Science 2.1 "How Are Plants Classified?"
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
vascular system
it moves water + nutrients from one part of this type of system to another by the processes of diffusion + osmosis
2
New cards
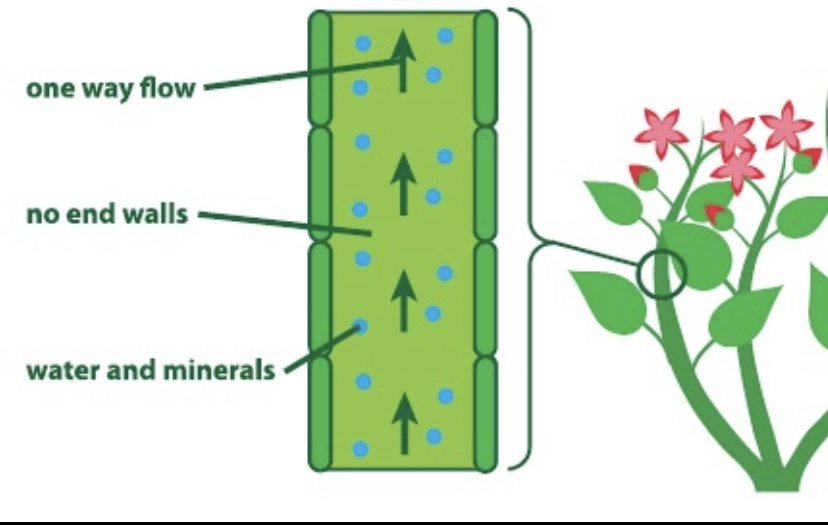
xylem
it transports water + inorganic nutrients, such as nitrogen + minerals, from the roots to the rest of the plant
3
New cards
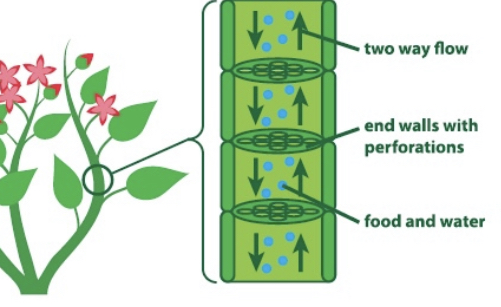
phloem
it transports the food, that the plant makes, to all the cells, including its roots
4
New cards
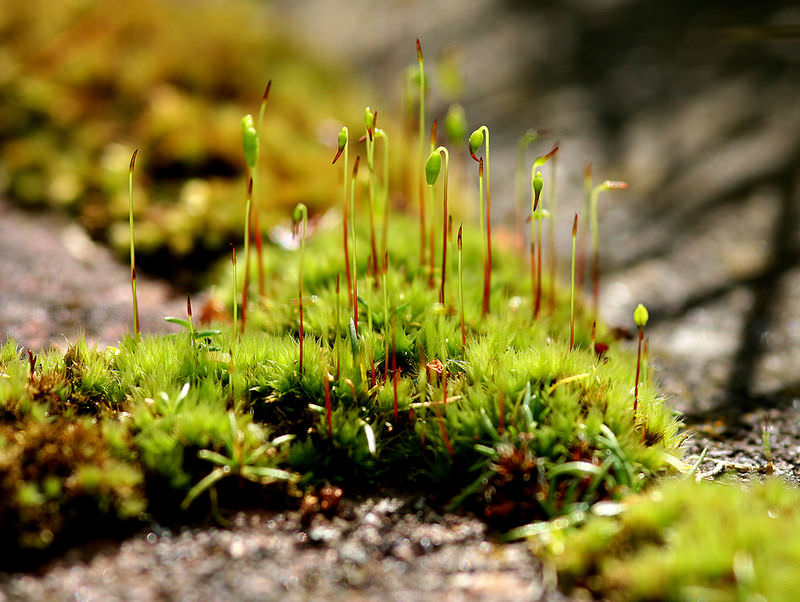

nonvascular plants
- plants without a vascular system to move water + nutrients (no xylem/phloem)
- absorbs water + nutrients instead (through diffusion + osmosis)
- tend to live in damp environments
- no vascular tissue to support plant (so they are usually only 2-3cm)
ex: moss, liverwort
- absorbs water + nutrients instead (through diffusion + osmosis)
- tend to live in damp environments
- no vascular tissue to support plant (so they are usually only 2-3cm)
ex: moss, liverwort
5
New cards
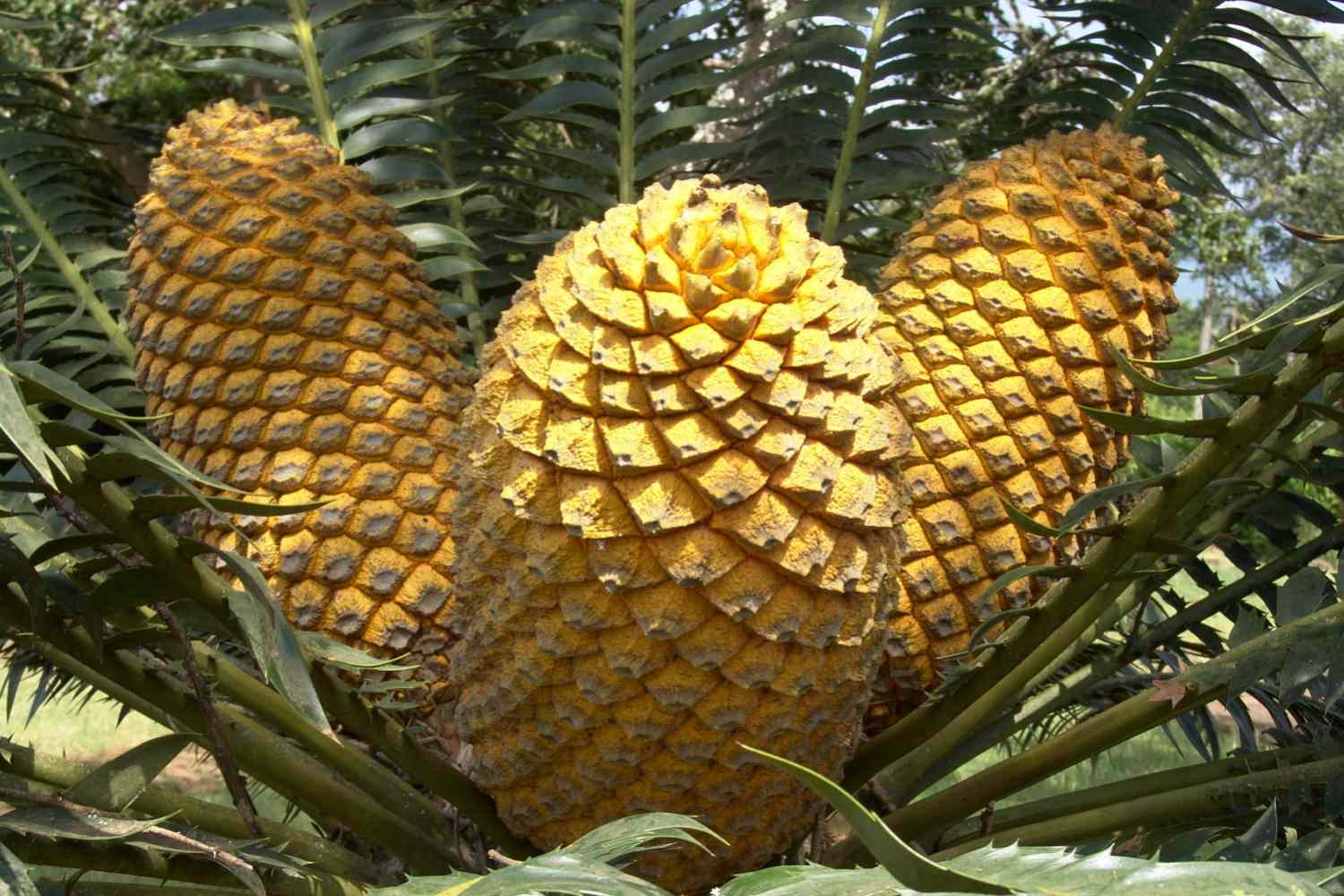

gymnosperm
- vascular plants (mostly trees) that produce seeds that aren't enclosed in fleshy fruits
- these structures in pollination become eggs in female cones + are fertilized by the sperm in pollen from the males cone from tree branches
