Chemistry Edexcel Topic 1
1/104
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
What are the three ideas in John Dalton's theory about the atom
Atoms cannot be created, divided or destroyed, atoms of the same element are exactly the same and atoms of different elements are different, atoms join with other atoms to make new substances
What was Dalton's original atom model
Tiny spherical objects that cannot be divided any further
What discovery caused the original Dalton model of an atom to change
The discovery of subatomic particles
How did JJ Thompson discover the electron
He experimented using a cathode ray tube - the beam moved towards the positively charged plate so he knew that the particles must have a negative change
Describe the atomic model proposed by JJ Thompson
Plum pudding model - a positively charged ball with negatively charged electrons scattered throughout
What did Ernest Rutherford discover from his gold foil experiment
He shot a beam of positively charged particles at sheet of gold foil - most of the particles passed straight through suggesting that atoms were mostly empty space, a few particles were deflected and a few bounced directly back showing that there must be a tiny, dense and positively-charged nucleus
Describe Rutherford's new model of the atom
Mass concentrated in the central nucleus, mostly empty space, electrons travelling in random paths around the nucleus
Describe the structure of an atom
Small central nucleus made up of protons and neutrons with electrics orbiting around the nucleus in shells
What is the radius of the nucleus - how large is it compared to the radius of an atom
The radius of the nucleus is 1x10^-14m which is 1/100000 of the atomic radius
What are the relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons
Proton: 1
Neutron: 1
Electron: 1/1836
What are the relative charges of protons, neutrons and electrons
Proton: +1
Neutron: 0
Electron: -1
Why do atoms contain equal numbers of protons and electrons
Atoms are stable with no overall charge - protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged and the charges in an atom are balanced so there must be an equal number of protons and electrons
Where is the mass of an atom concentrated
In the nucleus
What does the atomic number of an atom represent
The number of protons
What does the mass number of an atom mean
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons found in the nucleus of an atom
What do atoms of the same element contain
The same number of protons in the nucleus - the number of protons is unique to that element
What is an isotope
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons (have the same atomic number but different mass numbers)
Why is the relative atomic mass not always a whole number
Different isotopes of the same element have different mass numbers - the relative atomic mass is an average of the masses of all these isotopes
What two values would be required to calculate the relative atomic mass of chlorine
Mass numbers and relative abundances of all the isotopes of chlorine
How would you calculate the relative atomic mass of an element
(Sum of (isotope mass x abundance))/100
How did Mendeleev arrange the elements in his periodic table
Elements arranged with increasing atomic masses and elements with similar properties put into groups (due to periodic trends in chemical properties) with gaps left for undiscovered elements
How was Mendeleev able to predict the properties of new elements
He left gaps in the periodic table and used the properties of elements next to the gaps to predict the properties of undiscovered elements
Mendeleev's table lacked done accuracy on the way he ordered his elements - why was this
Isotopes were poorly understood at the time and protons and neutrons had not been discovered at that time - he thought he'd arranged the elements in order of increasing relative atomic mass but it was not always true because of the relative abundance of isotopes of some pairs of elements in the periodic table
How are elements arranged in the modern periodic table
In order of increasing atomic number, in rows called periods
What similar property do elements in the same group (column) have
Chemical properties
Why do elements in the same group (column) have similar chemical properties
They have the same number of outer shell electrons - the number of outer shell electrons determines how an atom reacts
What does the period (row) number tell you about all the elements in that period (row)
They have the same number of electron shells
What does the group number tell you about all the elements in that group
All elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in the outer shell
On which side of the periodic table are the metals positioned
On the left hand side
What determines whether an element is metal or not
The atomic structure of the element - all metals form positive ions so have 1-3 electrons in their outer shell, and non metals generally have 5-7 electrons in their outer shell
