A&P II: Lymphatic/Immune System - Midterm Review
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Lymphatic System
assists the cardiovascular system by transporting the excess fluid from the body tissues**
Lymphocytes
made in bone marrow; type of WBC**
Lymphokinesis**
Movement (flow) of lymph
Lymphatic Organs & Tissues
Primary lymphatic organs:
Red bone marrow - where lymphocytes are produced
Thymus - mature and become immunocompetent (able to fight off disease)
Secondary lymphatic organs/tissues:
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Lymphatic nodules
Thymus
“boot camp”
immature T cells migrate from the red bone marrow to the thymus where they mature
most active in the fetus & child
located below thyroid gland
necessary for t cell maturation (immunologically competent)
Lymphatic Nodules
small unencapsulated masses of lymphatic tissue
destroys pathogens that penetrate the epithelium
Tonsils - lymph nodules of the pharynx**
Peyer’s patches - nodules of small intestines**
Two main types of immune responses**
Non-specific (innate) immunity - born with it; 1st & 2nd line of defense
Specific (adaptive) immunity - cell mediated immunity & antibody mediated immunity
Innate (non-specific) immunity - defense cells**
Natural killer cells: destroys foreign cells by rupturing the cell membranes; lymphocytes that kill many types of tumor cells
5 classes of antibodies:
IgM: first produced antibody by B cell; 1st response in allergic reactions
IgG: most abundant antibody; can cross placenta immunity from mother to fetus
IgA: found in mucous membranes; tears & saliva, colostrum & breast milk
IgE: produce allergic responses; can be harmful - hypersensitivities
IgD: present in blood; function unknown
T & B cells are responsible for __________ immunity
specific adaptive immunity
Antibodies are made by the
B lymphocytes
T-cell originate in the
bone marrow
There are how many types of antibodies?
5 types - IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, IgD
The first antibody to be made is
IgM
What antibody is found in tears and saliva?
IgA
T-lymphocytes are responsible for what immunity?
cell-mediated
The largest anatomical defense is the
skin (integument); 1st line of defense
What antibody is made during the second contact with an antigen?
IgG
The proteins on the surface of a cell that identify that cell are called
antigens
T-lymphocytes mature in the
thymus gland
________ are lymphoid tissues found in the small intestines
Peyer’s patches
Thoracic lymphatic collecting ducts empty their contents into the _________ veins
left subclavian
Right lymphatic duct
right upper quadrant
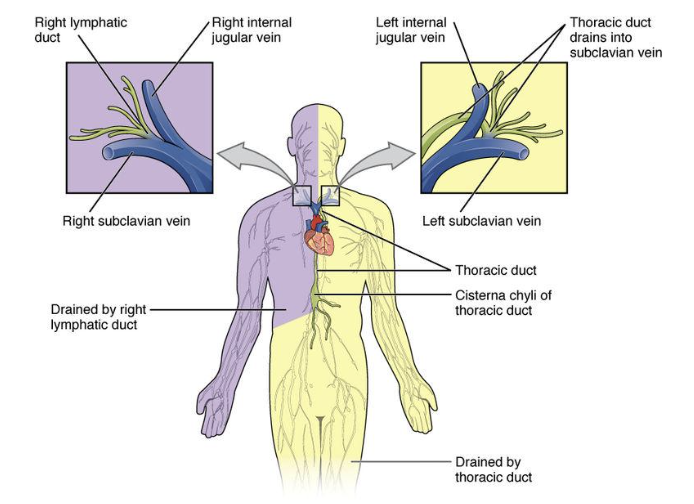
Thoracic duct
rest of the body
Active Vs. Passive Immunity
Active immunity: occurs when our own immune system is responsible for protecting us from a pathogen.
Passive immunity: occurs when we are protected from a pathogen by immunity gained from someone else.
_____ immunity results when immunity to a disease that has developed in another individual or animal is transferred to an individual who was not previously immune.
Passive
Which two special types of lymphocytes play a major role in immunity?
B cells and T cells
Adaptive immunity, part of the body’s third line of defense, is orchestrated by two different classes of a type of white blood cell called the
lymphocyte
The body’s defense mechanisms can be organized into one of two major categories of immune mechanisms; these are
innate and adaptive immunity.
Because T cells attack pathogens more directly, T-cell immune mechanisms are classified as _____ immunity
Cell mediated
The function of T cells is to produce
Cell-mediated immunity
The lymphatic system serves various functions in the body. The two most important functions are
Fluid balance
Immunity