Week 1 - Anatomical Position, Terms of Direction and Motion
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
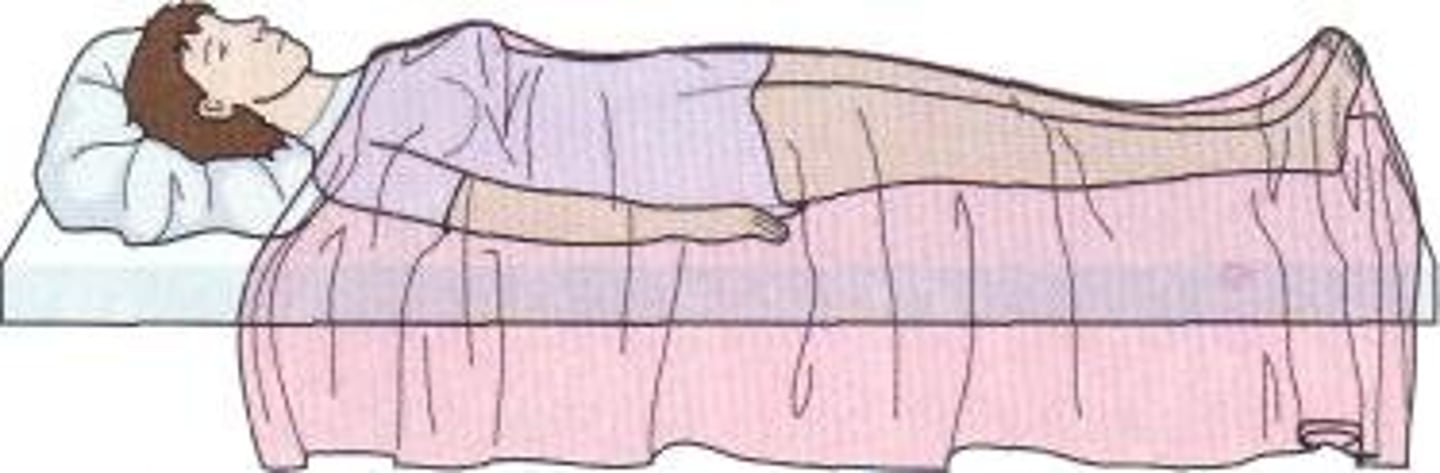
supine position
ventral side up position
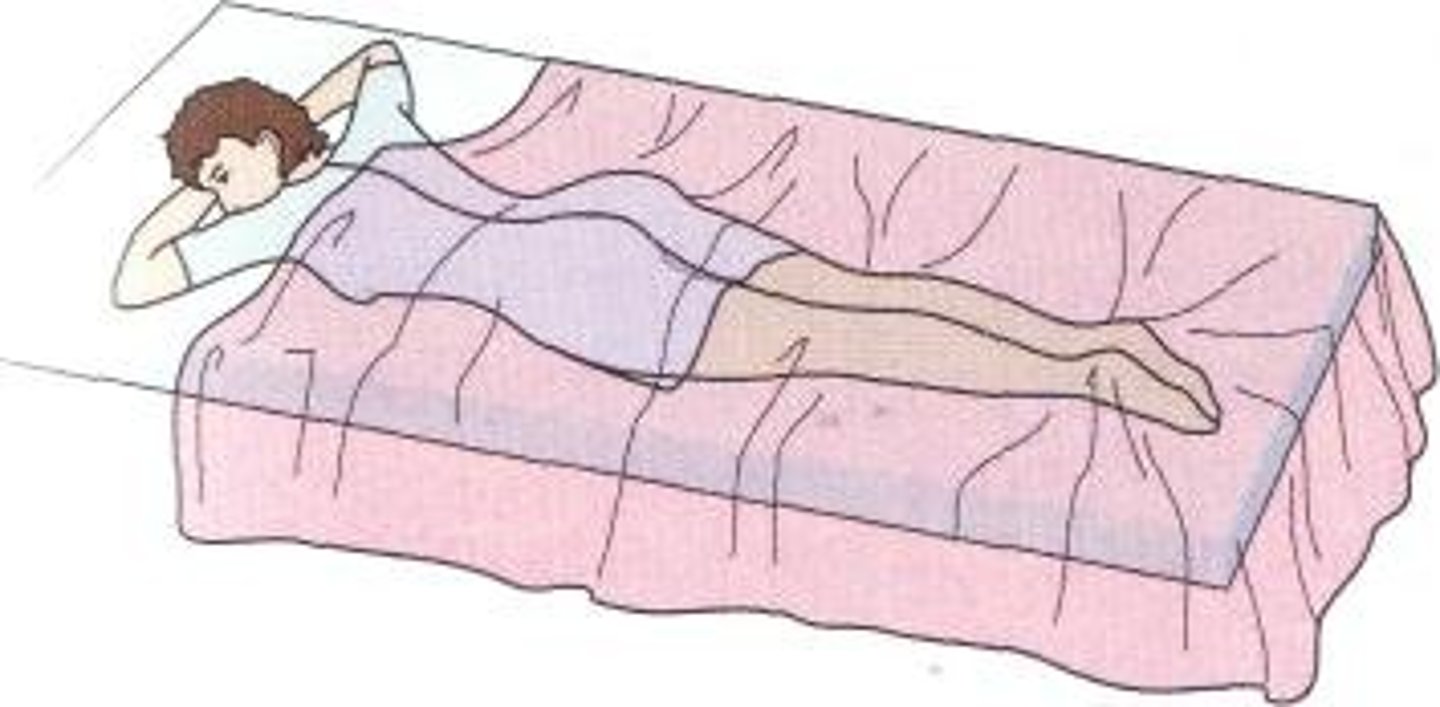
prone position
ventral side down position
What part of the body is being referred to when saying "prone" or "supine" position?
Only the torso (limbs may be in any position)
What is the anatomical position?
standing erect, facing forward, upper limbs at the sides, palms facing forward and thumbs out, toes facing forward at shoulder width
sagittal plane
vertical division of the body into right and left portions
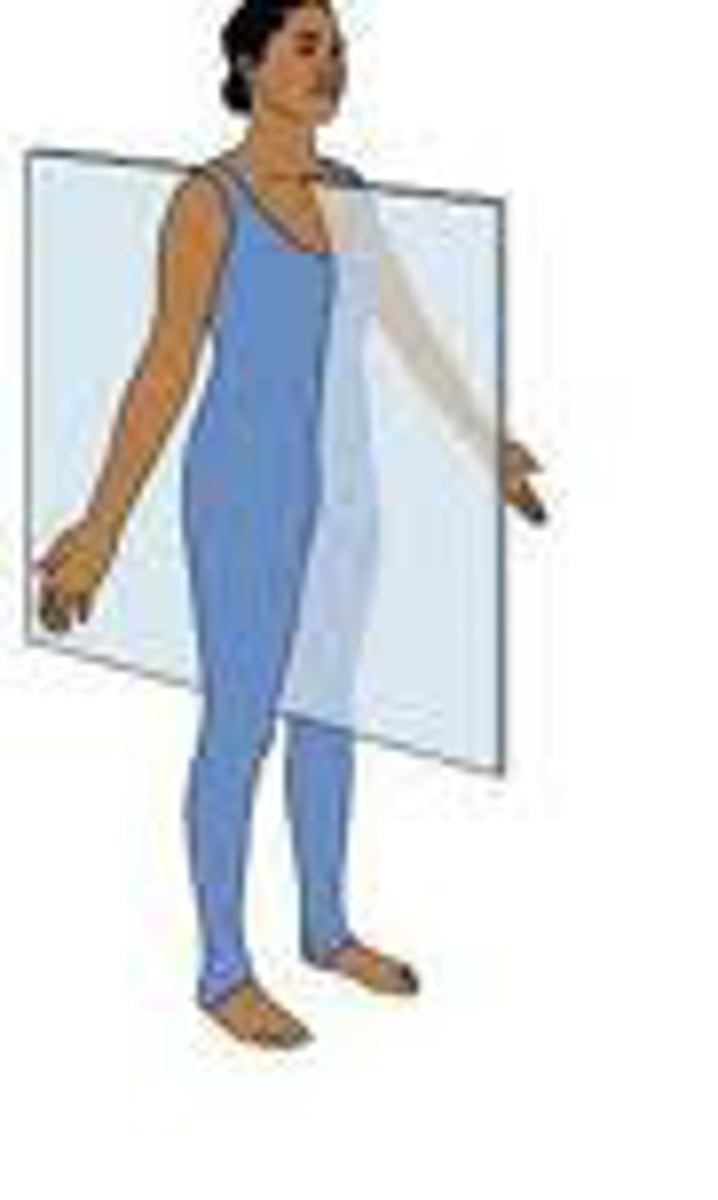
mid-sagittal plane
divides the body into equal left and right halves
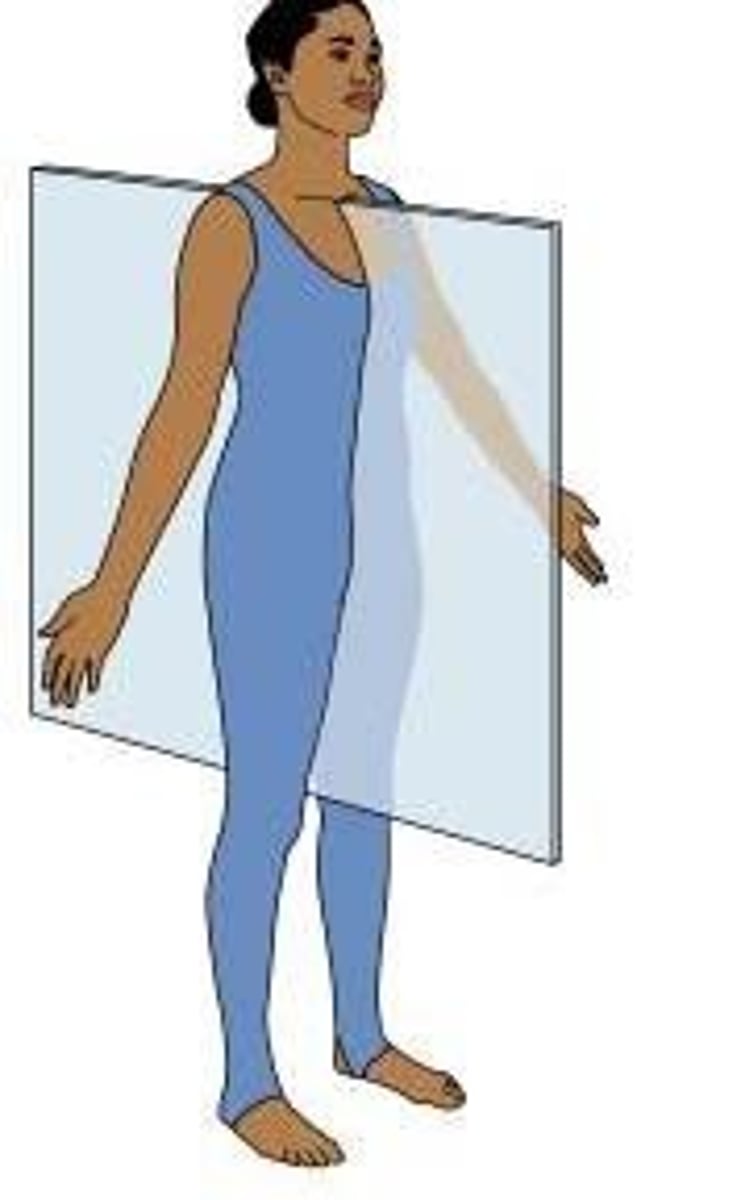
para-sagittal plane
divides the body into unequal left and right halves
What are synonyms for sagittal plane?
