Comprehensive Exercise Physiology: Muscle, Cardiovascular, and Metabolic Responses
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms
What promotes catabolic reactions?
Low cell energy
Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
Mitochondria
What drives the reduction of pyruvate to lactate?
Mass action effect, Low redox potential, PFK stimulation
What is the product of ATP hydrolysis?
ADP + Pi + H(ion) + heat + energy
What is the process of adding a phosphate group called?
Phosphorylation
How much ATP does a 16-carbon fatty acid yield from the Krebs cycle?
80 ATP
What is responsible for lowering the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
Enzyme activity
Why is CHO relied on more than fatty acids as exercise intensity increases?
CHO yield more ATP per oxygen molecule
What is the primary ATP source for an 800 meter running event?
Anerobic glycolytic system
Why is muscle glycogen preferred during exercise?
It yields more ATP than blood glucose and fatty acids
What is a function of lactate in the body?
Fuel source, acts as a buffer, converted back to glucose via Cori cycle
What is an example of an energy substrate?
Palmitic acid
What explains Carl's increase in muscle size after resistance training?
Hypertrophy increasing myofibril size and myonuclei formation
What is the functional unit of skeletal muscle?
Sarcomere
What are the characteristics of type 2a (IIa) motor units?
Fast contraction velocity, high glycolytic and oxidative capacity
What happens to the sarcomere during contraction?
Actin slides past myosin
What is the role of the Na+/K+ ATPase pump?
Maintain resting membrane potential
What occurs during hyperpolarization?
More negative resting membrane potential
What is the role of the basal ganglia?
Aids in initiating repetitive movements
What ion is most important for repolarization?
K+ (potassium)
What is the effect of sympathetic nervous system stimulation on metabolism?
Stimulates lipolysis
What type of contraction occurs in quadriceps while descending stairs?
Eccentric contraction
What happens to muscle fiber type with training?
Type 2x transitions to type 2a
What is the effect of muscle glycogen depletion on motor unit recruitment?
Induces motor unit fatigue, increasing energy cost of movement
What is true about leg muscles of sprinters vs. marathon runners?
Force generated by similar-sized muscle fibers is similar
What is the recruitment strategy during prolonged isometric holds?
Asynchronous motor unit recruitment
What is the relationship between muscle strength and cross-sectional area?
Positively correlated
What is the Compromise of her hypothalamus?
According to Heneman's size principle, which motor units are recruited first?
Small motor units
Which proprioceptor is NOT part of a motor reflex?
Chemoreceptor
What is generated if membrane potential changes from -70 mV to -55 mV?
Only an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
What is the first event following exercise-induced muscle damage?
Local inflammatory response (IL-6) and neutrophil infiltration due to chemotaxis
What is a correct exercise intensity prescription for Francine to oxidize 50% carbohydrates?
2.5 mph
What occurs at running speeds above lactate threshold?
VO2 drift
What is the primary concern of conducting a graded exercise test with 1 minute stages?
It is unknown whether steady state will be achieved
Which equation yields the most accurate estimation of energy expenditure during walking?
LCDA
Why is Lactate Threshold important in endurance events?
Athletes cannot sustain exercise intensity above the pace at which blood lactate accumulates for longer than 30-35 minutes
What causes acute muscle soreness?
Accumulation of fluid and H+ that sensitize nociceptors
Which is NOT a cause of strength loss with DOMS?
Accumulation of lactic acid in muscle tissue
DOMS is ____________ the development of fiber hypertrophy.
Not essential for
What is a risk factor for exercise-associated muscle cramping?
Exercise unmatched to fitness
What metabolic pathways bridge the ATP gap during oxygen deficit?
PCr (anaerobic) and Glycolysis (anaerobic)
What occurs during uphill walking?
Localized muscle glycogen depletion will occur, primarily in the quadriceps and gastrocnemius
What can be inferred from Ronda's graded exercise test results?
A VO2max was achieved
What is a typical RER value for a fasted individual at rest?
0.75
At what intensities do muscle fatigue and inefficiency occur during whole body exercise?
Above the lactate threshold
What can motivational self-talk decrease and increase during exercise?
Decrease: RPE, Increase: Endurance
When does the lactate threshold typically occur in untrained individuals?
50% VO2max
Why does aerobic performance continue to improve with training after VO2max plateaus?
