Revision Legal Studies AOS 3 Unit 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Indictable offence
a serious criminal offence which entitles the defendant to a trial by judge and jury

Summary offence
minor less serious offence that can be heard in the Magistrates court

Can Police are your name and address even if they do not believe you have committed an offence
Yes but only if you a driving a vehicle or you have information that may assist them in an investigation for an indictable offence

Arrest
take a suspect into custody

Custody
situation where a person is kept imprisoned while awaiting trial or convicted of a crime

Bail
an agreement to release a person accused of an offence into society whilst awaiting trial,

Examples of bail conditions
hand in passport, report to police station, do not contact witnesses

Offences that have specific powers to detain a suspect for 14 days with charge.
Terrorism

What rights do you have when taken into custody
Telephone a lawyer
Telephone a family/friend
Silence

Body searches
Can only take place if under arrest
In a designated area
Designated Area
incidence of violence has occurred within 12 months or where a person is likely to be carrying a weapon

Type of body searches
Wand to detect a weapon
Pat down

Police can only search private property when...
making an arrest otherwise they need a warrant

Intimate sample
blood
saliva
scraping of mouth
Non - intimate
hair sample
matter under the fingernail
external part of body sample

Fingerprinting can occur when...
10 years or more but under 15 (consent from parents)
15 years or more reasonable force may be used (15 - 17 must have a parent or independent person present)

What is the procedure for bringing a suspect to court
Police question a suspect
Charge the suspect (serious offence only) or issue a summons to appear on court
Should suspect be granted bail
If bail denied then suspect is remanded

5 Purpose of sanctions
Just punishment
Deterrence
Rehabilitation
Denunciation
Protections

Examples of sanctions
Prison (most serious)
Drug treatment order (crime must have been caused by the addiction)
Community based orders (conduct community service)

Concurrent sentences
Defendants ordered to serve more than one prison sentence will serve them at the same time ie 5yrs, 3yrs and 2 yrs. Defendant will serve 5 years

cumulative sentences
Sentences are added together and served one after the other

Importance of crime statistics
Give a picture of crime rates in society
Highlight trends in crime
Provide independent information
Helps provide for improvements in law
Arguments for the death penalty
Deterrence
Removes worst people from society
Saves money (prisoners costs money)
Retribution

Arguments against the death penalty
Person can be innocent
Does not deter crime
Does not respect the right to life
Deserve an opportunity to rehabilitate

Indonesia Stance (death penalty)
Right to life is observed in their constitution with exception of drug offences, argument that it is saving lives as less people will be affected by the scourge of drugs
Australia Stance (death penalty)
Abolished death penalty
Right to life
Not a deterrence
Appellate jurisdiction
When a court is hearing an appeal it operates it's appellate jurisdiction.

