Neuropsychology Final
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
What are sulci in the brain?
Grooves or indentations between the gyri
Name the fluid-filled cavities in the brain
Lateral Ventricles, Third Ventricle, Fourth Ventricle
Schwann Cells
Supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin.
Motor Control
How the central nervous system integrates internal and external sensory information with previous experiences to produce a motor response.
right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
related to monitoring and attending activity
left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
selecting a possible range of responses, and suppressing inappropriate ones; manipulating the contents of working memory
What occurs during the Recognition Trial of the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test?
Participants are given a list of 24 words (12 target words and 12 distractors) and asked to identify the words they previously learned.
What does the Secondary Visual Cortex receive information from?
V1
Where does the dorsal stream go through?
Posterior parietal lobe. "Where" path
In-Vivo Imaging
Non-invasive, detailed structural and functional imaging, high spatial resolution, various contrasts (e.g., metabolic, magnetic)
Ablation
a physiological research procedure where small portions of the brain are removed or destroyed in order to explore the function of a neural system. Used to remove tumors
What is the Localization of Functional hypothesis?
Different regions of the brain are involved in specific and separate aspects of psychological functioning.
How is the brain organized
Left Hemisphere: Often associated with language, logical reasoning, and analytical tasks.
Right Hemisphere: Associated with creativity, spatial ability, and holistic thought.
Gyri and Sulci
Gyri: These are the ridges or raised portions on the surface of the brain.
Sulci: These are the grooves or indentations between the gyri. The patterns of gyri and sulci increase the surface area of the brain, allowing for more neurons.
Lobes:
The brain is divided into four main lobes, each with specific functions:
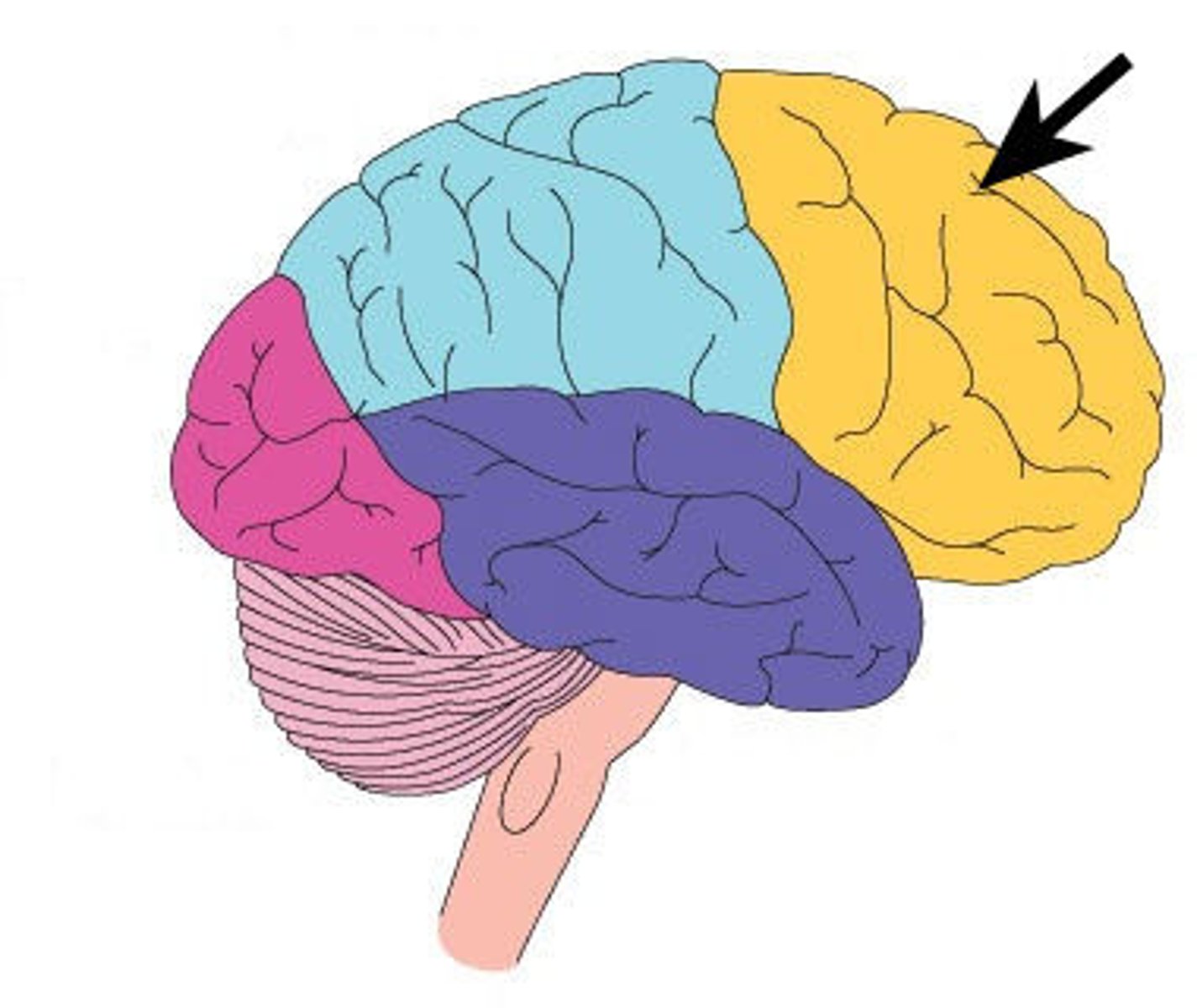
Frontal Lobe: Involved in decision-making, problem-solving, and planning.