longitudinal plane, anteroposterior plane
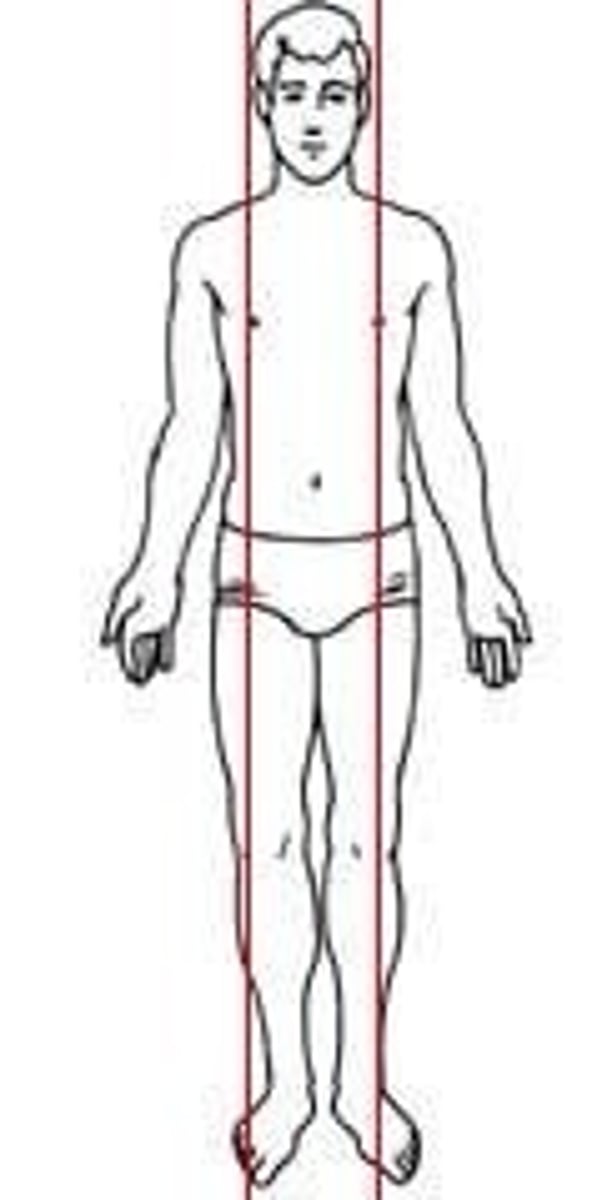
frontal plane
divides the body into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) portions
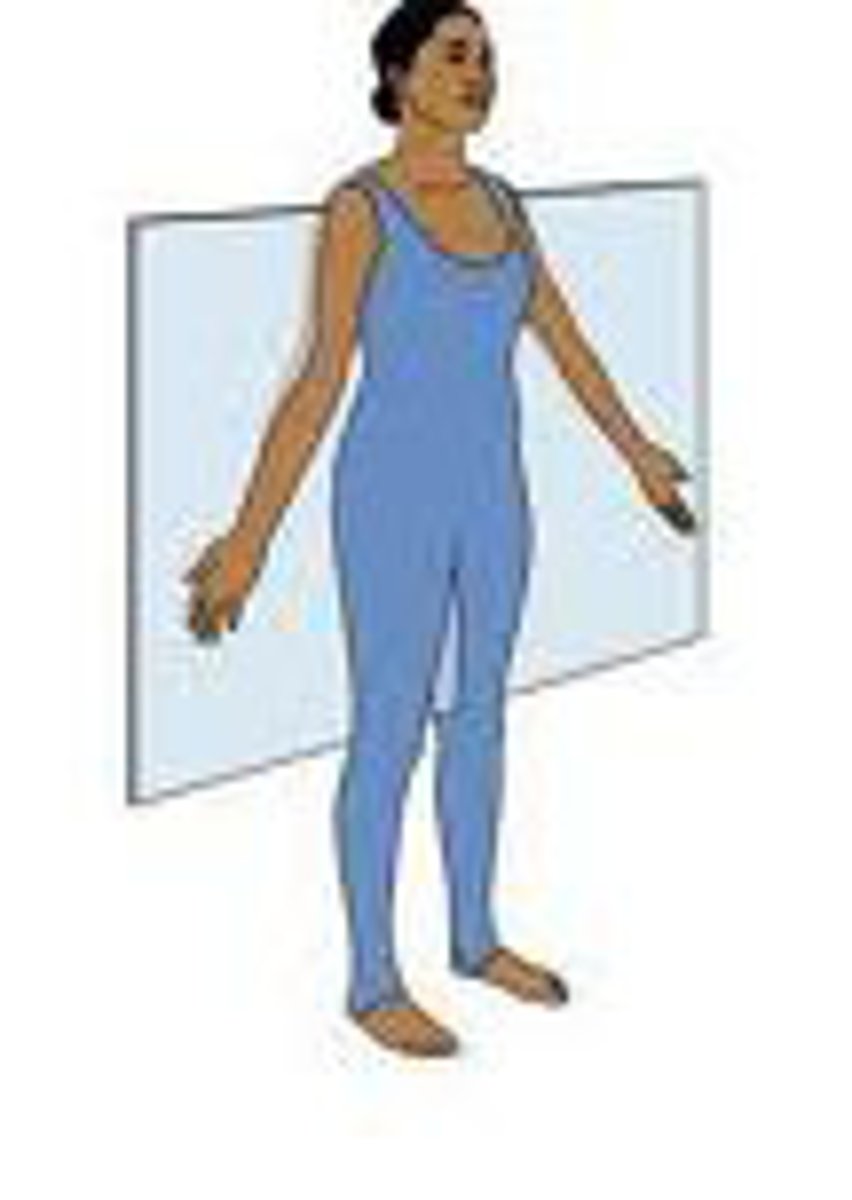

What are synonyms for frontal plane?
vertical plane, coronal plane
horizontal plane
plane dividing the body into superior (rostral/cranial )and inferior (caudal) sections
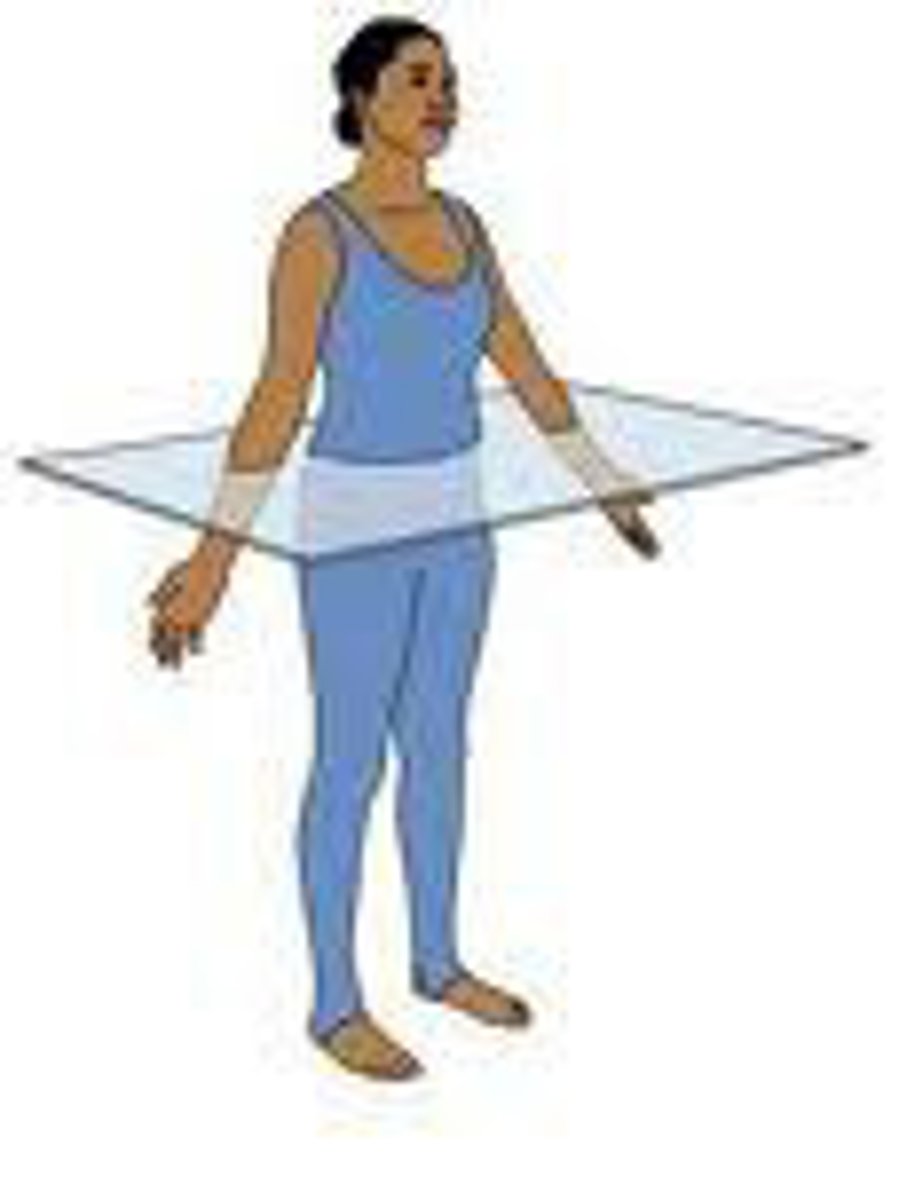
What are synonyms for horizontal plane?
transverse, axial (common in medical imaging)
What is it called when a section being studied is not parallel to one of the 3 anatomical planes?
oblique
How is movement described with reference to anatomical position, planes, and axis?