Lactate Threshold continues to improve with training
What is a hallmark of acute muscle soreness?
Increased concentrations of muscle enzymes circulating in the bloodstream
What happens when movement economy is improved?
Less VO2 is consumed for any given submaximal speed
What is the most likely source of reduced force production in Bonnie's study?
Central Nervous System Fatigue
What is true about the inflammatory response post muscle damage?
It is necessary for satellite cell differentiation and proliferation
When is oxygen deficit incurred?
O2 demand > O2 consumption in early exercise
During prolonged distance running, where does muscle fatigue occur most often?
Gastrocnemius
What occurs when RER < 0.7?
Diet-induced gluconeogenesis is occurring
What cells are attached to the injury site first after z-line disruption?
Neutrophils
What happens when liver and glycogen stores run low in an endurance race?
FFA metabolism is slower than glycogen metabolism
What occurs in the cell if muscle pH falls to 6.4?
Glycogen breakdown becomes severely diminished
Steroid hormones are derived from what, making them what type of soluble?
Cholesterol, lipid soluble
What is slower, FFA metabolism or glycogen metabolism?
FFA metabolism is slower than glycogen metabolism.
What occurs in the cell when muscle pH falls to 6.4?
Glycogen breakdown becomes severely diminished.
Steroid hormones are derived from what and how soluble are they?
Cholesterol; Lipid soluble.
What happens as a result of altitude training over 2,500 meters?
Hypoxia induces EPO release from the kidneys, increasing hemoglobin concentration.
How is hormone secretion characterized?
Pulsatile.
What does the renin angiotensin aldosterone system help restore?
Blood volumes and blood pressure.
At what exercise intensity do norepinephrine concentrations increase?
Moderate exercise intensity.
At what exercise intensity do epinephrine concentrations increase?
High exercise intensity.
What stimulates glucose mobilization?
Glucagon.
What stimulates glucose uptake by cells?
Insulin.
Why do plasma glucose concentrations decline after prolonged exercise?
Liver glycogen stores are depleted.
What is the primary means by which hormones maintain homeostasis?
Negative Feedback mechanisms.
Which hormones typically act in opposition?
Insulin and Glucagon.
In which exercise domain is VO2max achieved?
Moderate, Heavy, Severe, Extreme.
What is the primary glucocorticoid that mobilizes FFAs?
Cortisol.
What happens to glucagon and insulin concentrations during exercise?
Glucagon increases; Insulin decreases.
Which hormone is NOT secreted by the anterior pituitary gland?
Renin.
What senses blood osmolality?
Hypothalamus.
What is the normal body fluid osmolality?
Approximately 300 mOsm/kg.
What happens when PO2 is approximately 20 mmHg?
Loading O2.
What occurs if phase 3 of the ventilatory response to exercise is blunted?
Steady state would be less 'steady'.
What is the pressure gradient in the pulmonary circulation?
Approximately 10 mmHg.
What occurs when chemoreceptors stimulate an increase in breathing rate?
Excess CO2 needs to be removed.
What moves from plasma into red blood cells to prevent ionic imbalance?
Chloride (Cl-).
What type of test is required to determine ventilatory threshold?
Graded exercise test.
What is the effect of endurance training on respiratory muscles?
Improves oxidative capacity.
What does the Respiratory Compensation Point (RCP) indicate?
Uncoupling of regulation of ventilation by PCO2 and acidosis.
Will Chris P. Bacon's performance be impaired at Mt. Washington?
No, > 97.5% hemoglobin saturation.
What is significant about the O2-hemoglobin and O2-myoglobin dissociation curves?
Myoglobin's curve is steeper, indicating off-loading O2 at lower PO2.