- after fertilization, the female cone falls to the ground so the seeds can be deposited in the soil
- these structures in pollination become eggs in female cones + are fertilized by the sperm in pollen from the males cone from tree branches
- after fertilization, the female cone falls to the ground so the seeds can be deposited in the soil
6
New cards
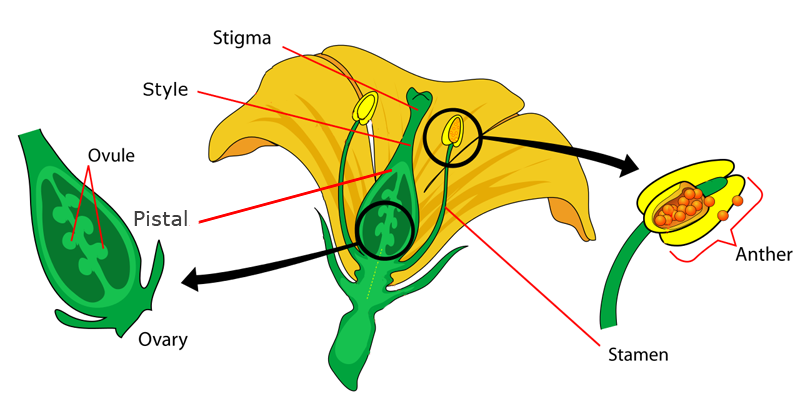
angiosperm
vascular plants that prouduce seeds in the ovaries of flowers
- some seed bearing plants have flowers that contain both female + male parts; they fertilize their own gametes (egg + sperm)
- other plants have separate female + male parts; they have to reproduce through pollinators (bees/butterflies) that carry pollen from male flower to female flower + have the female egg fertilized by the sperm in male pollen
- once gamete is fertilized, the plant develops fruit to protect the growing seed
- some seed bearing plants have flowers that contain both female + male parts; they fertilize their own gametes (egg + sperm)
- other plants have separate female + male parts; they have to reproduce through pollinators (bees/butterflies) that carry pollen from male flower to female flower + have the female egg fertilized by the sperm in male pollen
- once gamete is fertilized, the plant develops fruit to protect the growing seed