Movement occurs from anatomical position, about an axis, within a plane
Antero-posterior axis (sagittal axis)
Extends from the front of the body to the back, at intersection of the sagittal and transverse planes
supero-inferior axis (vertical)
passes vertically from superior to inferior, formed by intersection of sagittal and frontal planes

left-right axis (horizontal)
runs horizontally from left to right, formed by intersection of frontal and transverse planes
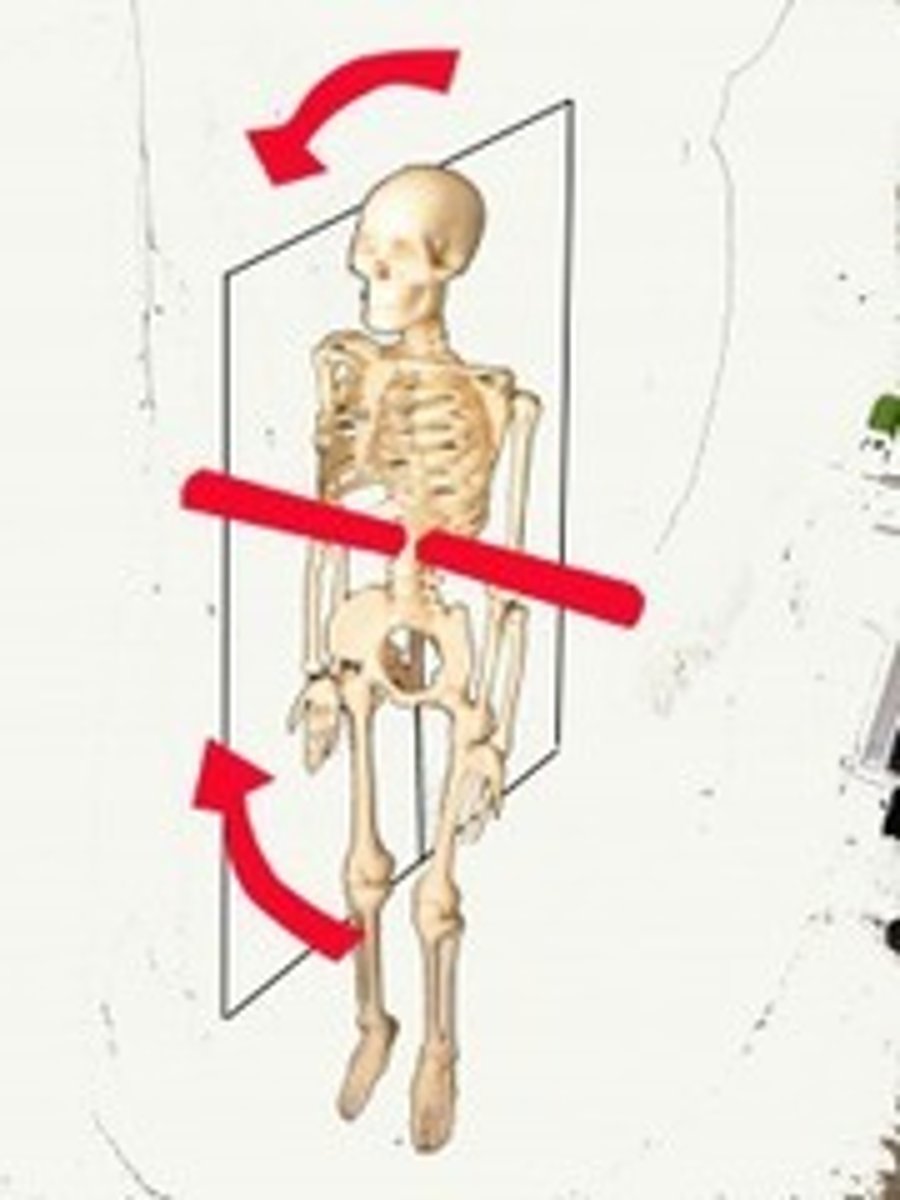
medial
toward the mid-sagittal plane
lateral
away from the mid-sagittal plane
ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
unilateral
on one side of the body
bilateral
on both sides of the body
proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
Where do anatomical terms change in bipeds?
At the midbrain (top of brainstem)
What does dorsal mean in the brain?
superior