Original jurisdiction
When a court hears a dispute for the first time
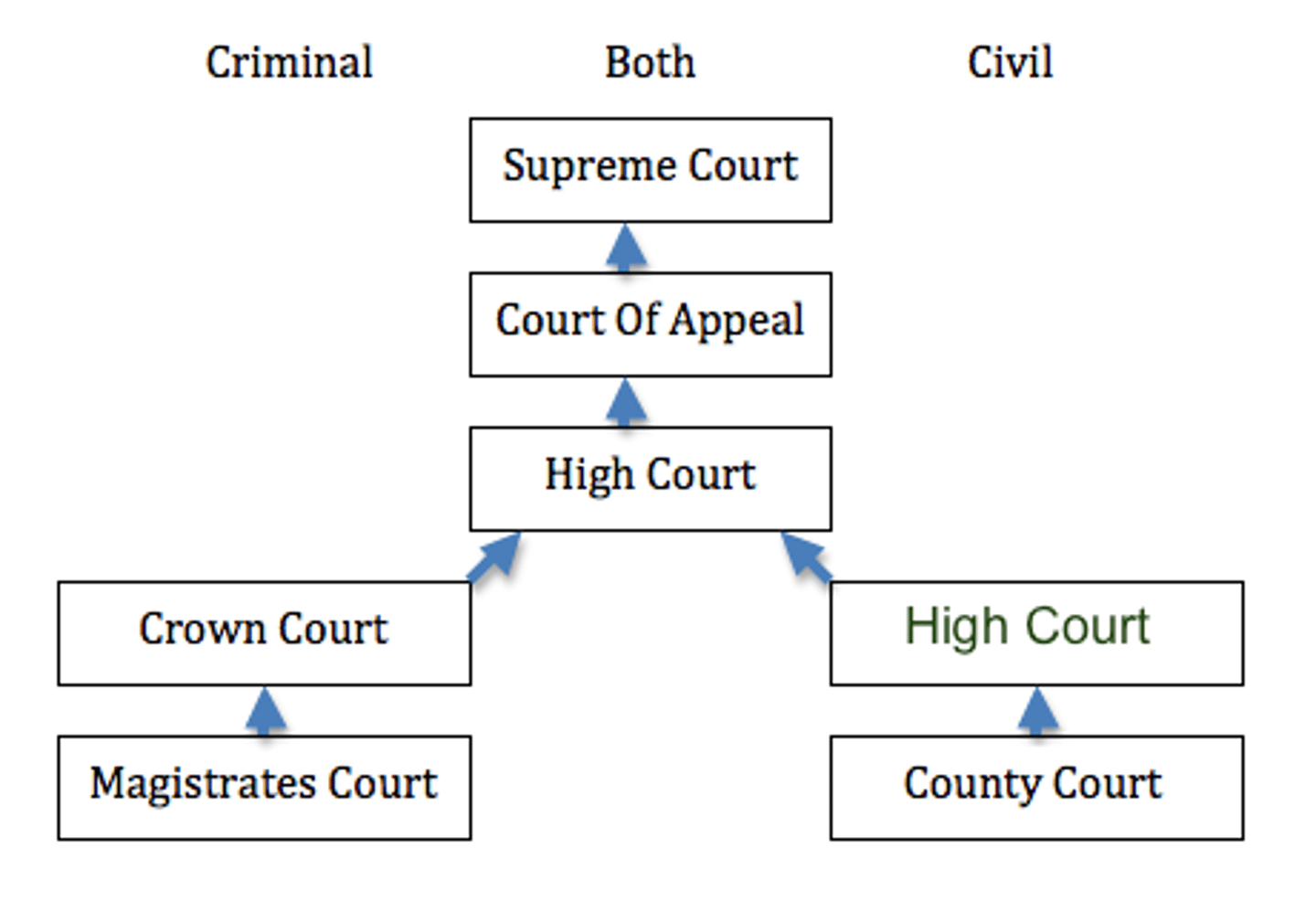
Court Hierarchy
Magistrates Court > County Court > Supreme Court > High Court
Special courts Childrens and Coroners Court at the Magistrates level
Victim Impact Statement
Designed to give an account of the emotional, physical, psychological of what the victim suffered and this is taken into consideration in sentencing

Reasons for Court Hierarchy
Allows each court to deal with specific types of cases according to the seriousness of the crime and the courts jurisdiction. It also allows for specialisation and administrative convenience
Grounds for appeal
Conviction based on a question of fact
Conviction based on a question of law
Severity of the sentence

Doctrine of Precedent
Principle governing the operation of common law, which provides that higher courts are superior over lower courts in similar cases in the same hierarchy.
The decisions of higher courts are binding on lower courts
Provides certainty in law

Magistrates Court appeals to ...
County or Supreme Court depending on case

County Court appeals to...
Country Court Appeal

Supreme Court trial division appeals to...
Supreme Court Appeals Division

Adversary System
A legal system used in the common law countries where two advocates represent their parties' positions before an impartial person or group of people, usually a jury or judge, who attempt to determine the truth of the case.

Tipstaff
Judge's personal attendant

Witness
Swears oath or affirmation to tell the truth

Defence Lawyer
Represents the accused and questions witnesses in court

Jury
12 people who are randomly selected and decide beyond reasonable doubt whether the defendant is guilty or not guilty

Judge
Oversees court proceedings an ensures parties follow strict rules of evidence

Prosecutor
Presents the case to the jury on behalf of the Crown and has the job of proving the accused committed the crime

Remand
Person who is denied bail
Committal Mention hearing
A hearing to establish whether the accused is going to contest the charges

Committal hearing
Hearing to decide whether there is enough evidence to proceed to a trial

Features of the adversary system
Strict rules of evidence ie no prior convictions or hearsay evidence allowed
Parties present their own case
Independant umpire

Jury advantages
Judged by your peers
Represent cross - section of the community
It has stood the test of time

Jury Disadvantages
Too difficult for ordinary people to listen to legal argument
Not representative because jurors can be excused
They do not give reasons for their decisions
Issue of being unbias due to the exposure to media