7
New cards
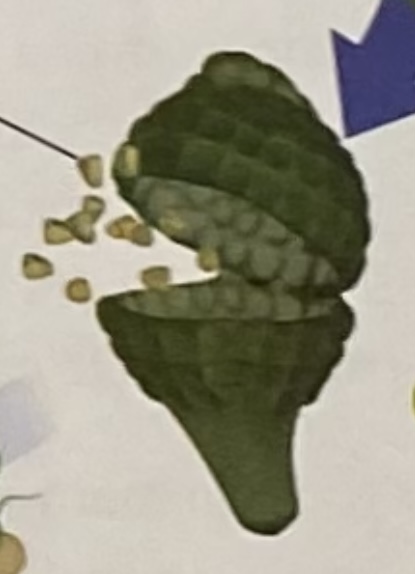

spore
- a reproductive cell that can develop into a new individual without being fertilized
- used for reproduction if plants don’t use seeds
- in non-vascular (ex: moss) + vascular plants (ex: fern)
- single-celled
-small and can be blown in the wind or carried by something (animal) to another location
- it can survive poor condition + will produce organisms when conditions are right
- used for reproduction if plants don’t use seeds
- in non-vascular (ex: moss) + vascular plants (ex: fern)
- single-celled
-small and can be blown in the wind or carried by something (animal) to another location
- it can survive poor condition + will produce organisms when conditions are right
8
New cards
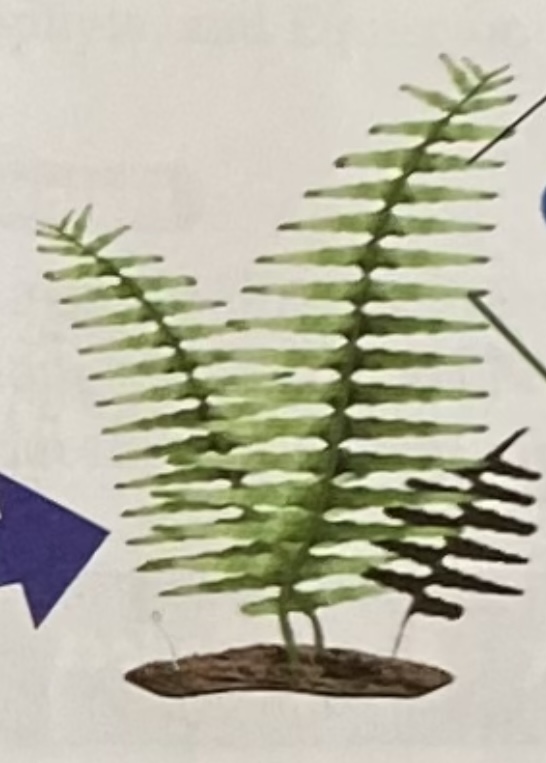

sporophyte
- term means, "spore plant"
- it is the form of a plant that produces spores during one part of the two-part reproduction cycle
- the dominant stage of vascular plant life cycle
- it is the form of a plant that produces spores during one part of the two-part reproduction cycle
- the dominant stage of vascular plant life cycle
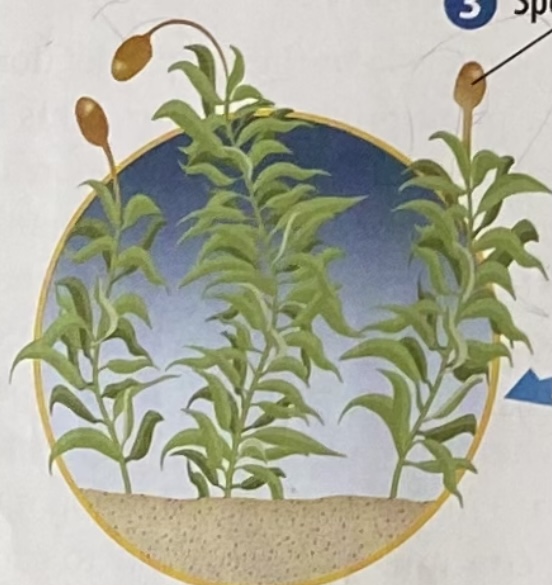

9
New cards

gametophyte
- means "gamete plant"
-it is a generation of plants that produce gametes
-it is the form of a plant that develops from a spore in the second part of the two-part reproduction cycle