What does ventral mean in the brain?
inferior
What does rostral mean in the brain?
anterior, toward the nose
What plane do flexion and extension occur within?
sagittal plane
flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint (generally anterior movement)
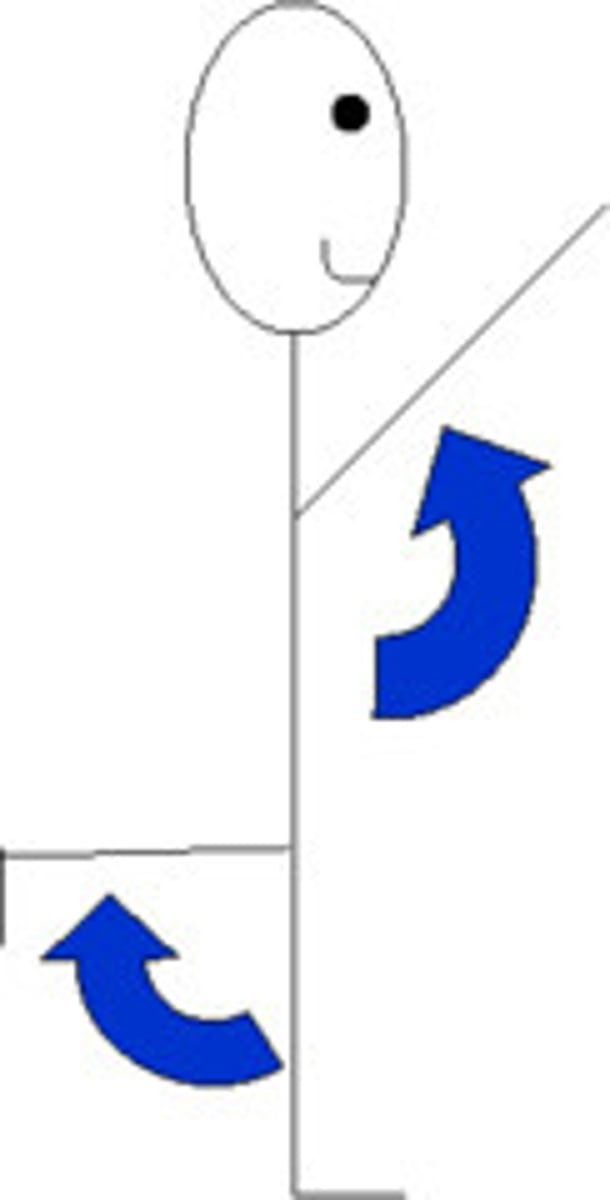
extension
increases the angle of a joint (generally in posterior direction)
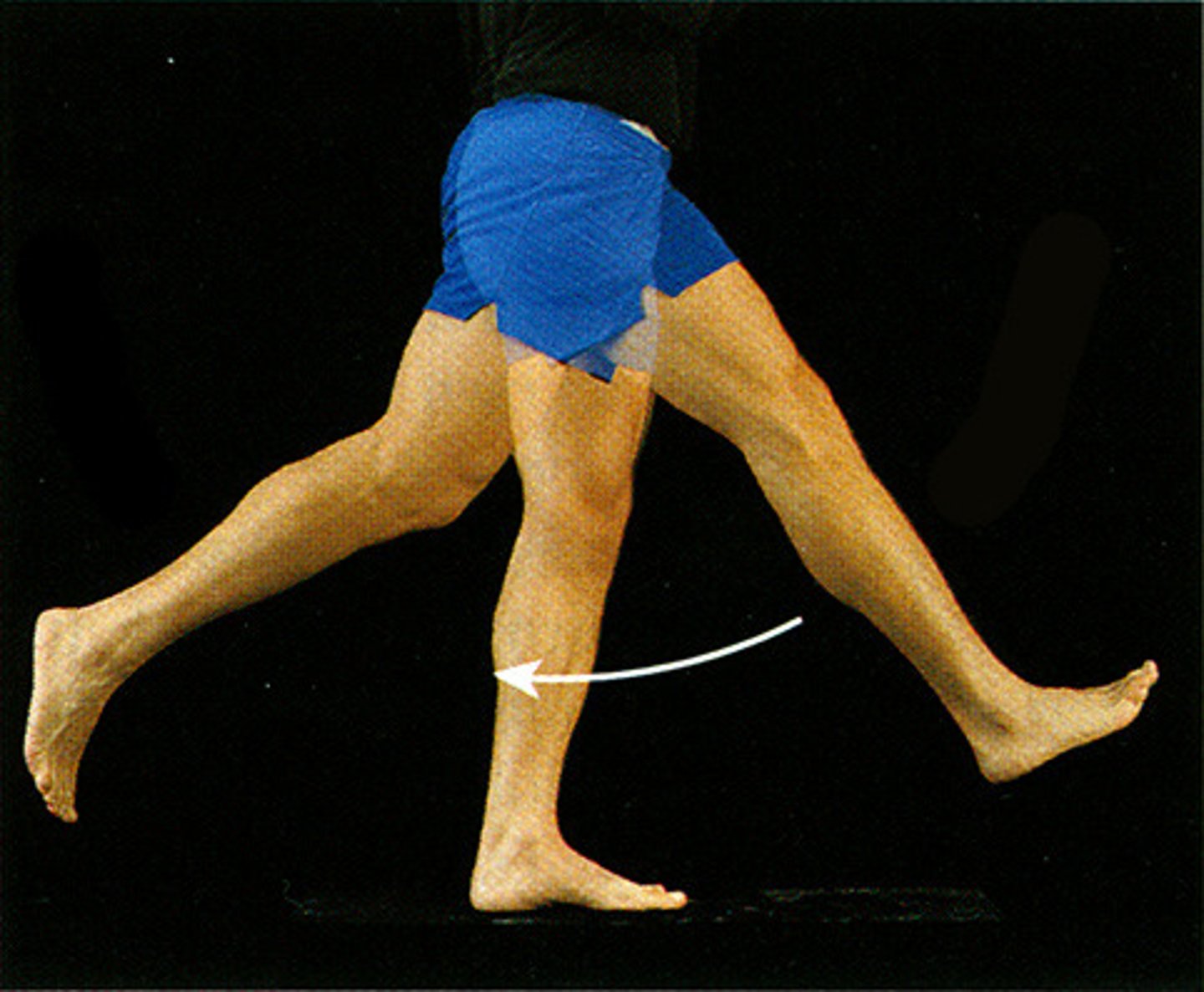
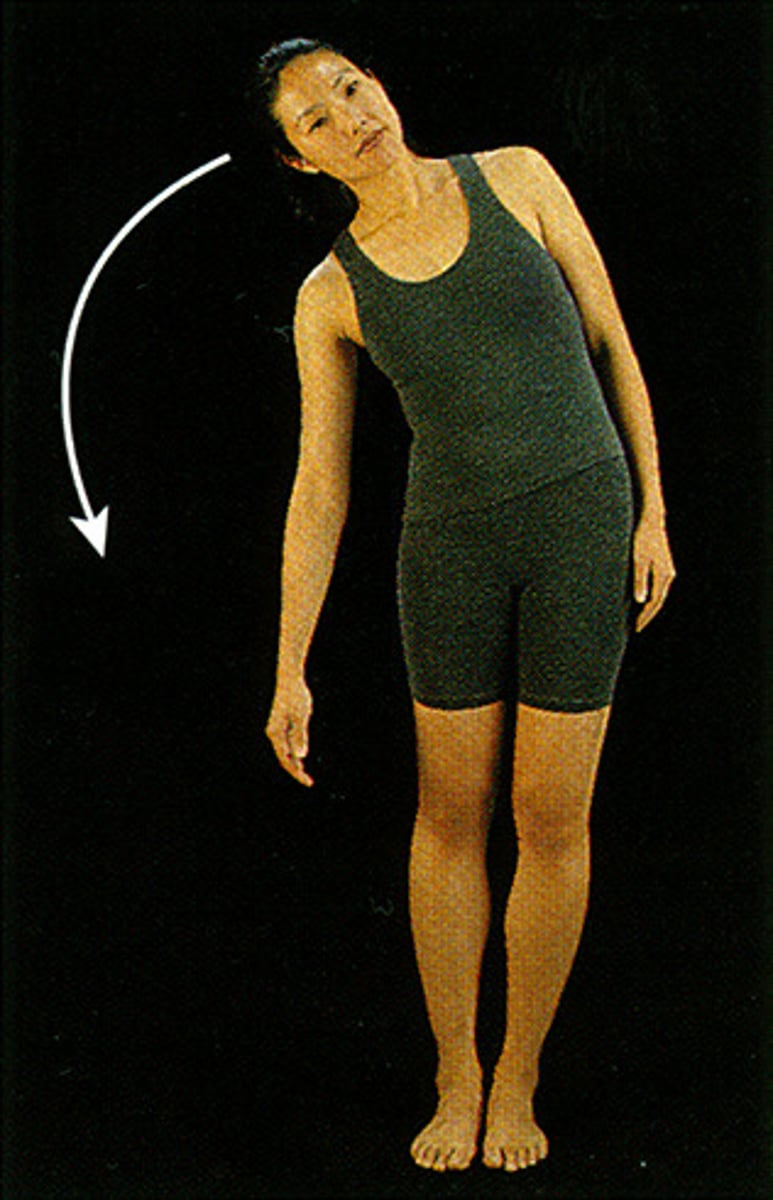
lateral flexion
bending of neck/body toward the right or left side
What plane do abduction and adduction occur within?
frontal plane, toward or away from the mid-sagittal
adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
What is the point of reference for abduction and adduction of the fingers and toes?
midline of the hand/foot
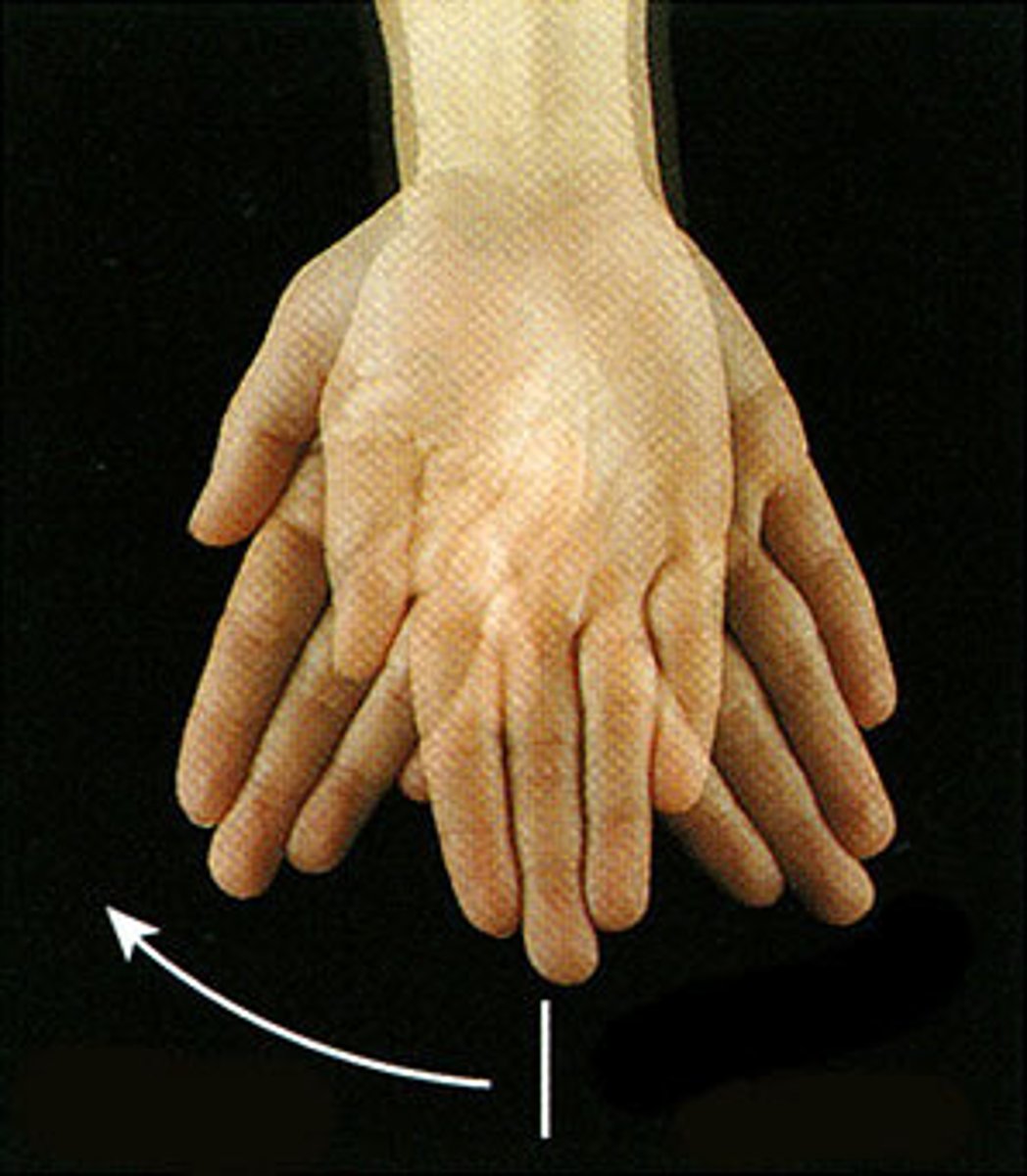
What is abduction of the hand at the wrist synonymous with?