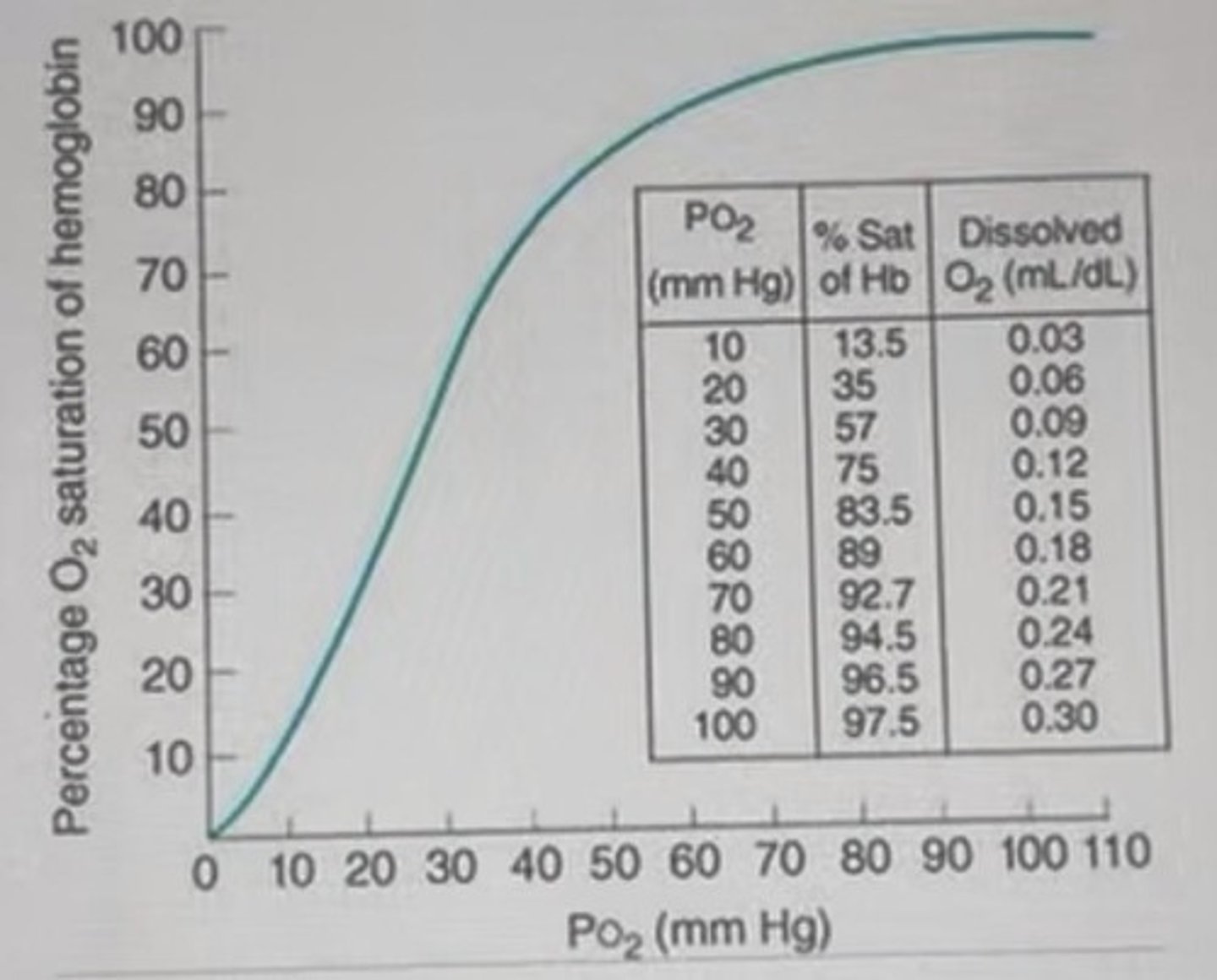
What limits maximal endurance performance?
Ventilation is not a limiting factor except in elite athletes or at altitude.
During moderate exercise in heat, which vascular beds receive the most blood flow?
Muscle and skin.
What does the Valsalva Maneuver do?
Reduces preload, cardiac output, and arterial blood pressure.
How can Cardiac Drift occur quickly?
Hot environmental conditions or dehydration.
What effect does increased blood pressure during exercise have on plasma volume?
It decreases plasma volume.
Which mechanism does NOT increase stroke volume during exercise?
Catecholamines stimulation of the SA node.
What percentage of cardiac output do respiratory muscles receive during maximal exercise?
15% of cardiac output.
What leads to an increase in stroke volume due to norepinephrine?
Increased contractility and preload.
What explains the cardiorespiratory responses to an acute increase in exercise intensity?
Tidal volume and stroke volume increase more than heart rate and respiratory rate.
Which does NOT contribute to ventilatory regulation during exercise?
Baroreceptors in carotid sinus.
What leads to vasodilation during exercise?
Accumulation of metabolic by-products (H+, CO2, Heat).