Psychosis NRS 317
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Psychosis Definition
An abnormal condition of the mind that results in difficulties telling what is real and what is not, secondary to complex neurobiological changes.
Psychosis Attributes
Alteration in perception of reality
Alteration in behavior
Culture variation
Psychosis Attribute —> Alteration in perception of reality
Hallucinations
Delusions
Psychosis Attribute —> Alteration in Behavior
Disorganized thoughts
Disorganized motor behaviors
Withdrawal from society
Lack of interest or motivation
Psychosis Attribute —> Culture Variation
"Madness" born of "poison, demons, fecal matter and blood trouble" (1500 BC)
Term psychosis not coined until 1845
How is the term "psychotic" used today?
Pathophysiology of Psychosis
Many theories about the cause being related to neurotransmitter communication
Pathophysiology of Psychosis —> Dopamine
Too much dopamine in the synaptic cleft = positive symptoms
Not enough dopamine in the synaptic cleft = negative symptoms
More on negative & positive symptoms soon!
GABA, serotonin, glutamate, and acetylcholine likely also involved
Pre-frontal cortex
regulation of complex behavior: thoughts, actions, emotions
Limbic system
emotional processing of sensory info
Psychosis Scope
absence of psychosis
subclinical symptoms
clinical mild
significant moderate
psychosis severe
Primary Psychosis —> Psychiatric etiology
Examples:
schizophrenia spectrum
major depressive disorder
bipolar disorder
brief psychotic disorder (such as postpartum psychosis)
Secondary Psychosis —> Organic Etiology
Examples
intoxication
delirium
dementia
medication toxicity
medical illnesses such as hepatic encephalopathy
Primary and Secondary Psychosis Notes
These are not mutually exclusive --> they can occur at the same time and may even potentiate one another
Psychosis Consequences —> Physiologic
Physical symptoms
Duration, intensity, impairment level are dependent on etiology
Side effects from medication
Neural degradation
Untreated psychosis is a persisting neurotoxic state --> inflammatory markers released
Psychosis Consequences —> Physiologic (Extra Notes)
Dementia occurs 2x as often in pts dx with schizophrenia spectrum disorder
Psychosis Consequences —>Psychosocial
Behavior is influenced by symptoms and treatment
Psychotic symptoms + sedating effects of medications
Substance abuse is well documented
Withdrawal from community
The community does not always support this population
Concerning for employment, housing, and having basic needs met = vulnerable population
Psychosis Consequences
—>Psychosocial (Extra Notes)
Nearly 50% of those diagnosed with schizophrenia spectrum are alcohol or illicit drug dependent, 70% are nicotine dependent
Psychosis Risk Factors
All individuals are potentially susceptible to psychosis regardless of age, gender, race, and/or ethnicity
Common variables seen in patients experiencing psychosis include:
Psychosis TYPES OF Risk Factors
Family history psychosis
past psychotic episode
substance use
stress intolerance —> lack of sleep
ineffective coping skills
pre- existing psychiatric illness
Risk Factors of Psychosis —> Schizophrenia-specific Risk Factors
Low IQ as a child
Low SES
Large population density
Genetic – first degree relative increases risk, but 60% of pts have no family hx
Increased stress, poor coping
Psychosis Assessment: Symptoms of Psychosis —> ADDED to behaviors positive
Agitation
paranoia
delusions
hallucinations
catatonia
disorganized thinking
disorganized motor behavior
Psychosis Assessment: Symptoms of Psychosis —> cognitive
memory deficits
attention deficits
loss of executive function
Psychosis Assessment: Symptoms of Psychosis —> REDUCED from behaviors negative
Alogia,
asociality/social withdrawal
anhedonia
avolition
poor self-care
poor judgment
poor insight
blunted affect
Psychosis Assessment: Nursing —> Medical hisotry & patient interview
Can be difficult r/t impaired cognition and changes in reality
Collect data from pt and also utilize another source like family or friends
Keep questions straight forward and open-ended, provide extra time to answer
Building rapport can be difficult r/t paranoia and delusions
Avoid using words such as hallucination, delusion, etc. Instead ask, "Do you ever see or hear things that other people do not?"