radial deviation
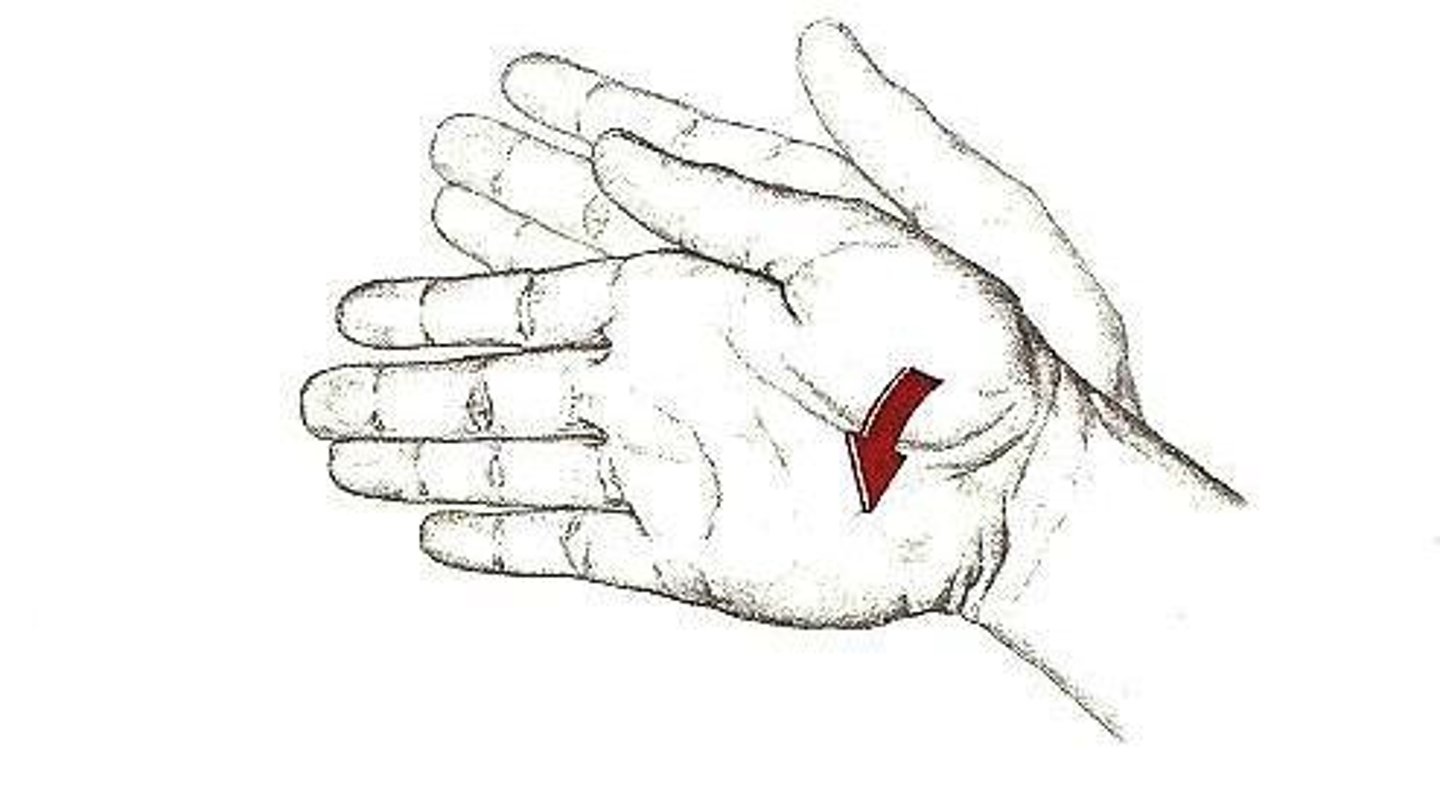
What is adduction of the hand at the wrist synonymous with?
ulnar deviation
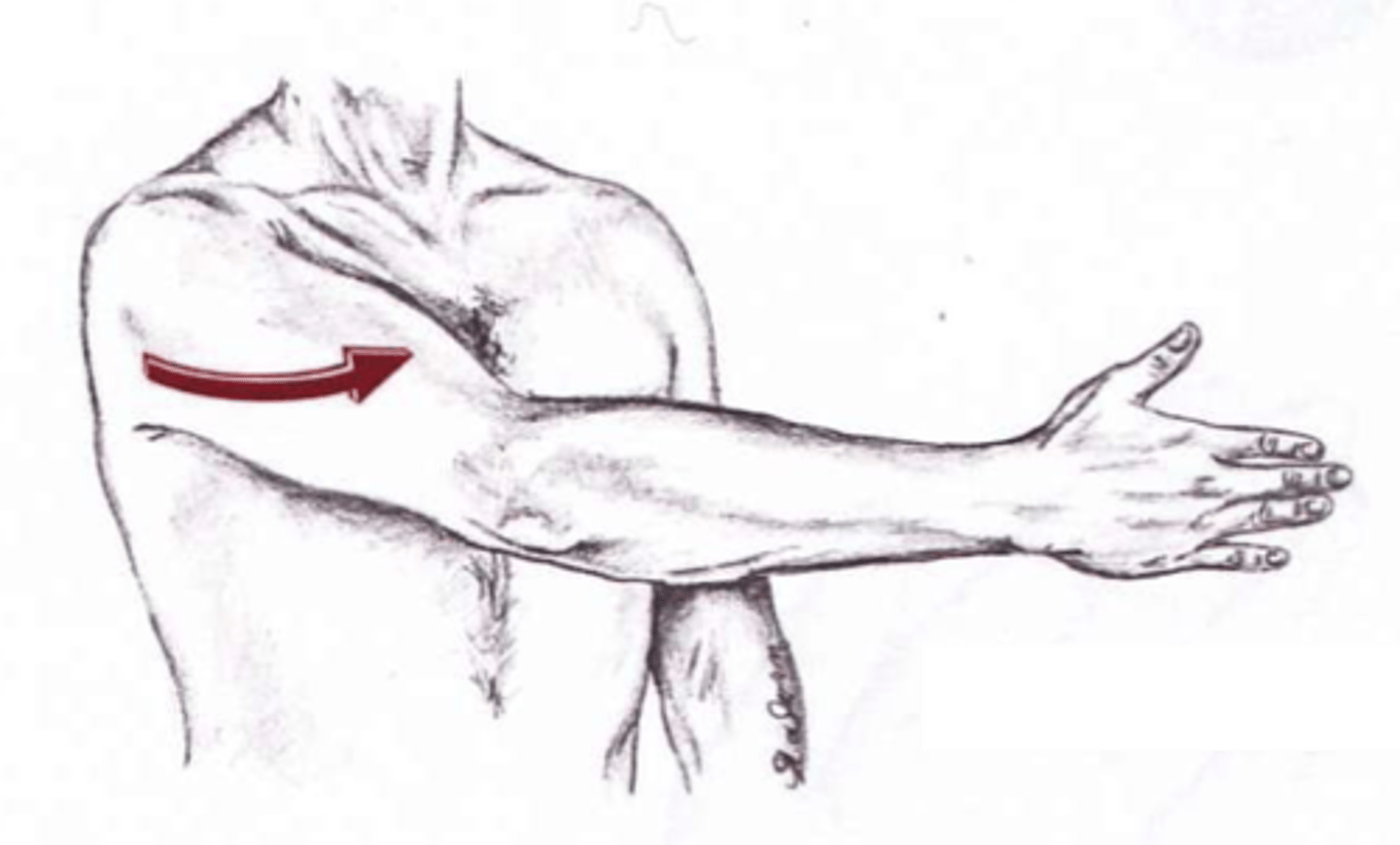
horizontal flexion/adduction of arm at shoulder
movement within transverse plane bringing the arms to the anterior portion of the body, where the starting position has the arms at 90 degrees of abduction
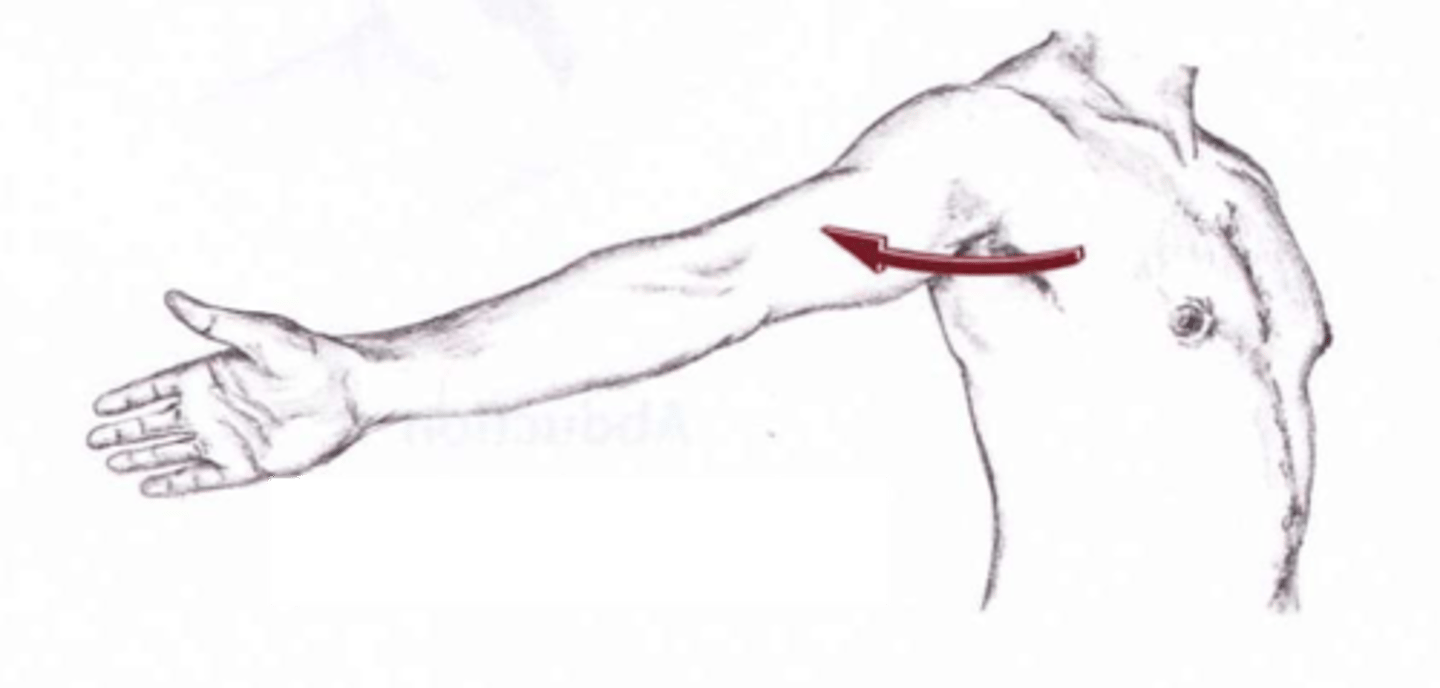
horizontal extension/abduction of arm at shoulder
movement within the transverse plane where the arms start at 90 degrees of abduction and are moved toward the posterior side of the body
circumduction
circular movement of limb where the proximal end is relatively stationary and the distal end is moving, sequence of flexion, adduction, extension, abduction (or reverse)
What plane and axis does rotation occur within/about?