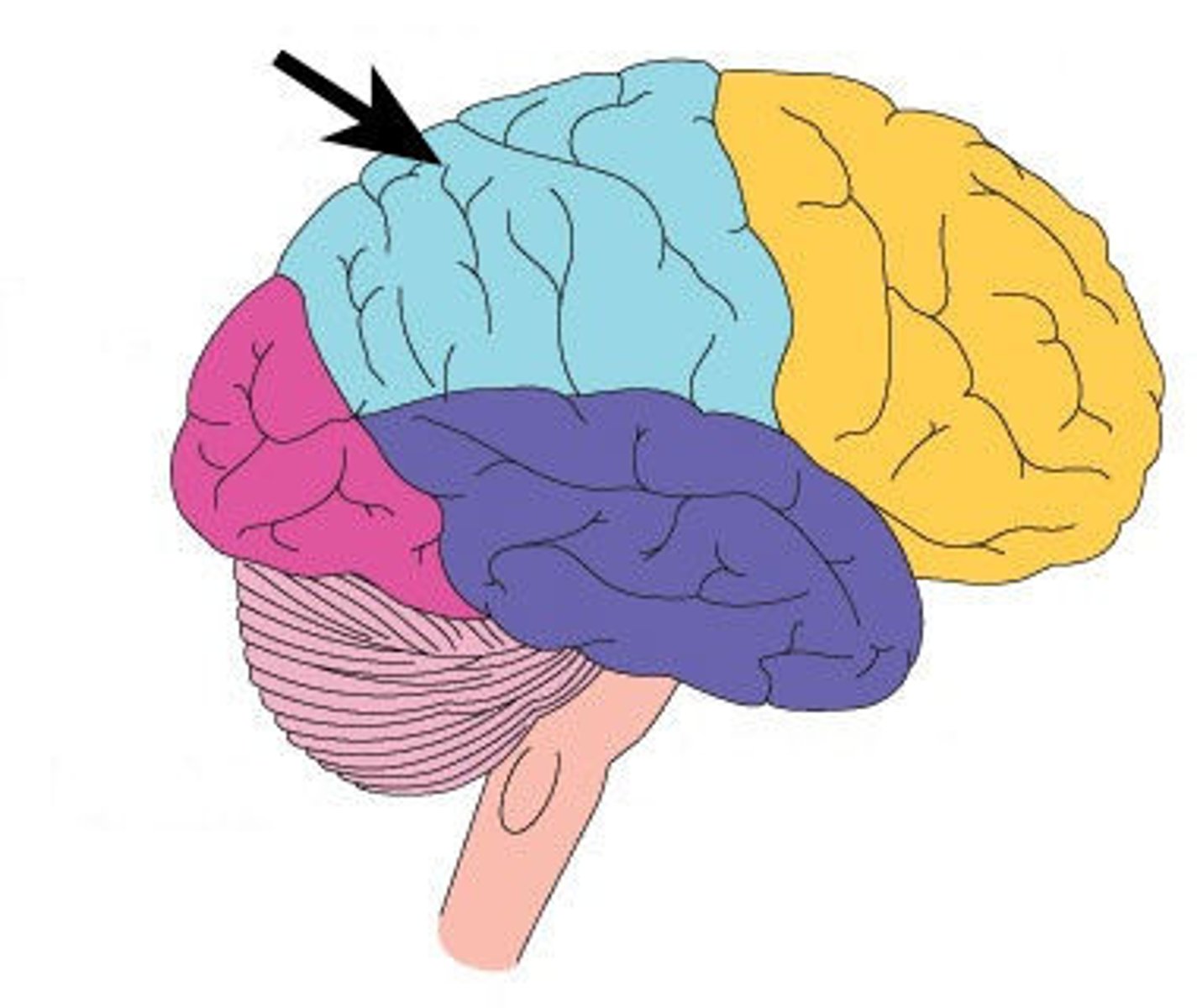
Parietal Lobe: Processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain.
