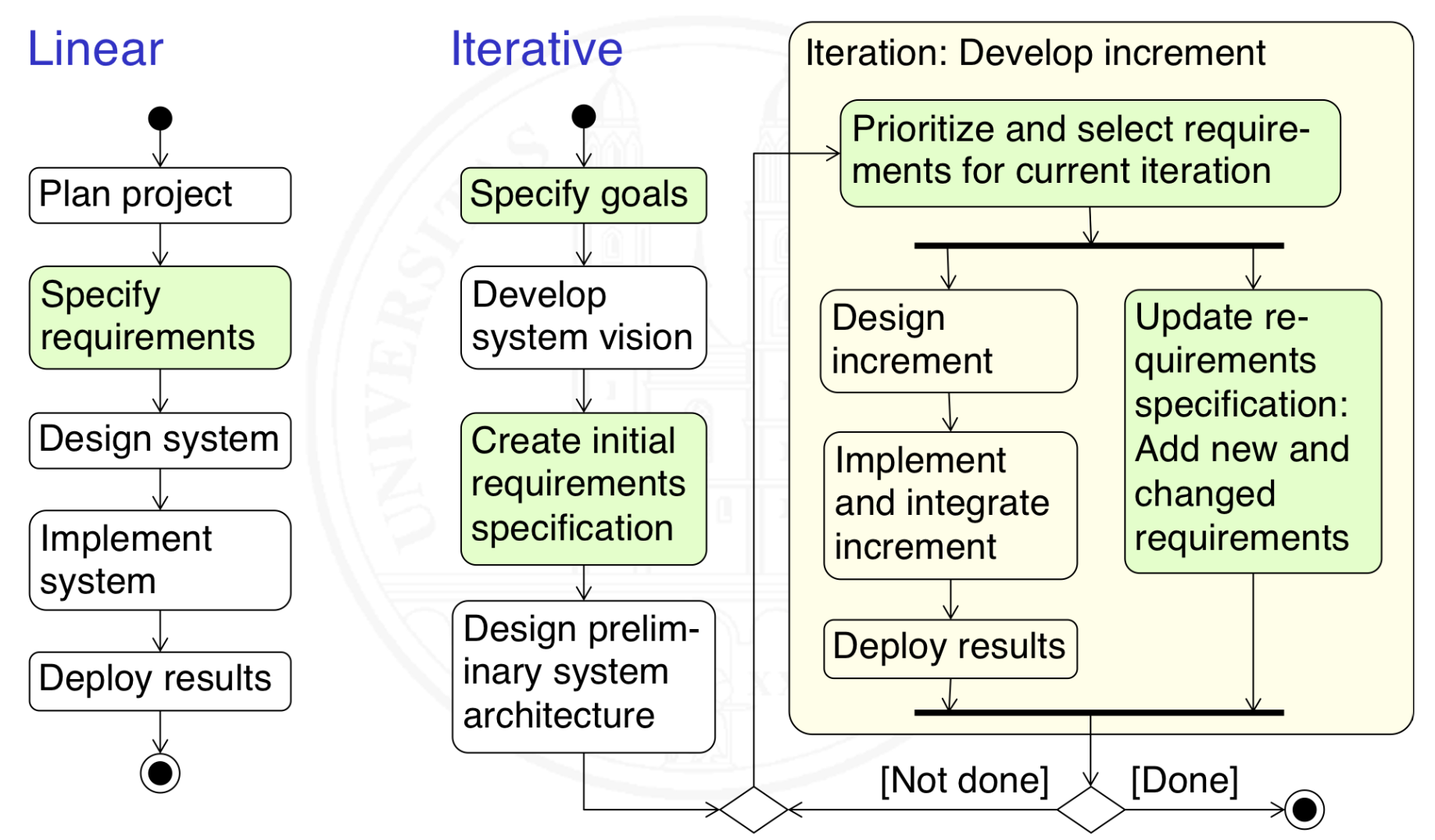
What is the purpose facet?
Prescriptive:
Requirements specification is a contract: All requirements are binding and must be implemented
Selection criteria:
Customer requires fixed-price contract
Functionality determines cost and deadlines
Design and implementation tendered or outsourced
Explorative:
Only goals known, concrete requirements have to be explored
Selection criteria:
Stakeholders only have a vague idea about their requirements
Stakeholders strongly involved, provide continuous feedback
Deadlines and cost take precedence over functionality
Customer is satisfied with a framework contract
Not a priori clear which requirements actually shall be implemented and in which order à Prioritization needed
COTS-Driven:
Requirements must reflect functionality of chosen COTS solution
Selection Criteria:
System will be implemented with COTS software
Only requirements not covered by the COTS solution shall be specified
What is Commercial of the Shelf (COTS)?
A system or component that is not developed, but bought as a standard product from an external supplier.
What is the target facet?
Customer-Specific:
System is ordered by a customer and developed by a supplier for this customer
Selection criteria:
The system will be mainly used by the organization that has ordered the system and pays for its development.
The important stakeholders are mainly associated with the customer’s organization.
Individual persons can be identified for the stakeholder roles.
The customer wants a requirements specification that can serve as a contract.
Market-Oriented:
System is developed as a product or service for a market
Selection criteria:
Developing organization (or one of its clients) intends to sell the system as a product or service in some market segment
Prospective users not individually identifiable
Requirements engineers have to design the requirements so that they match the envisaged needs of the targeted users
Product owners, marketing people, digital designers and system architects are primary stakeholders
What are typical facet combinations?
Linear and prescriptive are frequently chosen together
Explorative processes are typically also iterative
Market-Oriented does not combine well with Linear and Prescriptive
What are typical process configurations?

What if none of the typical process configurations fits?
Try to tailor the configuration with the closest fit
Get help from an RE process expert for building a process from scratch
What are disadvantages when expressing requirements with natural language?
Natural language can be
Ambiguous
Imprecise
Error-prone
Careful writing and reading is needed
What are some rules for specifying in natural language?
Use active voice and defined subjects
Build phrases with complete verbal structure
Use terms as defined in the glossary
Define precise meanings for auxiliary verbs (shall, should, must, may,...) as well as for process verbs (for example, “produce”, “generate”, “create”)
Check for nouns with unspecific semantics (“the data”, “the customer”, “the display”,...) and replace where appropriate
When using adjectives in comparative form, specify a reference point: “better” ➜ “better than”
Scrutinize all-quantifications: “every”, “always”, “never”, etc. seldom hold without any exceptions
Scrutinize nominalizations (“authentication”, “termination”...): they may conceal incomplete process specifications
State every requirement in a main clause. Use subordinate clauses only for making the requirement more precise
Attach a unique identifier to every requirement
Structure natural language requirements by ordering them in sections and sub-sections
Avoid redundancy where possible
Provide an example of a typical phrase template and a requirement using that template.