DONT ASK “WHY” questions —> its judgemental
Psychosis Assessment: Nursing —> Physical Assessment
Physical symptoms often follow pt's etiology of psychosis
Look for side effects from medications
Assess pt's ability to provide self-care, evidence of drug/alcohol abuse
Psychosis Assessment: Nursing —> Mental Status Assessment
Mental status = a large picture including behavior
emotion
personality
mood
cognitive functioning
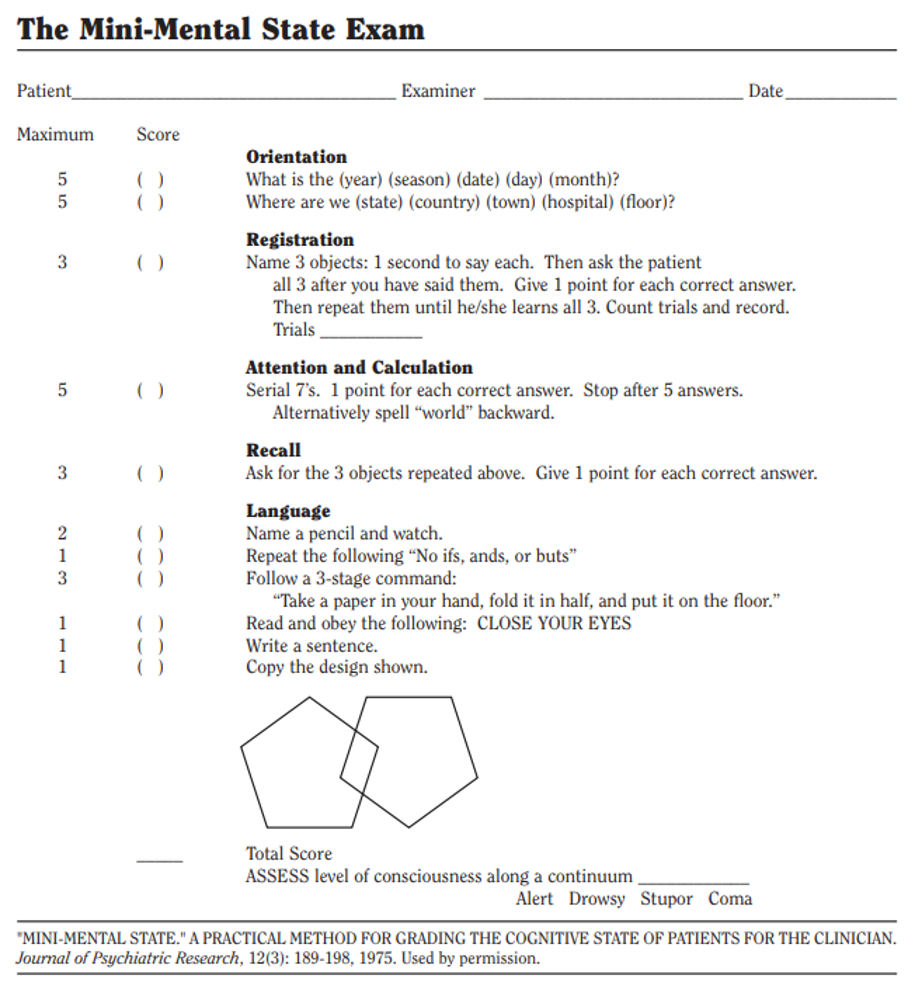
psychosis mini mental status exam
Focus on
memory
language skills
attention level
ability to engage in mental tasks
Can be modified for use in children over the age of 4
Psychosis Diagnostics
Lab tests to differentiate between primary and secondary etiologies
Ex: rule out organic etiologies with CBC, thyroid, RPR (syphilis), urinalysis, urine drug screen, and more)
A psychiatric evaluation of the patient performed by a provider can medically diagnose a primary etiology such as schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Diagnosis —> 2+ of the main 5 symptoms
•Delusions
•Hallucinations
•Disorganized or incoherent speaking
•Disorganized or unusual movements
•Negative symptoms
Schizophrenia Diagnosis —> Duration of symptoms
•Key symptoms lasting for at least 1 month
•General effects must last for at least 6 months
Schizophrenia Diagnosis —> Social or Occupational Disfunction
•Disrupts ability to work or relationships (friends, romantic, professional, etc
Clinical Management: Planning & Interventions —> General Goals
Treat underlying cause when applicable
Emphasis on recovery and rehabilitation. Goal = prevention of relapse & independence
Clinical Management: Planning & Interventions —> Collaborative Interventions
Pharmacological
Non-pharmacological (social skills & differing types of therapy)
Lifestyle modifications (address behaviors that could worsen condition, case management, and more)
Community integration
Group therapy & support groups
Clinical Management: Planning & Interventions —> Indepenedent Interventions
Therapeutic communication/rapport building – important to validate pt experiences but also ground them in reality
Prevent injury/promote a safe environment
Close monitoring and documentation of symptoms
Provide treatment as ordered
Provide education to patient and support system
Advocate for the patient
Background: different medications
Dopamine antagonists = block dopamine activity at the synapse and decrease the effect that dopamine has on the brain
Antipsychotic drugs fall into two major groups:
First-generation antipsychotics (FGAs) = typical/conventional antipsychotics
Second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs) = atypical antipsychotics; also block serotonin receptors in addition to dopamine
Dopamine Blockers: Prototype drugs
aka. first gen. antipsychotics
haloperidol (Haldol)
Dopamine Blockers: How does it act? (mechanism of action)
block actions of dopamine
Dopamine Blockers: What does it do? (primary symptom target)
↓ hallucinations
↓ delusions
↓ agitation
Dopamine Blockers: TYPES OF Adverse outcomes
Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS)
Tardive Dyskinesia (TD)
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) (Rare but Life-Threatening)
Sedation
Anticholinergic Effects
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS) (Monitor)
Muscle stiffness
tremors
rigidity
bradykinesia
akathisia (restlessness)
dystonia (sustained muscle contractions)
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS) (Response)
hold and notify provider
anticipate order for anticholinergic
Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS) response, what medication should you anticipate
anticipate order for anticholinergic
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Tardive Dyskinesia (TD) (monitor)
involuntary movements of the
face
tongue
or extremities
often irreversible.