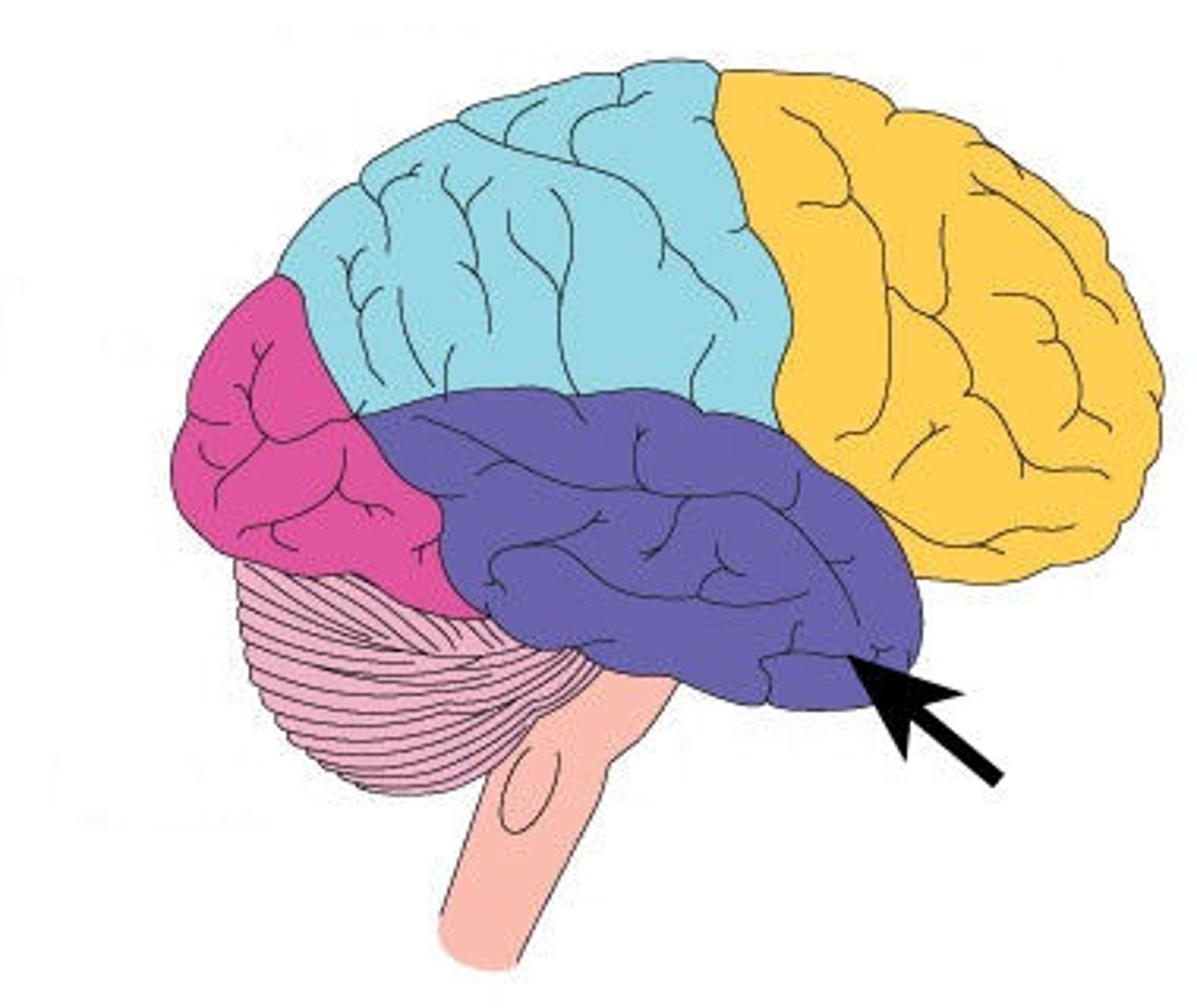
Temporal Lobe: Responsible for hearing, memory, and language.
