Stage 1 - Atomic Structure and Bonding
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SACE - Stage 1 Chemistry
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
1
New cards
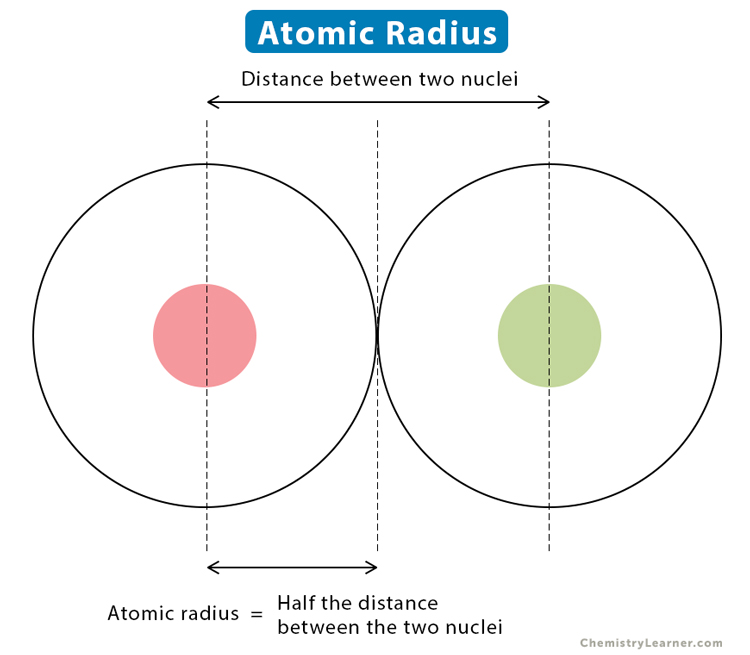
Atomic Radii
The average distance from the centre of the nucleus to the boundary of the valence shell.
2
New cards
Electronegativity
The tendency of its atoms to attract electrons from other atoms.
3
New cards
As Electronegativity increases…
Atomic Radii decreases across the period.
4
New cards
As Electronegativity decreases
Atomic Radii increases across the period.
5
New cards
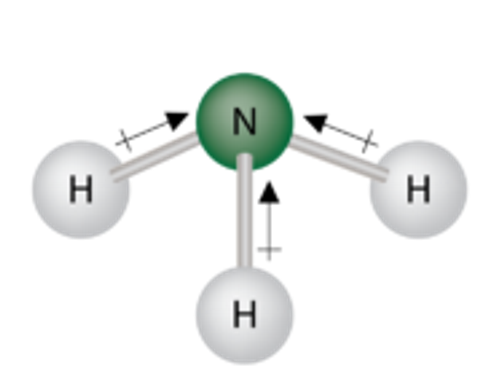
Polar covalent bond
An uneven share of electrons.
6
New cards
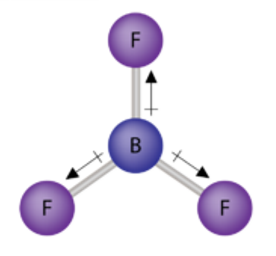
Non-polar covalent bond
An even share of electrons.
7
New cards
When an atom loses electrons…
It forms cations.
8
New cards
When an atom gains electrons…
It forms anions
9
New cards
How to determine if molecule is polar?
* Electronegativity difference is above 0.5.
* Nucleus cloud charge is unbalanced.
* Nucleus cloud charge is unbalanced.
10
New cards
How to determine if molecule is non-polar?
* Electronegativity difference is below 0.5.
* Nucleus cloud charge is balanced.
* Nucleus cloud charge is balanced.
11
New cards
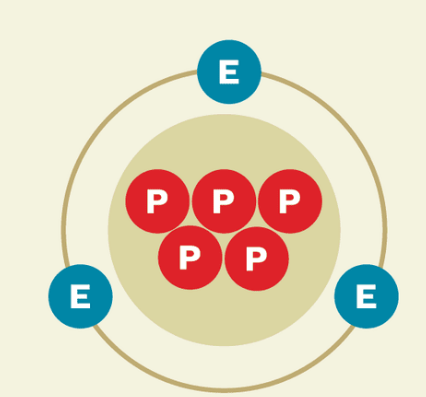
Cations
Positively charged ions.
