Nitrogen-containing organic compounds
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Amines
N atoms bound to >= 1 C-containing molecular fragment
biologically significant (in amino acids, DNA, RNA)
organic derivatives of ammonia (substituted ammonia)
H-N can form HB
Classifying amines
no of R groups attached to N atom
Nomenclature of primary amines
locate longest C chain containing -NH2 group
change -e to -amine (do not remove -e for di/tri anime)
lowest number to C bearing NH2
add substituents to front
(amines have low priority, as substituent: amino)
Bonding of amines
polar covalent, form HB stronger than LDF in many molecules
weaker than H2O (same extensiveness, O-H more polar)
tertiary amines cannot form HB with its own molecules (can still form with water)
Boiling point of amines
higher than hydrocarbons as require more energy to overcome (HB)
Solubility of amines in water
longer C chain → less soluble (>= 6C insoluble)
all amines form HB with water
Smell of amines
sharp penetrating odour
decaying animal tissue
toxic, carcinogen, absorbed through skin
N-N-dimethylmethanamine
animal tissues
fish odour
Nicotine
in tobacco
stimulant
habit forming, tar formation
Piperidine
in food seasoning (e.g. black pepper)
4-aminobenzoic acid
active ingredient in sunscreen
Amines as neurotransmitters
Serotonin - regulate sleep, mood, appetite and digestion
Popamine - brain reward system
amines as hormones
adrenaline
synthesised by adrenal gland
increase blood glucose level & heart rate
contract blood vessels
dilates air passages
fight or flight response
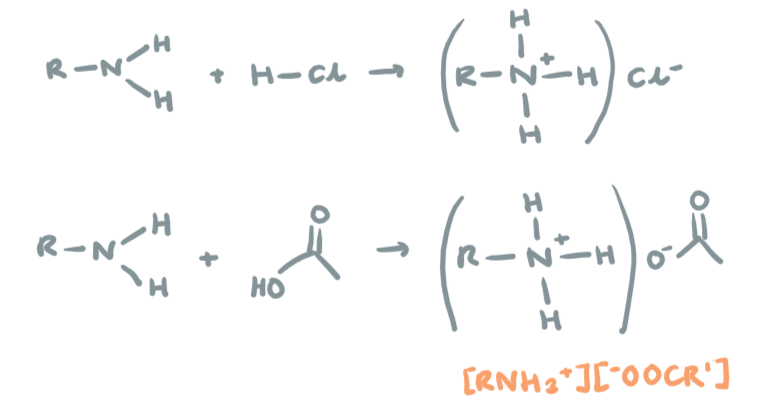
Neutralisation of amines
React with acids to form salts (all amines can do neutralisation)
R-NH2 + HCl → R-NH3+Cl-
Dissociation of amines
Weak base in water, similar to ammonia
R-NH2 + H2O → R-N+H3 + OH-
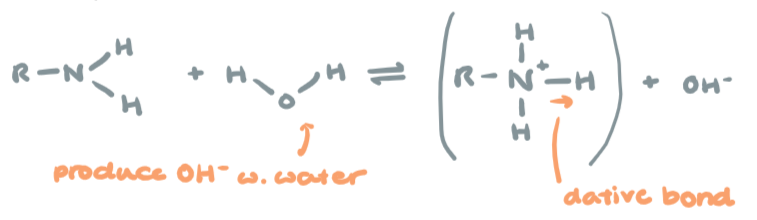
Salts of amines
similar physical properties as ionic compounds
white crystalline solids
high melting points
more soluble in water than amines
odourless (amine drugs in salt form)
amides
amine derivatives of carboxylic acids
RCOOH + R’NH2 (not tertiary) → RCONHR’
conditions: heat
note position of amide linkage
polyamides (e.g. nylon)
Primary amide nomenclature
carboxylic acid carbon is C1
-oic acid → amide
melting point and boiling point
strong IMF, hence high melting and boiling point
Solubility
if >= 6 - insoluble; if < 6 - soluble
energy to break HB between water and HB/LDF between amide VS energy released by HB between water and amide
Natural amides