Unit 2: Cells, Tissues, And Organisms
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Prokaryotic cells
Lacks a membrane-surrounded nucleus and organelles
have a nucleoid
endosymbiont theory
A host cell engulfed a prokaryote, which evolved into the mitochondria, thereby becoming the eukaryote. Later on, it engulfed a photosynthetic prokaryote, which became the chloroplast.
why is a high surface to volume ratio important
It is important becase a high ratio allows for more effcient exchange of materials
origins for mitochondria
Aerobic (oxygen using) nonphotosynthetic prokaryotes
origins of chloroplasts
photosynthetic prokaryotes
Evidence fort the endosybiont theory
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have 2 membranes bound around them
Both contain their own circular DNA and ribosomes
reproduce independently by binary fission (asexual reproduction)
surface area to volume ratio
SA / V
what materials must pass across a cell’s membrane
oxygen:
for cellular respiration
carbon dioxide
as a waste product
water:
for maintaining cell volume and fluid balance
organization unit of life
The cell
Nucleus
Control cente of the cell: houses DNA, controls cell growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
plant cells, animal cells
Nucleolus
production and assembly of ribosomes
plant cells, animal cells
Cell Wall
Maintains the cell’s structure and rigidity
It is fully permeable to water because its material creates pores
plant cells: cellulose, chitin (fungi)
prokaryotes: peptidoglycan
nuclear envelope and pores
Envelops the nucleus and controls what goes in or out
plant cell, animal cell
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
membranes that house ribosomes that produce proteins that will be secreated out of the cell
plant and animal cells
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
lipid synthesis, detoxification, calcium storage
plant and animal cells
Ribosomes
Protein synthesis (translation)
plant and animal cells
prokaryotes
Golgi Apparatus
Cellular postoffice: modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids into vesicles to be shiped
plant and animal cells
lysosomes
cellular digestion - macromolecules are
hydrolyzed here
animal cell
Central Vaculole
Stores water, nutrients, and waste
plant cell
Mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell, creates ATP via cellular aeirobic respiration
plant and animal cell
Chloroplast
conduct phtosynthesis to create glucose that will power the cell
plant cells
peroxisomes
detoxification/neutralization of free radicals and metabolism
Plant and animal cells
Microtubules
Maintains the cell’s shape and structure, forms mitotic spindles for division, and forms intracellular highways
plant and animal cells
microfilaments
maintain cell structure and allow the cell to have ameboid movement
plant and animal cells
cilia and flagella
locomotion and sensory processing
cilia: animal cell
flagellum animal cell, prokaryote
free floating ribosomes Vs RER ribosomes
Free floating ribosomes create proteins that will stay in the cell
RER ribosomes will go outside of the cell
endomembrane system
It is a network of organelles that work together to prepare and transport lipids and proteins pout of the cell
Key organelles in the endomembrane system
nuclear envelope
the endoplasmic reticulum,
Golgi apparatus
lysosomes
various kinds of vesicles and vacuoles
the plasma membrane.
pathway of synthesis of a protein destined to be secreted from the cell synthesis
RER ribosomes produce proteins that are packaged into transport vesicles
they travels to the Golgi apparatus’ cis face for further processing and sorting, and then exits the Golgi’s trans face in secretory vesicles to be released from the cell via exocytosis at the plasma membrane
plasmodesmata
microscopic channels that directly connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells and enabling intercellular communication and the transport of molecules
Plasma membrane
selectively permeable, controlling the movement of substances into and out of the cell
ECM
an intricate network composed of an array of multi domain macromolecules organized in a cell
creates structural support
cell signalling
Plant and Animal cell key differences
cell wall (PC)
Chloroplasts (PC)
Central Vacuole (PC)
Rectangulaar Structure Vs Irregular shape
Lysosomes (AC)
Centriols (AC)
fluid mosaic model
refers to the flowing nature of the phospholipids along with the proteins embedded within it
enables
transport
signaling
cell growth
division
How fast and in what orientation do lipids move within a membrane
They move side to side in a wave, and it takes them 1 second.
Unsaturated versus saturated hydrocarbon tails.
Saturated = viscous: phospholibids are all packed tightly together bc fatty acid tails are straight
Unsaturated = fluid: phospolipid tails have kinks so there’s gaps
Cholesterol within the animal cell membrane
Acts as smth that maintains the homeostasis of the membrane
reduces membrane fluidity at moderate temperatures by reducing phospholipid
increase membrane fluidity at low temperatures by hindering solidification by disrupting the regular packing of phospholipids
what is the role of carbohydrates in the cell membrane
cell recognition and communication, acting as unique molecular identifiers on the cell surface
Storage, since they’re sugars, is used in cell respiration
difference between integral and peripheral proteins
Integral proteins extend through the whole membrane
peripheral proteins only extend halfway or not at all in the membrane
how can some nonpolar molecules pass easily through the phospholipid bilayer
NP molecules aren’t repelled by the polare hydrophilic heads of the phosopholipids
aquaporins
facilitates the movement of water across the membrane
passive transport
when molecules move across the membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
facilitated transport: this happens with the help of a protein channel
passive transport: molecules diffuse directly through the membrane
active transport
molescules are moved low to high (against concentration gradient) using ATP
diffusion
movement of molecules from a area of high concentration to a area of low concentration
Osmosis
The process of water moving to an area of low water, high solute, and leaving an area of high water, low solute
Osmotic activity depends on the solute concentration
More solute, more osmotic pressure, more water enters
hypertonic
there is more solute outside then inside the cell. cell will lose water and shrivel
hypotonic
there is less solute outside the cell then inside the cell. cell will gain too much water and lyse
isotonic
there is equal concentration of solute outside and inside the cell. water will diffuese in and out at the same rate
gated channel proteins
membrane proteins that controls what Ions go accross the membrane with a specific signal
sodium potassium pump
3 Na in 2 K out
powered by ATP
membrane potential
difference in electrical voltage across a cell's membrane, created by moving ions against their concentration gradient
cotransport
when the movement of one substance down its concentration gradient provides the energy for the other substance against the concentration gradient
substance A goes out the cell, Substance B is trying to come in the cell. Substance A moves down its concentration gradient but subsstance B wants to go against the conc gradient.
substance A leaving provides substance B a force to piggyback off of and allows it too go in
tissues
collection of similar cells that are orgainzed to have a specific function
organs
group of tissues that combine to perform a specifc, specialized functions
organ systems
a group of organs that work together to perform a specific life process
interstitial fluids
liquid that is between cells
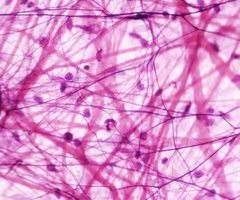
Areolar tissue
Loose connective tissue
Provides support, helps protect organs, binds skin together, and gives it elastic properties, found in the digestive and respiratory systems
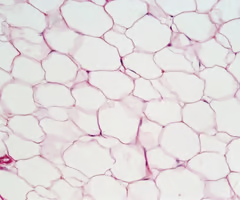
Adipose Tissue
Loose connective tissue
found throughout the body, stores lipids , insulation, protection, and long term energy
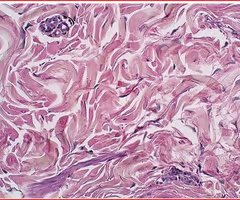
dense irregular connective tissue
Function: able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength
Location: dermis of the skin;
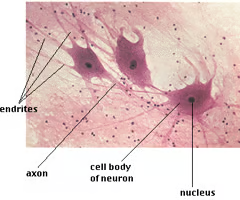
Neurons - nervous tissue
found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, allows for cells to communicate