transverse plane, about vertical axis
medial rotation (internal)
brings the anterior surface of a limb closer to the median plane
lateral rotation (external)
anterior surface rotates away from median plane
supination
rotation of the forearm and hand so that the palm faces anteriorly or superiorly
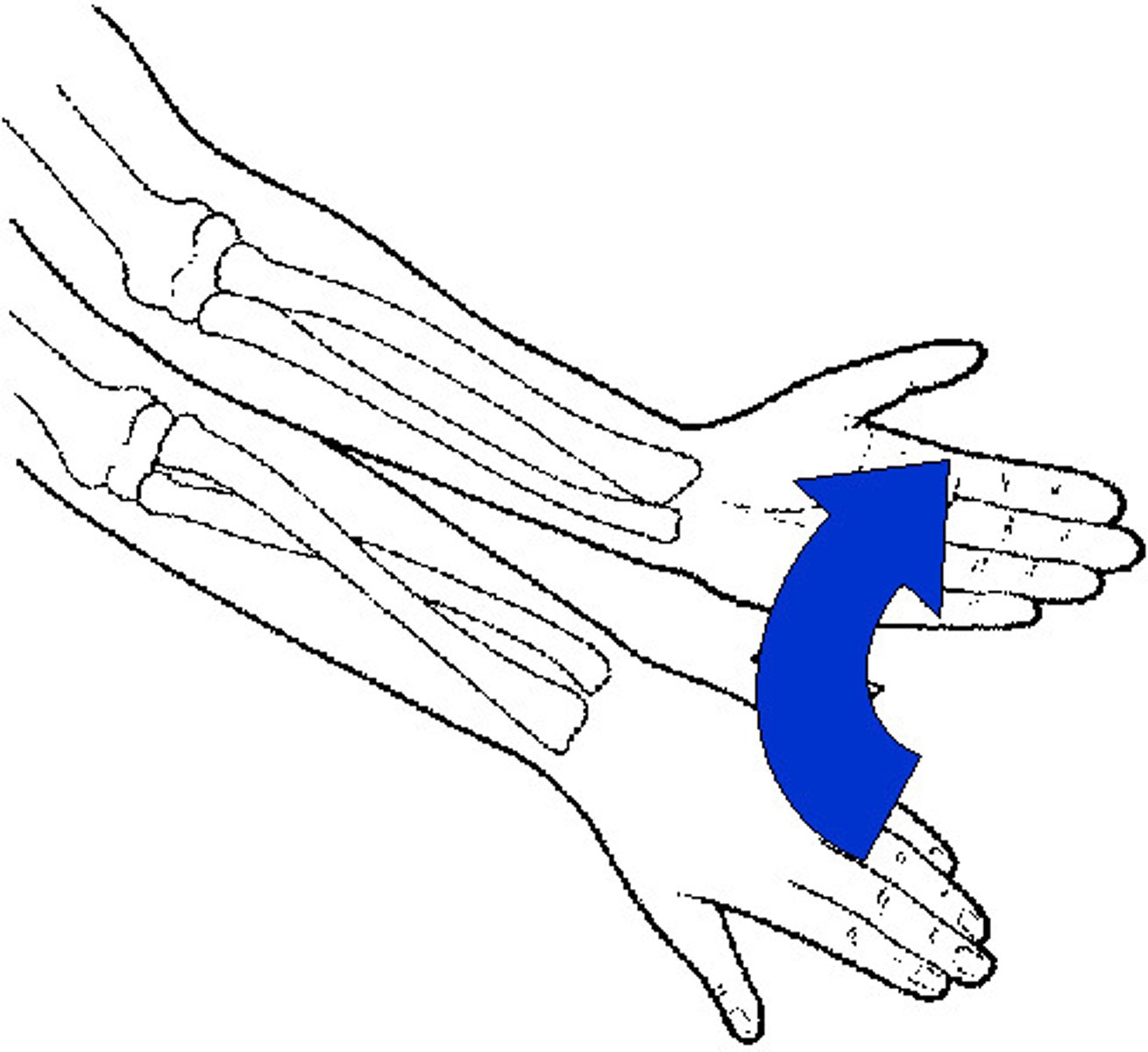
pronation
rotation of the forearm and hand so that the palm faces posteriorly or inferiorly
What is special about pronation, supination, horizontal flexion, and horizontal extension?
They do not start of the anatomical position
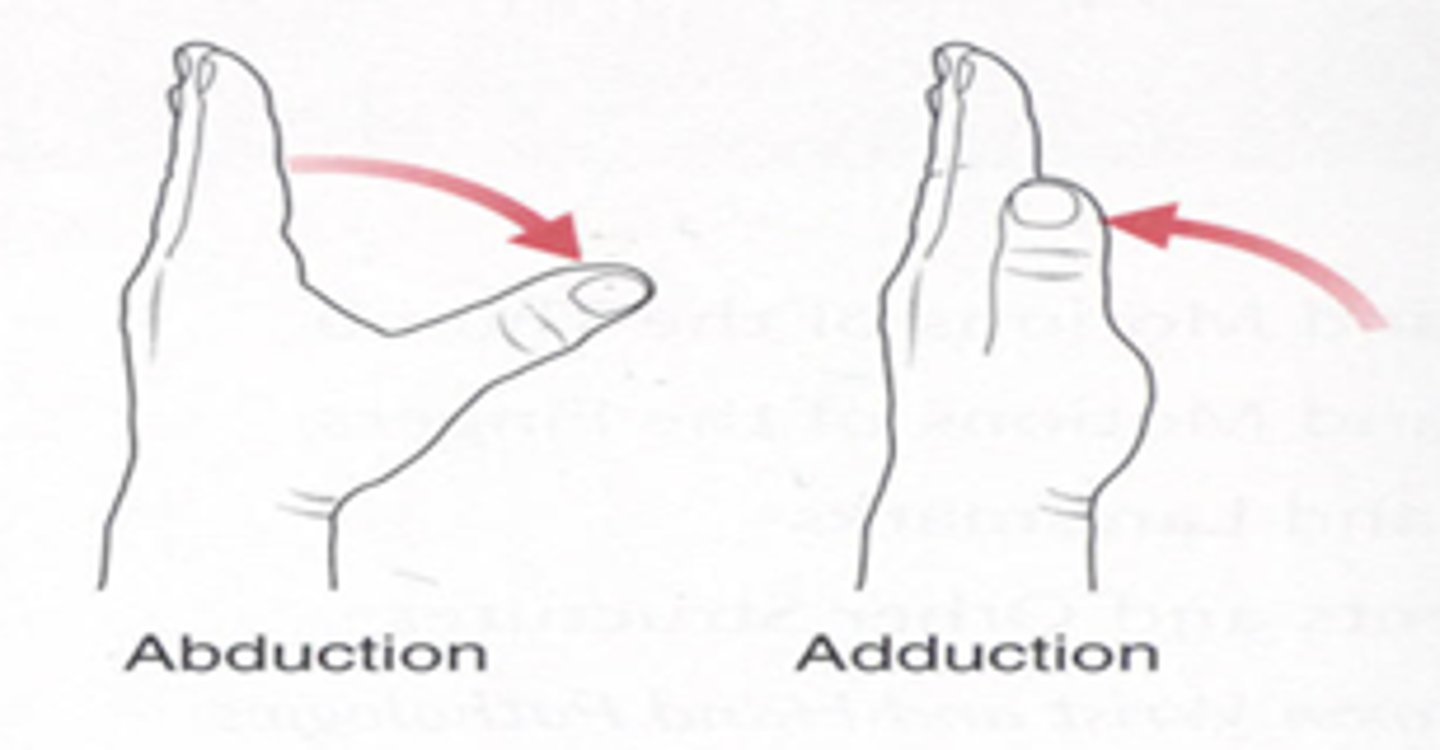
What movement does the thumb (first digit) do within the sagittal plane?
adduction and abduction
What movements do digits 2-5 do within the sagittal plane?
