Chapter 16. A&P
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
The 9 Major endocrine structures & key functions
Hypothalamus – controls pituitary, links nervous & endocrine systems
Pituitary gland – master gland, regulates other glands
Pineal gland – melatonin, sleep cycles
Thyroid – release hormones that regulate metabolism, growth and development. (T3 & T4)
Parathyroids – raises blood calcium (PTH)
Adrenal glands – cortex: cortisol/aldosterone; medulla: fight-or-flight hormones
Pancreas – blood glucose control (insulin, glucagon)
Ovaries/Testes – sex hormones, reproduction
Thymus – T-lymphocyte development and maturation
Compare and contrast how the nervous system and endocrine system control bodily functions
The endocrine system sends hormones into the bloodstream to regulate long-term processes such as homeostasis, reproduction, and metabolism. The nervous system uses electrical signals and neurotransmitters to control rapid, short-term actions like movement, reflexes, sensory perception, and cognition.
Types of chemical signaling
Endocrine – Long-distance text message. Hormones travel in the blood to far-away cells.
Paracrine – Whisper to a neighbor. Chemical only affects nearby cells.
Autocrine – Talking to yourself. Cell releases a chemical that comes back and acts on itself.
Gap junction – Secret tunnel. Two cells are connected, chemicals slip directly through.
Neurotransmitter – Fast doorbell. Nerve cell sends a quick chemical signal to the next cell.
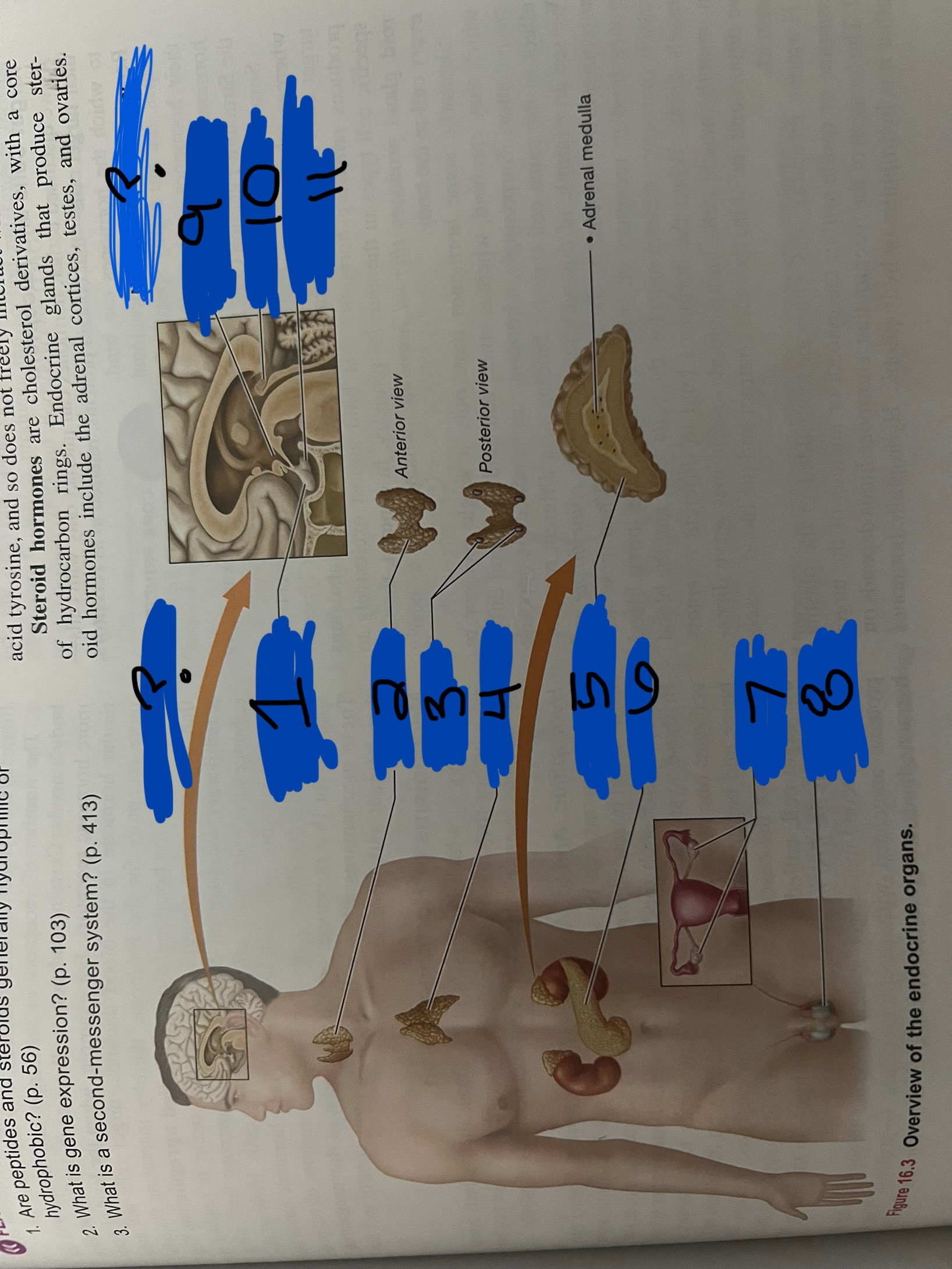
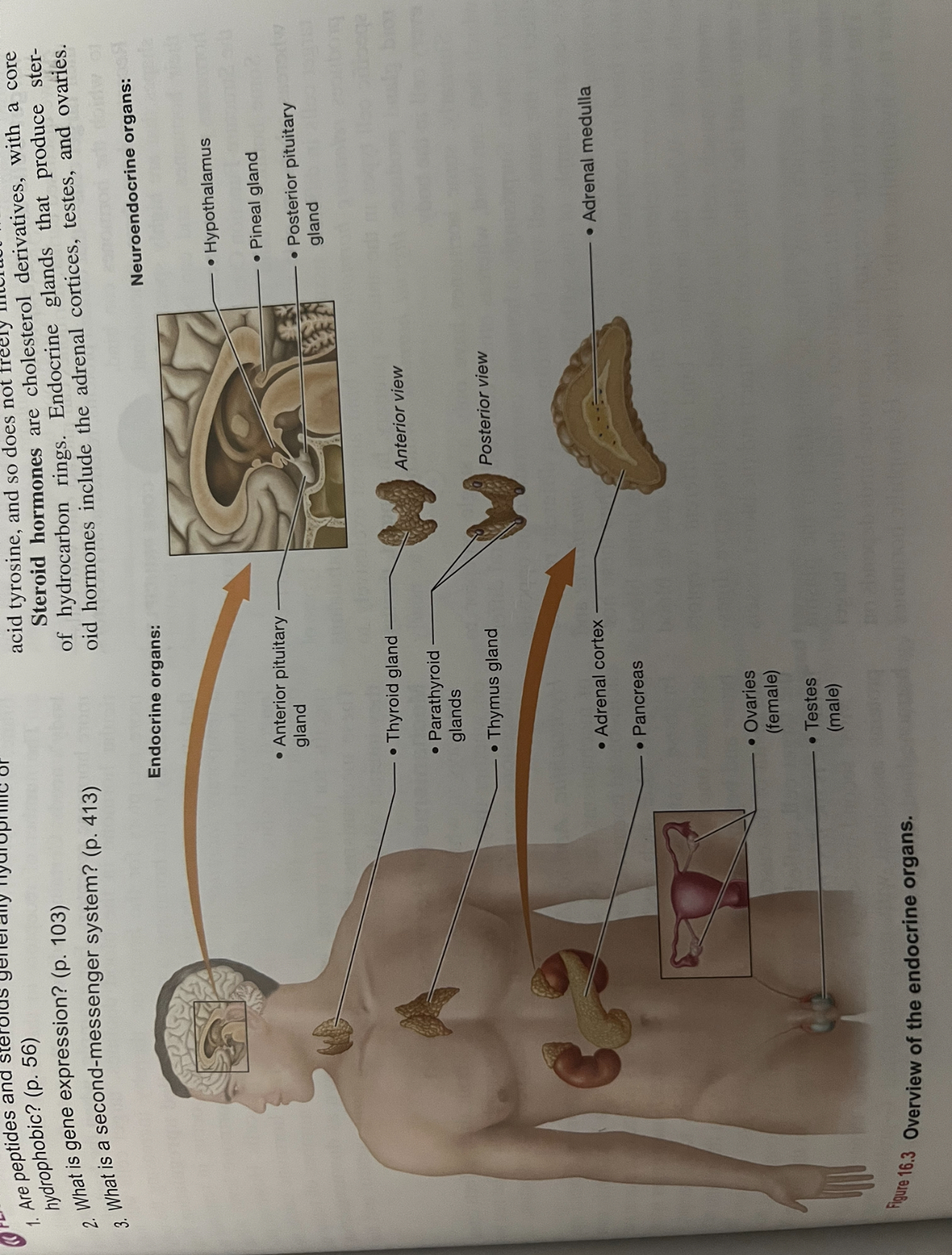
Endocrine organs? Neuroendocrine organs?
Endocrine: - anterior pituitary gland: situated in sphenoid bone of skull
thyroid gland: located in anterior neck
3-5 small parathyroid glands: found on posterior thyroid gland
Paired adrenal cortices: located on the superior surface of kidneys
Endocrine pancreas: found on left side of abdominal cavity mostly posterior to stomach
Thymus: located in superior mediastinum
Paired ovaries or testes: former in pelvic cavity and latter suspended below the pelvic cavity in men
Neuroendocrine
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland
Adrenal medulla
What does the half-life of a hormone mean?
half-life of a hormone is the time it takes for half of the hormone’s concentration in the blood to be broken down
cAMP?
cyclic adenosine monophosphate