What is the maximum number of electrons allowed in each of the first 3 shells
First: 2
Second: 8
Third: 8
When are atoms most stable
When they have full electron shells
How is the electron configuration of an element related to its position in the periodic table
Number of shells is the period, number of electrons in the outer shell is the group, the total number of electrons is the atomic number
What is an ionic bond
A bond between a metal and non metal involving the transfer of electrons
How are ionic bonds formed
When an atom transfers electrons to others to produce cations and anions
In terms of electrons, describe what happens to the metal and non metal when an ionic bond forms
The metal atom loses electrons to become a positively charged cation and the non metal atom gains electrons to become a negatively charged anion
What is an ion
An atom or group of atoms with a positive or negative charge
If an ion is positively charged, has it lost or gained electrons
It has lost electrons - there are fewer negatively charged electrons to cancel out the charge of the positive protons, making the overall charge positive
Na+ has the atomic number 11 and the mass number 23 - how many protons, neutrons and electrons are in this ion
Protons - 11, electrons - 10, neutrons - 12
O2- has the atomic number 8 and the mass number 16 - how many protons, neutrons and electrons are in this ion
Protons - 8, electrons - 10, neutrons - 8
Why do elements in groups 1, 2, 6 and 7 readily form ions
They don't need to lose or gain many electrons to become more stable and gain a full outer shell so will more readily form ions to achieve a more stable structure
What type of ions do elements in group 1 and 2 form
Cations - group 1 metals will form 1+ ions and group 2 metals will form 2+ ions
What type of ions do elements in group 6 and 7 form
They are non metals so form anions - group 6 will form 2- ions and group 7 will form 1- ions
What does it mean if an ionic compound ends in -ide
The compound contains 2 elements
What does it mean if an ionic compound ends in -ate
The compound contains at least three elements, one of which is oxygen
Describe the structure of an ionic compound
Lattice structure with a regular arrangement of ions held together by strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions
What is a covalent bond
A bond formed when an electron pair is shared between two non metal atoms
What forms as a result of covalent bonding
A molecule
Draw a dot and cross diagram for the formation of methane (CH4)
Are covalent bonds weak or strong
Strong
Are intermolecular forces weak or strong
Weak
Which is smaller, an atom or a molecule
An atom - simple molecules consist of atoms joined by strong covalent bonds within the molecule
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points
Strong electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative ions which requires a lot of energy to overcome
When do ionic compounds conduct electricity
When molten or in solution (aqueous)
Why can ionic compounds conduct electricity
Because the ions are charged and free to move and carry charge when the ionic compound is molten or in solution - when it is solid, the ions are fixed in a lattice structure so cannot move and carry charge
Why do simple molecular compounds have low melting and boiling points
They have weak intermolecular forces (forces between molecules) which only require a little energy to overcome
Do simple molecular compounds conduct electricity
No because there are no charged particles
Do giant covalent structures have a high melting point
Yes because they have lots of strong covalent bonds (and no intermolecular forces because there are no molecules) which require a lot of energy to break
Can giant covalent structures conduct electricity
They generally don't conduct electricity because they generally don't contain charged particles (apart from graphite and graphene)
What are giant covalent structures
Huge networks of covalently bonded non metal atoms with no intermolecular forces as there are no molecules - they can also be called giant lattices and have a fixed ratio of atoms in the overall structure
How do metals conduct electricity and heat
The positive ions are fixed in a sea of delocalised electrons which are free to move and carry charge
Are metals soluble in water
No
Name two giant covalent structures formed from carbon atoms
Graphite and diamond
Describe the structure of graphite
Each carbon atom is bonded to 3 other carbon atoms which form hexagonal rings of carbon atoms and has one delocalised electron per atom - there are many layers of carbon rings with weak intermolecular forces between layers
Describe and explain the properties of graphite
Graphite is soft and slippery because there are only weak intermolecular forces between the layers which allows the layers to slide over each other - graphite also conducts electricity because there is one delocalised electron per carbon atom which forms a sea of delocalised electrons which are free to move and carry charge
