Red meat slaughter - sheep & pigs
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
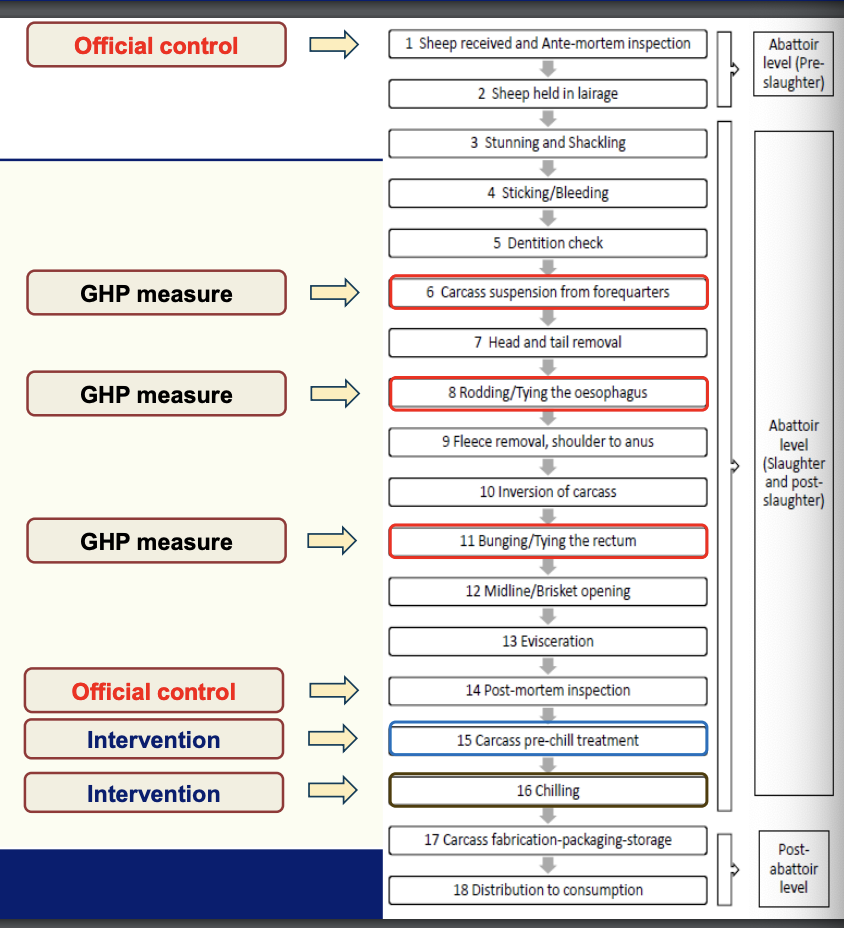
Sheep slaughter process flow diagram:
What methods are used for stunning sheep?
captive bolt used rarely
more common electrical “head-only” (reversible method)
“head-to-back” (irreversible, stun-to-kill method)
How is sticking/bleeding carried out in sheep?
Neck cut and chest cut used (depending on carcass position)
Bleeding at least 20 seconds
Frequent rotation of knives
Why is a dentition check done in sheep?
Check for overaged sheep (i.e. over 12 mo, with permanent incisors erupted)
If overaged, carcass tagged and split after dressing and spinal cord removed (specific risk material - SRM)
What is inverted dressing of sheep carcasses?
Process where carcasses are inverted and hanged for their fore limbs to ensure more hygienic fleece/pelt removal.
After fleece removal carcasses are inverted back for evisceration
How is the fleece of sheep removed?
Mechanical hide pullers to pull fleece away from carcass
Fleece is hygienically removed (most significant source of carcass contamination), same principles as with cattle hide
Is oesophagus tying compulsory in sheep?
Yes (same as cattle)
When are the carcasses split in sheep?
Only in overaged sheep (to removal spinal cord)
What are the most common interventions in sheep?