-it is the dominant stage of nonvascular plant life cycle
-it is a generation of plants that produce gametes
-it is the form of a plant that develops from a spore in the second part of the two-part reproduction cycle
-it is the dominant stage of nonvascular plant life cycle

10
New cards
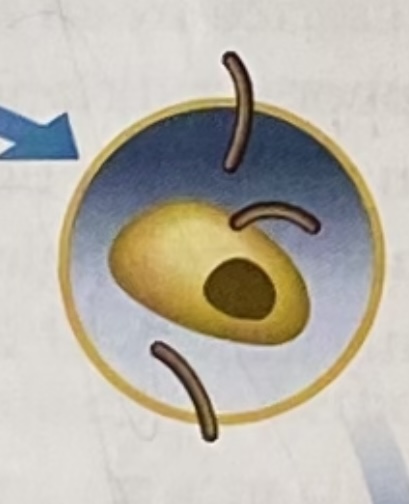
gametes
a male (sperm) or female (egg) reproductive cell
11
New cards
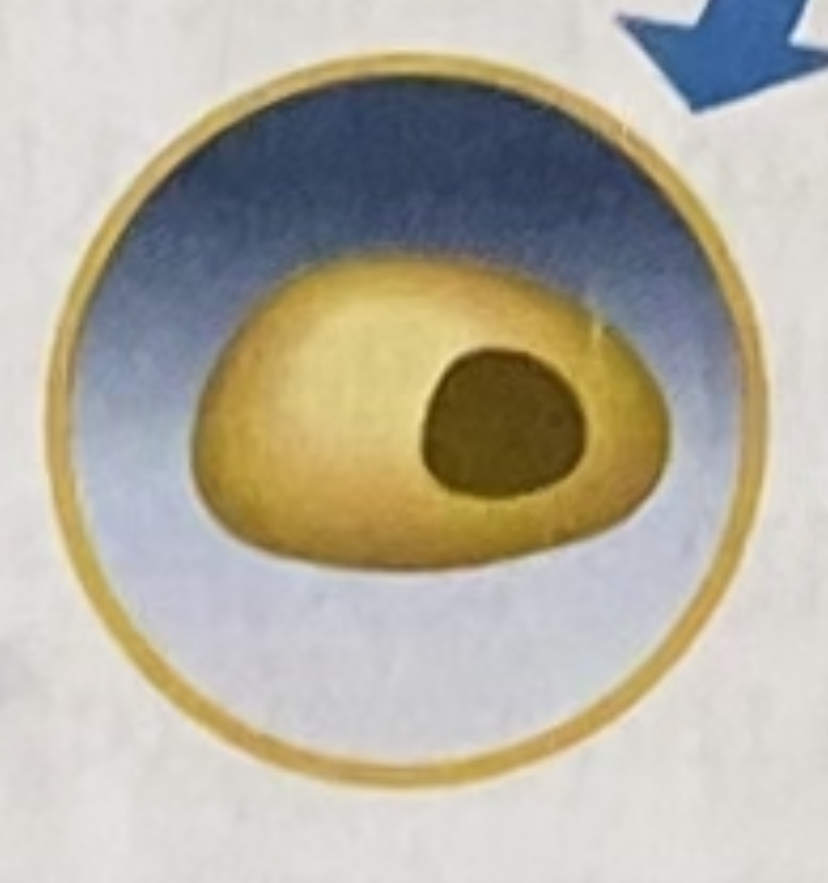

zygote
-it is formed when sperm and eggs are gametes, and they unite.
-this then later develops into an embryo
-this then later develops into an embryo

12
New cards
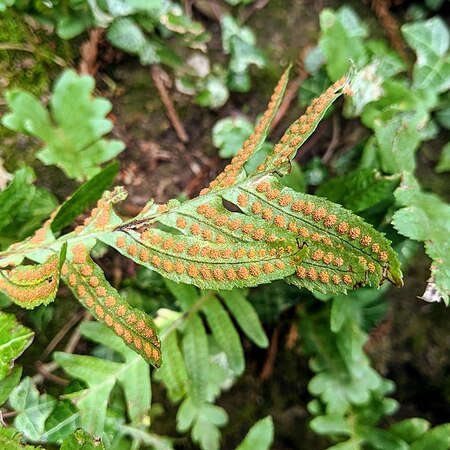

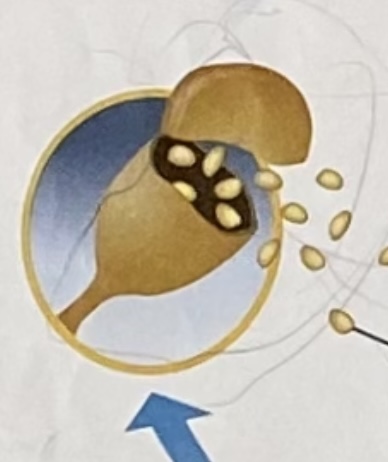
sori
the reproductive structures of the sporophyte
-it is often found on the underside of a fern
-it is often found on the underside of a fern

13
New cards
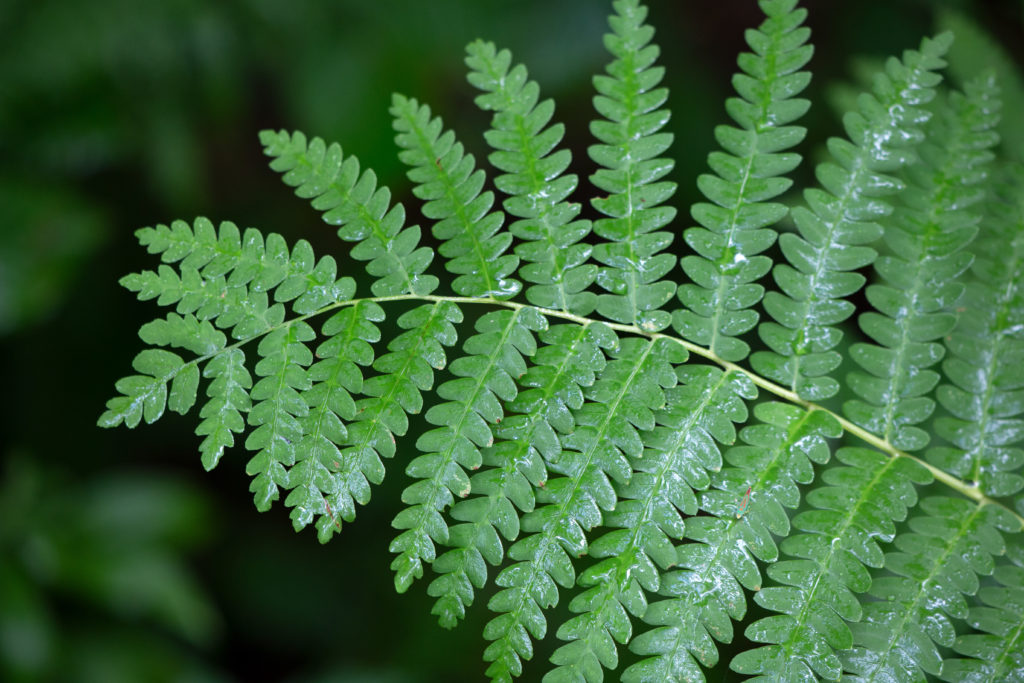

frond
the leaf of a fern
14
New cards
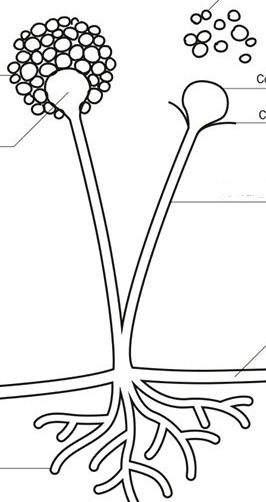
sporangia
the structures on each sorus that produce spores

15
New cards
domain Eukarya
has multicellular organisms like kingdom Protista, Fungi, Animalia, + Plantae
16
New cards
two main characteristics
- based on how plants are classified:
if they have vascular tissue or seeds
if they have vascular tissue or seeds
17