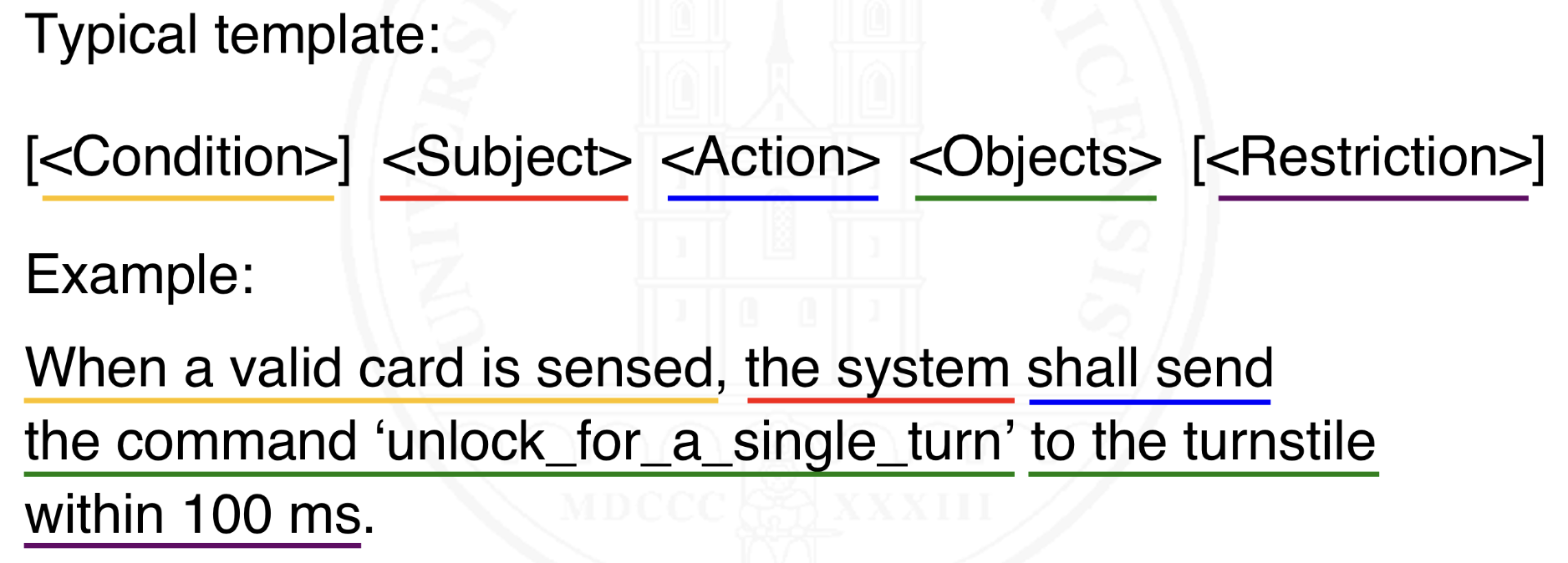
What is EARS?

What are user stories?

What are form templates?
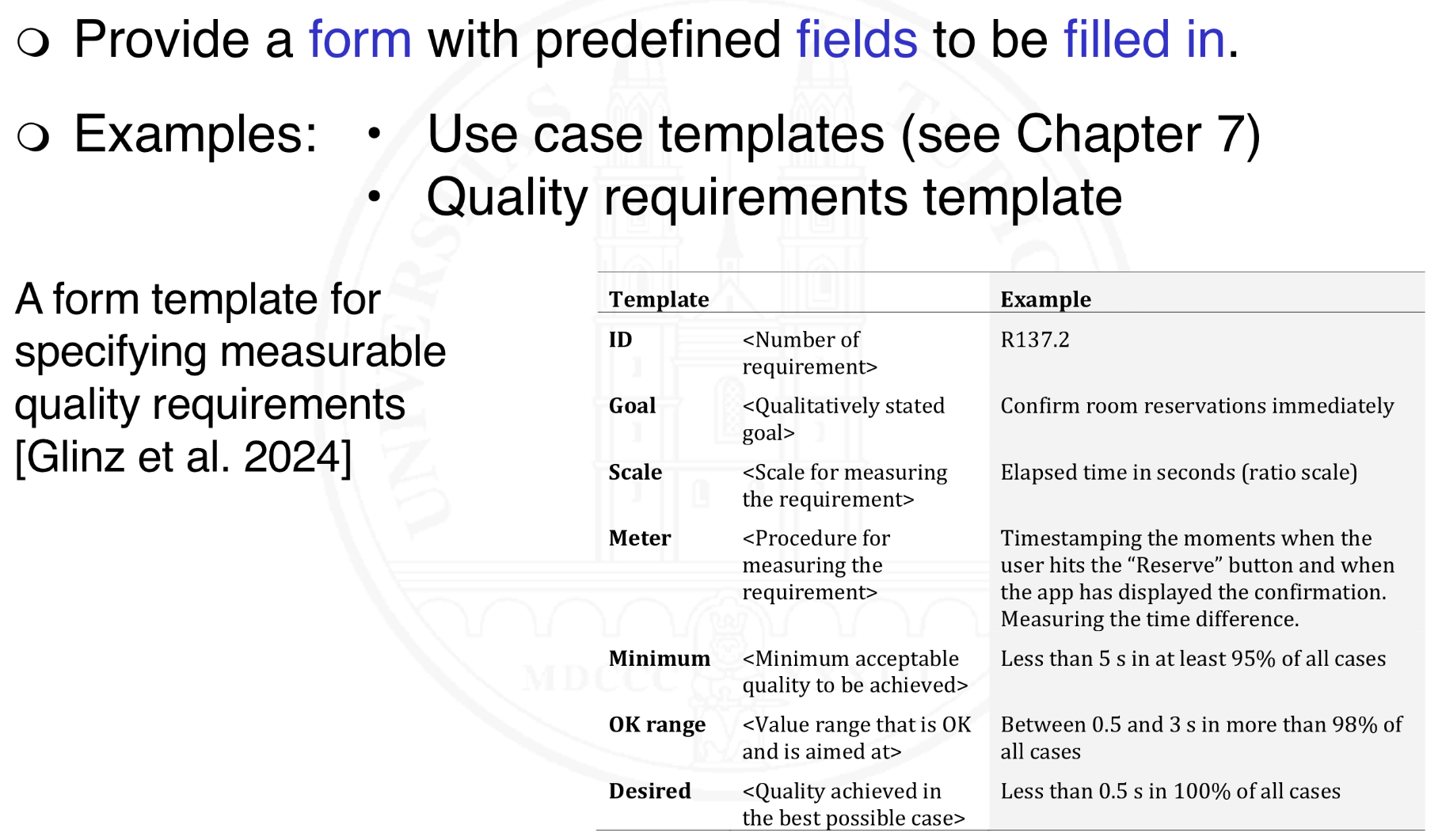
What are the motivations for modeling requirements?