12
New cards
Anions
Negatively charged ions.
13
New cards
Proton
Positively charged subatomic particle.
14
New cards
Electron
Negatively charged subatomic particle.
15
New cards
Neutron
Neutral charge subatomic particle.
16
New cards
Energy level
The specific amount of energy an electron has.
17
New cards
Excited state
a state in which an atom has more energy than it does at its ground state.
18
New cards
Ground state
The lowest energy state of an atom.
19
New cards
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons.
20
New cards
Valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom.
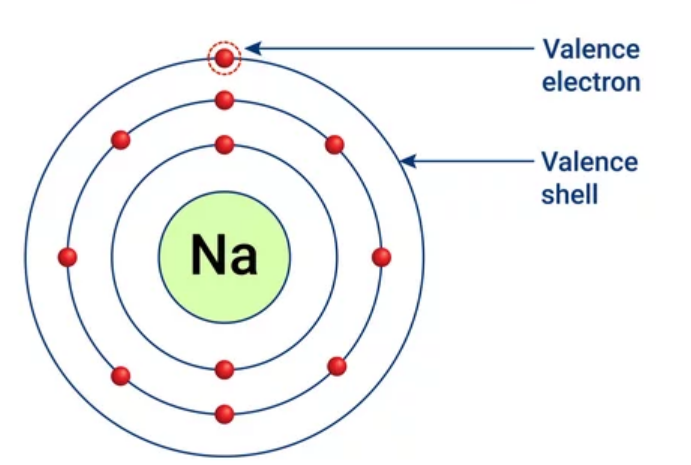
21
New cards
Valence shell
Outermost electron shell.
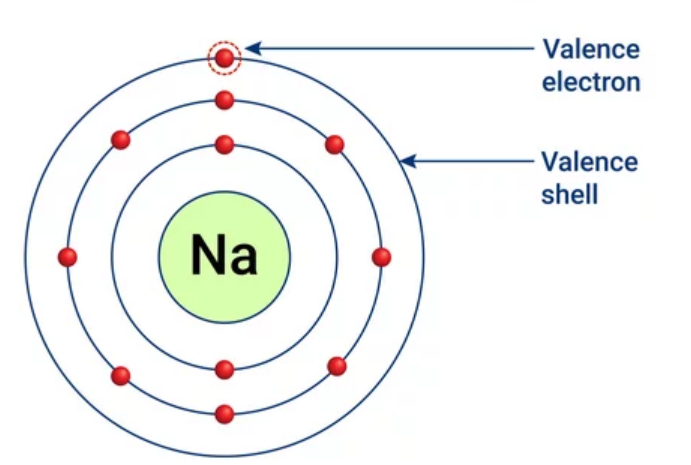
22
New cards
Metallic Bonding
the chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal cations and the surrounding sea of electrons.
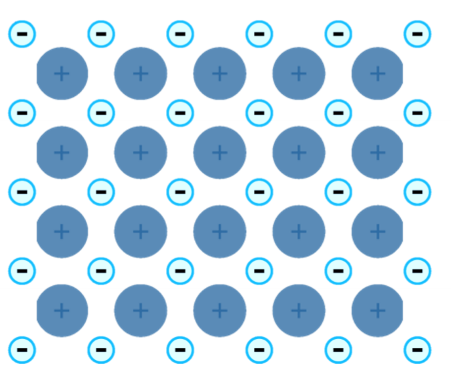
23
New cards
Ionic Bonding
Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between non-metals and metal.
