Pediatrics 2025 (TOTAL)
1/1011
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1012 Terms
Dysentery
A child coming in with bloody diarrhea falls under what classification using the IMCI?
Co-trimoxazole x 5 days
Drug of choice for Dysentery based from IMCI?
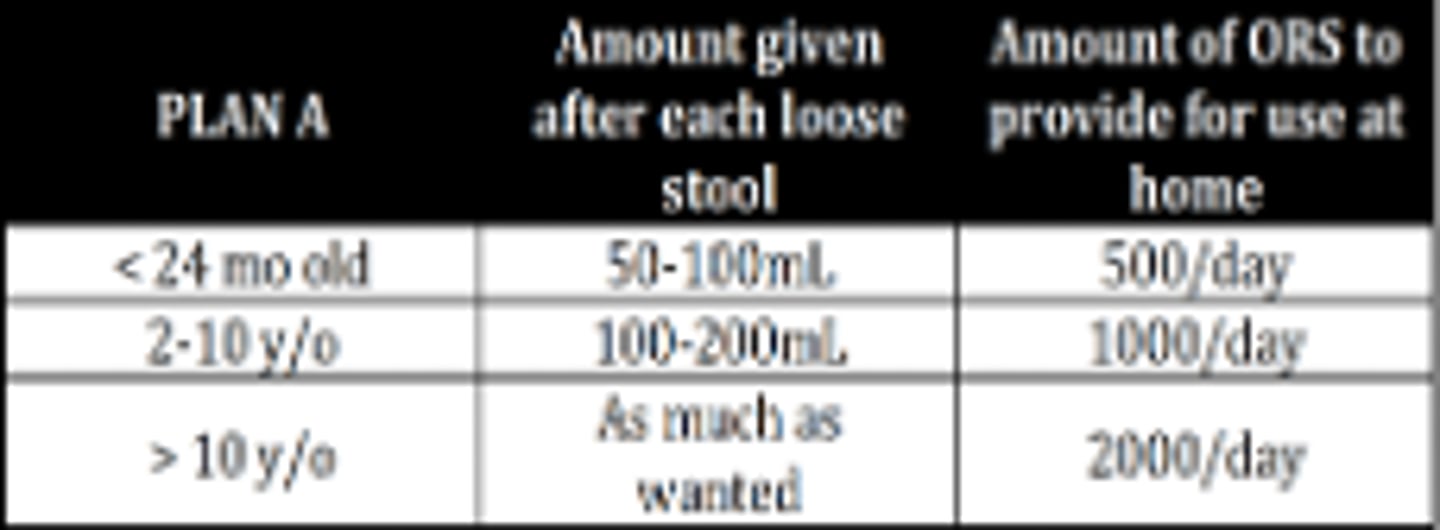
No dehydration
A child with a history of AGE but can drink, has no sunken eyeballs or sensorial change, and with good skin turgor is classified based on IMCI as?
Treatment for AGE with no dehydration based on IMCI?
Some dehydration
A child with AGE presenting with irritability, sunken eyeballs, and eagerness to drink is classified based on IMCI as?
Fluid replacement as follows:
• Weight (g) x 0.075
• Weight (kg) x 75
Management for patients classified as some dehydration based on IMCI?
Severe dehydration
A child with AGE coming in with drowsiness, sunken eyeballs, refusal to drink, and poor skin turgor is classified based on IMCI as?
Management of a child with severe dehydration based on IMCI?

Tetracycline
If a child with AGE is 2 y/o and above and there are cases of cholera in the community, the DOC will be?