Gain an overview of a set of requirements
Understand relationships and inter- connections between requirements
Focus on some aspect of a system, abstracting from the rest
What is a model?
DEFINITION. Model – an abstract representation of an existing part of reality or a part of reality to be created.
Requirements models are problem-oriented models of the system to be built
Architecture and design information is omitted
What can requirements models be used for?
Specifying requirements (as a means of replacing textually represented requirements)
Paraphrasing textually represented requirements to improve understanding of complex structures and dependencies
Testing textually represented requirements to uncover omissions, ambiguities and inconsistencies
Decomposing a complex reality into comprehensible parts
Which aspects can be modeled?

What are static system models and static domain models?
Static system models: Information that a system needs to know and store persistently
Static domain models: The (business) objects and their relationships in a domain of interest
What is data modeling with entity-relationship models?
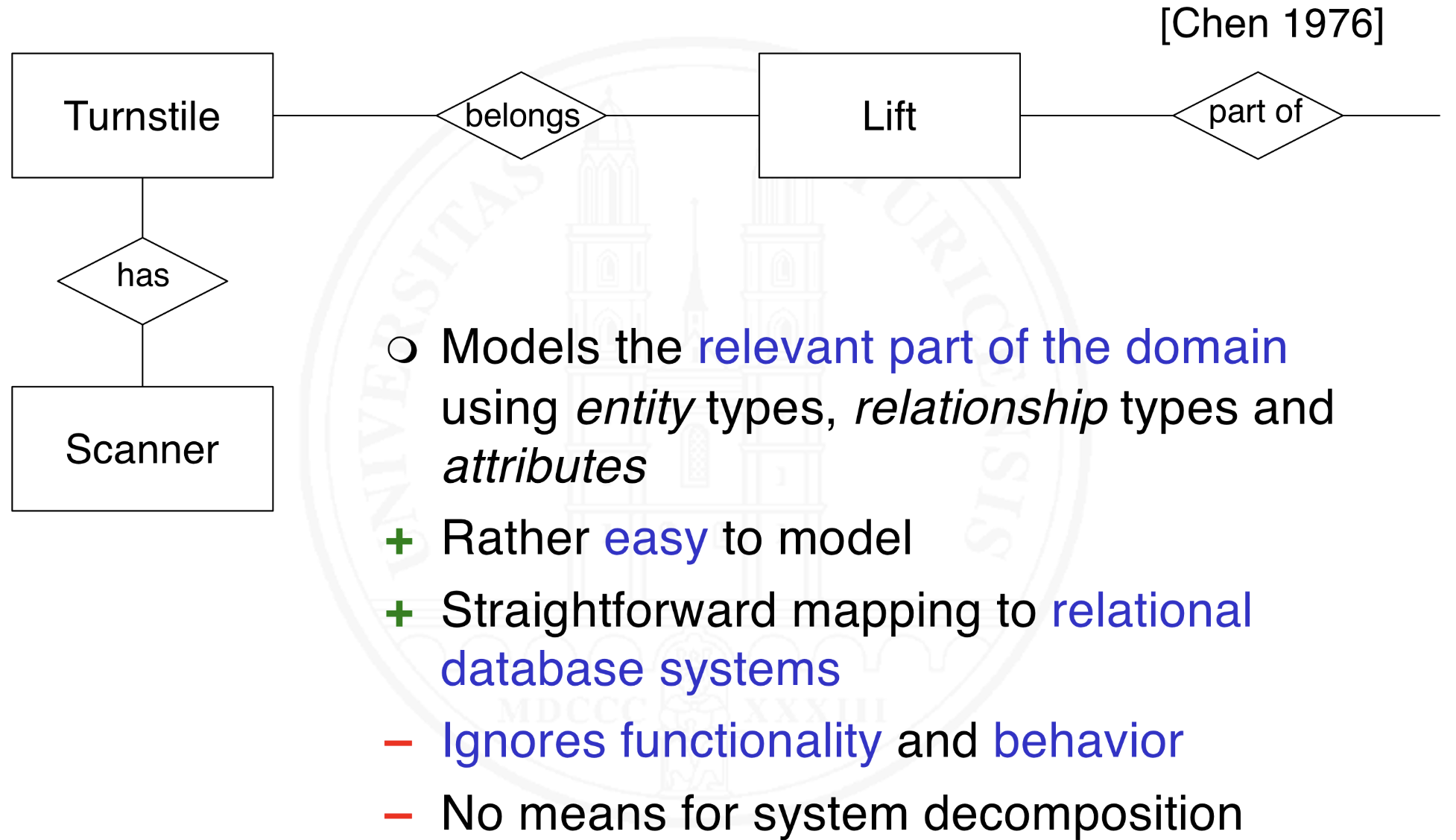
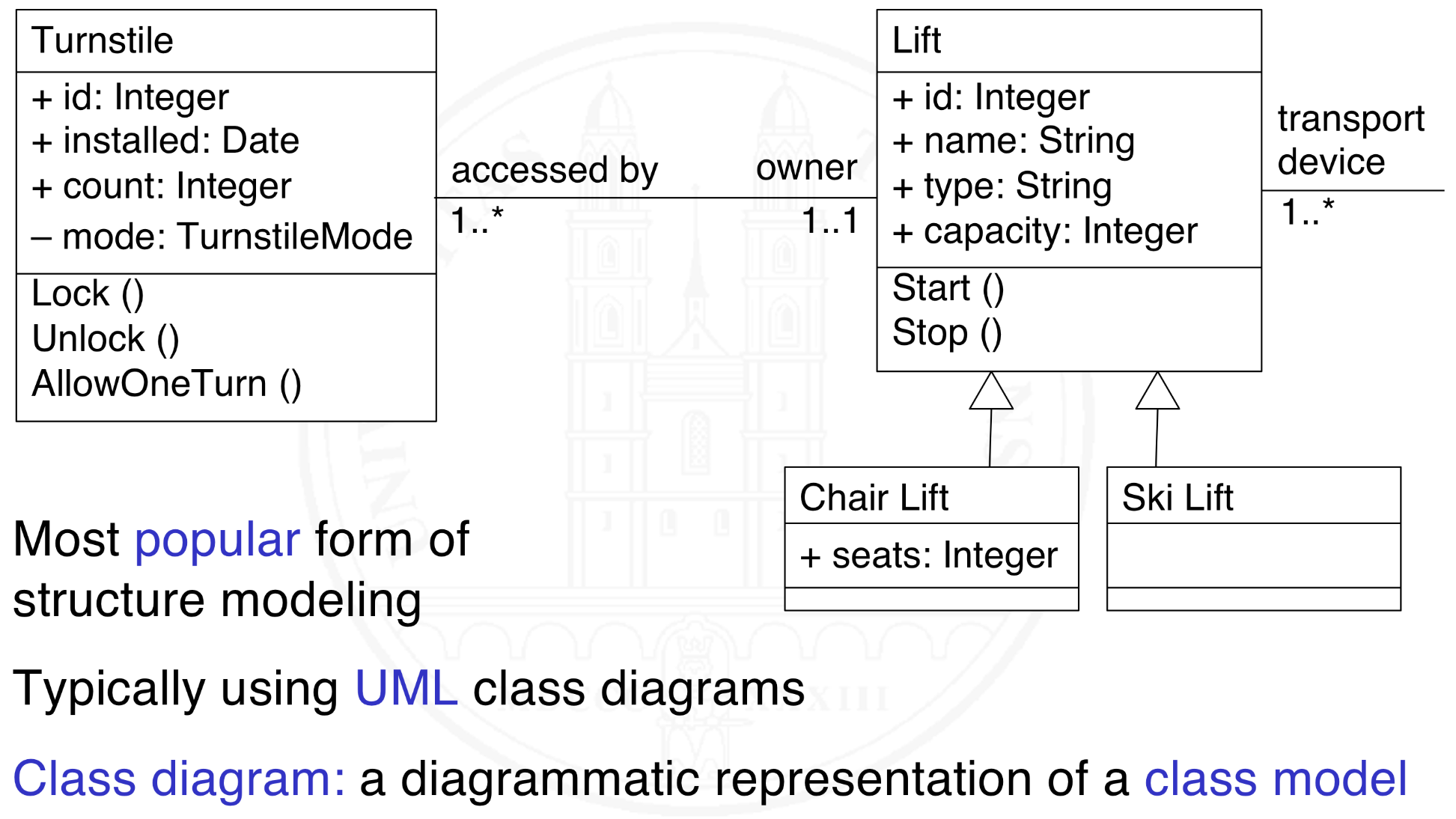
What is object and class modeling?