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Tardive Dyskinesia (TD) (response)
hold and notify provider
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) (Rare but Life-Threatening) (monitor)
hyperthermia
muscle rigidity
altered mental status
autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, blood pressure changes)
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) (Rare but Life-Threatening) (response)
hold and notify provider
RRT
anticipate order for dantrolene
With Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) (Rare but Life-Threatening) response which medication should you anticipate?
anticipate order for dantrolene
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Sedation (monitor)
excessive sleepiness
drowsiness
↓LOC (sometimes desired effect if agitation is present)
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Sedation (response)
hold and notify provider
educate on taking at night time
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Anticholinergic Effects (monitor)
Dry mouth
constipation
urinary retention
blurred vision
Dopamine Blockers: Adverse outcomes —> Anticholinergic Effects (response)
provide symptomatic treatments (e.g., stool softeners, artificial saliva)
monitor for severe complications like urinary retention
notify provider
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: Prototype Drugs
aka. second gen. antipsychotics
olanzapine (Zyprexa)
aripiprazole (Abilify)
risperidone (Risperdal)
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: How does it act (mechanism of action)
block actions of dopamine and serotonin
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: what does it do (primary symptom target)
↓ hallucinations
↓ delusions
↓ agitation
↓ negative symptoms of schizophrenia (anhedonia, avolition, etc.)
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: TYPES OF adverse outcomes
Metabolic Syndrome (Weight Gain, Hyperglycemia, Dyslipidemia)
Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS)
QT Prolongation
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: Metabolic Syndrome (Weight Gain, Hyperglycemia, Dyslipidemia) (monitor)
weight
blood glucose levels
lipid profiles
waist circumference
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: Metabolic Syndrome (Weight Gain, Hyperglycemia, Dyslipidemia) (response)
hold and notify provider
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: QT Prolongation (monitor)
ECG for QT interval prolongation
potassium and magnesium levels
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: QT Prolongation (response)
hold and notify provider
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS) (monitor)
Muscle stiffness
tremors
rigidity
bradykinesia
akathisia (restlessness)
dystonia (sustained muscle contractions)
DOPAMINE & SEROTONIN BLOCKERS: Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS) (response)
hold and notify provider
anticipate order for anticholinergic
Mechanism of Action: Dopamine Blockers First-Generation (Typical)
Primarily block dopamine (D2) receptors
Mechanism of Action: Dopamine & Serotonin Second-Generation (Atypical)
Block dopamine (D2) and serotonin (5-HT2A) receptors
Symptom Target: Dopamine Blockers First-Generation (Typical)
Effective for positive symptoms (hallucinations, delusions)
Symptom Target: Dopamine & Serotonin Blockers Second-Generation (Atypical)
Effective for both positive and negative symptoms
Examples: Dopmaine Blockers First-Generation (Typical)
haloperidol (Haldol)
Examples: Dopamine & Serotonin Blockers Second-Generation (Atypical)
olanzapine (Zyprexa),
aripiprazole (Abilify)
risperidone (Risperdal)
Key side effects: Dopamine Blockers First-Generation (Typical)
High risk of EPS (tardive dyskinesia, dystonia)
Key side effects: Dopamine & Serotonin Second-Generation (Atypical)
Higher risk of metabolic side effects (weight gain, diabetes)
Nursing Considerations: Dopamine Blockers First-Generation (Typical)
Monitor for movement disorders (EPS)
Nursing Considerations: Dopamine & Serotonin Blockers Second-Generation (Atypical)
Monitor for metabolic changes, weight gain, diabetes
Too much dopamine in the synaptic cleft is
positive symptoms
Not enough dopamine in the synaptic cleft is
negative symptoms
Is Catatonia a positive or negative symptom? What does it mean?
a positive symptom where it disrupts the person’s awareness of the world around them
is Alogia a positive or negative symptom? What does it mean?
a negative symptom where causes patient to speak less or use fewer words
is Anhedonia a positive or negative symptom? What does it mean?
a negative symptom where the patient has a persistent loss of interest and pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable
is Avolition a positive or negative symptom? What does it mean?
a negative symptom where the patient has a lack of motivation or inability to start or complete goal-directed activities