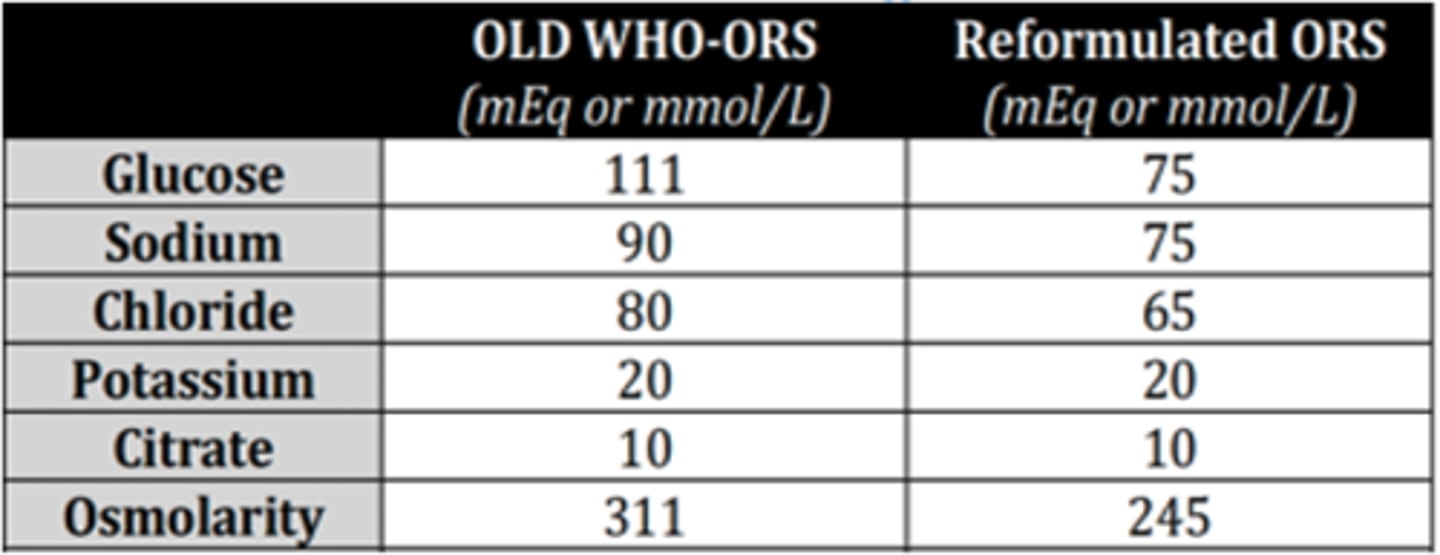
245 mEq/L
[vs 311 mEq/L in the old WHO ORS]
Read:
Osmolarity of reformulated Oral Rehydrating Solution?
Zinc 10-20 mg of Zn per day for 10-14 days
[reduces the number of diarrheal episodes in the 2-3 months after supplementation]
Supplementation with which micronutrient reduces severity and duration of, and prevents subsequent episodes of diarrhea?
• Lethargy/unconsciousness
• Vomiting
• Convulsions
• Inability to drink / breastfeed
Danger signs stated in the IMCI
5q23-35
Gene region implicated in allergic diseases and pathogenesis
• Allergen causing symptoms (etiological classification)
• Duration of symptoms (Intermittent or Persistent)
• Severity of clinical symptoms (depending on impact of disease on QOL)
Disease pathophysiology (limited use)
Criteria for classifying Allergic rhinitis
Seasonal
AR which occurs only during specific periods of the year: e.g. pollination, mold sporulation
Perennial
AR triggered by allergens formed in the patient's environment at concentrations sufficient to induce symptoms all year round: dust mites, pet fur, cockroach.
Episodic
AR after exposure to a specific airborne allergen on a sporadic and short-term basis
Intermittent
AR with symptoms less than 4 days/week or less than a month/year
Persistent
AR with symptoms ≥ 4 days/week or ≥ a month/year
Mild AR
AR which symptoms do not affect sleep, no impairment in ADLs, work, school, and no troublesome symptoms
6 y/o
Diagnosis of AR is generally established by what age?
Oral H1-antihistamine
OR
Intranasal H1-antihistamine
AND/ORDecongestantORLTRA
Treatment options for mild intermittent AW
Intranasal corticosteroids
Drug added for step up therapy among patients with moderate-severe intermittent and mild persistent AR
B cell Immunodeficiency (Bruton Disease)
An infant was born normal until when he reached 6 months old, he has recurrent ear infections, bronchitis, pneumonia, and dermatitis. Total Ig < 250 mg/dL. Impression?
SCID
A young infant came in with failure to thrive, chronic otitis media, chronic diarrhea, recurrent pneumonia, and candida infection. On xray, there was absent thymic shadow. Impression?
CATCH 22
• Cardiac defect
• Abnormal facies
• Thymic aplasia
• Cleft palate
• Hypocalcemia
22q11.2 chromosomal deletion
Features of Di George syndrome?
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
A child presenting with immunodeficiency signs but with Thrombocytopenia and Eczema. Impression?
Hyper IgM syndrome
A profoundly neutropenic 2 y/o child came in for recurrent pyogenic infections and was later diagnosed with P. jiroveci pneumonia. Lab test showed depressed IgA, IgE, and IgG but normal IgM. Impression?