Occipital Lobe: Primarily involved in vision.
Meninges
The brain is protected by three layers of membranes called meninges:
Dura Mater: The tough, outermost layer.
Arachnoid Mater: The middle layer that looks like a web.
Pia Mater: The delicate, innermost layer that clings to the surface of the brain.
Ventricles
The brain contains a system of fluid-filled cavities called ventricles:
Lateral Ventricles: Located in each hemisphere.
Third Ventricle: Located in the midline of the brain.
Fourth Ventricle: Located between the brainstem and the cerebellum.
These ventricles produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that cushions the brain and removes waste products.
Neurons and Glia
Neurons: The primary cells responsible for transmitting information throughout the brain and nervous system. They consist of dendrites, a cell body, and an axon.
Glia: These are supporting cells that provide structural support, nourishment, and insulation for neurons. Types of glial cells include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and Schwann cells.
What functions are associated with the Right Hemisphere?
Creativity, spatial ability, and holistic thought
What are gyri in the brain?
Ridges or raised portions on the surface of the brain
Name the four main lobes of the brain
Frontal Lobe, Parietal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, Occipital Lobe
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
Broca's Aphasia
aphasia associated with the damage to the Brocas area of the brain demonstrated by the impairment in producing understandable speech
Nonfluent Aphasia
Speech is not fluent/production is lacking. Comprehension remains intact. Will affect production of both spoken and written words
Superior Colliculus
Located in the midbrain, it is involved in the orienting of visual attention. It helps direct the eyes toward objects of interest in the visual field
The Parietal Lobes and Attention
Areas of the parietal lobe work alongside the cingulate to direct attention to information in the space in and around us. Damage to those areas creates hemispatial neglect
cerebral cortex (gray matter)
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
Visual Neglect
failure to respond to visual stimulation on the side of the visual field that is opposite a brain lesion
Personal neglect
lack of awareness of the side of the body opposite the brain lesion
superior medial cortex
This region is involved in higher cognitive functions such as decision-making, motivation, planning, and attention. It plays a crucial role in managing complex cognitive tasks and emotional regulation
How might impairments to goal-directed behavior affect a person's everyday life?
can lead to difficulties setting and achieving goals, disorganization, and procrastination. This can hinder career advancement, educational achievements, and personal life goals.
mild trauma induced brain injury
loss of consciousness <30 mins
Loss of memory < 1 hour
Alteration in mental state < 24 hours
What is the cause of Jason's behavior?
Damage to the reticular formation, a diffuse nerve network that connects the brain stem to the prefrontal lobes
Implicit memory
knowing previous experiences or procedures, Non-Declarative-doesn't require intentionally learning or retrieving the information
Explicit memory
recall of facts and events Declarative-requires you intentionally learning the info and trying to recall it
retrieval
the process of getting information out of memory storage
What type of memory declines later in Alzheimer's disease?
Memory for distant past events.
What are some other symptoms of Alzheimer's besides memory decline?
Disorientation to place and time, spatial disorientation, impaired learning, attention, judgment, and communication.
What cognitive abilities does the Rey-O Complex Figure test evaluate?
Visuospatial abilities, memory, attention, planning, and working memory (executive functions).
What is the ventral stream responsible for?
Identifying and recognizing objects.
What is the dorsal stream responsible for?
Helping the motor system to find objects and move towards them.
Visual agnosia types
apperceptive and associative. Topographagnosia, prosopagnosia
topographagnosia
Impairment in the interpretation of maps, house plans, etc.
prosopagnosia
inability to recognize faces
primary motor cortex
the section of the frontal lobe responsible for voluntary movement
Primary Motor Cortex Arrangement
is arranged from medial to lateral, representing different parts of the body. The lower body (e.g., legs) is represented medially, while the upper body (e.g., arms, face) is represented laterally.
What are the three subcortical structures of the basal ganglia?
Caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus.
What is the function of the DIRECT pathway in the Basal Ganglia?
To make the movements we want (like a gas pedal).