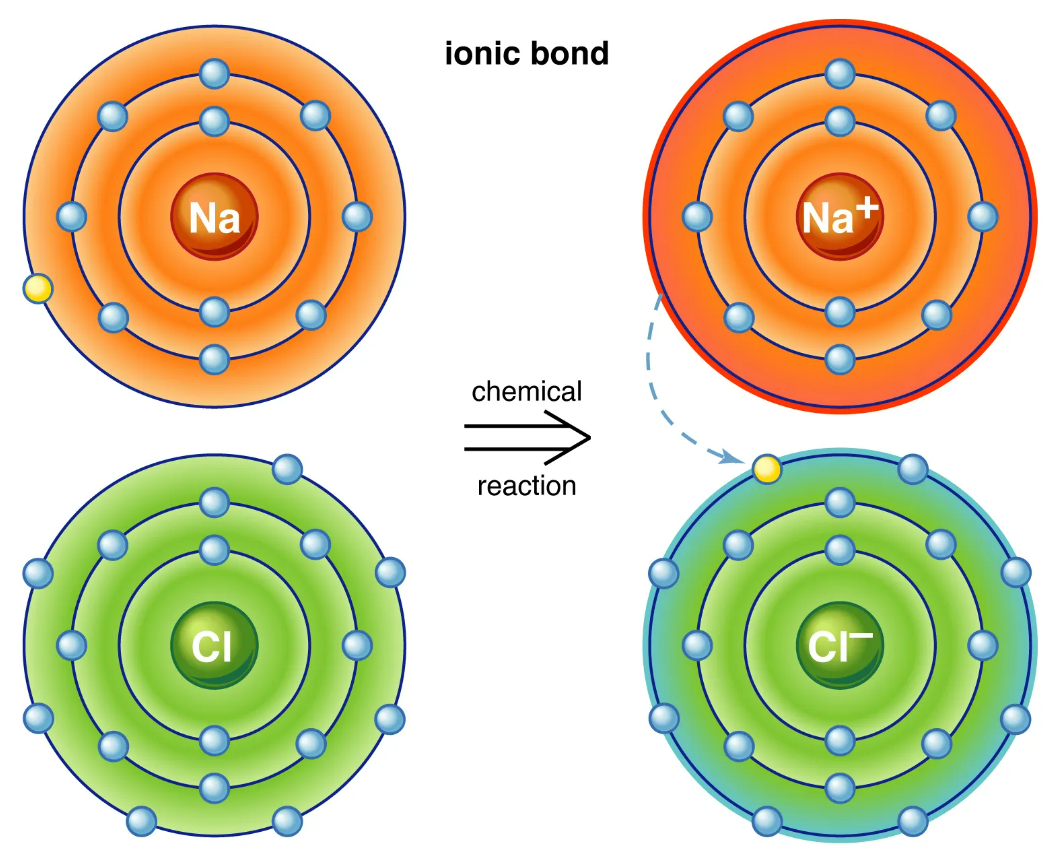
24
New cards
Covalent Bonding
Involves the sharing of electrons between non-metals.
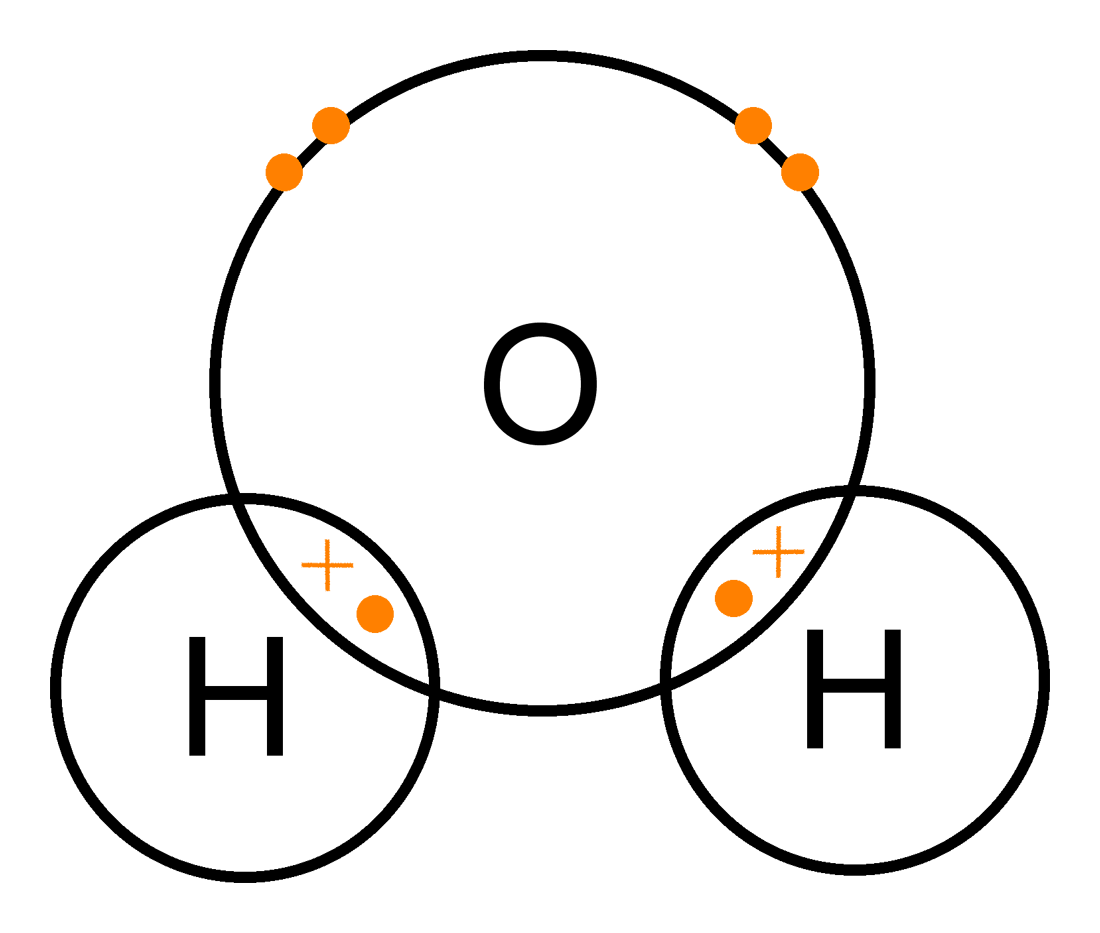
25
New cards
Lattice
A repeating arrangement of atoms in a solid.
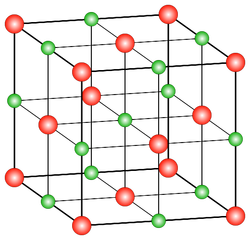
26
New cards
Two properties of metal
* Ductility.
* Conduct electricity.
* Conduct electricity.
27
New cards
Three properties of ionic compounds
* High melting points
* High boiling point
* Soluble in water
* High boiling point
* Soluble in water
28
New cards
Three properties of covalent compounds
* Low melting points
* Poor electrical conductivity