Identify those entities in the domain that the system has to store and process
Map this information to objects/classes, attributes, relationships and operations
Represent requirements in a static structural model
Modeling individual objects does not work: too specific or unknown at time of specification
Classify objects of the same kind to classes: Class models
or select an abstract representative: Object models
What is an example of a class model?
What is an example of an object model?
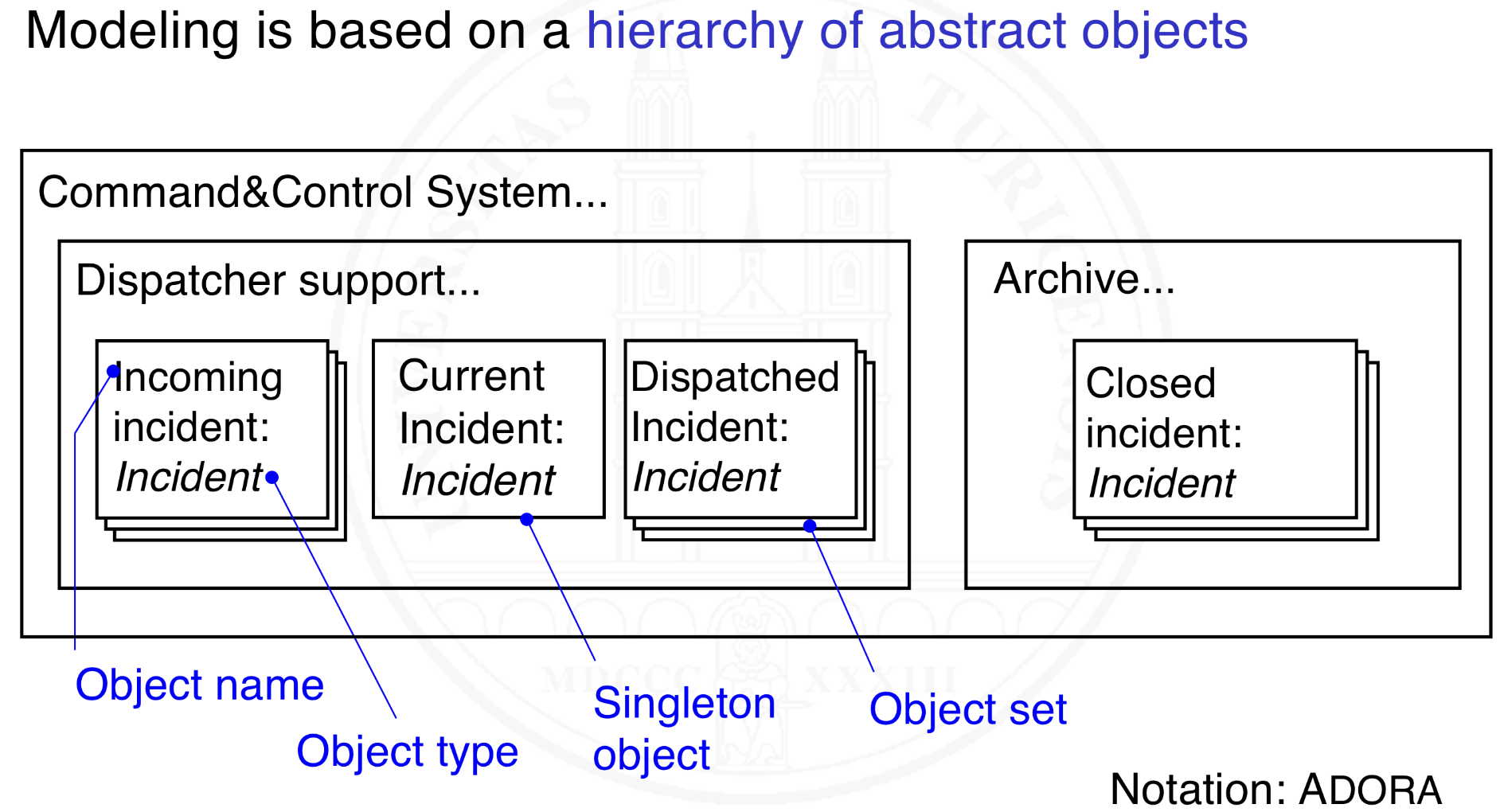
What is ADORA?