Which specific parts of the brain are affected in Huntington's Disease?
The caudate nucleus and putamen (striatum).
In-Vivo Imaging examples
CT/CAT, PET, MRI, fMRI, DTI
Autopsy
a thorough examination of a deceased person's body to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death. This procedure involves dissecting the body and examining its internal organs and tissues. They can be performed for various reasons, including legal investigations, medical research, and educational purposes. Used for Huntington's and Alzheimer's
EEG
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
MRI
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain. Better resolution than CT (1mm)
fMRI
Detects areas of oxygenated blood consumption. When blood/oxygen is used, brain power is used.
Pro: detailed about when
Con: not very detailed about where
DTI (diffusion tensor imaging)
uses same tech as fMRI but images the axonal connections in white matter rather than the cerebral regions (in grey matter).
Pro: very detailed about how areas are connected
Con: can't provide temporal info
Temporal Resolution:
High: EEG
Medium: fMRI, PET
Low: MRI, CT/CAT, DTI, Autopsy, Lesion, Ablation
What does the Coronal Plane divide the brain into?
Front (anterior) and back (posterior) parts.
Three Imaging Planes
Sagittal Plane, Coronal Plane, Axial (Transverse) Plane
Neuropsychology
scientific study of psychological processes (thoughts, feelings, behaviors) in relation to brain structures and systems
clinical
focused on effects of brain damage/disease on psychological processes for the purpose of classifying impairment and recommending treatment
cognitive
focused on effects of brain damage/disease on psychological processes for the purpose of better understanding how the brain works and how it is structured
What functions are associated with the Left Hemisphere?
Language, logical reasoning, and analytical tasks
What is the primary function of the Frontal Lobe?
Involved in decision-making, problem-solving, and planning
What is the primary function of the Parietal Lobe?
Processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain
What is the primary function of the Temporal Lobe?
Responsible for hearing, memory, and language
What is the primary function of the Occipital Lobe?