* Various colour
* Poor electrical conductivity
* Various colour
29
New cards
What does Bohr’s Law state?
Electrons don’t absorb energy or emit energy from the nucleus, unless they transition or jump from orbits.
30
New cards
Why are metals ductile?
They are able to be drawn out into a thin wire because the electrons are free to move which surround the cations.
31
New cards
Molecule
A neutral group of atoms joined together by chemical bonds.
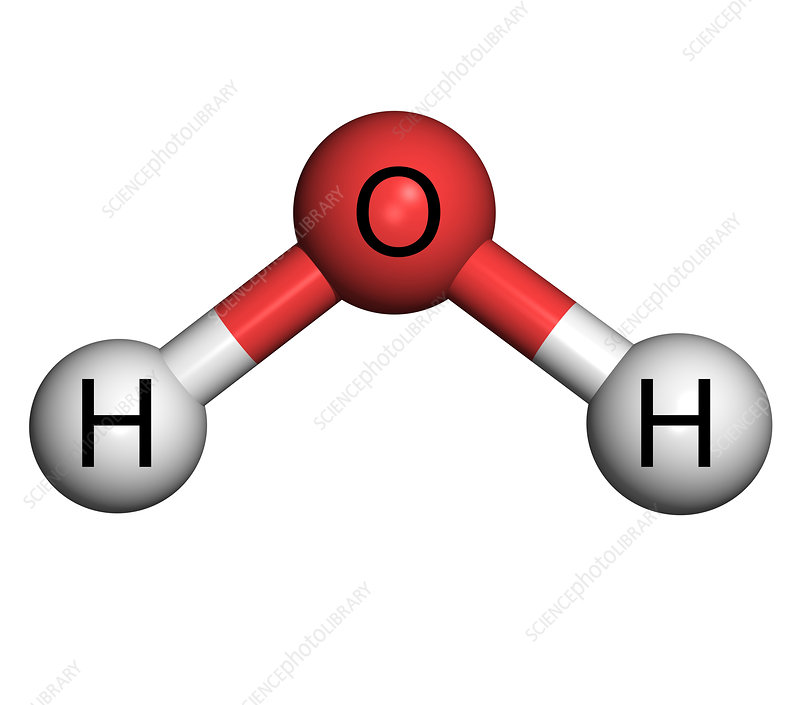
32
New cards
Intermolecular Bonding
Attractive forces between molecules that determines physical properties.