flexion and extension
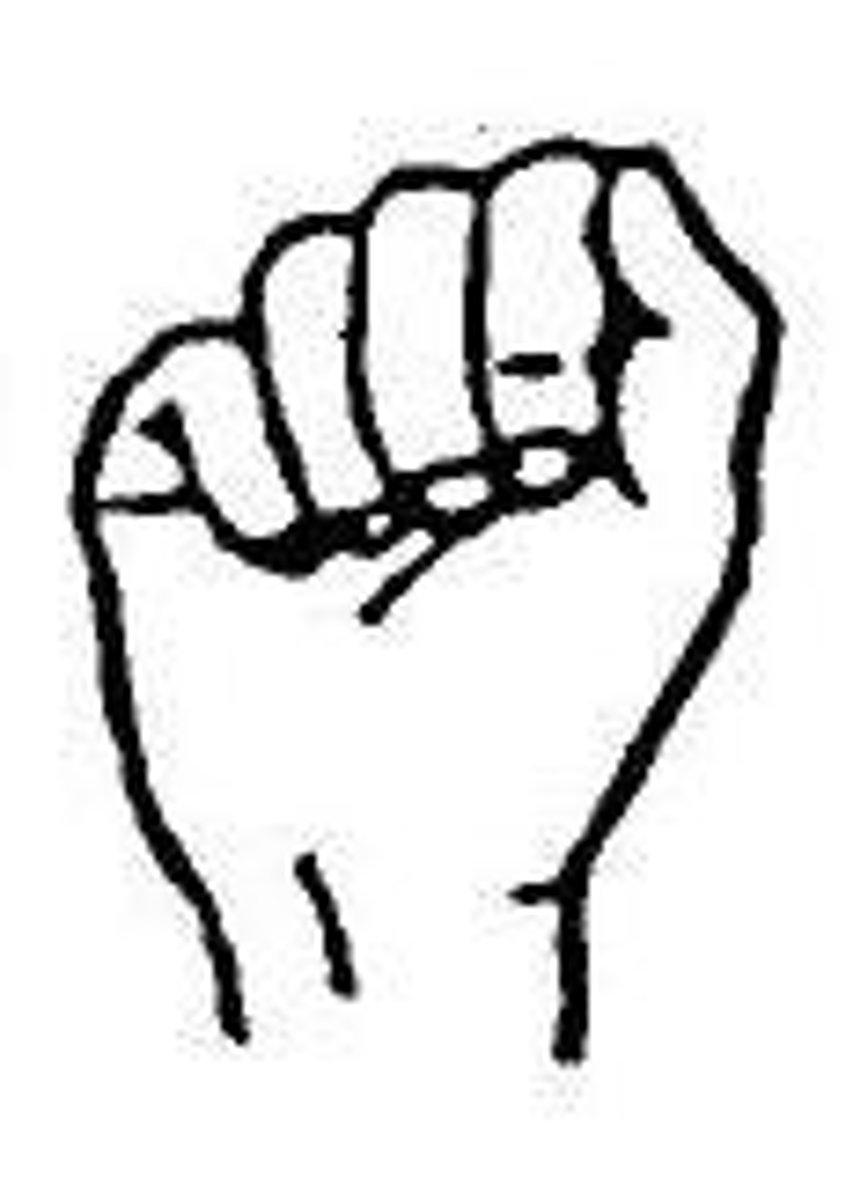

what plane does thumb flexion and extension occur within?
transverse plane
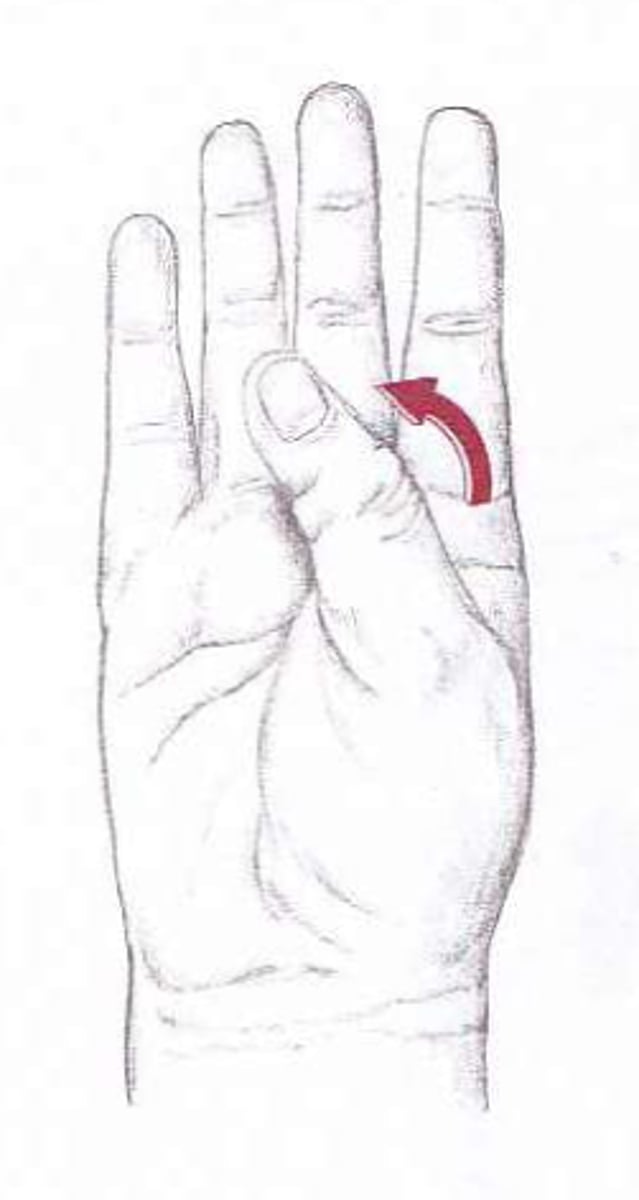
what is opposition of the thumb?
Combination of abduction, flexion, and rotation of the thumb (digit 1) Which allows for the thumb to touch the tips of other fingers on same hand (composite movement initiated at first carpometacarpal joint between trapezium carpal bone and first metacarpal bone)
what is reposition of the thumb?
movement of thumb as it returns to anatomical position from opposition with hand and/or fingers
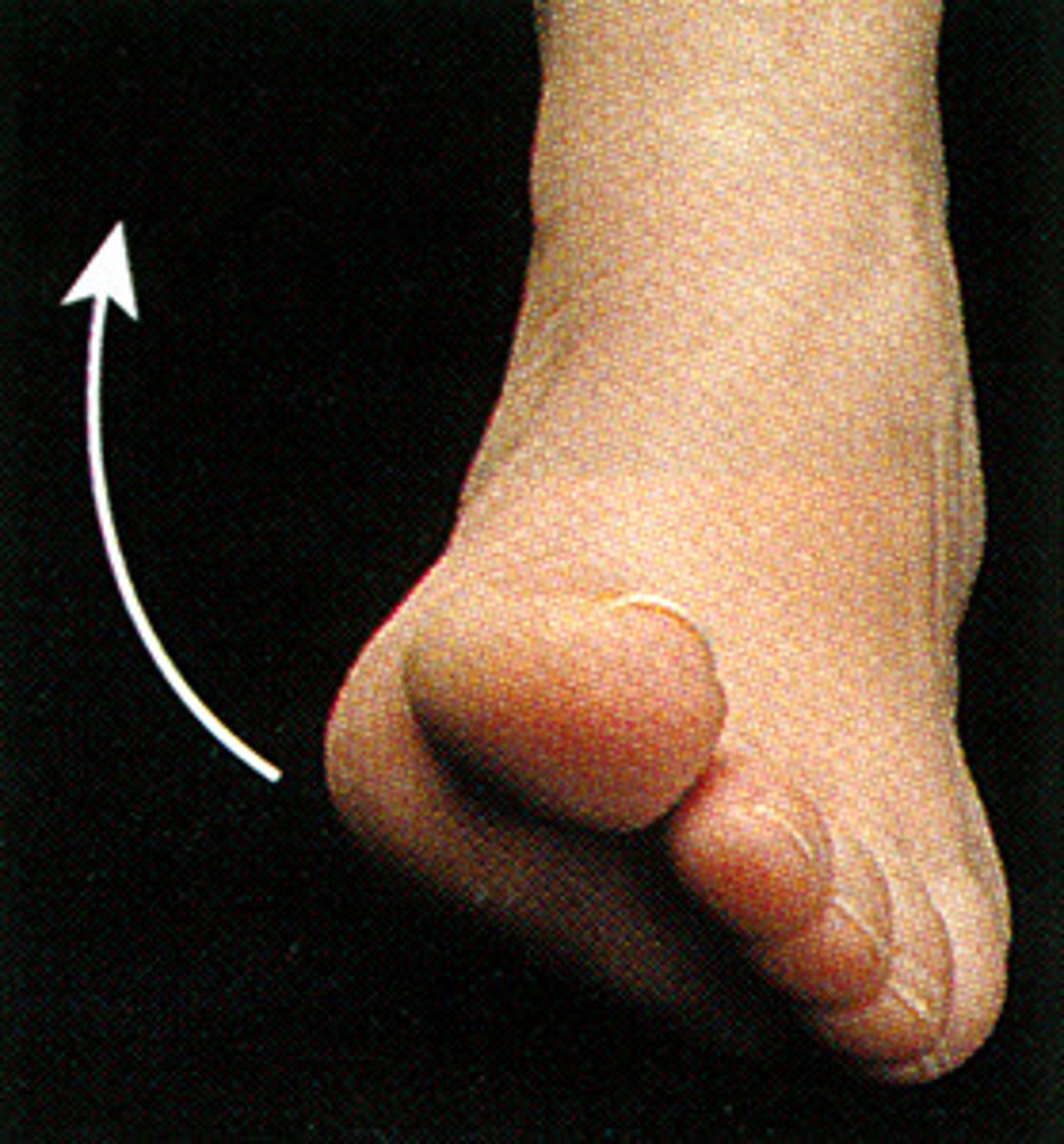