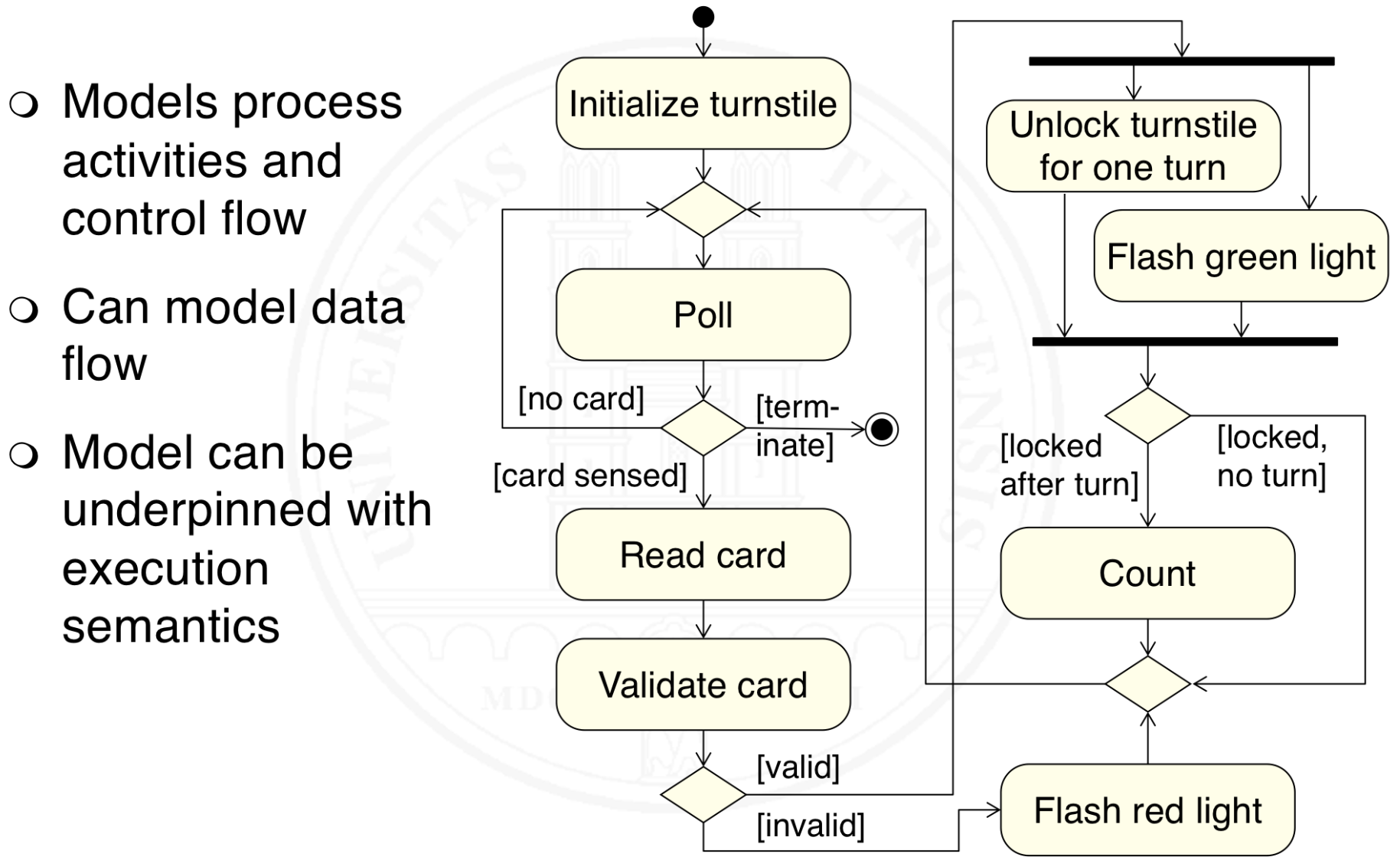
What is activity modeling, using UML activity diagrams?
What are data and information flow models?
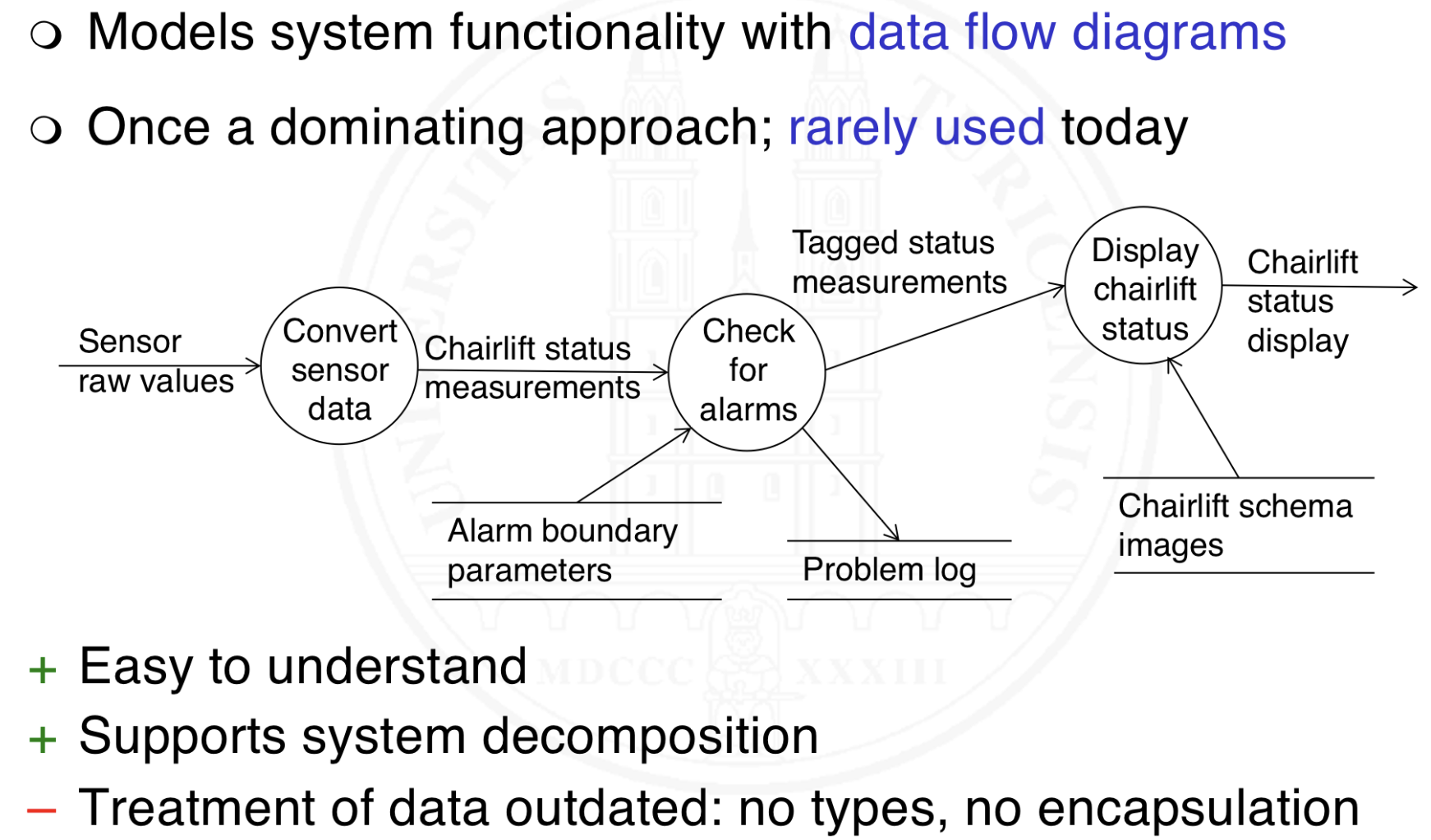
What is process and workflow modeling and what are the typical languages used for it?