New cards
ways of transporting nutrients
1. through the vascular system: plants w/ vascular tissue
2. through the non-vascular system: plants w/ out vascular tissue
2. through the non-vascular system: plants w/ out vascular tissue
18
New cards
vascular plant
- has vascular tissue
- use xylem + phloem to move nutrients + materials from roots, stems, leaves + back
- use diffusion + osmosis
- can grow to a great height due to vascular tissues support (ex: North America Redwoods more than 100 meters)
- use xylem + phloem to move nutrients + materials from roots, stems, leaves + back
- use diffusion + osmosis
- can grow to a great height due to vascular tissues support (ex: North America Redwoods more than 100 meters)
19
New cards
Plants
- needs nutrients to live (like all living organisms)
- they rely on diffusion + osmosis to absorb water + nutrients
-produce food through photosynthesis
- they rely on diffusion + osmosis to absorb water + nutrients
-produce food through photosynthesis
20
New cards
diffusion
- the natural tendency of molecules to move from an area of of great concentration to an area of lesser concentration
- method used when gases exchange during photosynthesis
- method used when gases exchange during photosynthesis
21
New cards
osmosis
- water being diffused across a semipermeable membrane (plant cell)
- during this process, only water moves across the membrane
- water moved both ways across membrane until concentration of other substances are the same
- process is in work when roots absorb water + when the plant moves water upward to the rest of its structures
- during this process, only water moves across the membrane
- water moved both ways across membrane until concentration of other substances are the same
- process is in work when roots absorb water + when the plant moves water upward to the rest of its structures
22
New cards
method of reproduction
vascular plants that produce through:
1. gymnosperms
2. angiosperms
plants are classified by these methods
1. gymnosperms
2. angiosperms
plants are classified by these methods
23
New cards
gymnosperm examples
pine + cedar trees, shrubs, pygmy pine, Morman tea bush
24
New cards
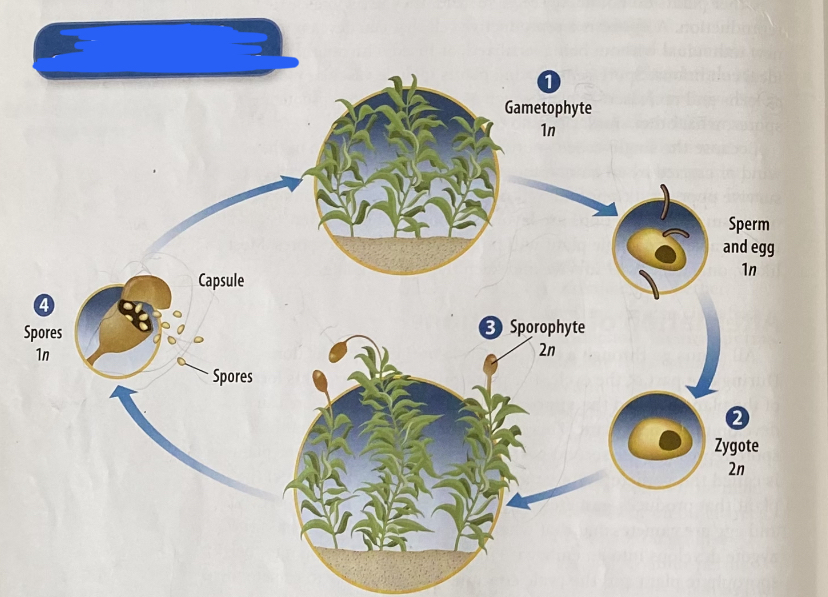
alternation of generations
the two-phased reproduction cycle progess in all plants, where it alernates between a spore (sporophyte) + a gamete (gametophyte)
1: the plant reproduces spores (sporophyte generation)
2: the spores develop into a new plant (gametophyte generation) + produce gametes (egg + sperm)
that unite, creating a zygote which then becomes an embryo
-the embryo will become a sporophyte + the cycle will start over again
(cycle is different for vascular + non-vascular plants