Judicious use of antibiotics for infections
Regular IVIG/SubQ Ig
Primary B cell defect treatment
Bone marrow transplant
Management of SCID
Hyper IgE syndrome
A child came in for recurrent bacterial abscesses, aspergillosis, and mucocutaneous candidiasis.
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
This Neutrophil function disorder is characterized by recurrent pyogenic infections, mild bleeding diathesis, partial oculo-cutaneous albinism, progressive peripheral neuropathy, and photophobia.
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency
Infant with recurrent bacterial infection associated with a lack of pus formation, bleeding tendency; delayed umbilical cord separation with significant omphalitis.
Chronic granulomatous
disease
Infant presenting with recurrent pyogenic infections with catalase-positive microorganisms, lymphadenitis, and granuloma formation.
SMR 4
Adolescent female with areola forming SECONDARY MOUND and with CURLY pubic hair. Tanner stage?
SMR 3
Boy with BEGINNING pubic hair and PENILE enlargement. Tanner stage?
SMR 2
Enlargement of testes in males and thelarche in females are characteristics of what tanner stage?
9 y/o (males); 8 y/o (females)
At what age is precocious puberty defined in males and females?
14 y/o (males); 13 y/o (females)
What age cut-off is DELAYED puberty defined in males and females?
SMR 2-3
A girl's peak height velocity coincides with what SMR stage?
SMR 3-4
A boy's peak height velocity coincides with what SMR stage?
Thelarche
FIRST SIGN of puberty in FEMALES?
Testicular enlargement
FIRST SIGN of puberty in MALES?
Short stature
The most common clinical feature of Turner syndrome (45, X)
Short stature
Condition defined as 2 or more standard deviations below the mean height for children of that gender and chronological age.
Familial short stature
A child came in for short stature. On further assessment, he has normal birth history and gestational weight. He has normal linear growth velocity for age and bone age is consistent with chronological age. Impression?
Constitutional growth delay
A child came in for short stature. On further assessment, there is delayed growth in one parent but average final stature. He has normal birth history and growth for first few months. Chronologic age is greater than bone age (CA>BA). Impression?
[Father’s Ht – 13) + Mother’s Ht] / 2
Girls' midparental height (cm) is computed as?
[Father’s Ht + Mother’s Ht +13] / 2
Boys' midparental height (cm) is computed as?
Failure to thrive
Defined as persistent weight < 5th percentile for age with growth curve crossing 2 major percentile lines on growth chart.
SIADH
Child with HYPOnatermia, LOW serum osmolality, and HIGH urine osmolality in the absence of any renal, adrenal, thyroid insufficiencies or any other attributable conditions. Impression?
Fluid restriction
Management of SIADH
Diabetes Insipidus
Child with polyuria and polydipsia with HYPERnatremia, HIGH serum osmolality (>300), and LOW urine osmolality (<300). Impression?
Water deprivation test and ADH administration
Test to differentiate central vs nephrogenic DI?
• Fluid therapy; long-acting
• Vasopressin analog dDAVP
Management for central DI?
Treat underlying disorder; thiazides
(decrease urine flow to DCT, induce formation of functional receptors)
Management of Nephrogenic DI
Primary polydipsia
After water deprivation, a child with polyuria and hypernatremia had elevation of urine osmolality. Impression?
Hyperthyroidism (Grave’s disease)
An adolescent came in for palpitations and sweating which started about several months ago but are increasing in frequency. PE reveals marked proptosis and fine tremors were noted as well. Lab results showed decreased TSH, Increased T3 and T4. Impression?
Thyroid storm
Acute-life-threatening surge of thyroid hormone in the blood usually precipitated by surgery, trauma, infection, acute iodine load or long-standing hyperthyroidism.
TRSAb
Disappearance of this antibody predicts remission of Grave's disease
Radioactive iodine ablation or thyroidectomy
Definitive treatment for Grave's disease
PTU
Medication that Inhibits extrathyroidal conversion of T4-T3
Hypothyroidism
An infant with hypotonia and prolonged jaundice came in for consult. He has developmental language delay and appears to have large tongue. Labs showed Low serum T4 & T3; elevated serum TSH. Impression?
Sodium-L-thyroxine 10-15 ug/kg/day
Management of hypothyroidism?