33
New cards
Intramolecular Bonding
Bonding forces within molecules that determines chemical properties.
34
New cards
Dispersion Forces
A temporary attraction of one molecule’s nuclei for the electrons in neighbouring molecules.
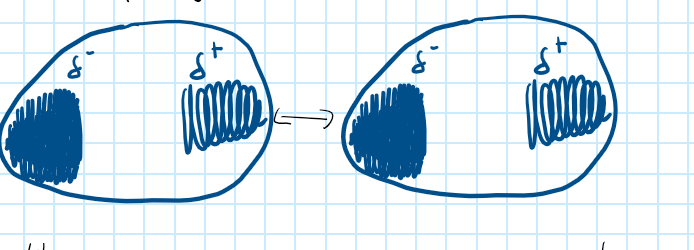
35
New cards
Temporary Dipole-Dipole
A result of an uneven distribution of electrons in one neighbouring molecule that results in an induced dipole.
36
New cards
Dipole-Dipole Interaction
An attraction that results from the partially positive end of a polar molecule with a partially negative end of an adjacent molecule.
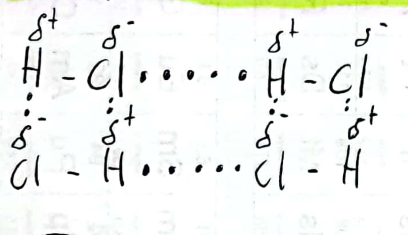
37
New cards
Hydrogen Bonding
The strongest form of dipole-dipole interaction that results from a partially positive Hydrogen with a partially negative Nitrogen, Oxygen, and Flourine.
38
New cards
3 types of intramolecular bonds
* Ionic Bonding
* Covalent Bonding
* Metallic Bonding
* Covalent Bonding
* Metallic Bonding
39
New cards
3 types of intermolecular bonds
* Dispersion Forces
* Dipole-Dipole Interaction
* Hydrogen Bond
* Dipole-Dipole Interaction
* Hydrogen Bond
40
New cards
Nanomaterial
Substances composed of particles ranging from 1-100nm.
41
New cards
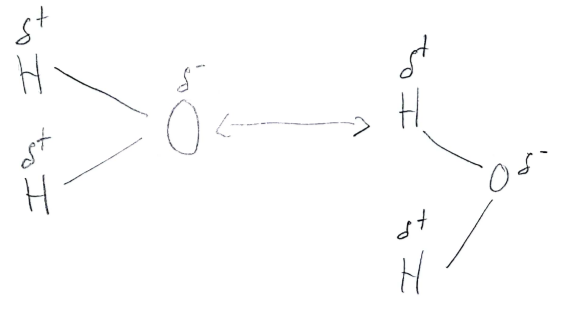
Electrolyte
An aqueous solution which produces ions to conduct electricity.
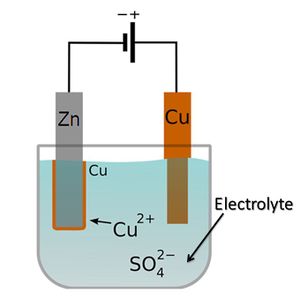
42
New cards
Polyatomic Ion
A group of atoms that have charge (covalent).