Primarily involved in vision
What are the three layers of the meninges?
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
What is the Dura Mater?
The tough, outermost layer of the meninges
What is the Arachnoid Mater?
The middle layer of the meninges that looks like a web
What is the Pia Mater?
The delicate, innermost layer of the meninges that clings to the surface of the brain
What is the function of the ventricles in the brain?
They produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that cushions the brain and removes waste products
What are neurons?
The primary cells responsible for transmitting information throughout the brain and nervous system
What are glia?
Supporting cells that provide structural support, nourishment, and insulation for neurons
Name types of glial cells.
Astrocytes, Oligodendrocytes, Microglia, Schwann Cells
Astrocytes
Provide structural and metabolic support for neurons and removes waste material when neurons die. Part of the glia
Microglia
Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system. Part of the glia
Oligodendrocytes
Type of glial cell in the CNS that wrap axons in a myelin sheath.
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
Wernicke's area
controls language reception - a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
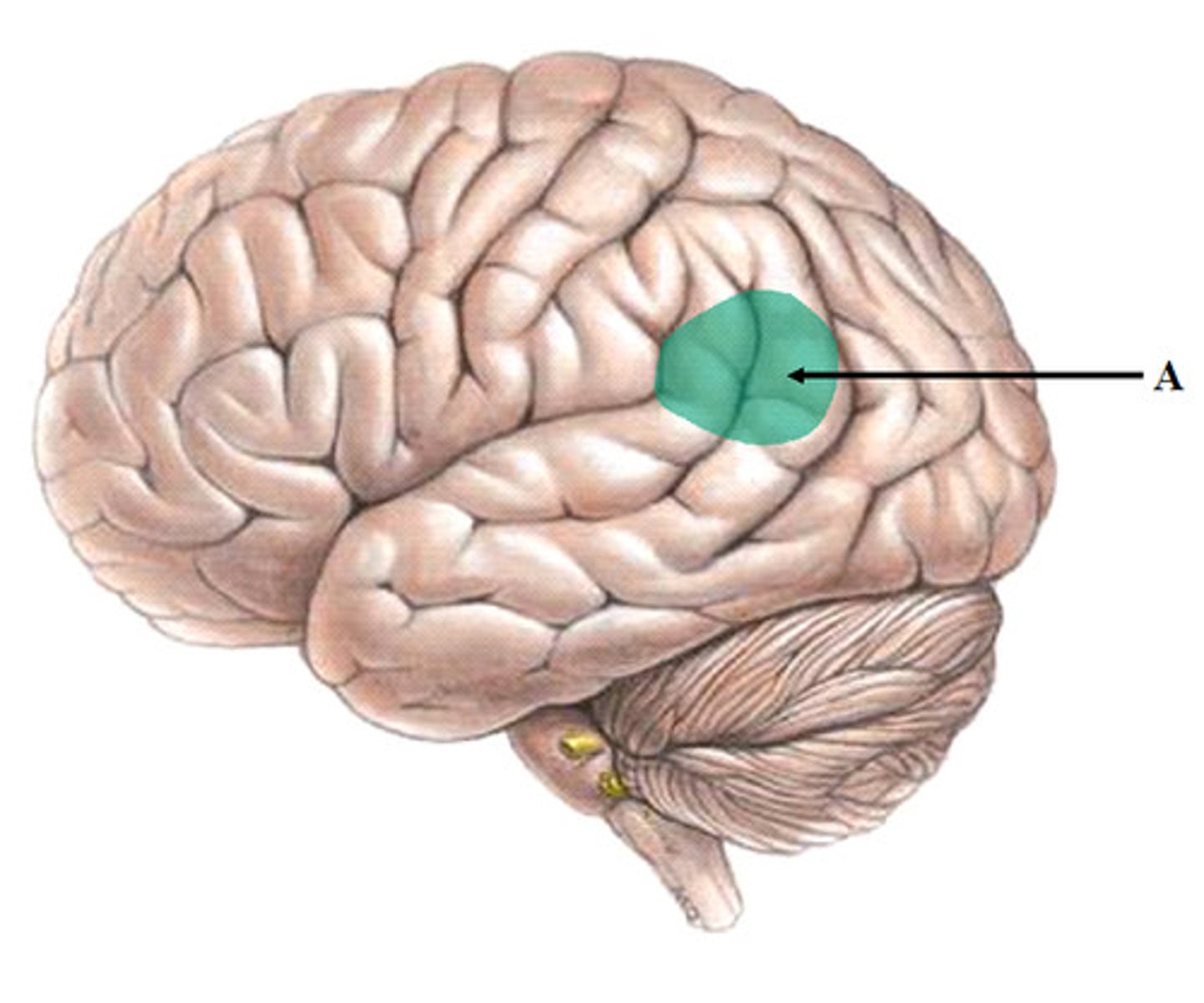
Broca's Area
controls language expression- an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movement involved in speech
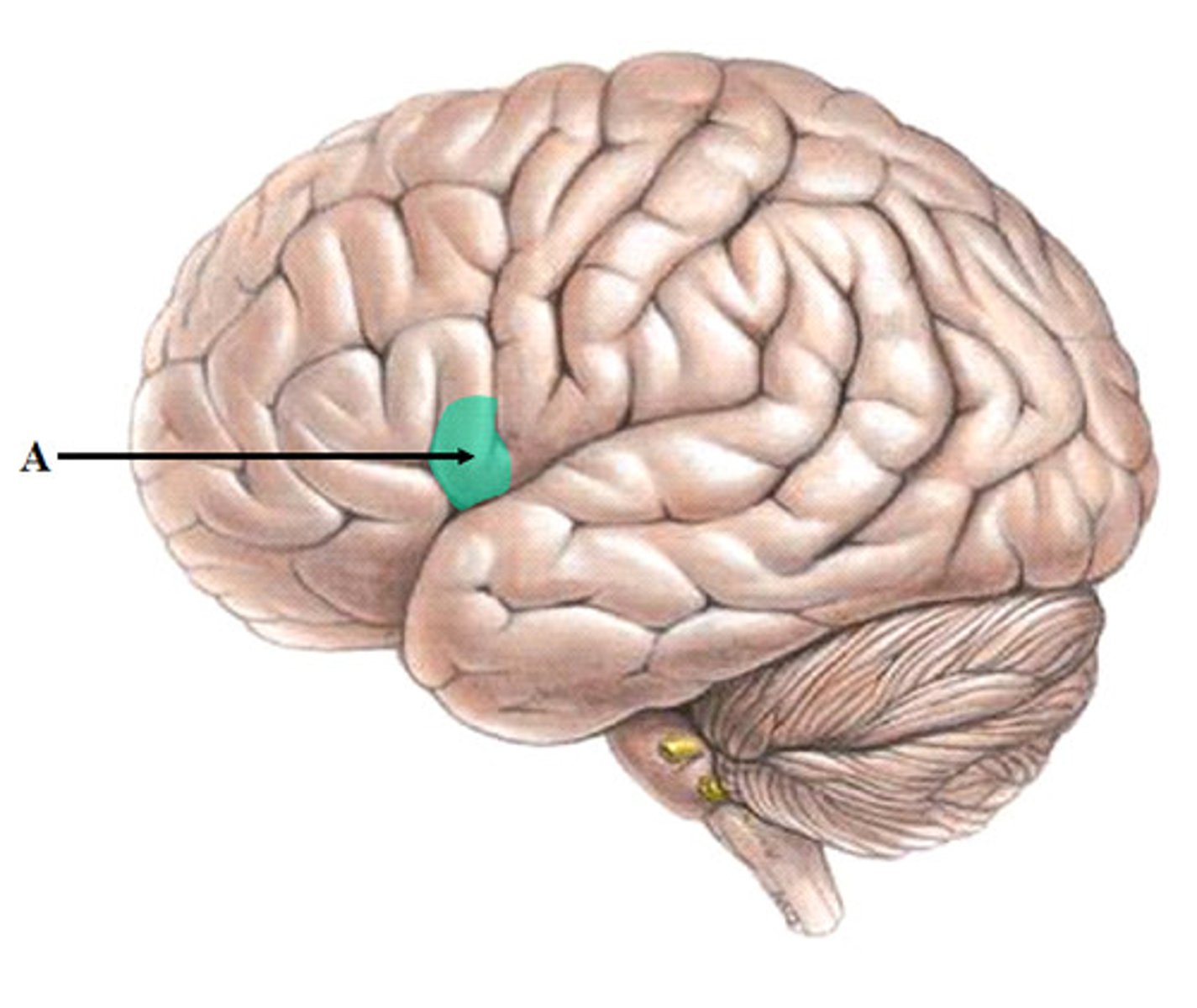
expressive aphasia
trouble communicating thoughts through speech or writing
Wernike's Aphasia
Unable to understand language: the syntax and grammar jumbled
Aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca's area (impairing speaking) or to Wernicke's area (impairing understanding).
Fluent Aphasia
speech remains fluent/productive comprehension is lacking will affect understanding of both spoken and written language
Conduction aphasia
can speak, name objects, and understand speech but cannot repeat words
Anomic aphasia
can comprehend speech, produce meaningful speech and can repeat speech.great difficulty naming objects
Global aphasia
labored speech and poor comprehension
Typical cause of aphasia
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Ischemic Stroke
Aphasia test batteries examine