Elements
Process steps / work steps
Events influencing the flow
Control flow
Maybe data / information access and responsibilities
Typical languages
UML activity diagrams
BPMN
Event-driven process chains
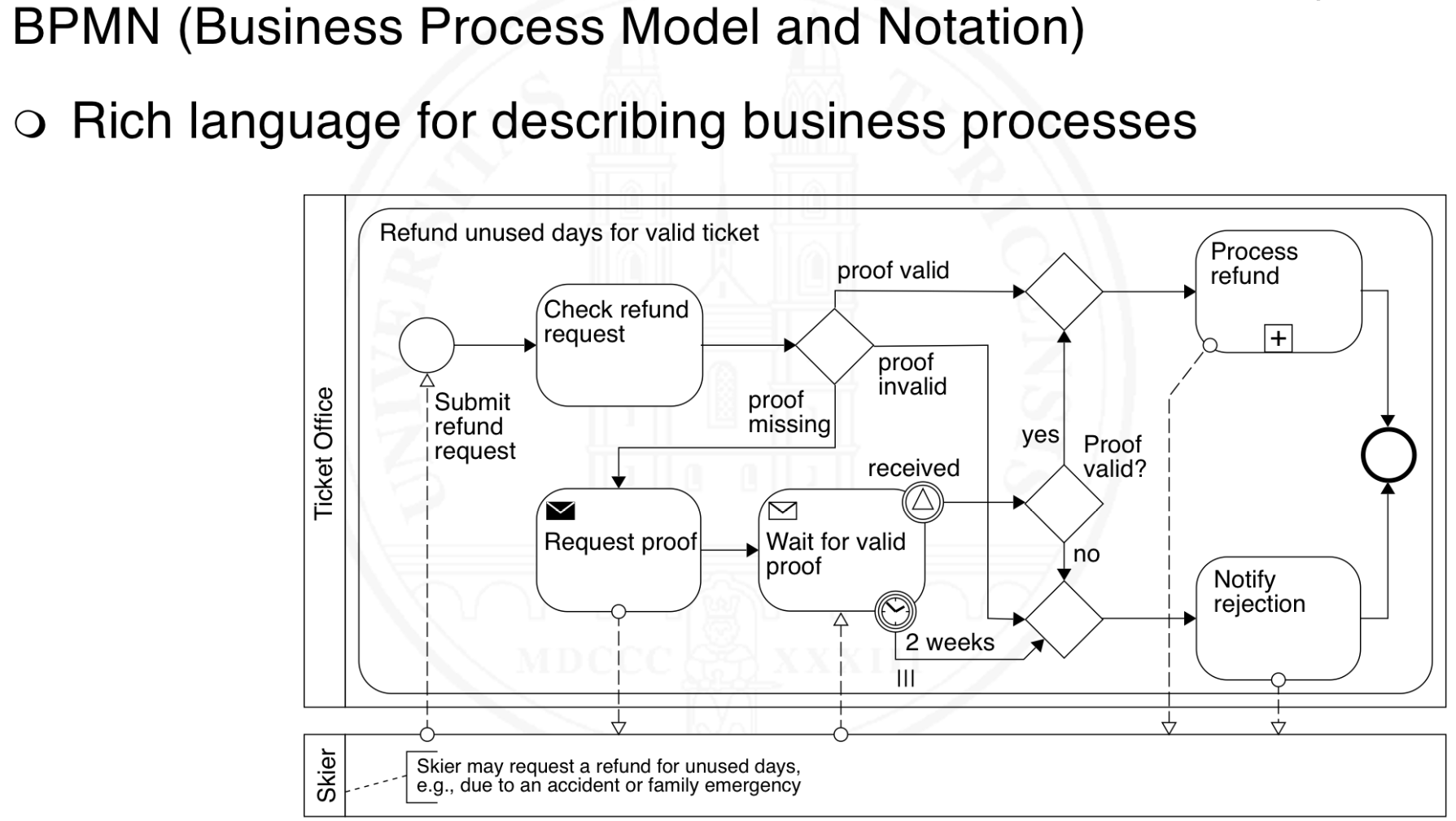
What is BPMN?
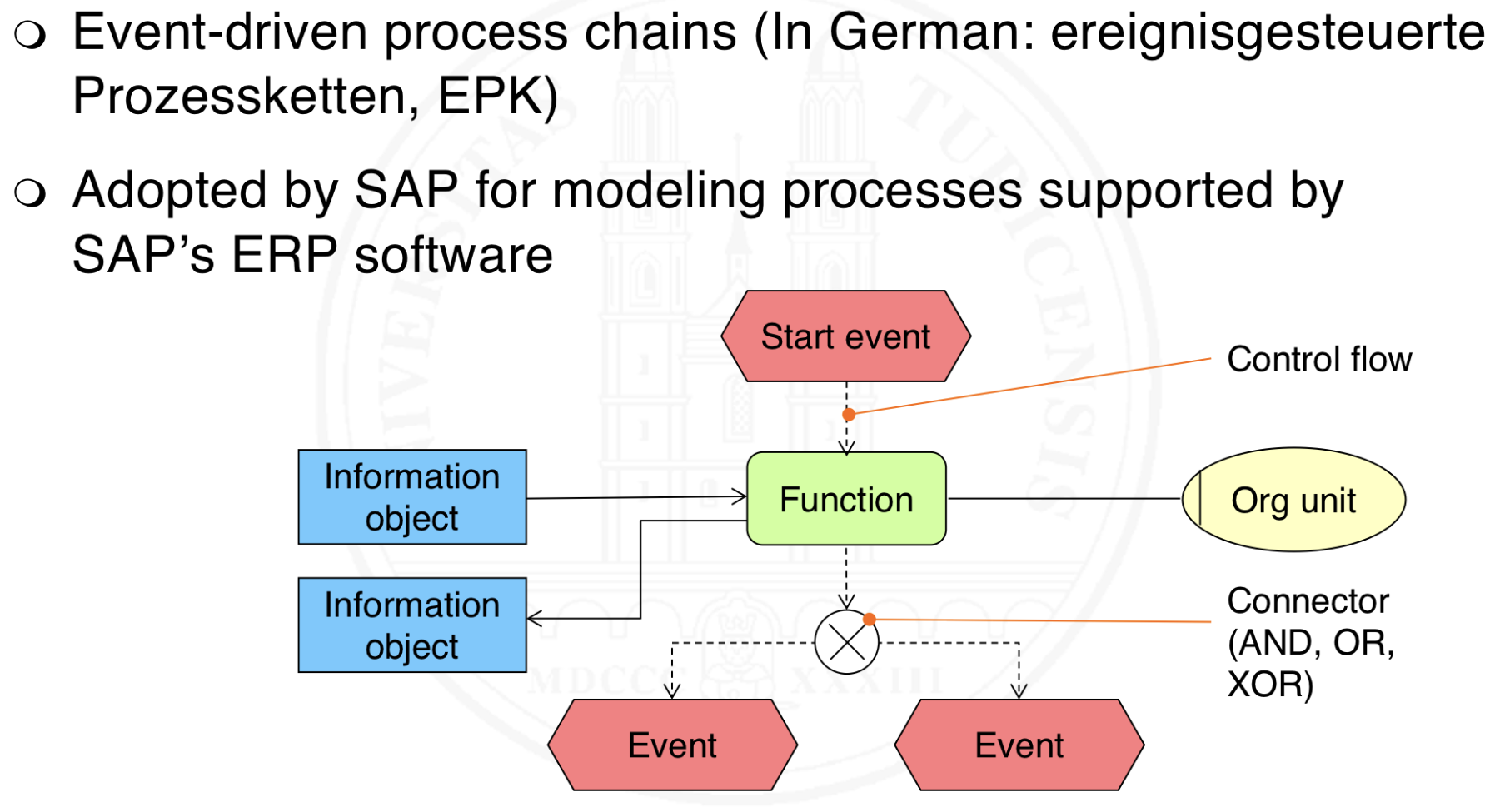
What are Event-Driven Process Chains (EPC)?