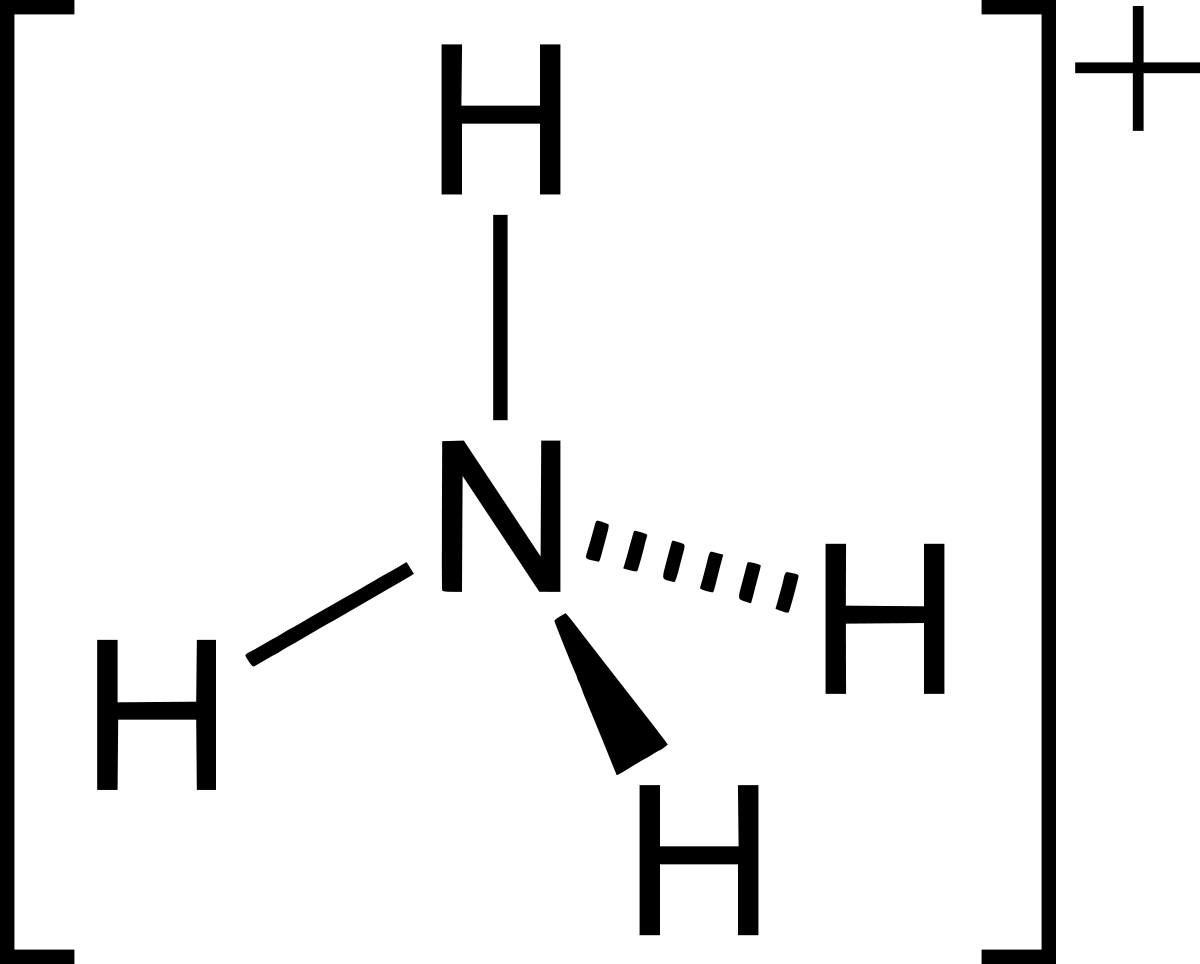
43
New cards
What’s the difference between ion and atom?
Atom is electrically neutral, and ion is electrically charged due to loss or gain of electrons.
44
New cards
Relative Atomic Mass
The average mass of all naturally occurring isotopes of the element, relative to the mass of carbon-12.
45
New cards
What does VSEPR stand for?
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion.
46
New cards
What is common with atomic number?
No. of protons and electrons in an atom.
47
New cards
How to calculate neutrons?
Mass number-atomic number.
48
New cards
Thermal Conductivity
Ability to conduct or transfer heat energy.
49
New cards
Electrical Conductivity
Ability to conduct or transfer electrical charge.
50
New cards
Melting Point
The temperature at which a substance changes state, from solid to liquid.
51
New cards
Boiling Point
The temperature at which liquid boils and turns into gas (vapour).
52
New cards
Density
The density of a substance is its mass per unit volume.