auditory and visual comprehension, oral and written expression, conversational speech
Luke and his symptoms
suffers from Broca's Aphasia. Brain hemorrhage. Difficulty in expressing speech and writing. Nearly every sound requires a fresh start. Words are expressed in a staccato manner. Many words are incorrectly punctuated.
What did Irene suffer from?
receptive (Wernicke's) aphasia. they struggle with understanding language, speaking coherently (yet speaks fluently), reading comprehension. Blockage of an artery. they had phonetic paraphasia (substitutions based on pronunciation) and semantic paraphasia (substitution based on meaning), neologisms (non-existent words),
Overt visual attention
attending to something with eye movement
covert attention
shifting attention from one place to another while keeping the eyes stationary
Vigilance
to maintain our concentration/focus/attention on one area or thing for a prolonged period of time
Exogenous
Produced outside the body
Endogenous
produced from within; due to internal causes
Reticular activating system
the part of the brain that is involved in attention, sleep, and arousal
Cingulate gyrus
Deliberate control
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
Located in the brainstem, the it is crucial for maintaining arousal and consciousness. It filters sensory input and determines which information is important enough to receive attention.
Thalamus
Acts as a relay station for sensory information and plays a key role in regulating consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Acts as a wingman for the primary motor cortex and keeps it from getting out of hand.
Prefrontal Cortex
Particularly the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, is involved in sustained attention and executive functions. It helps manage working memory and decision-making processes.
Parietal Lobe
Particularly the posterior parietal cortex, plays a key role in spatial attention and orienting. It integrates sensory information from different modalities and helps in directing attention to specific locations.
Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC)
Involved in detecting errors, managing emotional responses, and regulating attention. It plays a role in conflict monitoring and cognitive control.