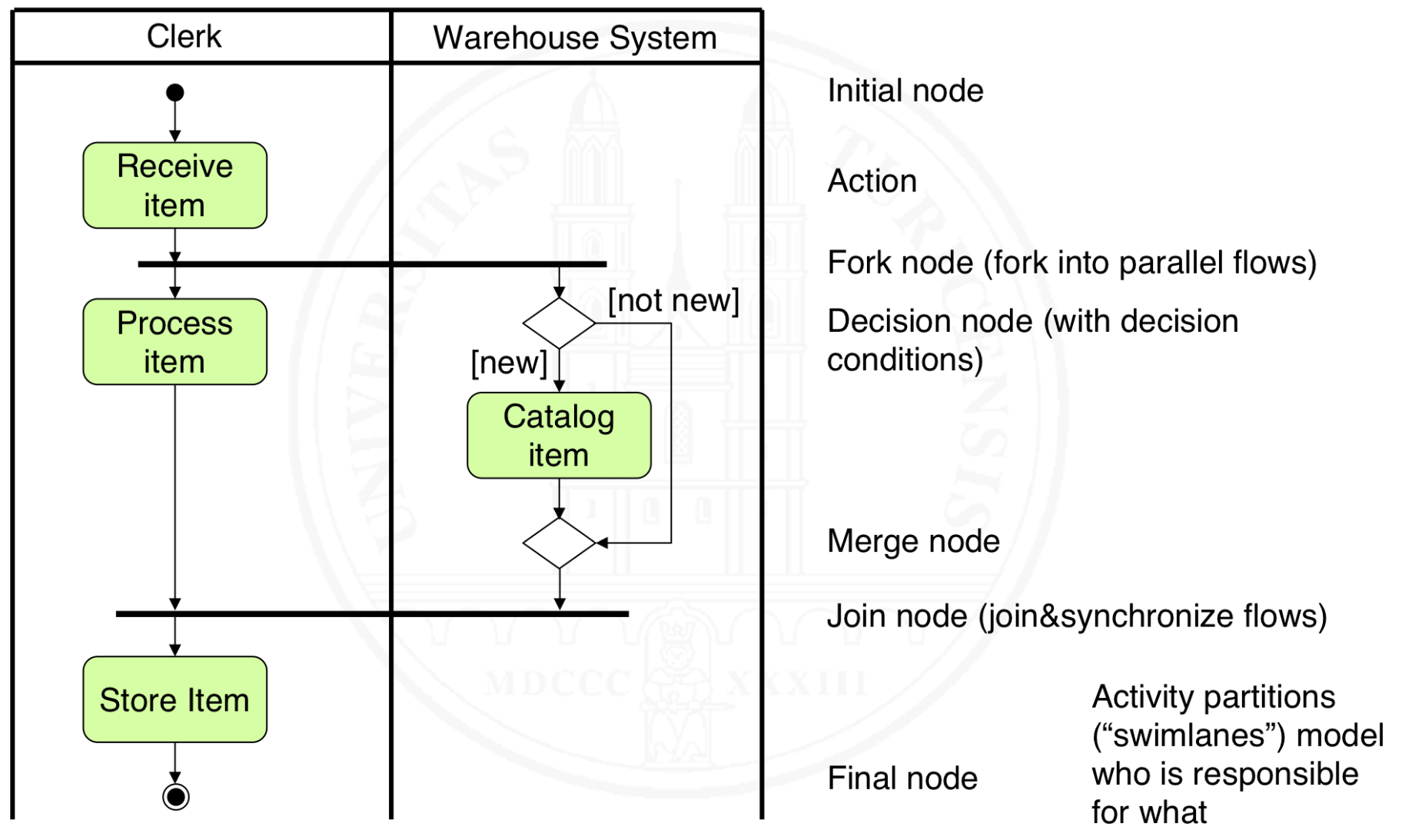
What is a UML activity diagram?
What are domain story models?