Thyroiditis
Most common cause of thyroid disease in children and adolescents
HLA-DR4, HLA-DR5
Markers associated with an increased risk of goiter & thyroiditis
Thyroid anti-peroxidase antibodies (TPOAbs)
Seen in the sera of 90% of children with thyroiditis; inhibit enzyme activity & stimulate natural killer cell cytotoxicity
May be self-limited.
But if with evidence of hypothyroidism, give sodium-L-thyroxine (50-150 ug/day)
Management of thyroiditis?
Deficiency of 21-hydroxylase
This deficiency accounts for 90% in all patents with CAH
Salt-losing CAH
A child suspected of CAH SHORTLY after birth was noted with progressive weight loss, prominent vomiting, and dehydration. She has pronounced virilization of external genitals. Type of CAH?
Non-salt-losing
An infant was normal at birth but was noted with SMALL testes & ENLARGED penis. Type of CAH?
Hydrocortisone 10-20mg/m2/day orally in 2-3 divided doses
Cornerstone treatment for CAH
Adrenal crisis
A child previously diagnosed with CAH came in for septic shock unresponsive to fluid resuscitation and inotropes. Impression?
Cushing syndrome
Child with obesity with associated hypertension because of abnormally high blood levels of cortisol resulting from hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex.
Pheochromocytoma
A child with seizures, headache, palpitations, abdominal pain underwent abdominal imaging that showed a tumor in adrenal medulla. Impression?
Vanillylmandelic acid (major metabolite of epi-, norepi- & metanephrine) excretion is increased
Expected urine biochemical finding in Pheochromocytoma?
DM Type II
Syndrome of metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia due to insulin resistance?
DM Type I
Syndrome of metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia due to absolute insulin deficiency?
Symptoms of diabetes PLUS:
• Random plasma glucose >200 mg/dL
OR
• Fasting plasma glucose >126 mg/dL
Polyuria, polydipsia, & unexplained weight loss with glucosuria & ketonuria
Diagnosis of DM in children?
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Constellation of hyperglycemic crisis symptoms accompanied with:
• Glucose >200
• Venous pH < 7.3 or bicarbonate <15mmol/L
• Ketonemia (B-hydroxybutyrate 3 or more mmol/L) or moderate or large ketonuria
Serum pH
Serum bicarbonate
DKA severity is based on levels of?
• Careful volume replacement
• Electrolyte management
• Glucose and Insulin administration
• Bicarbonate (as needed: pH <7.2)
Management of DKA
HbA1c
Represents the fraction of Hgb to which glucose has been non-enzymatically attached in the bloodstream and reflects the average blood glucose concentration in the preceding 2-3 months.
Chlamydia trachomatis
Neonate with mild to severe swelling of eyelids with copious purulent discharge; incubation period 5-14 days. Causative agent?
Adenovirus
Child with red itchy eyes, THIN exudate, with pain & photophobia. Noted history of cough and colds. Causative agent?
Staphylococcus
Child with conjunctivitis and presence of purulent discharge. Causative agent?
Chlamydia
Child with conjunctivitis, purulent discharge, and inclusion bodies in scrapings.
T. cruzi
Child with unilateral inflammation of the eyelid and around mouth. Noted Hx of travel to Mexico or South America
Echinococcus granulosus
All cestodes/flatworms are treated with Praziquantel except one that is treated with Albendazole?
Ascaris, Ancylostoma, Necator, Capillaria
Albendazole is DOC for which parasites?
Pyrantel pamoate
DOC for Enterobiasis
DEC
DOC for Filariasis?
Cytomegalovirus
A neonate born to a mother with hx of drug abuse was noted with retinopathy w/ keratitis in. Causative agent?
Staphylococcus
A child with furunculosis over the neck, face, axillae, and buttocks. Usual causative agent?
Pseudomonas
A child with furunculosis over the neck down and loves to play in bathtub. Usual causative agent?
Propionibacterium
An adolescent with folliculitis over the face and neck. Usual causative agent?
Ecthyma
Child with multiple dry, heaped up, encrusted wounds on the lower
extremities which started as mosquito bites and child kept on scratching them.
Measles
Child with high grade fever and rash with accompanying coryza, cough, conjunctivitis. Impression?
Koplik spots
Enanthem of Measles described as clustered white lesions of buccal mucosa, adjacent to 2nd-3rd lower molar is called?
Rubella
Child with LOW grade fever and exanthematous rash proceeding in a cephalo-caudal pattern. Notable posterior auricular lymphadenopathy. Impression?