dorsiflexion
movement in the sagittal plane that brings toes closer to the shin, reducing the angle between the dorsal portion of the foot and anterior surface of the leg
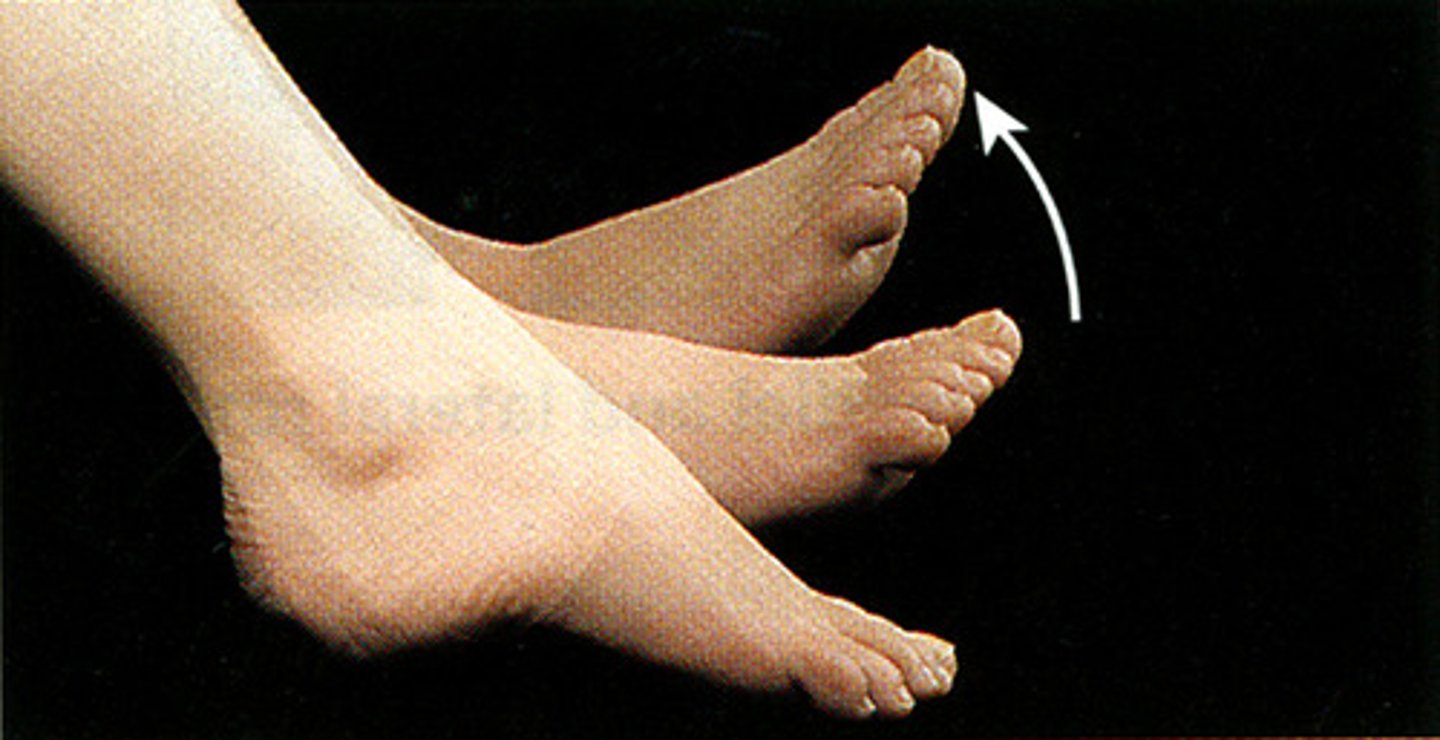
plantar flexion
movement in the sagittal plane where the toes are moved away from the shin, reducing the angle between the ventral/plantar surface of the foot and the posterior surface of the leg
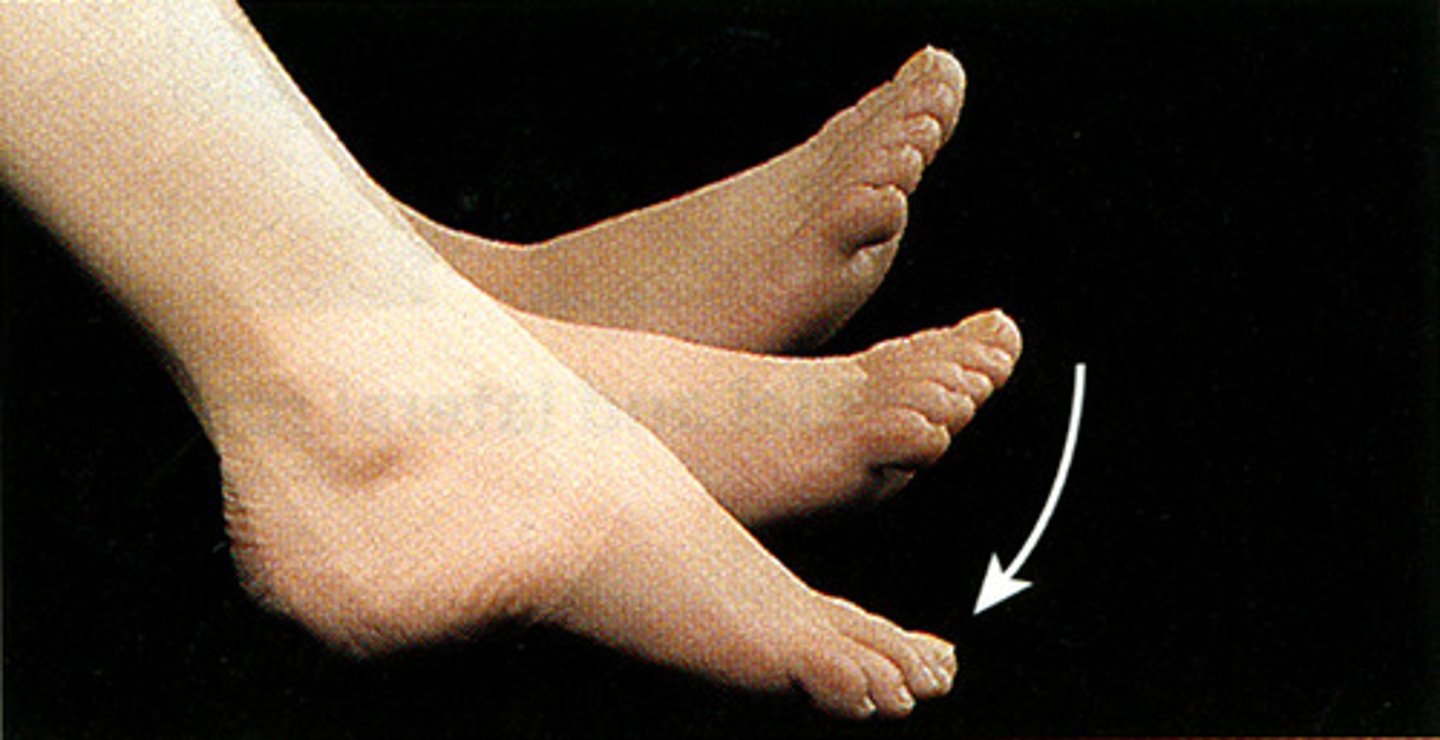
eversion
moving plantar surface of foot laterally away from midline
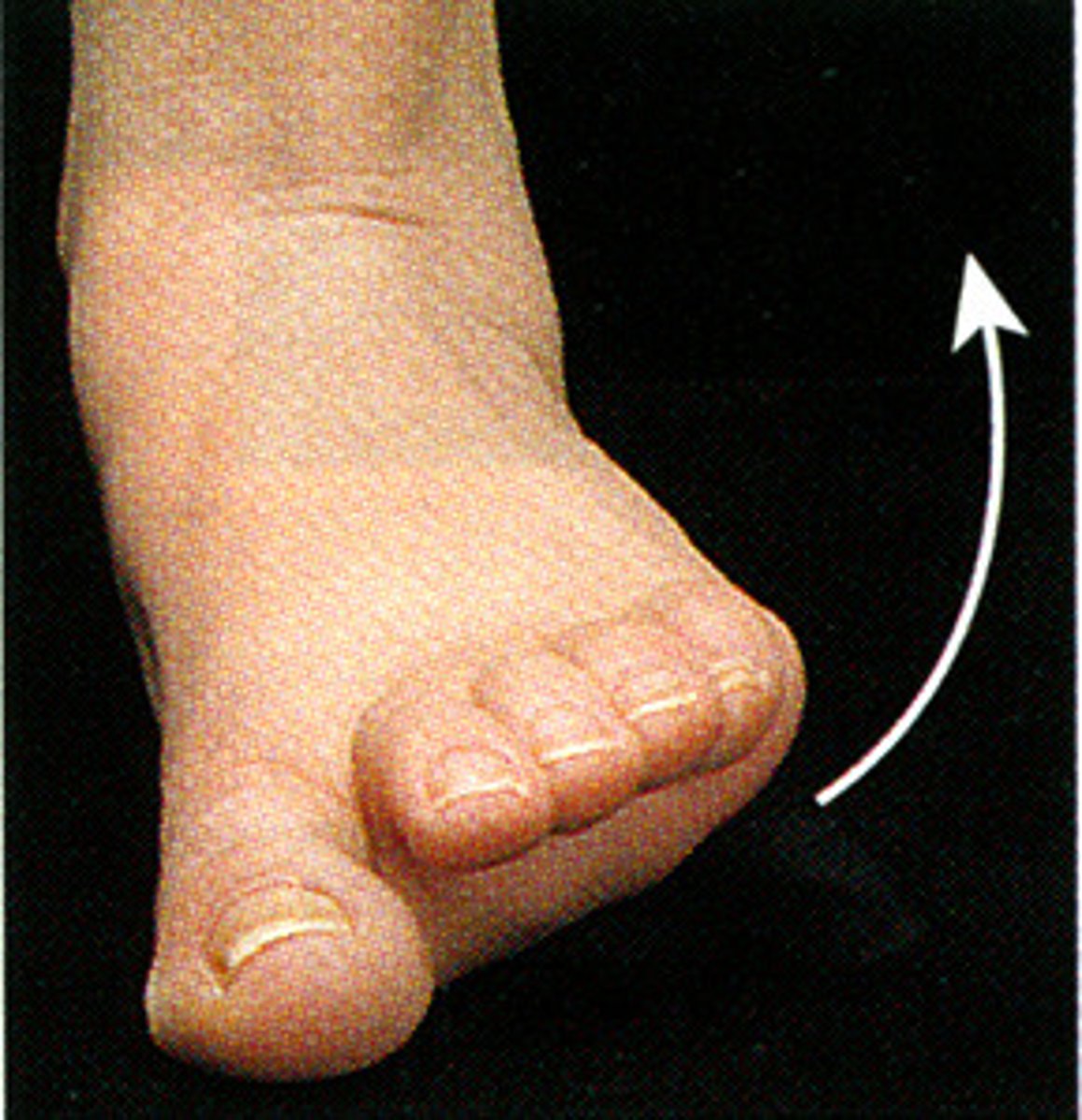
inversion
moving the plantar surface of the foot toward the midline (greater range of motion)