Describe the structure of diamond
All carbon atoms are covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms and there are no delocalised electrons
Describe and explain the properties of diamond
It is very hard and has a strong melting point because it contains strong covalent bonds which require a lot of energy to break, and it does not conduct electricity as there are no charged particles
Why is diamond hard and graphite soft
Graphite is soft because it has weak intermolecular forces between its layers whereas diamond has no molecules so is hard due to its giant covalent lattice and many strong covalent bonds
What are the uses of graphite
As electrodes because graphite conducts electricity and has a high melting point and as lubricant because it is slippery (the layers in graphite can slide over each other)
Why is diamond used in cutting tools
Because it's very hard
What is a fullerene
A molecule made of carbon which is shaped like a closed tube or a hollow ball
Name two fullerenes
Graphene and C60 (buckminsterfullerene)
What are the properties of the fullerene C60
Slippery due to the weak intermolecular forces, has a low melting point due to intermolecular forces, spherical, has strong covalent bonds between the carbon atoms in the molecule and has a large surface area
What are the properties of graphene
High melting point due to covalent bonding between carbon atoms and conducts electricity because it has delocalised electrons
Why is graphene useful in electronics
It is extremely strong, has delocalised electrons which are free to move and carry charge so can conduct electricity, and it is only one atom thick as it is only a single layer of graphite
What is a polymer
A long chain of molecules formed from many monomers
What are simple polymers
Simple polymers consist of large molecules containing chains of carbon atoms
Name a polymer
Polyethene
Draw the structure of polyethene
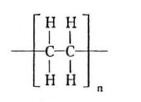
What bond is formed between carbon atoms in polymer molecules
Covalent bonds
What are the properties of metals
High melting point, high density, good conductors of electricity, malleable and ductile, and generally shiny
Explain why metals are malleable
The atoms are arranged in uniform rows which can slide over one another so are easier to bend and shape
Explain why metals can conduct electricity
The electrons in the metal are charges that can move
What are the properties of non metals
Low boiling points, poor conductors of electricity and brittle when solid
List the limitations of dot and cross diagrams when representing ionic compounds
Doesn't show a lattice structure or ionic bonds between the ions
List the limitations of 2D diagrams when representing ionic compounds
Only shows one layer of the ionic compound and doesn't show the formation of ions
List the limitations of 3D diagrams when representing ionic compounds
Shows spaces between the ions and doesn't show the charges of the ions
List the limitations of dot and cross diagrams when representing covalent molecules
Doesn't show relative sizes of atoms or intermolecular forces
List the limitations of ball and stick diagrams when representing covalent molecules
Bonds shown as sticks rather than forces and doesn't show how the covalent bonds form
How do you calculate the relative formula mass (Mr) of a compound
Add together all the relative atomic masses of the atoms in the compound
What is the empirical formula
The empirical formula is the smallest whole number ratio of the atoms of each element in a compound
What 2 values could be used to calculate the empirical formula of a simple compound
Reacting masses or percentage composition
What is the empirical formula for Fe2O4
FeO2
What is the molecular formula
The actual number of atoms of each element in a compound
Describe an experiment to work out the empirical formula of magnesium oxide
1) Weigh out a sample of magnesium
2) Heat the sample in a crucible
3) Weigh the mass of magnesium oxide at the end
4) Calculate the mass of oxygen (increase of mass)
5) Calculate the moles of magnesium and oxygen using the experimental mass and the relative atomic mass
6) Work out the whole number ratio of the number of moles of magnesium to oxygen
What is the law of conservation of mass
No matter is lost or gained during a chemical reaction
If a reaction is carried out in a closed system, what can you say about the total mass of the reaction throughout the experiment
The mass stays constant
If a reaction is carried out in an open system and a gas is produced, what can you say about the total mass of the reaction throughout the experiment
The mass decreases as the gas escapes
What equation links mass, moles and relative atomic mass
Mass = Mr x moles
How can you calculate concentration of solutions in g/dm^3
Concentration = mass/volume