Chapter 32 - Plant Reproduction
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
mitosis
cell division
meiosis
cell divides twice to produce four sex cells
calyx
the sepals of a flower that enclose the petals
corolla
ring of petals of a flower that includes the flowers reproductive organs
carpel/pistil
female reproductive parts of a flower. includes stigma, style and ovary
stamen
male reproductive parts of a flower. includes anther and filament
monoecious
both male and female flowers on the same plant (ex: walnut)
dioecious
male and female flowers on separate plants (red maple)
pollination
pollen containing the male genetic material is transferred to the female part of a flower (the stigma)
pollination syndrome
set of flower characteristics that are linked to specific pollinators
nectar guide
visual patterns on flowers that help pollinators locate nectar and pollen
cotyledon
first leaf of a plant seedling
hilum
scar or mark on a seed that marks the point of attachment to its seed vessel
vernalization
plants are induced to flowering process by exposure to cold temperature
scarification
process of breaking down a seeds hard outer coat to encourage germination
cutting
a piece of a plant that can be used to make a new independent plant
grafting
two or more plants are joined together so they grow as a single plant
senescence
natural process of aging in plants
five examples of asexual reproduction for plants
rhizomes, stolons, bulbs, corms, tubers
vegetative propagation
cuttings and graftings
sexual reproduction
two types of seed plants
angiosperms
flowering plants, seeds enclosed in carpel/fruit, broad leaves, double fertilization, pollination by animals more common
gymnosperms
naked seeds in cones with male and female gametophytes on separate male/female cones
difficult for self pollination
wind pollination more common
no fruits
needle like or scale like leaves
examples of angiosperms
grasses, flowers, herbs, shrubs, and most deciduous trees
female gametophyte
enclosed in ovule of ovary (part of pistil)
male gametophyte
pollen grains in anther (part of stamen)
complete flower
sepals, petals, pistils, stamens
double fertilization
one sperm cell fuses with the egg to form the embryo. the other fuses with the nuclei and forms the endosperm
female cone
higher on tree
male cone
lower on tree
pollination
pollen from anther to the stigma. pollen develops into tube cell and sperm cell
self pollination
same plant, quick
less genetic diversity
does not require nectar and pollen for pollinators
reliable, no pollinators needed
cross pollination
different plants, need pollinators
more genetic diversity
preventing self pollination
pollination and ovary mature at different times
different lengths of filament and style
location of male and female parts on the same plant
male and female parts on different plants
self incompatibility
mechanisms of cross pollination
wind, water, insects, birds, bats, manual/human aided
factors affecting germination time
moisture and temperature, seed size, depth in soil, light requirement
fruits main goal
seed dispersal
methods of seed dispersal
wind, water, animals, mechanical
types of fruit
simple, aggregate, accessory, multiple
simple fruits
single carpel or fused carpels of single ovary (ex: pears, watermelon)
aggregate fruits
more than one carpel (ex: raspberry blossom)
multiple fruit
cluster of flowers fuse to form fruit (ex: pineapple blossom)
accessory fruit
not from the ovary (ex: apple)
fruit
seed bearing structure that develops from the ovary
vegetable
edible leaves, stems or roots of a plant
asexual reproduction
involves one parent, no gametes, genetically identical offspring
sexual reproduction
involves two parents, fusion of male and female gametes, genetically varied offspring
staminate flower
has stamens only (male)
carpellate flower
has carpels only (female)
three female structures of the carpel
stigma, style and ovary
stigma
receives pollen
style
connects stigma to ovary
ovary
contains ovules
anther
produces pollen
filament
supports the anther
two male structures of the stamen
anther and filament
complete flower
has all four whorls (sepals, petals, stamens, carpels)
incomplete flower
missing one or more whorls
reproduction in corn
tassels - male flowers that produce pollen
silks - female structures, each silk is attached to an ovule
wind pollinates corn, pollen from tassels lands on silks
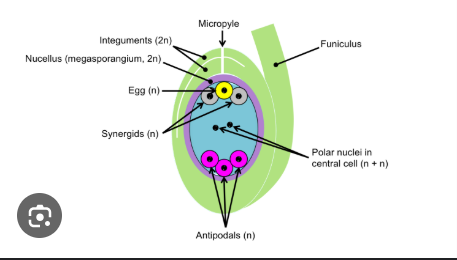
egg cell
located at the bottom of the embryo sac
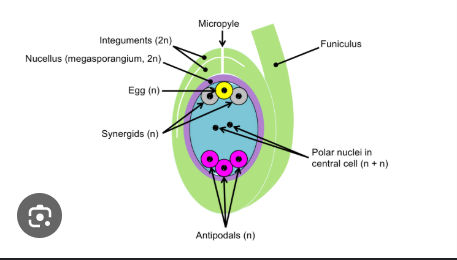
central cell with polar nuclei
in the center, becomes endosperm after fertilization
tube cell
forms pollen tube
generative cell
divides to form two sperm cells
endosperm formation and purpose
formed when one sperm fertilizes the central cell (double fertilization)
nourishes the developing embryo
plumule
becomes shoot
hypocotyl
stem region below cotyledons
radicle
becomes root
endosperm
food reserve
cotyledon
stores/transfers nutrients
corpse flower
pollinated by carrion flies
skunk cabbage
pollinated by beetles and flies
giant water lily
pollinated by beetles
seed germination factors
water availability, temperature, light exposure, oxygen availability
importance of seed dormancy
allows survival during unfavorable conditions, ensure germination at optimal time