Knife trimming and steam vacuuming
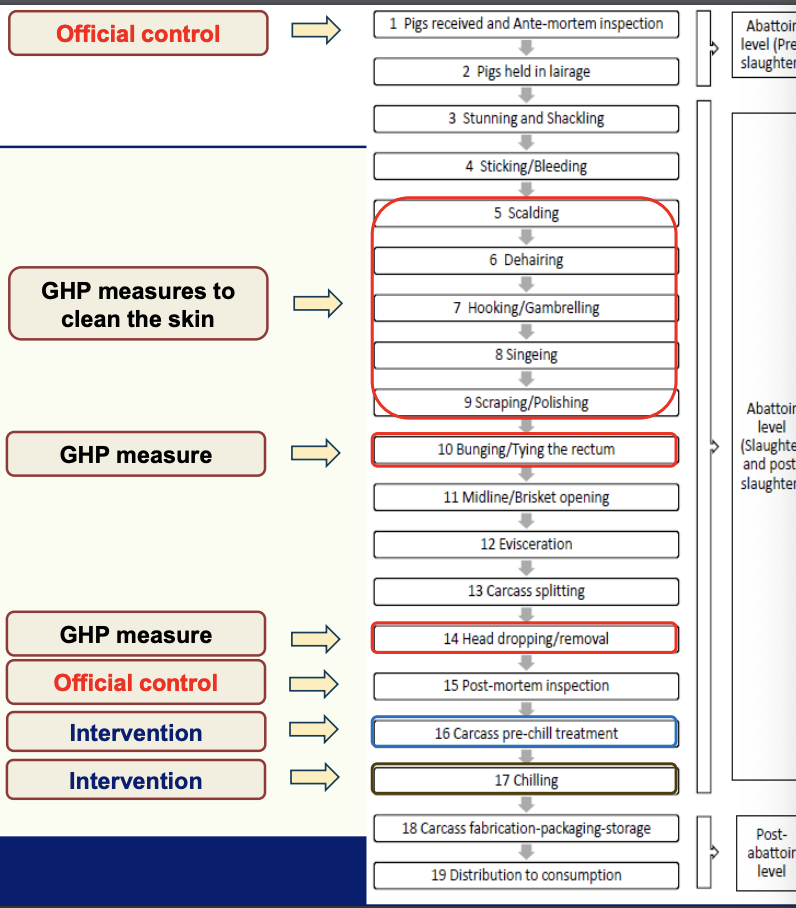
Pig slaughter process flow diagram
What is analysed in the FCI of pigs?
Same principles like in cattle/lamb
Animal ID —> slap marks/ear tags, movement licenses
More emphasis on Trichinella ,residues and if holding has Salmonella control plan
Recall what the withdrawal period is
Period between giving the animal its last dose of a drug and it, or its food products being allowed into the food chain
What is the Maximum residue limit (MRL)?
Maximum concentration of residue accepted in a food product
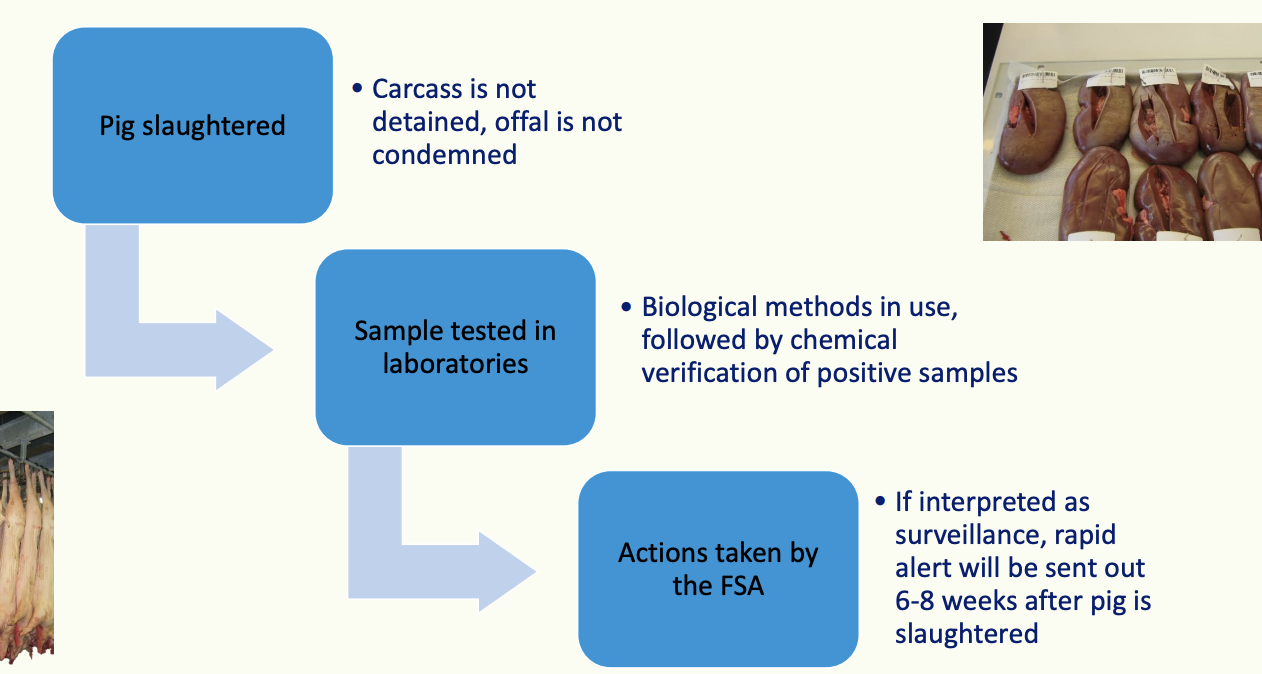
How does residue surveillance occur?
Random testing for residues in meat performed by food standards agency (FSA)
What methods are used for stunning pigs?
captive bolt used rarely (only in emergency slaughter)
electrical “head-only” (reversible method) in small abattoirs
electrical “head-to-chest” (irreversible stun-to-kill method)
gas (CO2) stun-to-kill method most common in big abattoirs
How is sticking/bleeding performed in pigs?
Only chest cut used
Bleeding at least 20 sec
Frequent rotation of knives
What are the pig skin cleaning steps?
Scalding
Sprayed with hot water/steam or immersed in hot water (62-65°) softens hair
Dehairing (depilation)
Remove loosened hair in closed dehairing machine
Carcasses spin on horizontal rotating cylinder with rubber 'fingeres rubbing across skin, removing bristles
Gambrelling
Gambrel table where operators insert gambrels into hind legs before gambrel elevator lifts carcasses onto evisceration line
Singeing