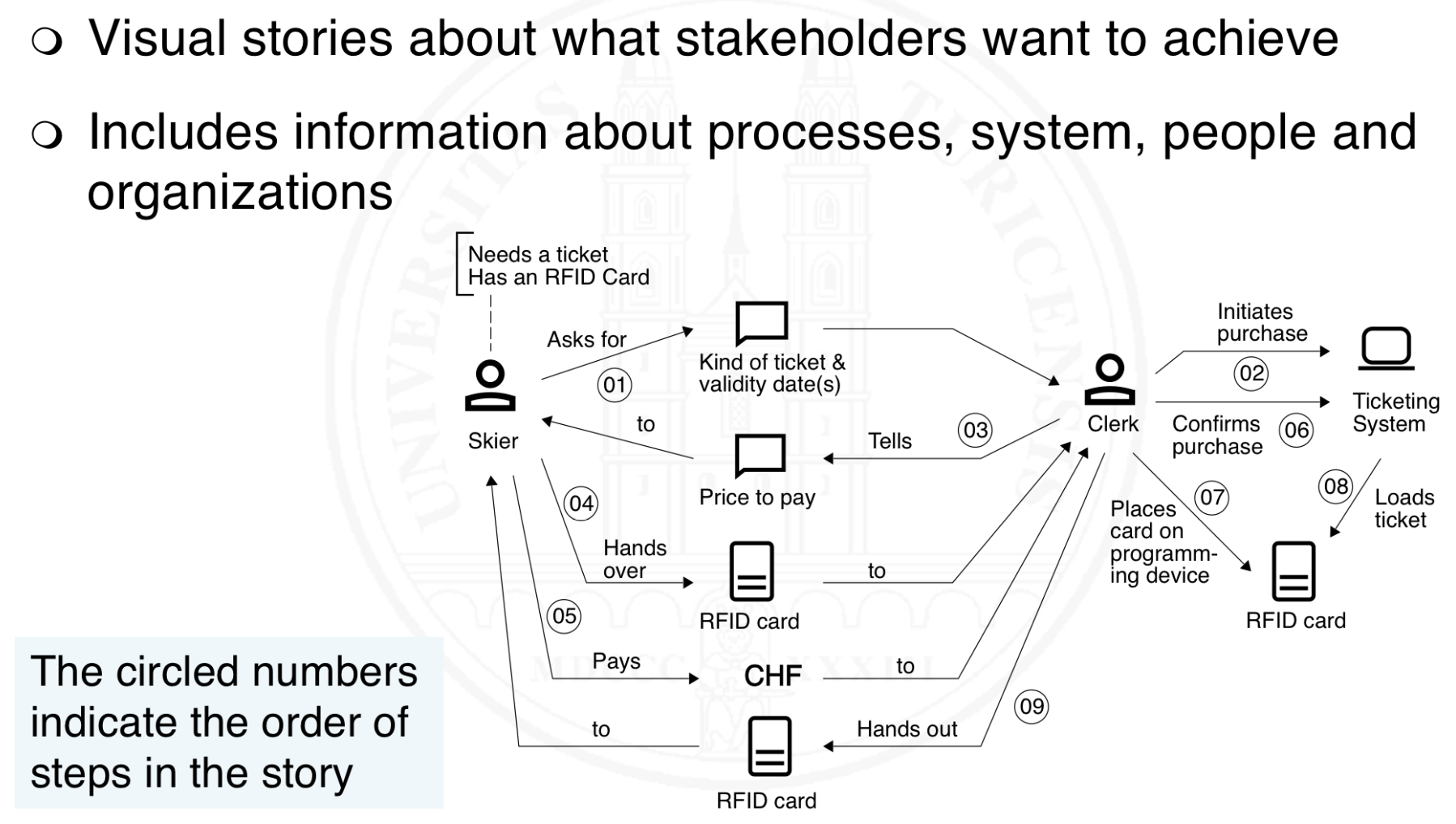
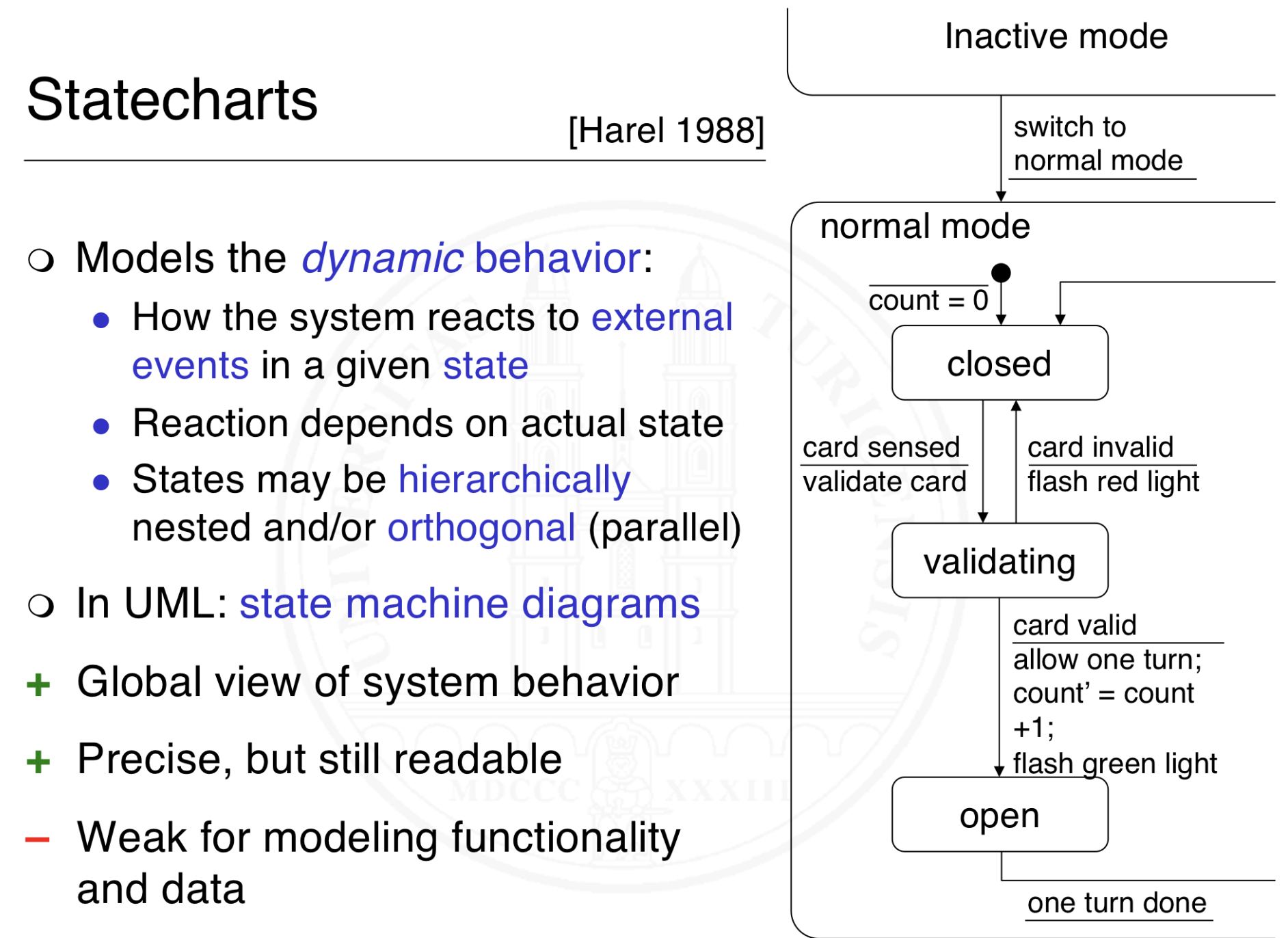
What is state and behaviour modeling and how can we achieve that?
What are statecharts?