1: the plant reproduces spores (sporophyte generation)
2: the spores develop into a new plant (gametophyte generation) + produce gametes (egg + sperm)
that unite, creating a zygote which then becomes an embryo
-the embryo will become a sporophyte + the cycle will start over again
(cycle is different for vascular + non-vascular plants
25
New cards
alternation of generations in mosses
gametophyte stage is the dominant stage in non-vascular plants:
1. mature gametophyte produces gametes (egg + sperm)
2. sperm swims in water to egg + combine to form a zygote which develops into a sporophyte plant
3. sporophyte plant grows out of gametophyte plant
4. spore that grows at the end of a thin stalk gets enclosed in a capsule + is released when matured
5. spores fall on ground + germinates to create a protonema which will turn to a gametophyte plant (and the cycle restarts)
1. mature gametophyte produces gametes (egg + sperm)
2. sperm swims in water to egg + combine to form a zygote which develops into a sporophyte plant
3. sporophyte plant grows out of gametophyte plant
4. spore that grows at the end of a thin stalk gets enclosed in a capsule + is released when matured
5. spores fall on ground + germinates to create a protonema which will turn to a gametophyte plant (and the cycle restarts)
26
New cards
angiosperm examples
marigold, oranges, water lillies
27
New cards
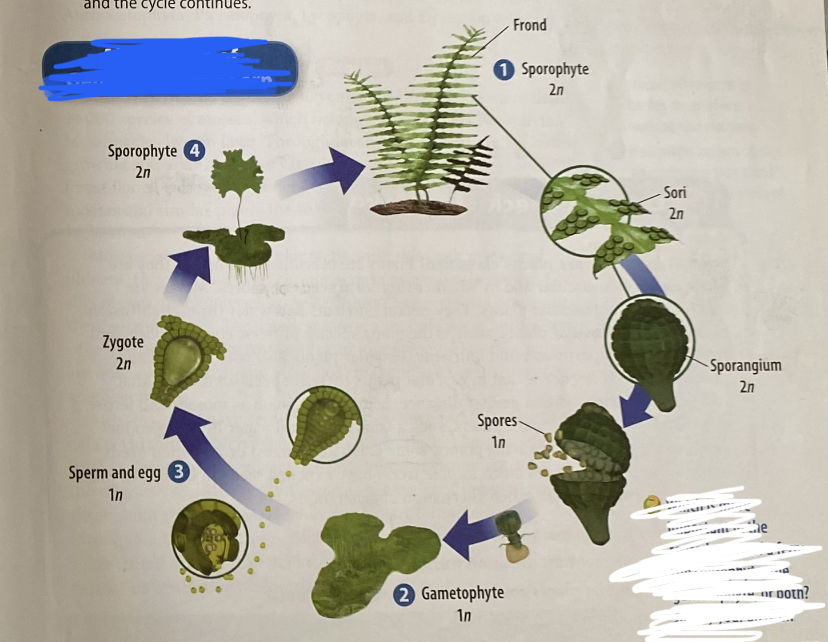
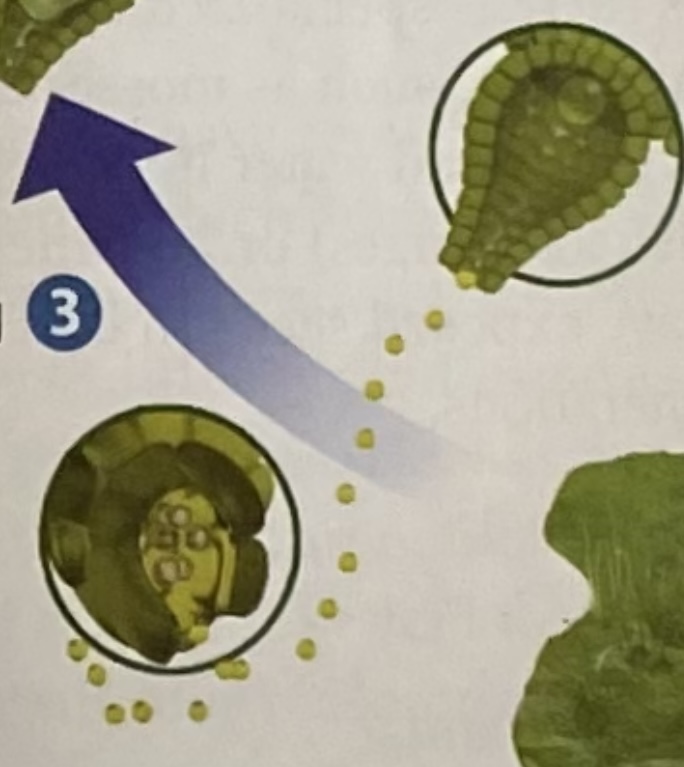
alternation of generations in a fern
sporophyte stage is the dominant stage in vascular plants:
1. reproductive structures (sori) of sporophyte located on the frond (leaf of a fern) contain sporangia that produce spores that fall on the ground
2. spores germinate when conditions are right + become a prothallus (a gametophyte plant)
3. gametophyte plant produces the male + female reproductive structures (egg + sperm). sperm swims to fertilize the egg + become a zygote, which becomes a sporophyte plant
4. tiny sporophyte grows + develops fronds + a rhizome (underground stem). when fronds are mature, the sori release spores (and the cycle restarts)
1. reproductive structures (sori) of sporophyte located on the frond (leaf of a fern) contain sporangia that produce spores that fall on the ground
2. spores germinate when conditions are right + become a prothallus (a gametophyte plant)
3. gametophyte plant produces the male + female reproductive structures (egg + sperm). sperm swims to fertilize the egg + become a zygote, which becomes a sporophyte plant
4. tiny sporophyte grows + develops fronds + a rhizome (underground stem). when fronds are mature, the sori release spores (and the cycle restarts)