Carcass surface burned for a few seconds (1000° gas-flame oven) to remove remaining hair and reduce pathogens
Polishing
Removes burnt hair off by passing through machine with hard rotating brushes
Skin removal
Skin of older pigs may be required by leather industry so cannot be singed
For skinning same principles as cattle/sheep
What are the problems with the polishing step of skin cleaning?
Build-up of bacteria on brushes from many carcasses, frequent recontamination of carcasses with bacteria that survived singeing process
Because of this, some abattoirs use second singeing or carcass washing
How does rectum tying, brisket opening and evisceration differ in pigs?
Sample principles as cattle processing but
No need for oesphagus tying
Rectum tying is optional
Red offal and green offal are removed from line and separately processed
Explain carcass splitting in pigs
Using automatic equipment which must be cleaned and sterilized between animals
Spinal cord then removed but it is not SRM
Sample for Trichinella testing (if required) taken from diaphragm at this point
When is testing of diaphragm sample required (Trichinella)?
Breeding domestic swine (sows and boars)
Wild boars (any age, whether wild or farmed)
Solipeds (any age)
All pigs that have not been reared in premises officially considered to apply controlled housing conditions (e.g. free range and organic)
What are the alternatives for Trichinella testing?
Freezing (only allowed for domestic pigs)
Not often used by industry
What are the most common interventions in pigs?
knife trimming
steam vacuuming
sometimes whole carcass wash with cold water